The ventilation system of a private house should ensure a flow of fresh air into all rooms of the house and stimulate its renewal. The air duct system and openings for air flow are called supply air. Air ducts and exhaust openings are exhaust. Everything seems to be simple.
But in practice, the question of the most efficient design of a ventilation system is one of the most controversial. One of the most controversial issues is whether ventilation can be vented into the attic. It may be better to dispose of waste and contaminated air mass directly, i.e. through the wall?
In the article we presented, all aspects of constructing a ventilation system for a country house are discussed. We will introduce you to the regulatory requirements and nuances of the organization. Our recommendations will help you decide on the most practical option.
Well-designed attic roof
In modern construction, they try to provide all structures with maximum thermal insulation and seal them in order to reduce heat loss.
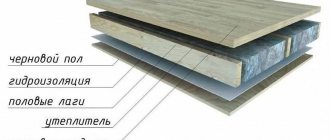
This concerns structures enclosing the attic, perhaps most of all. After all, it is through the roofing system that the greatest amount of heat can escape. If the layers of hydro-, steam- and thermal insulation in the roofing pie are folded without ventilation gaps, the insulation system will practically not work. Moisture that falls out in the form of condensation due to temperature differences, household fumes, and rainwater that has penetrated under the roof will not have the opportunity to escape outside.
Water is an excellent conductor; due to its content in the insulation, heat waves will freely pass outside. In addition, it provokes rotting of the wood from which the rafter frame is made, and often the cladding of the attic.
Draining the roofing pie is perhaps a separate extensive topic. However, its effectiveness significantly affects the microclimate of the attic, especially in the summer heat, when the top layer of the roof warms up to +100C. Therefore, we will briefly talk about how this should be arranged.
With proper organization of the roofing pie, with the installation of ventilation ducts of the required cross-section, the insulated slopes are regularly washed by air currents. As a result, the dried roof does not allow heat waves to pass through, and building structures do not get wet or fail.
The purpose of any roof ventilation devices is to ensure air movement from the overhangs to the ridge. The easiest way to do this is under a roof made of slate or ondulin: under the waves of roofing material, the air freely rises to the ridge; in this case, the overhangs are not tightly hemmed.
The situation with metal tiles and corrugated sheets is almost the same, but it is advisable to provide their eaves with ventilation grilles or cover them with an air-permeable seal. The relief roof must be separated from the waterproofing by a spacer bar - it forms a ventilation gap required to remove fumes and atmospheric water accumulated under the coating.
Other materials, in particular soft tiles or sheet metal, require the artificial creation of 1 or even 2 ventilation layers of 3–5 cm, separating the vapor barrier from the insulation, and the waterproofing film from the coating.
For the inflow and exit of air flows into the roofing system, openings must be made to allow the flow to move freely
For this purpose, ventilation ducts are arranged by laying sheathing and counter-lattice. Air will rise between the slats. If the thickness of the rafters is not enough to lay all layers of the roofing pie and provide ventilation gaps, the rafter legs are extended with bars.
For inflow into the roof overhangs, perforated inserts are used - soffits or ventilation grilles, at regular intervals along the entire length of the overhang. For exhaust, a special ridge with aeration or point aerators are installed.
The total cross-sectional area of all openings for ventilation of the under-roof space should be 1 m2 for every 300 - 500 m2 of roof slope area.
Both the under-roof space and the gable sheathing can be ventilated through point aerators if the organization of long aerators or slots is impossible
Ventilation of the gables is carried out between the sheathing and the façade cladding material. If the sheathing is installed horizontally, then the sheathing supports are vertical, and they do not interfere with natural ventilation.
If the frame slats need to be fixed horizontally, there are several solutions for gable ventilation:
- Fasten small sections of slats horizontally in a checkerboard pattern. It's economical and efficient, but it can be difficult to get everything level.
- Install long slats, but make holes in them in a checkerboard pattern.
- Construct a vertical counter lathing. Ventilation in this case will be most effective, but the most material will be required.
If the sheathing is diagonal, preference should be given to the vertical arrangement of the slats.
