Author: Website editors
Publication date: 29.04.2019
Issues discussed in the material:
- Why are there different types of room ventilation?
- What are the types of ventilation systems?
- What features does natural ventilation have?
- What is mechanical ventilation
- What features does supply and exhaust ventilation have?
- Duct and ductless ventilation systems
- Ventilation with recovery
- What is the difference between stacked and monoblock ventilation systems?
- What are the most common types of industrial ventilation?
- How to install ventilation in production
- What kind of air ducts are used for ventilation?
- What types of ventilation filters are there?
- What types of smoke ventilation are there and what you need to know about them
Normal operation of any facility or even a separate room is impossible without a well-thought-out ventilation system. For this purpose, various types are used to supply fresh air and remove exhaust air. They can provide air exchange processes in different ways, which affects the quality of the microclimate and the cost of ventilation. In order to choose the right project, you need to know what types of ventilation exist and what their differences are. The answers to these questions can be found in our review.
What is ventilation
Ventilation is the movement of air in a room. Air enters any building from the street. Getting inside the room, the air is filled with various substances: carbon dioxide from our breath, dust, chemical emissions from objects, animal hair, etc. This already polluted air moves to the hood and is discharged out through it. At this time, a new portion of fresh air from outside enters the room, which also goes into the hood. This whole process is called ventilation.
Climate control equipment that ensures the correct functioning of the described process is also called ventilation. It can be natural and mechanical, channel and compact, supply and exhaust, and much more. All types of ventilation and their features are described below. In the meantime, let's figure out how important ventilation is in an apartment or house
Calorifiers-heaters
When air is taken in, it organizes a preliminary increase in the flow temperature. The option is effective in any use scenario. With a closed circuit, the heating efficiency remains as high as possible. Once inside the home, the characteristics do not change significantly. The automation system is often supplemented with not one heater, but several at once.
It is not always worthwhile to equip the system with all the solutions that exist on the market at once. The choice is determined by the needs of the customer and the capabilities of the specialist responsible for solving the problem. Preliminary accurate calculations help to avoid overpayments. This will make it easier to decide which functions are most important for a particular house or apartment. It is important to pay attention not only to personal comfort, but also to maintaining a healthy environment in general. Fresh air strengthens the immune system and eliminates a large number of negative effects. The correct organization of the systems themselves is also important.
Why is ventilation needed?
It is thanks to ventilation that a healthy and comfortable microclimate is created in the room, namely:
1. Carbon dioxide levels are normalized
Carbon dioxide is always present indoors: after all, we exhale it! The only question is how much it is. When carbon dioxide accumulates excessively, it has a negative effect on the human body. It interferes with the full supply of oxygen to the blood and organs. The brain begins to become “lazy,” and we feel tired, lethargic, and become inattentive. A high concentration of carbon dioxide is also associated with a feeling of stuffiness.
Good ventilation ensures constant air renewal. The air coming from the street replaces the air in the room along with the carbon dioxide accumulated in it. It is not stuffy and comfortable to be in such a room.
2. Humidity is normalized
Proper ventilation implies that excessively humid air from the premises is promptly released into the exhaust hood. This eliminates the formation of eternally damp areas in corners and on walls where mold actively grows.
The ventilation system may also have additional functions. For example, air filtration allows you to remove contaminants from the air at the entrance to the room and make the air healthy and safe. And the heating function in the ventilation prevents the risk of catching a cold from cold air from the street.
Instead of a resume
Let's try to summarize the above. Of course, it is impossible to cover all the nuances of choosing a ventilation system for a specific facility in a review article. We can only give a basic idea of why a ventilation system is needed, what it can and cannot do, and what the consumer should pay attention to when choosing such a system.
Now about the main thing. Remember, you always have the opportunity to deepen your knowledge, clarify what is left “behind the scenes” in the article, by asking a question to the experts, simply by filling out the feedback form, which you will find below. It's free, convenient, fast and informative. You can also receive a commercial offer free of charge and quickly by sending your request through the feedback form. Good luck!
What kind of ventilation is there?
