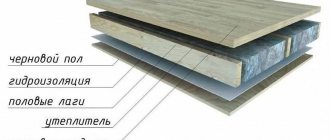
To ensure that the premises are comfortable and the air exchange occurs in accordance with the standards, each residential building is equipped with a ventilation system. This also applies to multi-storey buildings, which represent the main segment of urban housing.
During construction, standard schemes of ventilation systems in an apartment building are used, thanks to which various air circulation modes are implemented.
In this article we will analyze the features of traditional schemes, the subtleties of arranging forced ventilation and the nuances of arranging ventilation for a sewer system.
Purpose of ventilation
Insufficient ventilation has a direct impact on the health and well-being of residents living in the apartment. Lack of fresh air provokes headaches, depression, drowsiness, and fatigue.
In each high-rise building, according to building codes, there is a centralized ventilation system, which is a set of ventilation shafts and channels that remove exhaust air masses from the rooms to the attic or to the street. Air ducts are located in the ceilings, and their installation is carried out during the construction stage.
There are three approaches to organizing ventilation in multi-storey buildings:
- Natural air supply and exhaust system. Used in most typical high-rise buildings. A clear advantage of this solution is that it works without being connected to a power supply.
- Forced ventilation using special installations. It is used where the power of natural air exchange is insufficient.
- Combined ventilation systems use a combination of mechanical and natural ventilation systems.
It is also possible to add additional units to the home ventilation system.
For example, installing a recuperator (a device capable of accumulating heat from exhaust air and releasing it to the supply air) allows you to save a lot of money on heating.
Or another element - a deflector, which is installed on the roof, above the outlet of the shaft. Performs two functions: protecting the ventilation shaft from precipitation and enhancing traction using wind energy.
Optimal additional ventilation systems
If the problem with cleaning ventilation shafts and channels cannot be solved, then you will have to take everything into your own hands and solve the problem yourself. There is only one way out - to establish additional ventilation. What are the solutions to this problem. There are basically few options:
- kitchen hood;
- exhaust fan and supply valves.
Kitchen hood
Manufacturers of kitchen hoods offer two options that differ significantly from each other.
- Recirculation.
- Flow-through.
The first ones purify polluted air and supply it back into the room. This option is not suitable for ventilation. The second are devices connected to a ventilation shaft or to the street by an air duct. That is, air is exhausted outside the apartment. In this regard, the best option is to throw it outside.
How effective is this option? Everything will depend on how often the hood is turned on. And since it is used mainly in the process of cooking, this is several hours a day, which is clearly not enough to ventilate the entire apartment space. This device can be used as an addition to the kitchen air exchange, but it cannot replace the entire ventilation system.
Exhaust fan and supply valve
This is the best option for creating forced ventilation in an apartment, which you organize yourself. As mentioned above, inflow and exhaust do not exist without each other. Therefore, when installing an exhaust fan, you must immediately think about the method of air flow.
There are two options here:
- Window air valve.
- Wall.
The first is installed in a plastic window structure system. It can be a slit type or in the form of a handle with which the window sashes are opened. The first ones have been used for a long time, but the second models appeared recently and have already gained quite a popularity. The most important thing is that as many doors as there are, so many handles can be installed. Moreover, valves of this type are adjustable. With special strips you can block the holes or reduce their number, thereby regulating the flow of fresh air from the street.
As for slotted models, they are installed either on the window frame profile, or at the junction of the frame and sash. This option is convenient in that the adjustment can be done manually or using a special mechanism operating from a remote control.
The second models of air valves are mounted into the wall of the house. To do this, through holes are made under them. Here it is important to understand the fact that in winter, cold air entering in large quantities reduces the temperature inside the rooms, which cannot be allowed. Therefore, supply valves are installed under window sills on top of heating radiators. That is, when the air enters the room, it immediately heats up.
Inlet valve for window
Exhaust fans
As for fans, they are often installed in the bathroom, toilet and kitchen. It may happen that a fan installed in the ventilation shaft can provide exhaust even in a clogged duct. If this does not help, then you will need to mount it in a wall with the polluted air vented directly to the street.
Manufacturers today offer two models of exhaust fans, which are often used in apartments:
- axial wall;
- axial channel.
They differ from each other in that the first are attached to the wall, the second are inserted into a through hole made in the wall. Both options are actively used today; installing both with your own hands is not a problem. The most difficult thing in this matter is to drill a hole in the wall, for which you need to have a hammer drill and a diamond bit, which is used to drill a concrete wall of a panel house.
Exhaust fan
If a wall-mounted model is installed, then a plastic pipe must be inserted into the wall, which forms a channel for exhaust air. The latter must be covered with a grille from the outside. The duct fan is simply inserted into the hole, where it is secured only with mounting foam, which fills the gap between the wall and the device.