Content
Let's start with the fact that the attic in a residential building serves as a kind of buffer zone between the open sky and living rooms, and therefore regulates heat and humidity fluctuations and creates comfortable living conditions. And here, proper ventilation of the attic and insulation of its floors decide a lot. If the removal of heat and steam has not been thought out, then residents will have to face several disadvantages of such a roof arrangement. Look, for example, at what happens over time to an attic that had no ventilation at all:
Maintaining the required roof temperature
It is high-quality ventilation that helps get rid of such serious problems as ice and icicles:
The thermal balance of the roof is determined by the amount of heat that passes through the attic floor. And not only through a layer of thermal insulation, but also through such thinner structures as a hatch, doors (depending on what leads to the attic), as well as technical elements.
Effective ventilation of the attic space really helps in winter in the fight against ice and icicles and reduces the amount of melt water in the spring. But on those days when it is warm during the day and frosty at night, the problem will remain. And to solve this problem, special heaters for cornices are produced today.
And on hot days, heat balance is especially valuable:
Protection of insulation from dampness and blowing
For good attic ventilation, it is extremely important that its volume is large enough, and that there are no partitions inside that would interfere with the air flow. The fact is that no matter how reliable the vapor barrier is, steam from living quarters still penetrates through the ceiling. The only 100% vapor barrier is an aluminum sheet. The films have 95-97% protection. That is why it is important that there is a waterproofing membrane on top of the insulation with vapor permeability to allow excess fumes to escape outside. This top layer of insulation is needed to protect the insulation from moisture from the outside and from accidental leaks from the roof. At the same time, it is important not to confuse: vapor barrier is installed from below, from the ceiling, waterproofing - from above.
And finally, ventilation rids the attic of fungus, which loves stagnant air so much. By the way, many people believe that attic ventilation is only needed in the summer. In fact, temperature changes occur all year round, and it is ventilation that will smooth out this difference.
Nuances of arranging ventilation systems for cold and warm attics ↑
To ventilate a room under a roof, it is not at all necessary to create complex engineering systems or install exhaust fans. As a rule, in such cases, ordinary vents are made in the attic, which are able to ensure natural circulation of air flows.
Ventilation system without attic insulation ↑
Natural air circulation through the vents Adjusting air flows in accordance with the need at one time or another is very important, so you should leave free access to the grilles without covering it with rafters. You also need to make dampers on the ventilation ducts, which will allow you to increase, decrease or even block the air flow.
Such an adjustment system is necessary for a hermetically sealed roof, for example, corrugated sheets or metal tiles, where the sheets fit tightly at the joints. If the ceiling is made of materials such as wave slate or ondulin (in the absence of a waterproofing film), vents should not be made - there are enough gaps between the waves for air circulation.
Ventilation on the gable through a dormer window
All gable and mansard roofs have gables, where a grille is installed for ventilation of the attic space, and on one side it is placed with the holes down, and on the other, adjustments are made. In cases where the structures have hip, half-hip or multi-gable gables, as a rule, there are no gables, but, nevertheless, a dormer window can be made there where a grille can be placed.
Pipe device (aerators) for roof ventilation
If there is no entrance from the street into a cold attic, and there are no dormer windows, which is often found in modern architecture of private housing construction, then roof fans - aerators - are installed. Such a device is a pipe in the form of a glass, protected from above from precipitation by a headband. In some cases, a check valve is also added there.
Ventilation system calculation
Ventilation system for a warm attic ↑
The situation with air circulation in a heated attic, that is, an attic, looks somewhat different. In the room itself, the air exchange process occurs, as in living rooms - through doors, windows, vents and grilles specially provided for this (possibly with forced exhaust). But here it is necessary to separately provide a ventilation gap under the roofing material in view of its insulation from the bottom side.
Air circulation diagram in the attic with heating
If the roofing material on your house is ondulin or slate, then to ensure good circulation it is enough to maintain a distance of 20-30 mm between the roof and the insulation (waterproofing) - the air will pass through the wave joint. But in cases where corrugated sheeting, metal tiles, seam or soft coverings are used, the roof will be sealed, which will contribute to the formation of condensation and, as a result, fungal mold.
In addition, condensation will destroy the metal coating, and moisture can also penetrate inside through a loose connection of the waterproofing. In such cases, gaps for air circulation are left at the eaves hem (below) and under the ridge (above). For metal, additional waterproofing is also used during its installation.