Ventilation is a set of devices and measures to ensure normal air exchange in a building. Based on this concept, the classification of ventilation is divided as follows:
- according to the method of air movement and pressure - artificial and natural ventilation;
- by use - exhaust and supply ventilation;
- by service area - general and local;
- By design - ductless and duct ventilation.
By considering each type in order, you can determine the main advantages and disadvantages of ventilation systems. In order to maintain the necessary microclimate, it is necessary to carefully study the issue of classifying ventilation units and apply them in accordance with the necessary parameters. The types of ventilation in residential buildings are not very different from those installed in industrial and public buildings.
Video description
For a clear overview of ventilation in a private house, watch the video:
Usually, the doors from the staircase to the floor must be closed for the normal functioning of natural ventilation
In the attic it is always necessary to install forced ventilation, since the standard natural draft is not provided due to the low height of the ventilation ducts.
Kitchen ventilation
To ventilate the kitchen, builders of a private house must provide a separate ventilation duct into which the exhaust air flow will be sucked.
The channel is mounted from galvanized steel sheets or other stainless materials. The surface of the channel should be smooth so that greasy fumes from the kitchen and soot from the stove do not settle on it. The inlet and outlet openings of the channel are protected by grilles.
As in the whole house, air circulation in the kitchen is carried out by natural and forced methods. Those. vents and windows are opened, or a hood is purchased. The latter option is clearly preferable, since the inability of natural ventilation to cope with the odors that appear during cooking is beyond doubt.
Classification of ventilation systems
Systems are classified according to different criteria:
- method of submission;
- purpose;
- air exchange method;
- design.
The type of ventilation is determined at the design stage of the building. In this case, both the economic and technical aspects, as well as sanitary and hygienic conditions, are taken into account.
Types of ventilation system according to supply method
Based on the methods of supplying and removing air from the room, 3 categories of ventilation can be distinguished:
- natural;
- mechanical;
- mixed.
Ventilation design is carried out if such a solution is capable of providing air exchange that meets established standards.
When natural ventilation does not meet the requirements of sanitary and hygienic standards, the second option is chosen - a mechanical method of activating the air mass.
If it is possible, in addition to the second ventilation option, to partially use the first one, mixed ventilation is included in the project. In residential buildings, air flow occurs through windows, and exhaust equipment is located in the kitchen and sanitary room. Therefore, it is important to establish good air exchange between rooms.
Mixed ventilation. It is used when natural ventilation cannot be the only option. For high-quality air exchange in rooms with very polluted air, mechanical ventilation is installed
Types of ventilation by purpose
Based on the purpose of ventilation, there are working ventilation systems and emergency ones. While the former must constantly provide comfortable conditions, the latter come into operation only when the former are switched off and an emergency occurs when standard living conditions are disrupted.
These are sudden failures when air pollution occurs with toxic fumes, gases, explosives, toxic substances.
The types of ventilation systems for all types of premises are almost the same. Having studied all their types and weighed all the advantages and disadvantages, you can choose the best option for a particular building
Emergency ventilation is not designed to supply fresh air. It only provides a gas outlet and does not allow the air mass with hazardous substances to spread throughout the room.
Ventilation systems by air exchange method
Based on this criterion, general and local ventilation systems are distinguished. The first must provide the entire volume of the room with sufficient air exchange while maintaining all the necessary air parameters. Additionally, it must remove excess moisture, heat, and contaminants. Air exchange can be carried out either through a ducted or ductless system.
General exchange supply ventilation reduces the level of concentration of harmful substances remaining after the operation of the local and general exchange exhaust ventilation system
The purpose of local ventilation is to supply clean air to specific places and remove polluted air from the points where it is formed. As a rule, it is arranged in large premises with a limited number of workers. Air exchange occurs only in workplaces.
Separation of systems by design
Based on this feature, ventilation systems are divided into ducted and ductless. Duct-type systems consist of a branched route consisting of air ducts through which air is transported. Installation of such a system is advisable in large rooms.
When there are no channels, the system is called channelless. An example of such a system is an ordinary fan. There are 2 types of ductless systems - ceiling-mounted and under-floor. Ductless systems are easier to implement and consume less energy.
