It is difficult to call a cottage without an effective ventilation system comfortable to live in. The flow of fresh air into it from outside must be constant and sufficient, otherwise the microclimate in the rooms will become unfavorable.
Ventilation in a private house is done according to one of two schemes - with natural or forced draft. Moreover, it is quite possible to install it yourself. But in some cases the project will have to be ordered from professionals.
There are simplified calculations for air exchange devices in low-rise residential buildings, but they are not always suitable. Here you need to be as careful as possible to do everything correctly.
What is it for?
The purpose of installing a ventilation system in a private home is to remove exhaust air (carbon dioxide, impurities) and supply clean air with a high oxygen content.
What types of pollution are present from human activity:
- Water vapor in kitchens (during cooking), bathrooms.
- Moisture vapor released during the breathing of humans and animals.
- Carbon dioxide.
- Unpleasant odors, incl. from animals living in the house.
- Dust particles.
Interesting! In order for excess moisture to form in the room, it is not necessary to systematically cook, wash, or turn on humidifiers. It is enough to light the kitchen stove - methane gas, when burned, forms carbon dioxide and water vapor. This is why kitchens without ventilation have very heavy air (stuffiness) and a feeling of excessive humidity.
Regulators
Regulators are one of the main elements of an automation system for ventilation, providing control of actuators based on the readings of various sensors.
According to their functional purpose, these elements of ventilation systems are divided into speed regulators and temperature regulators.
Speed controllers can be single-phase or three-phase (just like motors). They also come with smooth or step control, and the choice of control method depends on the power of the fans. The most modern and economical method is to speed up the rotation of pumps and fans using frequency converters (FCs). Despite their high cost, inverters are economically justified even on motors with a power of more than 1 kW.
Temperature regulators, depending on the control method, are threshold ones, controlling the temperature using a fully open or fully closed damper (for example, a car thermostat), and with proportional differential control (PID), allowing smooth control of the temperature in the operating range.
Regulators in ventilation automation systems are controlled from control panels.
What type of ventilation should I choose?
If you are planning to do ventilation in a private house with your own hands, then experts recommend choosing combined or natural. In the photo diagrams it may initially seem that the work is difficult to complete, but this is not the case.
Strong arguments in favor of arranging these two systems:
- Saving on electricity. Combined hoods turn on periodically and consume 100-200 Wh. For comparison, heated supply air units already take 500 W from each room in the house.
- Relatively low financial costs.
- Natural ventilation provides clean air to a 1-2 story building and is well suited for a country house.
- No separate room is required to mount and place the equipment.
- There is no need to clean channels and filters annually.
An important nuance . Even if you plan to do most of the work yourself, you cannot do without the advice and help of a specialist. Errors in design and installation of parts can cost financial losses and time.
It is better if an air ventilation system is initially provided for in a house under construction. If forced ventilation has not been designed previously, then you will have to work hard to place pipes in existing rooms, try to hide them under floors or double walls.
Planning stage
The cheapest and most common option is the natural drive system. It is suitable for both home and utility rooms: baths, cellars, chicken coops, etc.
It is a mistake to think that with natural ventilation, heat is lost from the house to the street. If the room is well sealed, there are no gaps in the frames, walls or floors, then the hood removes as much air as the influx allows.
Before you start installing ventilation, you need to calculate the total air exchange, the volume of supply air. Methods and standards are adopted exclusively in accordance with SNiP (clause 9 of SNiP 31-01-2003; SP 60 13330.2012 Appendix “K”). Preparatory calculation work for the preparation of technical documentation must be carried out by a specialist. You cannot do this on your own without specialized knowledge.
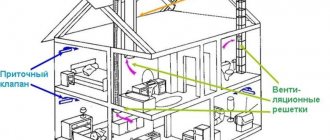
Example. The photo shows a diagram of how air flows move and where the supply and exhaust devices are located.
For the hood to work effectively you need:
- External inflow is done everywhere except the corridor, toilet, bathroom.