The importance of pipes for a ventilation system
Ventilation duct made of PVC sewer pipes can have any bend shape
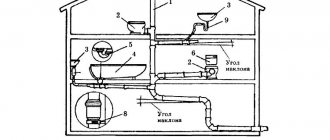
During the air exchange process, each citizen living in a given living space should receive about 30 cubic meters of fresh air. The ventilation system must provide it. Pipes are the arteries of a complex ventilation mechanism. Using them, vapors, gases, and odors are removed from the most contaminated rooms (toilet, kitchen, bathroom, workshop, etc.). Served in “safe” rooms (bedroom, living room, etc.).
When organizing natural ventilation in areas with the formation of pollution, vertical channels with outlet to the roof are installed to move air. Through them, the stale air flow escapes into the atmosphere at a considerable height: the higher the pipe, the more effective the thrust. Log houses and frame buildings, as well as buildings where ventilation was not provided for at the design stage, are equipped with plastic pipes.
For mechanical air exchange, the use of pipes is simply necessary. The system of pipes and shafts is complemented by supply and exhaust ventilation units. The forced system consists of a special piping of rectangular or circular cross-section. The supply is carried out to each room, producing air exchange in it.
Along with metal hoses, plastic pipes are increasingly being installed. This can be either polyurethane or polyvinyl chloride. Pipe type – medium and hard. The temperature of the passing air should not exceed +70°C, otherwise the strength of the material will be impaired. This applies in particular to kitchen hoods. Recommended list of rooms where sewerage pipes can be used as ventilation:
- one-story residential buildings of small area;
- production sites of small enterprises;
- garages;
- cabins;
- warehouses;
- corridors.
As you can see, these are objects where there are no increased requirements for ventilation, but it is needed, and the traditional air exchange system is too expensive.
Attic space: the need for ventilation
The device is the most important part of the design. Ventilation is involved in the heat exchange processes of the entire residential building.
During the hot season, the roof can heat up over one hundred degrees, and heated hot air enters the house, aggravating the heat in it. In cold weather, other problems may arise. Cooled air forms drops of condensation on insulated floors: this moisture negatively affects wooden elements.
Even basic ventilation can prevent premature deterioration.
Attic ventilation ensures mixing and equalizing the temperatures of the roof structure and the external environment. It prevents the formation of ice during the melting of the snow cover, avalanches and the appearance of large icicles
Arranging a high-quality air exchange system is actually extremely important
DIY installation
Before you start arranging the attic ventilation with your own hands, you need to create its design, carefully consider the layout of its components, and write down on paper the sequence of work. During the preparation process, it is imperative to inspect all areas of the attic space, take the necessary measurements, and note the design features of the attic. When performing forced ventilation, it is necessary to select an exhaust fan with the appropriate technical characteristics. Sequence of installation work:
- In the diagram, according to the established designations, the fixation points of the valves and the area for laying the exhaust pipe are marked.
- You need to drill holes in the roof using a drill or hammer drill. These works are carried out very carefully so as not to damage the layers of the roofing cake, the design of which includes roofing, sheathing, waterproofing, insulation and vapor barrier layers. Holes for supply valves are made in the cornice or pediment. You should definitely take into account the placement of supply and exhaust ducts. The first ones are equipped below.
- Valves are being installed in the wall. A tube is inserted into a pre-drilled hole, which is covered with a grille on the street side. A filter is installed on the inside and the valve body is attached. All these elements are included in the valve delivery kit. The gaps between the structural elements and the wall surface are carefully sealed.
- On the roof surface where the hole for the pipe is drilled, the lining is securely fixed, and the quality of sealing of the connecting sections is checked. Next, the pipe is installed strictly vertically. It is imperative to maintain all calculated distances.
- A fan is mounted to the pipe on the inside of the building, and a deflector is mounted on the outside. The ventilation system is ready for operation. The effectiveness of its work is tested over the course of several days.