How to ventilate rooms at work during coronavirus?
Infection with the virus is possible through airborne droplets. When a person coughs or talks, particles up to 5 micrometers in diameter are released. They remain in the air for several hours and can be transported with atmospheric currents over long distances.
Coronavirus parameters are up to 160 nanometers. Laboratory studies show that it can be detected in the air for up to 3 hours, and on objects for up to three days.
However, ventilation in any way will prevent more coronavirus particles from settling on the surface of furniture and equipment. In general, there is an increased risk of illness in indoor spaces that are not regularly ventilated.
The Federation of Engineers recommends, if possible, 24-hour ventilation at reduced air speed. If this possibility is excluded, ventilate for 15 minutes before the start of the working day, during breaks and staff changes. Improving the health of the space should not cause hypothermia and colds. In this case, the air is exhausted only in one direction - the outside.
It is not recommended to use recirculation systems and local equipment, as well as any systems with air supply, so that the removed virus, after settling on the walls of the ventilation system, is not returned back. Such equipment can only be turned on with the recirculation dampers closed, especially during outbreaks.
In toilet rooms with ventilation, the windows should be closed during ventilation to avoid creating a backflow of air.
Toilet exhaust systems must operate 24/7, as constant humidification during washing and flushing toilets contributes to the formation of moisture droplets in the air, which spread the virus. For the same reason, flushing should be done with the toilet lid closed.
Does an employer need to create a ventilation schedule during Covid?
Based on the mandatory recommendations of Rospotrebnadzor, the employer is obliged to draw up a schedule for ventilation of the workspace and keep a special log.
In the new version of the document from Rospotrebnadzor dated September 29, 2020, ventilation is listed as one of the preventive measures against coronavirus.
It is carried out every 2 hours. During the procedure, the doors of the toilet rooms must be closed, and employees must remain outside the premises to avoid colds.
Surfaces are disinfected before ventilation, so that fumes from these products are also removed.
If you cannot carry out the procedure regularly, you can purchase a bactericidal lamp to disinfect the air. It works in recirculation mode and kills all pathogens, including coronavirus.
Compilation rules
To streamline the implementation of preventive measures, an order is issued appointing a person responsible for drawing up a schedule and its implementation. Documentation is not mandatory, but will help track the regularity of the procedure.
The schedule indicates:
- the premises for which it was compiled;
- date, time;
- duration of the procedure;
- responsible person;
- signature of the person responsible for ventilation.
Instead of a graph, it is sometimes more convenient to keep a journal with similar data. In addition to the required details, you can specify the ventilation method. In the absence of personnel, open windows, doors, transoms or use ventilation.
The regularity of ventilation directly depends on the sanitary standards for this type of premises. In children's institutions, the procedure is carried out every 1.5 hours for 10 minutes, in schools - every break for 5-7 minutes, during the school day every 1.5 hours.
Purpose and types of ventilation
Modern ventilation systems come in different types and, depending on their purpose, are divided into several subgroups. This division is carried out according to several parameters: the direction of air movement, the method of bringing air masses into motion, the territory served.
Ventilation in the house
What kind of ventilation is there in rooms in the direction of air movement? According to this parameter, systems are divided into two large groups:
- inlet;
- exhaust
There is also ventilation and its classification according to the factor that sets the air in motion. According to this parameter they are divided into:
- with natural impulse (natural);
- with mechanical motivation (mechanical, forced).
There is also a division of ventilation, the types of which vary depending on the service area. According to this principle, ventilation systems are divided into:
- general exchange:
- local (local).
All types of ventilation systems considered can be used both separately and together in one building or even room.
Systems can also be classified as ducted or ductless, depending on whether they use ductwork or move air through openings in the walls or fans without pipes attached.
Let us examine in more detail all the types and subtypes of room ventilation systems, how they differ and what their tasks are.
Natural ventilation
As already mentioned, natural ventilation is one of the popular types of modern systems. This type of room ventilation implies that the air is driven by natural factors. More precisely, it is the pressure difference between the internal volume and the external atmosphere. For it to function, it is necessary that the pressure outside is slightly less than inside the room. If such a factor occurs, air begins to move through specially designed ventilation ducts.