Of course, solving the problem of ventilation in a panel house with the help of additional devices makes it possible to restore the required air exchange in the apartment. Sometimes the problem is even solved by installing two valves: supply and exhaust, as elements of natural ventilation. The main thing is to accurately calculate their cross-sectional area.
Operating principle and ventilation device options
The influx of outdoor air into the premises passes through loosely fitting window shutters or channels and valves provided for this purpose in double-glazed windows made of metal-plastic.
The hood is produced through vertical shafts (usually located in bathrooms and kitchens) running from the apartment to the roof or attic. Due to the difference in temperature indoors and outdoors, a draft arises in the shaft, ensuring air movement.
Note! In the cold season, traction is higher than in summer. In hot, windless weather, on the contrary, natural ventilation virtually does not occur.
The flow of fresh air moves through the rooms, gradually mixing with exhaust air masses, after which it is removed from the room through exhaust ducts.
If the air flow is blocked, normal air circulation in the apartment becomes impossible.
The following actions lead to disruption of this process:
- Installation of blind window frames.
- Installation of doorways without a gap between the floor and the door leaf.
- Constantly closed interior doors.
- Installation of periodically turning on fans at the entrances to ventilation shafts.
Of course, this should in no case be a reason to refuse interior doors or convenient plastic windows. For normal air exchange, it is enough to install transfer grilles in the door leaves, install special valves in the windows, and when installing fans, make sure that they do not completely block the exhaust duct.
Incorrect operation of the ventilation system is indicated by the formation of condensation on the walls, fogged windows, and the formation of mold.
For apartment buildings, several ventilation options are allowed:
- From each room in each apartment there is a separate shaft leading to the roof. The method is convenient because under no circumstances will odors from neighbors penetrate into the apartment. The pull here is also stronger and more stable. Developers use this method infrequently, since its implementation requires a large number of pipes and additional labor costs. In addition, in multi-story buildings such a ventilation system will require too much space.
- Exhaust ducts from individual rooms connect to a common collection duct in the attic, from where they are discharged to the street. If the diameter of the ventilation duct is insufficient, exhaust air masses can penetrate into rooms located on the upper floors. Because of this, the upper floors are often connected to the shaft directly, bypassing the box collector.
- The ventilation ducts lead directly to the attic, which acts as a kind of intermediate ventilation chamber. From there, the exhaust air goes outside through a collection channel. Not a very convenient method, since not only all sorts of odors will accumulate in the attic, but also an abundance of moist air. This will lead to the formation of condensation, mold and accelerated destruction of building materials. To reduce condensation, the channels must have good thermal insulation.
- Tree-like structure of the ventilation system. Small channels from individual rooms connect to the common vertical trunk. The method is economical, and therefore the most common. The main problem with this solution is that if the draft is disrupted, odors from one apartment will penetrate into neighboring ones.
Note! Regardless of the method of organizing ventilation, apartments on the upper floors are most vulnerable to disruptions in its operation. Here is the minimum distance to the exit of the exhaust duct and, therefore, the smallest draft. Possible solutions are the use of forced ventilation or separate ventilation ducts of greater height.
General information
Advantages and disadvantages
The first among the ventilation schemes in a multi-storey building can be called the one that means the presence of separate channels for all apartments, and there is its own exit on the roof. This approach to the ventilation system makes it possible to ensure air exchange at the best level even in buildings that are no more than 5 floors in height. At the same time, the inflow is additionally ensured by leaks in window and door openings. It is due to this that the desired difference in pressure for the ventilation duct is obtained. But most people rejected this approach for use in panel houses.
This is due to the following reasons:
- Lack of performance.
- Bulky.
- Lack of compensation and adjustment system.
Brick houses can be enlarged to the required size so that all the components that will help ensure normal life functions can be accommodated inside. But with buildings that were built using panel technology, this approach will not work. This is due to the fact that initially one block size was set, and now it is impossible to vary it.
At the same time, several channels for the ventilation system take up a lot of usable space, and for such a height, a multi-channel system is not able to provide sufficient air flow. As a result, moisture accumulates in the bathroom and an unpleasant aroma in the sanitary unit. The other side of the coin of such ventilation is that air leaves the living rooms quickly. This can lead to a decrease in pressure levels and the return of dirty air from the ventilation ducts.
The panel house design did not include compensators and regulators
They would help equalize the pressure level. This can lead to uneven ventilation depending on the number of floors, and the lower the floor, the better the ventilation. The result of this was increased coolant costs in winter for residents on the first floors, since all the heat is quickly blown out into the ventilation system. On the top floor there is another extreme, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning if ventilation is poor.
The importance of ventilation in a multi-storey building
A multi-storey building is a place where a large number of people, families with children and pets live all year round. It is not worth talking about what kind of thermal atmosphere is maintained in them. They build buildings from sealed materials, insulate them, and install plastic windows. These factors interfere with natural air exchange.
In each apartment of a multi-storey building, they wash the dishes every day, take a hot shower, do wet cleaning, and comb their hair. Pets often live here: cats, dogs, rodents or parrots. To get rid of moisture evaporation, unpleasant odors, and dust, exhaust ventilation of multi-story residential buildings is simply necessary.