It is important to understand that properly equipped attic roof ventilation is one of the conditions for comfortable living in a country house. When arranging it with your own hands, it is imperative to comply with established building standards, design it together with the structure of the house and equip it at the stage of erecting the roof of the building.. https://www.youtube.com/embed/VGCQE8ZgaSE
Ventilation system options for cold attics
The classic option would be to make a ventilation system through dormer windows. This ventilation device is quite simple and can be done independently. How to do it is another question, there are several schemes, but we will use the classic one.
Dormer windows should be mounted on opposite gables, their dimensions should be 600x800 millimeters. A fairly good installation method (due to the simplicity and level of the cross-section, which allows for the necessary air exchange), however, it is not without problems.
The main disadvantage of the technique is the appearance of stagnant air pockets or zones. To avoid this problem, you can make dormer windows of somewhat smaller sizes, combining them with a very effective cornice-ridge ventilation system.
You can also install vent hoods, and this method is very popular in Europe. Vents are openings in a building on which it is necessary to install grilles to protect against the entry of various atmospheric precipitation or debris from the street.
In addition to the use of dormer windows and vent openings, you can use deflectors or ventilation turbines (forced ventilation with a supply and exhaust system). The principle of their operation is similar, but they provide much better traction.
Basic rules for roof installation
Be sure to follow the rules for installing the ventilation system, regardless of what type of system you use. Ignoring the instructions can result in either the system becoming ineffective or unsafe.
Ventilation hood in the attic of a building
Basic rules and regulations:
- for any type of roof, the area of the ventilation ducts should be 400-500 cm²/meter, which will correspond to the required gap height of 40-50 millimeters;
- Please note that dust entering the gap of the ventilation system is hygroscopic, which means it can potentially lead to moistening of the insulation;
- It is imperative to additionally protect the vents if they are mounted on valleys, eaves or on ridges/ridges - protection must be installed from birds, various insects, litter from the street (including foliage);
- in cases where the length of the roof covering is more than 10 meters, it is highly recommended to use auxiliary structures to enhance the operation of the ventilation system;
- constantly monitor the ventilation system - if the air duct is narrowed, this will negatively affect the entire system, which can ultimately lead to condensation;
- do not try to make the gap height very large - this will in no way enhance ventilation, and even on the contrary, will worsen it due to the occurrence of turbulence and air resistance.
PIR boards
PIR boards - ventilation duct insulation
Insulation of a new generation, which is characterized by a rigid cellular structure. Both sides of the materials are covered with foil.
The positive aspects and characteristics are described as follows:
- Rot resistant.
- No risk of damage during installation.
- Low- and moderately flammable material.
- Service life up to 5 decades.
- 120 kPa is an indicator of compressive strength.
- No more than 1% water absorption.
- High thermal conductivity coefficient.
The question of choice is always decided in favor of external insulation. The reason is that the technology for carrying out work is too complex in the case of analogues.
thermal insulation of air ducts
Theoretically, work can be carried out inside and outside the system equally. But the outdoor option is chosen more often. The final quality of the material depends on the thickness of the layer. When choosing, you need to rely on several indicators at once:
- Temperature regime.
- Aggressiveness of the environment.
- Humidity, and so on.
The calculations are carried out by specialists, the formulas are given in the current SNiPs. The final result depends on a large number of factors, so it is not recommended to deal with the issue yourself.
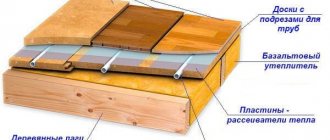
Basic elements of under-roof ventilation
The width of the ventilated under-roof space depends on the roofing material you use. The under-roof space is the air gap between the bottom of the roofing material and the waterproofing film or membrane, behind which there is a layer of insulation. For example, if the roof of your house is covered with metal tiles or any other metal-based material, the ventilated gap should be at least 2.5 centimeters.
When using soft (bitumen) tiles or other rolled materials, the thickness of the air gap must be at least 5 centimeters. The specified standards must be observed when ventilating the attic. The main elements of the under-roof ventilation system are aerators and soffits. The former play the role of exhaust openings, and the latter provide an influx of fresh air, and, therefore, prevent the formation of condensation and drip moisture.