A striking example of such ventilation is the installation of exhaust ducts in the walls of multi-storey and private houses. The main positive factor in using natural ventilation is its low cost. There is no need to use expensive equipment or organize an electrical connection. Air exchange occurs on its own. But you need to keep in mind that there are also negative sides to using such a system. First of all, this is a dependence on atmospheric parameters.
Air movement in natural channels occurs only with a negative pressure difference, but this is not always the case. There are times when the pressure inside and outside the room equalizes. Then the air exchange stops or even vice versa, reverse draft occurs. The natural system reacts very strongly to precipitation and weather changes. If in frosty sunny weather the draft can be several times greater than the calculated one, then in the fall on a rainy day there may also be movement of outside air into the room.
Mechanical ventilation
Considering further the types of ventilation systems based on the method of moving air, we will focus on the forced network. In it, unlike natural, electricity is used to move air. Air exchange occurs forcibly under the influence of ventilation units: fans, supply and exhaust units.
The main driving element of such a system is the fan. This is a device that consists of a housing and impeller of various types, as well as an electric motor. The electric motor drives the impeller, which is designed to capture air currents and move them from the fan intake to the exhaust.
Fans are generally classified into two broad types:
- axial;
- centrifugal.
In axial, air movement passes through the impeller perpendicular to the blades. In centrifugal fans, the air moves parallel to the blade, as if bending around it.
In addition to the fan, the forced-air system may consist of additional elements. First of all, this applies to duct systems, since in them the air moves through a network of connected air ducts (rigid and flexible), there is a need to use valves, air flow regulators, as well as other elements:
- filters for cleaning supply or exhaust air from dust and pollutants;
- silencers to reduce vibration and noise levels;
- heaters: water or electric units for heating supply air;
- grilles, diffusers, anemostats and other flow distribution devices.
A large number of additional and installation materials are also used. Including insulation, clamps and temperature and fan power regulators.
Supply systems
As the name suggests, these types of ventilation systems, such as supply ventilation, are designed to supply outside air into the room. They are both natural and mechanical. Mechanical systems are the most common because they allow precise control of the volume of air supplied and its characteristics.
Natural supply systems are used less often and are mainly used for uncontrolled air supply. That is, they have an exhaust system that operates according to design parameters, and the air flow is organized through cracks in the windows, special holes or grilles naturally due to the pressure difference.
Moreover, the supply system can work in tandem with an exhaust system of both natural and mechanical types. It should be borne in mind that both systems work interconnected, since the volume of supply and exhaust air must be the same.
Exhaust systems
Such types of ventilation systems as exhaust systems are designed to remove air from a room or part of it. They are both mechanical and natural. While natural supply systems are rare, their exhaust options have been used for a long time and effectively.
In housing, the main purpose of exhaust systems is to remove human waste products and other air pollutants. Firstly, it is necessary to remove carbon dioxide, which is formed during respiration. Moreover, quite a large amount of it is formed. In addition, it is necessary to remove water vapor, as well as polluted air from bathrooms and kitchens. In industry, exhaust ventilation is largely designed to remove contaminants that arise during the production process.
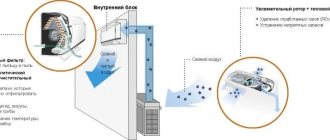
Supply and exhaust ventilation with recovery
We should also talk about systems with recovery. They are designed to save energy resources during operation. If the supply and exhaust are arranged separately, mainly using different mechanisms and units, then such types of ventilation units as supply and exhaust with recovery use one unit for operation, which moves both supply and exhaust air.
Placing two branches in one device is necessary so that the air flows intersect. At the intersection, a recuperator is used, thanks to which heat from the exhaust air is transferred to the supply air.
In some cases, this helps save up to 80% of heat and return it to the room rather than throwing it outside.
There are mainly 2 types of recuperators used: cross-flow (plate) and rotary.
General and local ventilation
As the name suggests, these types of ventilation systems, such as general exchange ones, work for the entire room. They are arranged in order to supply a certain calculated amount of supply air and remove polluted air from the entire volume of the room. They can be both comfortable (for human life) and production – they provide the parameters of the production process.