Air exchange contributes to the formation of a normal microclimate, protects the ceiling and walls from mold, and metal products from rusting.
A ventilation shaft in a high-rise building is provided for by engineers during design. The greatest attention is paid to air exchange in residential areas with increased evaporation.
Properly functioning ventilation is a necessity in an apartment building!
Requirements for general house ventilation
The ventilation system in an apartment building is designed to ensure the outflow of polluted air masses and a constant influx of new ones. Often, residents of high floors feel insufficient draft, odors accumulate in the kitchen, and dust accumulates in the corners of the rooms. These signs indicate problems with the ventilation.
The following requirements are put forward for the ventilation system in high-rise buildings:
- Air exchange in the kitchen should be carried out at a speed of 60 cubic meters. m of air per hour, in the bathroom 25 cubic meters. m per hour.
- The air exchange rate in other living rooms should be a multiple of 0.2 of the total volume of the room.
- Air circulation must be continuous.
- Ventilation should not lead to a decrease in air temperature in the apartment.
Each of the requirements is taken into account when drawing up a ventilation scheme for a building construction project. Houses now and decades ago were built quickly, so there are shortcomings in the operation of ventilation. Over time, they get worse and interfere with air circulation. The owners of the apartments have to fix the problems. It is impossible to retrofit ventilation in a multi-storey building.
It is prohibited to re-equip the ventilation system in a multi-storey building
Installing a fan in the bathroom and toilet
The ventilation device in a panel house also includes the installation of an additional fan in the bathroom and toilet. In this case, it is necessary to ensure its flow through the door slots, and the amount of removed and incoming air must be the same.
According to sanitary standards, air exchange in the bathroom and toilet must occur at least 8 times per hour, that is, the air in the room must change completely eight times in one hour. When choosing a bathroom fan, you should consider:
- equipment power;
- presence of noise coming from the device.
- design and colors.
- availability of additional functions.
Disadvantages in ventilation operation
The disadvantage of the horizontal box scheme is the presence of reverse draft. It appears if the lid in a horizontal box is installed too low. Residents of the upper floor suffer from reverse draft. There are two ways to eliminate the deficiency:
- Increasing the diameter of the box by 2.5 times, installing inside the “cuts”.
- Arrangement of ventilation ducts on the upper floors separately from the general system, leading them into the shaft above the duct.
All work must be carried out by professionals. Some channels on the upper floors require insulation.
The second ventilation design scheme has disadvantages:
- weak draft on the top floor;
- Ventilation does not work when the attic doors are open.
The lack of operation of the air duct in the entrance of an apartment building can be eliminated by lengthening the outlets of the ducts. Pipes 1-1.5 meters long are put on them. The joints must be treated with sealing material.
Supply and exhaust ventilation in apartments
The natural system of air supply and removal is important for each individual apartment in a multi-storey building.
Air movement in the apartment is achieved using several simple techniques:
- Exhaust ducts of the general natural ventilation system have exits in baths, toilets and kitchens.
- Clean air enters the rooms through open windows and vents.
- To allow air to move freely from room to room, gaps (1–2 cm) are left under interior doors.
This ventilation plan for a residential apartment is very simple, but not always effective. Over time, the air exchange system becomes clogged and ceases to fully perform its functions. Residents are prohibited from cleaning the ducts themselves; this is done by teams of specialists.
In old buildings, natural ventilation occurs through cracks in window frames and under baseboards.
Reasons why a mine may stop working
A typical air duct problem is air flowing backwards. It all depends on the features of the system used. For example, all shafts in an apartment direct waste streams to a common channel.
If an individual channel in one of the apartments fails, this will not affect the performance of the entire system. But if there are several such apartments, then the air flow simply will not be able to push itself further, and accordingly, it will go down. The last floors will draw in the exhaust air. Usually in this case they decide to bring their channel directly to the roof. The culprit for air exchange problems in individual apartments may be plastic double-glazed windows or the lack of a gap between the floors.
Forced ventilation in the apartment
The driving force in the operation of natural ventilation is the difference in temperature and pressure. Mechanical air exchange is carried out by special devices. There are several methods of mechanical ventilation of a living space:
- kitchen hoods;
- fans;
- supply valves.
The fans are connected to a common exhaust duct. Supply valves are installed in walls or near windows. Depending on the type, the hood can be connected to ventilation or work as a filter.
If natural ventilation in an apartment building for some reason does not fulfill its functions, you need to install a hood in the kitchen, and fans in the bathroom and toilet. Supply valves can be installed in any room.
Installation of air ducts in the kitchen
It will not be possible to install a hood without additional air ducts. Pipes are required for their installation. As a rule, corrugated air ducts or plastic channels are used. If you connect the hood to the main ventilation system, the quality of air exchange decreases significantly.