There are conventional aerators, mounted in the inclined plane of the roof slope, and ridge aerators, which are installed at the highest point of the roof, that is, on the ridge. The number of aerators depends on the type of roofing material and the manufacturer's recommendations, but there is a general rule. It states that for every 500 sq.m. the ventilated area should be 1 sq.m. ventilation holes. This ratio allows for high-quality ventilation of the room, avoiding noticeable heat leaks.
Ridge aerators are considered the most effective, as they have a large outlet area. Ventilating the attic floor using ridge aerators is quite simple and does not cause difficulties even for beginners. The main thing is to follow the instructions, use high-quality fasteners and ensure good waterproofing at the junction of the roofing material.
As mentioned earlier, soffits are an important part of roof air exchange systems. Soffits are perforated siding panels designed to cover the eaves of the roof along the entire perimeter of the building. In addition to the assigned functional load, they give the roof a complete look
Soffits are not only perforated, but also non-perforated. The required number of perforated soffits is determined taking into account the area of the roof slopes. The use of these elements is possible only if a special gap between the materials was provided when installing the “pie”
In addition to the assigned functional load, they give the roof a finished look. Soffits are not only perforated, but also non-perforated. The required number of perforated soffits is determined taking into account the area of the roof slopes. The use of these elements is only possible if a special gap between the materials was provided when installing the “pie”.
To achieve maximum effect, it is better to use one type of aerator: either ridge or inclined to ensure better air exchange. Correct installation of spotlights and aerators eliminates the formation of condensation and drip moisture. When forced ventilation is used, supply fans are installed in the under-roof space
Particular attention should be paid here to connecting the fan or fans to the power supply. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure fire safety and more or less free access for their maintenance, replacement or repair.
Characteristics of insulation
The choice of material for thermal insulation of ventilation pipes is carried out according to the following criteria:
- thermal conductivity;
- vapor permeability;
- resistance to various reagents;
- temperature limit;
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards
Each insulation for ventilation pipes has both its advantages and disadvantages, which are determined by its structure and technical parameters.
Mineral wool
It belongs to the traditional type of insulation and has good thermal insulation properties. In addition, mineral wool and other fibers are among the most affordable materials. However, when using it for internal insulation, a seal will be required, and for external insulation, reliable protection from moisture will be required.
Mineral wool with foil outer layer
Foamed polyethylene
Available in the form of shells that tightly fit the surface of the pipes, or in rolls. It is durable, long-lasting, affordable, resistant to moisture and chemicals. In addition, foamed polyethylene is not only a good insulator, but also helps to significantly reduce vibration of air ducts.
Expanded polystyrene
It is characterized by resistance to moisture, prevents the appearance of microorganisms and corrosion. This provides reliable protection of the metal from destruction, so polystyrene foam is used not only to insulate air ducts, but also to insulate the gas pipe.
Using shell-shaped insulation, you can provide access to the ventilation pipe for repair work.
Expanded polystyrene shell to protect ventilation pipes
Polyurethane foam
It is produced in the form of a shell and in many respects is the same as expanded polystyrene, but is more resistant to fire. Therefore, polyurethane foam will be a reliable barrier in the event of a fire and will not allow the fire to spread.
Cold attic ventilation
Cold attic ventilation needs to be regulated. Therefore, you should not cover the rafters and sheathing. Alternatively, you can make lining with gaps that will ensure unhindered air circulation. If slate or ondulin was laid on the roof, and there are no vapor- and wind-proofing films, there is no need to worry about ventilation - air can circulate freely between the waves of the roof, entering the attic and exiting out. Metal tiles are also capable of allowing air to pass through, but condensation forms on it. Therefore, the use of film is mandatory (read more: “How to eliminate condensation under the roof”).
You can make vents in the attic in a more economical way - install standard ventilation grilles. One grille needs to be turned with the holes down, and the other should be made adjustable. To prevent insects from entering the attic, install a mosquito net.
For a hip roof, ventilation is created using a different technology. The entrance hole is made in the hem, at the bottom, and the exit at the ridge, at the top. If the overhang lining is made of wood, the beams can be placed loosely, maintaining an interval of several millimeters between them. If the lining is plastic, there must be holes - these panels are called soffits.