In contrast, local or local systems work for a site or a specific area. They are designed to provide a localized supply of fresh air to the workplace or remove contaminated air directly from the point of origin. For example, at a welding station or over a kitchen stove.
Video description
For more information about recuperators, see the following video:
It is important! Including a recuperator in the supply and exhaust system allows you to save up to 70-90% of the heat of the exhausted room air.
Phases of operation of the recuperator in the supply and exhaust ventilation mode in the house Source moydomik.net
General ventilation with mechanical drive
Mechanically driven structures can be either supply or exhaust. Supply ventilation is sometimes performed in conjunction with central heating.
The air intake in such a system can take the form of holes in the building envelope, a free-standing or attached shaft. When installed outside the building, the air intake shaft is located above ground level or on the roof.
Layout of air intake devices: in the enclosing structure (a) near the outer wall (b) on the roof (c). Exhaust ducts and shafts are insulated from the outside, otherwise ice will form in them in winter
The choice of design and location of air intakes is influenced by the requirements for the degree of cleanliness of outdoor air, as well as the architectural features of the building. The bottom of the opening through which clean air enters must be located at a distance of at least 2 m from the ground, and if the building is located in a green zone - 1 m. External air intakes cannot be placed where there are harmful emissions.
Air masses enter the mine through a fan. Passing through the heater, they are heated, moistened or, on the contrary, dried and enter through air ducts with holes.
Air can also be supplied through branches equipped with nozzles that guide the supply air masses. The volume of supplied air is controlled by dampers or valves located in the branches.
Mechanical local ventilation of supply type
Local mechanical ventilation operating in a limited space is called air showering. This ventilation option is used in those work areas where the radiant heat intensity is more than 300 kcal/h. or production involves the release of toxins that cannot be removed using local exhaust.
Showering units can be mobile or stationary. The former, when providing the workplace with clean air, take it from the room. Sometimes water is supplied into the sprayed air mass. When its drops come into contact with the human body, they become an additional coolant. The latter supply clean outside air or pre-treated air through shower pipes.
General exhaust ventilation
Removing exhaust air from a room is the task of exhaust ventilation. Removal of used air from a room occurs by lowering the pressure in it. Thus, conditions are created for air to enter it from outside or from an adjacent room.
The exhaust ventilation design includes a cleaning device (1) fan (2) air ducts - central (3) suction (4). When there is no other type of ventilation in a room except exhaust, the pressure in it drops to a level lower than in adjacent rooms or lower than outside
When designing general-exchange hoods for production workshops, the point is taken into account that the elimination of dirty air should be carried out directly from the original source of formation of harmful emissions in the direction of their natural trajectory and not pollute clean areas. Such places are biological laboratories, workshops with harmful conditions.
Mechanical supply and exhaust ventilation
The supply and exhaust ventilation is based on 2 flows moving towards each other. It consists of two independent systems - supply and exhaust, or one unit. It has built-in all the equipment necessary to operate both supply and exhaust.
If there are 2 separate systems, ventilation operates without recirculation and is called open. The second type of ventilation system is called closed, and it works with recirculation.
The recirculation system saves energy spent on cooling or heating the air, because the air mass is not completely heated, but only the volume that comes from outside. The removed air in a recirculation system is returned to the room again with an admixture of fresh air, amounting to 10-15% of the total volume of the air mass.
The installation of such ventilation is possible in places where there are no dangerous pollutants. In regions with cold climates, a closed system is ineffective because recirculation and external air masses do not mix well enough.
Mechanical ventilation in case of emergency
In case of unusual situations, in addition to the working option, emergency ventilation is arranged. Invariably it is always exhaust. Mechanical emergency ventilation is installed in rooms where there is a threat of breakthrough of explosive vapors or gases. In this case, explosion- and spark-proof fans are installed.
The axial explosion-proof fan contains a motor in an explosion-proof enclosure. It is secured in such a way that, if necessary, it can be quickly replaced
There are dangerous components that cannot be removed using fans. Then the ejector is included in the system. Emergency ventilation should be switched on automatically as soon as the main ventilation stops working. Opening of openings through which dirty air will escape must be done remotely.