Important parameters of ventilation ducts
- The diameter of the air duct should be equal to the diameter of the exhaust duct or be slightly larger. A smaller pipe diameter will lead to additional load on the motor and the formation of extraneous noise.
- The number of pipe bends should be kept to a minimum. It is not allowed to install an air duct with sections where the angle of inclination is 90 degrees.
- The length of the ventilation duct must be less than 3 m.
Important! The hood in the kitchen is an additional ventilation and does not occupy the main channel. It is used as an element of complex ventilation.
When performing installation work to install a hood above the hob, it is worth considering the distance between these two objects, depending on the type of stove.
Selection criteria, types and elements of ventilation in an apartment building
The presence of certain elements will directly depend only on the type of system. But, regardless of the chosen option, it will contain the following mandatory components:
- air channels;
- ventilation shaft;
Regardless of the type, it will definitely be a supply and exhaust system. Accordingly, it is necessary to ensure not only the exhaust, but also the arrival in the same volume.
Depending on the type of impulse to initiate cravings, such systems are usually divided into:
- natural - traction appears due to the difference in temperature and pressure indoors and outdoors;
- combined - exhaust or injection is carried out electromechanically;
- forced - draft and injection occurs with the help of special fans and other devices.
If a multi-storey building uses natural ventilation of residential buildings, the presence of a ventilation shaft is mandatory.
Diagram of a typical communal ventilation shaft
The requirements for its arrangement are simple and the same for all buildings:
- tightness;
- throughput corresponds to the designed volume;
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards;
- fire safety.
Also, depending on the air exchange pattern, the system can be mixing or displacement. The first method is typical for impenetrable walls with a vapor barrier. The influx comes through ventilation holes and various cracks. Due to the relatively high initial speed, fresh street air mixes with polluted air. If the flow is not organized correctly, it will be difficult to extract air contaminated with impurities in this way.
To select the type of ventilation, it is necessary to take into account all factors, such as:
- number of floors;
- location relative to other structures;
- level of external noise;
- environmental pollution.
For houses with intra-block location and noise levels up to 51 dBA, it is recommended to install natural ventilation. If the building is located in a particularly polluted place, or the noise level is more than 51 dBA, it is necessary to use an air supply system and it is advisable to carry out filtration.
Arrangement of ventilation elements in a high-rise building
The location of air intake from the street is installed in certain places, depending on how the ventilation in the apartment building is arranged. If heating of the drawn air is not provided in the system under consideration, it must be brought as close as possible to the ceiling of the room. This will ensure that it is completely mixed with the warmer air in the room.
In order for the penetrating air to be heated under the influence of heating devices installed in the apartment, the input is carried out near these devices.
When heating occurs directly in the blowers, the supply is equipped at the bottom of the room.
Regardless of the type of system, inflow occurs only in living rooms, and exhaust in the kitchen and bathroom. The hole for the hood is installed at a height of at least 2 meters from the floor. The ventilation scheme in a multi-storey building assumes that there is no movement of air from sanitary and additional premises to living rooms.
It is recommended to provide separate ventilation ducts for different rooms with natural exhaust of polluted air, excluding single-level assemblies. If such a possibility is not available in an apartment building, it is necessary to provide for the supply of separate pipes into one vertical shaft.
Regulatory Requirements
Most of the standard parameters and data for calculation are set out in SNiP 01-31-2003 “Residential multi-apartment buildings”, SNiP 41-01-2003 “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning”. And also SNiP 2.09.04-87*, SNiP 2.08.02-89*.
Several parameters are used for calculation:
- Indoor air temperature: for living rooms +20-220С; kitchens with electric and gas stoves 16-180C; bathroom +250C; restroom +180C; combined bathroom +250C; corridor (lobby) +160С; pantry +120C; lift engine room +50C
- Air exchange rate: varies from 25 to 90 m3/h per person.
- Outdoor air flow is determined based on the area of the room: for living rooms it is 3 m3/h per square meter of area.
These are all generalized parameters, and each region can vary the values based on climatic conditions.
Designers have a certain margin of freedom:
- According to SNiP, in one of the bedrooms of an apartment consisting of several rooms, the calculated air temperature is +220C.
- In apartments adapted for the accommodation of disabled people, the maximum temperature value is shaved.
- Ventilation of corner apartments is calculated according to standard parameters plus 20C, but not higher than +220C.
Today, plastic window structures and sealed steel entrance doors completely nullify the effect of micro-ventilation through the gaps, so it is difficult for designers to achieve regulatory parameters for the microclimate. In luxury houses they follow the path of installing forced supply ventilation, but in budget apartment buildings everything is more complicated: it is necessary to increase the intensity of work, and therefore the size of the ventilation ducts. But this is not always possible from a building design point of view.
Standards for indoor arrangement
Building codes impose several requirements for the design of the ventilation system:
- The presence of at least one window with access to the street. Necessary for proper operation of natural ventilation.