A lot depends on the type of roof. For slate and euro-slate, a classic ridge is installed, for a flexible roof - a turtle (valve). A ceramic roof requires a special valve. The installation of a cold attic under a metal tile roof allows for ventilation using a regular ridge. It is not only a financially beneficial replacement for a valve. The ridge also allows you to create a ventilation system in a short time.
Sometimes a dormer ventilation window is made in the attic (it can be glazed or grilles installed), but this method of creating ventilation is more complex, and good practical and theoretical preparation is required to implement the plan.
Ventilation aerators
Installation of roof aerators
A roof aerator is a modern and convenient type of ventilation. It is a pipe covered with a cap on top. Aerators remove steam, moisture and stagnant air, providing ventilation for a cold attic in a private home. Aerators are installed on roof slopes, where air movement is ensured by differences in temperature and pressure, replacing ridge vents. Aerators can be continuous or point. Point aerators are equipped with fans and guarantee good air movement. Outwardly, they resemble fungi.
Continuous aerators are a plate along the ridge with holes. Being covered with a roof on top, they are practically invisible and provide intense air movement due to the large area of the holes.
Various types of aerators are created specifically for roofing from:
- bitumen shingles;
- flat roof;
- metal ceramics;
- ceramics.
Aerators are installed only where eaves vents are provided. There are other conditions for their installation:
- Only roofs with a slope of 15 - 45 degrees are suitable;
- a distance of at least 30 cm is maintained from the chimney or wall;
- aerators look 25 cm above the slot at both ends of the ridge;
- point models are mounted no further than 50 cm from the ridge.
Ventilation of a warm attic
Modern heating systems practically do not use natural circulation. Ventilation of the attic above the attic is simply necessary for a comfortable stay in the room. Thus, when converting an attic into an attic, you need to make the roof ventilated. For flexible tiles and sheet metal, a ventilated area is created - a counter batten is sewn onto the rafters. For metal roofs it is better to use windproof films. Counter battens for slate roofing are not necessary, since air must circulate freely from bottom to top.
The entrance is created in the binder, and the exit is created in the ridge. The attic will be ventilated in the same way as other rooms. Air will enter through the windows (VTK valves can be installed), and air will exit through the ventilation holes. When they are absent in the walls, fungal aerators are installed in place of the hood on the roof (read: “Under-roof ventilation and its importance”).
To get a consultation:
The attic in many houses is cold, since its insulation costs a lot of money. Thanks to the spacious intermediate zone, the issue of ventilation is easily resolved.
For efficient air passage, soffits or cornice vents are installed at the bottom of the overhang. The latter are located vertically. All of them have perforations, which allow air flow to pass through, but prevent insects from flying in.
If the cornice is covered with wooden planks, you should also leave small gaps between them. Air exhaust is carried out through the ridge, dormer windows, vents at the front or aerators.
| Photo | Description |
| Air exhaust through the ridge can be used for any type of attic (cold, warm). For this purpose, a vent is installed. It must be covered with a net. Condensation will flow down the roof rather than accumulate underneath it. | |
| A dormer window is a traditional solution for different types of roofs. Can only be used in cold attics. | |
| Vents on the gable of the attic perfectly remove air from the rooms. They are closed with grilles with rotating slats. | |
| Aerators are most often used above attics. The special design prevents condensation from getting inside. |
Dormer windows should be located on opposite sides. The optimal dimensions are 60x80 cm. If the roof has a complex configuration, valleys become a problem. For complete ventilation of the attic, point aerators are installed along the valley. But they can only be installed if the roof slopes have an angle of 45° or more.
If the angles are smaller, snow will accumulate in this area. Therefore, special electric fans are used to ventilate the attic.
Detailed plan as a starting point
They usually try to complete the arrangement of an attic in a country house with minimal financial investment. In this case, the plan still plays the role of an estimate, so it should not be neglected.
- Preliminary plan. Here you must decide what you want to see at the finish line. You can draw on paper or use 3D modeling programs. At this stage, you decide whether an additional window is needed in the attic, how to line the inside of the attic, in general, the desired design of the attic.
First, a sketch of the attic design is drawn
- Preliminary design. Next, take the documents for your dacha and, based on the plan, draw a sketch of the attic with dimensions in several projections. With it, it will be easier for you to calculate the amount of material, and at the same time draw the electrical wiring route, the location of the hatch to the attic, etc.