Pipes and grilles designed to allow air to escape during emergency ventilation are placed in places where hazardous substances are most likely to be concentrated in large volumes. Openings through which air is removed in an emergency should not be located in areas where people are constantly present. Umbrellas must not be mounted on emergency system pipes and shafts.
Emissions accidentally released into the atmosphere must be dispersed as much as possible and not allowed to enter confined areas of the territory adjacent to the building. MPCs are monitored using gas analyzers adjusted accordingly.
Features of local ventilation
Unlike all of the above ventilation systems, which are general types, that is, those that ventilate the entire space of the room at once, local ones ventilate only certain places.
At the same time, such systems can both supply air to the right places - a local supply-type ventilation system - and remove the waste mixture from them - an exhaust system.
Local supply system
Among the supply systems used in specific places are:
- air showers;
- curtains;
- oases.
The first type is a concentrated air flow supplied at a significant speed to a specific point in the room, most often the workplace.
Curtains are used to create partitions from the air or change the direction in which the air flow moves.
The last type is areas fenced off from the entire room into which a flow of low-temperature air is directed.
Often in production, a general exchange system is used simultaneously - to remove contaminants from the entire space at once, and a local one, providing maintenance to individual parts of the room.
Local ventilation
Local ventilation in production
Such a system is used when the place where the formation of pollution occurs is completely localized. At the same time, there is almost always a need to prevent the movement of contaminants throughout the entire space of the room.
The most effective in such cases are suction units - types of cabinet shelters, side suction units, umbrellas, casings for all kinds of devices, and the like.
Their use is often highly effective, since they quickly remove contaminants directly from work areas, preventing their appearance in the rest of the space. Since this results in a high concentration of pollutants, the operation of the system allows for an excellent sanitary effect, while at the same time it removes only a small amount of the air mixture.
But local systems are not the way to solve all ventilation requirements. Thus, not all air pollution is localized; more often they are dispersed throughout the available space. At the same time, supplying the air mixture to individual parts or removing it from them does not ensure the achievement of the required parameters of the air environment.
Fans
Ventilation system fans
According to the principle of operation, they can be axial or radial. The models also differ from each other in terms of functionality. Axial mechanisms are the traditional configuration. An impeller is fixed on the engine shaft, air is captured by the blades. Then the flows move in the right directions. Reverse connection is another difference from radial varieties. That is, air flows can be directed in all directions at once. With small pressure differences inside, the permeability remains high.
In the case of radial designs, the air accelerates between the inlet and outlet pipes. The impossibility of reverse movement is characteristic. Serious pressure can be created at the inlet and outlet, which also acts as one of the main differences.
Stacked and monoblock ventilation systems
The most common are stacked ventilation systems. They are assembled, like a construction set, from individual elements (fan, filter, muffler, air ducts, etc.), and the elements can be from different manufacturers. A typesetting system can be designed for any room, from a small apartment to an entire building, but only a specialist can correctly calculate and design it.
A monoblock installation is a ready-made ventilation system located entirely in one housing. In a monoblock system, a recuperator is often installed - a device in which heat exchanges cold supply air with warm air removed from the room, which allows saving from 30 to 90% of electricity. Installing a monoblock system takes several hours and does not require a large amount of consumables, but it will not fit into every room.
How to calculate the optimal air exchange rate?
When making calculations, you need to take into account the number of people living in the apartment. On average, 3 cubic meters of air should flow per square meter of living space per hour. However, the recommended rate of air replacement differs in different rooms. For a bathroom this is 25 cubic meters per hour, for a bathroom - 50 m3, for a kitchen with an electric stove - 60 m3 per hour, for a kitchen with a gas stove - at least 90 m3.
There is also another calculation recommendation: an adult consumes about 30 cubic meters of air per hour, a child about 20 cubic meters.
Features of ventilation design
Considering what types of ventilation there are and their main parameters, it is possible to achieve the desired result. Buildings with poor ventilation systems risk dust accumulation. The use of household chemicals and the use of household appliances lead to changes in the physical and chemical characteristics of the air. Designing a residential building or industrial buildings is not complete without a pre-thought-out ventilation system.