- Windows or supply grilles on the first floor must be at a height of at least 1000 mm from the surrounding snow cover, and in the summer - 2000 mm from the blind area.
- The cross-sectional area of the air ducts for the kitchen is 150 cm2, the combined bathroom and separate toilets and bathtubs are 100 cm2 each.
- The direction of air movement is strictly from residential premises to service premises, then through a common air duct to the roof.
- Electrical wiring must not be installed inside ventilation ducts.
- Ventilation routes should not intersect with each other or with cable ducts.
Features of arrangement and functioning in panel houses
If we talk about this common type of house, then the air exchange there is arranged according to a natural principle. The system is designed in exactly the same way in old brick houses, as well as in low-budget new buildings. Street air is sucked in through cracks and leaks in old frames or through special holes provided in modern plastic ones.
The drainage in them occurs due to the presence of a constant draft present inside the ventilation shaft-channel, which rises above the ridge of the roof or goes into the attic. Street air, entering living spaces through windows, thanks to the draft in the duct, tends to the exhaust vent in the bathroom or the hood in the kitchen. It turns out that the air, passing through all the rooms of the apartment, gradually displaces the polluted air into the street.
History of the creation of ventilation shafts
The first theories concerning the intensity of air exchange in a heated room appeared in the 18th century. However, history knows that the prototypes of modern ventilation shafts appeared in houses several dozen centuries ago. Such structures are also found in Egyptian pyramids.
For reference: by the 18th century, various directions for the development of this engineering system appeared, each of which set specific goals at the forefront. In particular, clinics began to organize mines that ensure the removal of harmful bacteria and the flow of oxygen.
During the same period, the first theoretical developments of devices appeared, which were later called fans. By the 19th century, the idea of creating full-fledged mines, with both natural and forced air ventilation, had formed. The result of the described work was the appearance of works by Russian scientists. Published books also from the 19th century describe the idea of creating supply and exhaust ventilation, in which the air coming from outside was additionally heated.
The order of operation of ventilation using the example of a typical project
The most common panel project is a nine-story building. The principle of operation of the hood is the same. Air from the street, through windows and cracks, enters the apartment. The exhaust occurs through satellite ventilation ducts in the kitchen or bathroom. One, or less often several, channels from the hood are connected to the main pipe. These channels are connected to the main shaft through two floors. These shafts are quite bulky and take up a lot of space. A large-panel house will most likely be equipped with such a system.
Such a scheme for a house of 9 floors assumes the presence of a warm attic. The outlet from the 8th and 9th floors goes directly into the atmosphere, bypassing the common channel. The scheme for a 9-storey building was designed based on the complete absence of wind and an outside air temperature of +5.
Despite the fact that natural ventilation in such houses is not very effective, it requires almost no maintenance, and blockages rarely occur. There have been cases where ventilation ducts became clogged with building materials during the construction of a house. Such a surprise subsequently affected the quality of the hood. Most often, cleaning the mine is required once every 5-6 years.
During repairs, many people block the air flow in some place. They unknowingly think that this will not affect the hood, but the process of air renewal in the apartment becomes difficult or stops completely.
The most common actions leading to interference and disruption of natural ventilation:
- installation of sealed plastic windows;
- interior doors with seal;
- installation of various fans in the hood.
In order not to disrupt the operation of the natural ventilation draft, it is forbidden to obstruct the inflow and outflow of air. For plastic windows, it is necessary to install inlet openings or arrange an external inlet separately. Doors between rooms are equipped with bars at the bottom. The cross-section of the exhaust duct should not be blocked by fans.
Possible options for arranging ventilation in high-rise buildings
Modern ventilation in a panel house is equipped with single exhaust pipes. From the sanitary facilities, each floor has its own pipe going to the roof. In this option, there is no possibility of penetration of foreign odors and the entire system functions evenly and reliably.
Another good option is when all vertical channels flow into a common horizontal collection manifold, which is located in the attic. The air from it exits to the street through one common pipe.
The most unstable method is when a small satellite channel from each apartment enters a common ventilation shaft. This ventilation scheme in a panel house is significantly cheaper to install and increases living space, but constantly brings a lot of problems to residents. The most common one is the flow of various odors from one apartment to another.
Vent. mine with satellite channel
The best ventilation option is electromechanical forced air supply and exhaust systems. They are used in modern new buildings, except low-budget ones. The supply installation of such a system is located in the basement or on the side of the main building. It supplies filtered and heated or cooled air to all rooms and spaces. On the roof, in turn, there is an electric exhaust fan with exactly the same design power as the supply fan. It is designed to remove contaminated mixtures from apartments through hoods.
This is one of the primitive schemes of the device. A more complex one, which can be equipped in a modern high-rise building, is equipped using new energy-saving technologies. For example, recuperators are devices that allow you to take heat or cold from the exhaust air and give it to the supply air.
Who should clean the ventilation in an apartment building?