Now you need to solve several issues that determine the amount of materials, the amount of work and the size of the budget.
A list of questions:
- Is roof insulation necessary?
- is it necessary to reinforce the ceiling;
- Is it necessary to insulate the floor;
- is a hatch needed and what kind of hatch will it be?
- what kind of staircase will there be?
- Costings. The next step is drawing up an estimate. You need to figure out what you have and calculate what and how much you still need to buy.
- Secondary measurement. Next, you need to clean out the attic and measure everything with your own hands with a tape measure, after which you can purchase the material and get to work.
This is interesting: Attic ventilation as the basis of comfort
After cleaning and actual measurement, the amount of material and scope of work may change significantly
Insulation of ventilation pipes
Ventilation pipes must be insulated in the attic and above roof level. This procedure is carried out to avoid the accumulation of condensation, which will accumulate on the internal walls and flow down. Since the joints of the ventilation pipes are not made airtight, moisture will penetrate the supporting structures, ruin the finish and lead to the gradual destruction of the building. And the ventilation ducts themselves suffer from contact with moisture if they are made of galvanized pipes.
In winter, the opening of the ventilation duct becomes overgrown with frost and in just a month a standard pipe with a diameter of 15 cm will completely close.
The appearance of condensation in ventilation ducts is inevitable: people exhale water vapor, wash dishes, bathe and do laundry. This releases moisture into the air. The humidity of warm air in a residential building can reach 100%. When water comes into contact with the cool surface of ventilation shafts, it settles on it.
To prevent this process, the ventilation pipes in the attic are insulated. This is where the boundary between the warm air of the house and the cold air of the unheated attic passes.
The cheapest insulation option: mineral wool. It does not burn, but when wet it completely loses its qualities. Corrugation with mineral wool insulation is easier to install.
Polystyrene foam in the form of special removable “shells” is very easy to install and inexpensive. But it burns well, emitting toxic smoke, so it is not recommended for residential buildings.
The best materials for insulating ventilation ducts: polyurethane foam, polyethylene foam, polypropylene foam.
Three main misconceptions and eliminating the consequences ↑
The principle of under-roof ventilation
In order for attic ventilation in a private house to be done correctly, in addition to knowledge of the basic requirements, it is necessary to get rid of the misunderstanding of its purpose. There are three main misconceptions that have falsely received the status of rules and are used in the design and construction of houses in the private sector.
The first misconception is about the seasons ↑
It is generally accepted that flowing air circulation in the attic is needed only in the summer (hot) season:
- Hot weather is not the only criterion for the need for attic ventilation. For unheated attics or for ventilation in warm rooms, it is necessary to maintain a minimum difference between the internal and external temperatures;
- When it gets cold outside, the lack of flowing air circulation leads to the formation of condensation. This moisture contributes to the formation of dampness and fungal mold, and in winter - frost;
- This situation is extremely dangerous because microbial spores can enter the living space through the ceiling. It will be extremely difficult to deal with the consequences.
Air flow diagram
Misconception two - it will be cold in the house ↑
Ventilation in the attic helps cool the living space, since warm air is used to heat the floors:
- In fact, the reason for cooling rooms is insufficient thermal insulation of walls, floors and ceilings. The room, to a greater extent, cools not from the loss of warm air, but from the penetration of cold;
- In addition, in the absence of waterproofing on the ceiling, not only heat but also moisture passes through it, which serves as an additional reason for the formation of condensation in the attic.
Misconception number three – size doesn’t matter ↑
The size of the holes for air circulation does not matter:
- this is not so, and if we are talking about a ventilation gap under the roof, then the minimum distance to the insulation should be 20mm. It is set by choosing the cross-section of the slats for the counter-lattice;
- when arranging vents for cold attics, you should adhere to the norm - 1 sq. m of ventilation holes (in total) per 500 sq. m of total room area;
- If you meet these requirements (ventilation gap or vent area), then you can get rid of condensation while avoiding critical losses of warm air.
Way out of the situation with poor ventilation ↑
Frozen condensation on the rafter system and sheathing
If ventilation was made taking into account the above misconceptions, then in the cold season condensation will form, which freezes in winter, as shown in the top photo. In such cases, you have to correct the situation, but there is a way out, and it leads to good results with simple actions.