Important! Calculations and conditions for ventilation systems are provided for by the relevant building codes and laws.
A properly planned system allows you to achieve the necessary microclimate indicators. Various types of ventilation of premises - residential, public, industrial - have their own standards and requirements. All this is an important engineering and technological aspect. Only competent design of ventilation systems will ensure consistently acceptable conditions in any buildings.
Diffusers
They also perform distribution functions, essentially the evolution of lattices. But the devices are more technologically advanced and modern. To smoothly change the amount and direction of air masses, they are equipped with additional sensors and regulators.
More often the term is associated with the arrangement of forced ventilation systems. Their main difference is the smaller diameter of the technological holes. Designers use the element when designing modern interiors, as their appearance is reminiscent of lighting fixtures. A dehumidifier is another type of add-on.
Stirring and displacement ventilation
There are two main, commonly encountered types of ventilation: mixing ventilation and displacement ventilation.
Before looking at these two types in more detail, it is necessary to review the most commonly used air quality terms.
Ventilation efficiency
Ventilation efficiency is a value that shows how quickly polluted air is removed from a room. It is determined by the ratio of the concentration of harmful impurities contained in the exhaust air to the concentration of harmful impurities in the room. Ventilation efficiency is often used to qualitatively assess a system's ability to provide comfortable, clean air. This indicator depends on the geometry of the room, the relative position of the supply and exhaust openings and the density of distribution of sources of harmful impurities in the room. Displacement ventilation allows ventilation efficiencies of over 100% to be obtained, while with stirring ventilation they do not exceed 100%.
Air exchange coefficient
This parameter characterizes the rate of air replacement in the room. It depends on the air distribution conditions in the room, the location and size of diffusers, the location of heat sources, etc. When using the displacement method, it is possible to obtain air exchange coefficient values from 50 to 100%, while when using mixing ventilation they do not exceed 50%.
Displacement ventilation
This is the most effective method traditionally used for ventilation of industrial facilities. In addition, this ventilation method has found wide application in so-called comfort ventilation systems. With a correctly calculated scheme, this method allows you to effectively remove excess heat and achieve maximum ventilation efficiency. For a more detailed description of this method, it is necessary to highlight the following concepts: working area and adjacent area
Work zone
Part of a room occupied or used by people. The work area is considered to be a space 50 cm from walls and window openings, and from 10 cm to 180 cm above the floor.
Adjacent zone
This is the space around the low-speed supply diffuser, where it creates a certain local air speed. For comfortable ventilation systems, it is generally accepted that the local air speed in the adjacent area should not exceed 0.2 m/s. Such requirements are imposed in order to reduce the adjacent area around the diffusers as much as possible.
Air speed and temperature
In displacement ventilation, air is brought to a lower level and flows into the work area at low speed. The supply air must be slightly cooler than the ambient room air for the displacement principle to work. For comfort systems, the supply air temperature should be 1 °C below room temperature, and for industrial or special systems this value is from 1 to 5 °C. If the inlet temperature is too low, there is always a risk of the formation of so-called. convection currents.
Advantages and disadvantages
Displacement ventilation is very convenient for use in industry, where there are a lot of harmful impurities and heat emissions. Properly designed displacement ventilation systems provide very good air quality, but this principle has some limitations:
- Supply diffusers require more space;
- Supply diffusers may be covered with something by mistake;
- The adjacent area becomes much larger;
- The vertical temperature gradient becomes very high.
When designing these systems, it is also necessary to take into account the relative position in height and power of heating devices, which affect the dynamics of air flows inside the room. When combined with extraneous air currents in the room, uneven heating in height in some cases causes the heated layers of air to shift downward. In practice, this leads to the functioning of the ventilation system according to a different principle - mixing
Ventilation by stirring
With mixing ventilation, supply air is supplied in one or more streams to the work area, entraining a large amount of indoor air into movement. The working area lies in the return flow zone, where the air speed is 70% of the speed of the main air flow.