Checking the ventilation in an apartment building is done like this: attach a sheet of paper or a paper napkin to the exhaust grille. If the sheet or napkin does not stay on the grill, then there is a problem with ventilation.
Possible reasons for lack of traction:
- The mine simply doesn't work.
If the house is old and the shaft is made of concrete blocks, then cracks may appear at their joints. - There is a blockage in the mine.
Dust, small debris, and insects get into the air ducts. Grease deposits may form on your kitchen hood. - No influx.
If fresh air does not enter the apartment, there is nothing to displace the exhaust air. In this case, the productivity of the supply and exhaust should be approximately equal: the air passing through a small window slit will not be enough for full ventilation.
You can only clean the grille on your exhaust vent yourself; The cleaning of ventilation shafts is carried out by specialists. If the ventilation does not work, diagnostics are carried out: a video camera is lowered into the shaft, which detects the cause of the blockage. All dirt is then removed using a pneumatic brushing machine.
Ventilation must undergo not only cleaning, but also disinfection. A sprayer with a flexible pipe is carried out to the middle of the shaft and cleans its walls with an antibacterial solution. For better treatment, you can contact the sanitary and epidemiological service: specialists will analyze the bacterial environment in the ventilation and select an individual disinfectant.
Service
During operation, any ventilation system inevitably becomes clogged. Dust from the street, grease particles from the kitchen, construction debris, etc. can get into it. The ventilation grill in the apartment may also become clogged.
We recommend that you read: Ventilation of a pigsty
It is easy to check the draft level in the ventilation duct shaft. It is enough to bring the flame of a lit match or lighter closer to the grate. When everything is in order with the draft, the fire will begin to tremble and noticeably rush towards the mine. If this does not happen, you need to remove the grill and repeat the test again. If the flame remains motionless again, the shaft needs to be cleaned.
It is important! Fire should be handled with care - an open flame can melt the plastic grate and even ignite dust accumulations in a heavily clogged shaft. An alternative way to determine if there is a blockage is to place a thin sheet of paper or napkin on the vent. Properly functioning ventilation should hold the sheet in place without any problems.
Sometimes the flame is completely deviated in the other direction, signaling the presence of reverse draft - an unpleasant phenomenon that allows air that is not the most healthy for health and not the most pleasant odors from the ventilation shaft to penetrate into the apartment. This can be avoided by installing grilles with a check valve that allow air flow in only one direction.
Complete and effective cleaning of ventilation shafts in multi-storey buildings is carried out only by professional organizations that have special equipment: pneumatic brushes with weights, special weights, video equipment, and other devices. It is recommended to carry out such a procedure at least once every 3-5 years. In addition to mechanical cleaning, disinfection is carried out.
It is almost impossible to clean the ventilation shaft on your own. All that can be done from the apartment is to clean the channel up and down at arm's length.
How is sewer ventilation done?
Removing unpleasant sewer odors is also necessary for comfortable living in apartment buildings. The sewerage “ventilation” system is simplified to the minimum: gases are removed through the same riser as the wastewater is discharged.
To prevent unpleasant odors from bothering residents, the riser is equipped with an extension that goes onto the roof - a ventilation (fan) pipe.
The diagram clearly shows how sewer ventilation is arranged. All apartment plumbing fixtures are “tied” to a common riser, which on one side ends with a drain pipe, on the other – with an outlet leading to the centralized city network
Knowing the diagram, you can understand why work on remodeling bathrooms requires permission. If you change the location of the riser or connect a large number of plumbing fixtures, the operation of the ventilation system may be disrupted.
When equipping the sewer network, taking into account the ventilation of the system, they are guided by SNiP 2.04.01-85 .
A kitchen hood is the easiest way to improve air exchange
When installing additional ventilation in the kitchen, that is, hoods, you must be guided by SNiP 41-01-2003. You can install different types of hoods:
- Hanging ones, which are mounted directly above the gas stove. Such models “catch” exhaust air and discharge it into an individual shaft.
- Built-in, which are mounted in a special wall cabinet. Some models of this type of hoods have retractable panels, which increase the grip area.
- Dome. This type of hood is installed directly above the stove and has a more modern look.
The hood cannot be connected to a common ventilation duct.
Any hood is equipped with a filter. To maintain freshness in the kitchen, it is necessary to promptly replace multi-layer grease filters. The hood is mounted using brackets or screws, and can also be decorated with a wall cabinet if desired. The wall cabinet also houses a socket for powering electrical equipment.
Natural ventilation of apartment buildings
Example of a supply and exhaust system
Residential buildings of mass construction (standard) are traditionally equipped with natural supply and exhaust ventilation. The operating principle is based on the difference in pressure and temperature of indoor/outdoor air. Windows are used for ventilation; exhaust is carried out through ventilation shafts located in the walls of the building.
In Soviet times, a cumbersome, not always justified ventilation scheme was used: each grille had its own channel leading to the attic, and there they were combined into one large one, leading into the exhaust shaft.