The simplest roof aerator
You can make additional vents or dormer windows, protecting them with bars so that pigeons do not fly into the attic and nest (they can also nest in the vents, if there is space there). But the most convenient thing, especially if the roof is made of metal (corrugated sheeting, metal tiles or seam roofing), is to install the simplest passive aerator. If desired, of course, you can purchase and install an electric or turbine hood of this type.
Depending on the roofing material, the base of the hood is selected - it can be wavy, like slate or ondulin, or flat, like corresponding roofing materials. As a rule, such devices are equipped with installation instructions from the manufacturer, a set of self-tapping screws, and outdoor sealant for fastening.
Attic ventilation is a necessity
To install such a ventilation system in the attic, you need to cut a hole in the roof, the area of which should not be less than the hole in the hood, but not exceed the dimensions of the mounting base. An angle grinder (grinder) is used for cutting, and the disc is selected in accordance with the roofing material (metal or diamond-coated).
To summarize, we can say that ventilation in the attic is not an arrangement for luxury homes, but an urgent need of every building, on which the comfort in the rooms depends. And the availability of doing the work yourself significantly reduces the cost and allows you to quickly correct the situation with poor air circulation.
A few final tips
- pay attention to the strength of the ventilation, it must withstand any weather fluctuations;
- you can put continuous soffits under eaves with fine screening mesh. To prevent corrosion, the holes should be made of aluminum or plastic;
- to prevent the formation of frost in the attic, install vents inside the room between the rafters and make holes so that they cannot become clogged with debris;
- You can install a fan on the roof for better air extraction. The distance between it and the supply system must be at least 8 m;
- the air supply unit should be placed in the cleanest place in the attic;
- install a recuperator that can cool or heat the air, thereby preventing condensation from forming in a cold attic;
- equip ventilation pipes with grilles or diffusers;
At first glance, there is nothing complicated in arranging ventilation, but in fact it is better to take this issue seriously and consult with specialists. After all, the microclimate in the house and your health, as well as the durability of the building itself, depend on its quality.
Forced, with exhaust fan
Considering the relatively small area of the vast majority of attics, they do not need forced inflow. In approximately 95-99% of cases, installing a forced exhaust system will be sufficient.
How to make an influx depends on a number of circumstances, but in most cases the classic scheme is suitable. In the classical scheme, the supply system is organized through gaps, windows (through micro-ventilation or simply opening a window, through a comb), window valves, or through the air duct system, if there is one.
The exhaust system is organized as an isolated/separate one directly to the street (a pipe with a fan that blows air from the attic to the street), or through an air duct system. The second option is relevant if the building has an exhaust air duct - a separate line is extended to the attic.
Doors and hatches to the upper attic floor
At the entrance from the stairs to the attic and to all upper floors, it is advantageous to install an entrance door that blocks the flow of air from the lower floors and divides and isolates the air space of the floors into independent blocks.
Ventilation on the floor will work more efficiently if you choose a door with a good seal and install a door closer that constantly returns the door to the closed position.
The topmost step of the stairs, directly in front of the door, must have a tread width of at least 60 cm.
For the purpose of dividing the air space of floors, doors can also be installed on the lower floor, at the entrance to the stairs upward.
The hatch acts as a door to the country attic. Approaches to the hatch opening must be fenced on three sides. The height of the fence is at least 0.9 m.
The hatch opens easily and smoothly thanks to gas springs (gas lifts) or an electric drive. In addition, the hatch must have a locking device in the open position. The hatch can be ordered from a hatch manufacturer, or you can make it yourself.
When making it yourself, experts recommend reducing the weight of the manhole cover and installing two gas elevators (you can choose automobile ones). Gas elevators must be installed with the rod down, and the cylinders must be attached to the hatch flap.
Gas springs - lifts are selected according to the location on the finished lid. Measure the force in kg. to lift the finished sash, convert to Newtons (kg x 10 = N), add 30% to the resulting value and determine the total power of the gas springs. Next, purchase a set (2 pieces) of gas elevators in the store with a capacity within the calculated values.