Jet length
The length of the stream is taken to be the distance from the air distributor to the cross section of the air stream, in which the velocity of the flow core is reduced to 0.2 m/s.
Ejection
Ejection is the ability of diffusers to mix adjacent room air into the stream. Jet-type diffusers (where air is swirled passing through nozzles at high speed) are prime examples of supply devices with a high degree of ejection. Diffusers for displacement ventilation have a low degree of ejection. To eliminate the feeling of draft when the supply air temperature is below room temperature, it is necessary to use supply diffusers with a high degree of ejection.
Layering effect
When the ventilation hole is located sufficiently close to a flat surface, the outgoing air current is deflected in its direction and tends to flow directly along the surface. This effect occurs due to the formation of a vacuum between the jet and the surface, and since there is no possibility of air mixing from the side of the surface, the jet is deflected towards it. For a spreading effect to occur, the distance between the inlet opening and the ceiling should not exceed 30 cm.
Air speed and temperature
Acceptable air speed in the work area depends on factors such as: room temperature, type of activity in the room, interior interior. It is noted that the feeling of draft is eliminated when the air speed is less than 0.18 m/s and the temperature is from 20 to 22 °C. Obstacles
The air flow is likely to change direction if there are obstacles hanging from the ceiling, such as lamps, ceilings, etc. If the projection does not exceed 2% of the ceiling height, then the air flow will go around the obstacle.
Symptoms of an attack
There are a number of clinical signs characteristic of the presence of sleep apnea:
- Pronounced loud snoring. Sometimes a person himself wakes up from his snoring.
- Increased sleepiness during the day. Occurs even with normal or higher than normal duration of night rest. Spontaneous uncontrollable falling asleep during the day is typical.
- Increased pathological motor activity during rest.
- Decreased libido (sexual desire), sexual dysfunction.
- Increased blood pressure. It is usually higher in the morning. Moreover, there is an increase in diastolic (lower) pressure.
- Hypnogagic hallucinations (sound, visual, tactile non-existent phenomena that occur at the moment of falling asleep).
- Enuresis (urinary incontinence) at night or frequent urination. They are not associated with any specific disease or condition (pregnancy, diabetes, cystitis).
- Headaches, morning or night.
- Decreased intelligence and performance.
- Shortness of breath, suffocation that occurs during sleep.
- Heartburn or belching at night.
- Increase in body weight. Weight gain can progress even with interventions aimed at combating obesity.
- Increased sweating during sleep. Especially in the face and neck area, upper torso.
Components of ventilation
As already noted, any ventilation that brings fresh air flow into the room is divided into types depending on the following characteristics:
- by appointment;
- service locations;
- the way the air flow moves;
- design features.
Regardless of the type of system used, almost all of them use a standard set of components:
- fans and ventilation units and units - devices that provide air movement in any direction;
- thermal curtains are used to prevent the passage of the air mixture into a certain area or change its direction;
- noise absorbers - for quiet operation of equipment;
- filters and air flow heaters - devices designed for cleaning and necessary air treatment;
- air ducts through which air flows move;
- regulating and locking devices that serve to control the operation of the entire system;
- air flow distributors that control its movement.
Thus, there are many types of air purification systems, thanks to which you can provide high-quality ventilation for any occasion and type of room.
Using ventilators
When talking about how to properly ventilate living spaces, it is worth mentioning fresh air ventilation devices. These are ventilators - very remarkable solutions installed in metal-plastic double-glazed windows or on external walls and operating in two modes (natural or forced).
The first are valves located in cracks or walls and do not include a fan. Any such system must function due to the pressure difference - respectively, in the apartment and on the street. To ensure effective air exchange in the room, exhaust ventilation must be installed - otherwise such a ventilator will be of no use.
As for systems that provide forced air supply to the home, they are equipped with fans and mounted in the walls. Also worthy of attention is such a useful function of such ventilators as filtering large and medium-sized particles, preventing them from penetrating into the room.
In addition, such devices can additionally purify the air from microscopic impurities (this filtration method involves the use of carbon to trap unwanted particles). Compact air handling units with climate control are also becoming increasingly popular - solutions that operate in automatic mode.