In modern construction, the method of individual channels is used for apartment buildings up to 4 floors.
Modern apartment buildings above four floors are equipped with ventilation according to the “trunk-satellite” scheme. This is the optimal solution that meets the requirements of regulatory documentation.
Scheme "trunk-satellite"
Ventilation diagram with satellite channels
Ventilation according to this scheme consists of a vertical collection channel (trunk) and its side branches (satellites). This system provides exhaust from kitchens, toilets and baths. Through the exhaust hole, air enters the side channel; at the level of the interfloor ceiling, it enters the main collection channel. This scheme is characterized by increased aerodynamic stability and meets all fire safety requirements.
There are two versions: the first provides a separate side branch for each intake point; the second allows you to power the kitchen and bathroom through one side branch (but only when it is located at least 2000 mm above the rooms served). This requirement is dictated by aerodynamic properties.
One or two last floors can be connected using a separate circuit. This is caused by the impossibility of connecting side branches to the main trunk due to the design features of the building.
Air enters the attic from several prefabricated vertical ducts. So the attic space is a horizontal section of the general house ventilation system. Through ventilation shafts, one or more for each section, it is removed into the atmosphere. To reduce heat loss, the attic must be insulated.
Air ducts are made in two versions. For standard apartment buildings, a floor-by-floor ventilation unit is used; it can be brick or reinforced concrete (panel buildings 86 and 800 series). Elite housing, as well as many modern apartment buildings, are equipped with steel exhaust air ducts.
The main positive property of the “trunk-satellite” ventilation scheme is the absence of energy costs. The movement of air masses occurs due to physical and aerodynamic laws.
Ventilation block structure
An example of the structure of a ventilation unit
The ventilation unit consists of a central duct with one or more branches and a transition valve. Almost all ventilation schemes for apartment buildings provide for the connection of side branches on each floor. But this was not always the case; previously, connection nodes were placed every 2-5 floors.
The blocks are connected to each other with cement-sand mortar; this is a quick but unreliable method of sealing: the seam may move or the mortar may fill the internal space, then the intensity of ventilation will decrease. To prevent undesirable consequences, the seams are sealed with silicone glue.
Example of ventilation of a 9-storey building
A standard Soviet-era residential building has 9 floors. Supply and exhaust ventilation with natural impulse, the inflow is carried out through windows and doors, and the exhaust operates according to the “trunk-satellite” scheme. In most projects, the alternation of side branches occurs through two floors, but sometimes a floor plan is also found. From the apartments of the last two levels, air is drawn through separate channels, and not into a common shaft.
Ventilation diagram for a standard residential building
The calculation of the power of the ventilation system is carried out on the ground floors without wind, taking the average temperature outside equal to +50C.
Disadvantages of natural ventilation
Ventilation blocks of a similar design are used in 10-story and 25-story buildings. This leads to the subsidence of air masses: they do not have time to gain sufficient speed to release waste from the branches of the apartments of the last level. If there is no wind or it blows on the opposite facade, then residents of the top floors can smell the smell from the apartments below.
In extreme heat, even if all the windows are open, the ventilation intensity with the classical natural ventilation scheme drops significantly, so it is recommended to install air conditioners to create comfortable microclimate conditions.
Basement ventilation
Exhaust ventilation of basements is carried out according to the same scheme as the main building. If there are no windows, fresh air is supplied through vents and openings in the basement of the building. From the outside they are closed with bars.
Vents Recently, there has been a tendency for residents of an apartment building to seal the vents. This is strictly prohibited and is a violation of the operating conditions.
Ventilation system design in Khrushchev buildings
Ventilation in Khrushchev buildings is arranged as follows: air circulates due to physical laws, according to a natural pattern.
Windows and doors act as ventilation. The hood is carried out through special openings covered with a plastic or steel grille. The pattern of movement of air masses looks like this: cold, clean air from the street enters through slightly open windows and doors. There is also a process of infiltration - ventilation through natural cracks between the window frame and the opening, door and jamb. Due to the lower temperature, as well as the pressure difference, the air rushes towards the ventilation grilles, along the way displacing warmer waste air, which is removed through the grilles.
The combined bathroom of the houses of some series was not equipped with a separate ventilation shaft, so for ventilation a small window was provided, located in the partition between the bathroom and the kitchen.
There is another air movement scheme: two rooms, separate toilet and bathroom, one shaft. A small 200x200 mm hole was punched in the wall between the rooms. The air from the toilet, under the influence of aerodynamic forces, rushes into the bathroom, and from there it is removed through the hole.
Ventilation schemes
Ventilation shaft location options
In houses built by Khrushchev, two schemes for installing ventilation shafts are used. Each belongs to its own period of capital development of the Soviet Union and has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Direct removal of waste air masses. It is not suitable for ventilation of a 5-storey residential building due to its massiveness. Each point of the fence has its own ventilation duct; on the roof they all gather into one large one and rise no less than 2,000 mm above the roof level. This is the normative value.
- A ventilation shaft with satellite channels is a more “advanced” system. Suitable for equipping five-story and higher apartment buildings. Consists of ventilation units delivered to the construction site assembled. There is a common ventilation shaft; satellite channels from each intake point are connected to it through the floor. Theoretically, this device circuit cuts off the possibility of exhaust air flowing from one apartment to another.
Construction of a ventilation shaft with satellite channels
In some standard projects, another additional scheme was used: the ventilation grille was installed in the space between the wooden floor and the floor slabs. Natural draft ventilated the wooden deck boards, significantly increasing their service life.
Kitchen ventilation with geyser
A feature of some mass-produced houses built by Khrushchev is the presence of a gas water heater for heating cold water. This creates certain problems, since during its operation a large volume of carbon monoxide is released, which is extremely dangerous for humans. According to standards, combustion of 1 m3 requires ten times more supply air.
The gas water heater is connected to a chimney (vent shaft), and backdraft may occur. When the inlet is closed and the hood intensively removes air, a zone of low pressure is formed, carbon monoxide from the column changes directions and begins to enter the apartment.
Proper operation of a gas water heater requires the fulfillment of a number of requirements:
- The geyser must not be covered or decorated.
- The minimum clearance to kitchen furniture is 100 mm.
- Windows in the kitchen, especially plastic ones, should be used year-round in micro-ventilation mode.
- A ventilation hole is installed above the interior door, the minimum size of which is 100x200 mm.
Bathroom ventilation
Here, too, there are two ways. The first is the same as the ventilation systems of Stalinist, Brezhnev and modern apartment buildings: a separate shaft with access to the roof, there is a nuance when there is only one for the toilet and bathroom. Then an outlet is arranged between the rooms. The second is used only in houses built by Khrushchev: ventilation through a window between the bathroom and the kitchen.
Calculation of ventilation of a residential building
It should be noted that forced and natural ventilation of a multi-storey building is calculated by serious design organizations. Residents receive it ready-made and cannot change anything in it without interfering with the building’s building structures. However, with the help of various additional equipment, air exchange can be improved, which requires a simple calculation.
For example, ventilation in a panel house does not work well, but you want to have an air environment favorable to health within your home. Then you should remember one rule: the amount of supply air should be no less than that removed by all hoods. This means that to increase the draft, axial fans are already installed at the shaft exits. So that they do not thresh the air in place and the exhaust ventilation functions normally, units of the same capacity should be installed on the supply side.
Advice. Avoid installing overly powerful fans in the kitchen and bathroom. For a one-room apartment, a capacity of 50 m3/h for each is enough, for a two- or three-room apartment – up to 100 m3/h.
You can organize a forced inflow with cleaning and heating using small installations built into the wall. Typically, the ventilation system of a residential building consists of several similar units located in different rooms. Through their work, they ensure the balance of the indoor air and its cleanliness. By the way, the amount of inflow can even prevail over the exhaust within 15%; there will be no harm from this.
Forced type systems
In modern housing construction, plastic and metal-plastic structures are used to seal window and balcony openings. Double-glazed windows made of polymers and aluminum are stronger than wood, but often completely block the natural channels for fresh air.
The doors also fit tightly to the floor, making the rooms completely airtight. There is no air intake, and in the absence of an effective supply system, the exhaust system becomes useless.
To solve the problem of access to fresh air in all apartments, special equipment is installed in luxury residential buildings - air handling units.
An example of installing a supply and exhaust system in an apartment building. Downstairs, in the basement or plinth, supply equipment with air filtration and heating is installed, on the roof - a chiller and a fan
The supply and exhaust ventilation system is quite complex, and to install its individual elements you will need to allocate space in the basement (supply air heating) and on the roof (fan and chiller).
Unlike natural ventilation, incentive ventilation is energy-dependent. In addition, it consists of a set of complex devices that are controlled from a single remote control.
The SHUV is installed next to the supply equipment, in the basement, and only qualified service personnel have access to it.
We can say that in residential high-rise buildings all three types of ventilation are present, with natural being the most common, and the installation of a forced or combined system is still limited.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
To improve ventilation on your own, you need to consult with professionals and choose the most economical and effective method.
Expert opinions from specialists:
On the uniform operation of two or more ventilation ducts:
Why are turbo deflectors needed:
How to install the inlet valve:
The natural ventilation mode, characteristic of apartment buildings, is not always fully justified. If the building does not have a forced centralized network, then you can organize the inflow/outflow of air yourself, using household devices.
What the regulations say
The common shaft of the ventilation duct of a panel high-rise building.
According to SNiPs, air exchange indicators for rooms in an apartment are established:
- Kitchen space 90 m3/hour;
- Toilet – 50 m3/hour;
- Bathroom and bathroom combined with it – 25 m3/hour;
- Living rooms - 3m3/hour per 1 m2.