- The flow of clean air should go from the rooms to the kitchen.
- Ventilation block It is better to install the channel at the junction of the kitchen and bathroom or attach it to the outside wall.
- Technical calculations will show what height the pipes should be raised to; for a 1-floor building this is at least 2 m.
- For the kitchen, bathroom, tech. rooms, wherever there is an unpleasant odor, separate ventilation systems are built. channels. Otherwise, the smells will flow into the rooms.
- To prevent condensation, the pipes that pass through the cold attic are insulated.
Organization of natural inflow
As noted above, without supplying fresh air from outside, natural exhaust will not function. Or a so-called reverse draft will occur, when a wider exhaust pipe overturns the draft in a channel of a smaller cross-section. It is necessary to supply inflow from the street into each room, for example, using valves cut into the window profile. Another way is to install a wall valve; its structure and installation diagram can be seen in the figure:
Air masses should flow freely into the corridor and move along it towards the exhaust shafts. Therefore, between the floor and the interior doors, you need to make a gap of 20-25 mm wide, and at the entrance to the kitchen and bathroom - at least 30 mm. If such gaps spoil the interior of your home, then it would be correct to make openings in the sashes and install decorative grilles there.
Types of ventilation systems
When choosing which scheme will need to be drawn up in order to properly install ventilation in a private house, you need to remember about the types of ventilation:
- Natural.
- Forced , equipped with mechanical devices.
- Combined.
Each of them has its pros and cons. But when choosing and further drawing up a diagram, you need to remember that you cannot make an exhaust hood without an inflow or outflow. That is, the air from the room must leave and be replaced with fresh air, otherwise all installation work will reduce the effectiveness of the final result to zero.
How does natural exhaust work?
Before you begin planning and installing natural ventilation in a private house with your own hands, you need to familiarize yourself with the principles of its operation. It functions due to the natural draft that occurs inside the pipes running vertically, while the air moves from bottom to top.
The traction force depends on:
- From the difference in atmospheric pressure at the top and bottom of the pipe. The pressure drop and traction power will increase by increasing the height of the fan. channel.
- Outdoor and indoor temperatures. The colder it is outside, the faster the cold air displaces the warm air in the house, causing it to rise up to the hood.
- Moisture saturation. If the temperature of saturation with water vapor is the same, the air mixture rises faster, it becomes lighter than dry air.
In summer, natural exhaust will work worse due to a slight temperature difference.
The natural ventilation inlet is an exhaust valve that is mounted on the ceiling or in the wall just below the ceiling. The exit is considered to be the top of the pipe. The design begins to work when there is a pressure difference at the outlet and inlet, approximately it starts from 10 m.
The natural inflow is installed at a level of 2 m from the floor or above the radiators.
What the hood is made of is of great importance. Spiral wound ducts are the preferred material.
But more often, for self-installation, sewer pipes with a diameter of 110 mm are chosen.
Pros: minimum material costs, no power source required, no malfunctions and no noise.
Cons : air circulation is weak, air exchange is not very good, its intensity cannot be adjusted. In warm weather, there is practically no air movement around the house, and in winter there is a possibility of a rapid outflow of warm masses outside.
The principle of arranging a compulsory system
Forced ventilation works in a private house using mechanical exhaust units. They are powered from the network, so if you do the equipment yourself, you will also need the skills of an electrician.
There are many schemes for such ventilation, the most popular are:
- Air flow is provided using breathers; they are installed in all rooms. A general fan is installed in the attic, to which all exhaust air is supplied and removed.
- Installation of separate supply and exhaust units with a recuperator, which is built into the external wall.
- Central air conditioner with a network of ventilation ducts.
- Fan coil units are local air heaters with heating/cooling functions.
Pros : there is no dependence on the height (number of floors) of the house and weather conditions, the air coming from outside is clean, at the required temperature and humidity.
Cons : you need to connect electricity, the equipment itself and maintenance are expensive.
Combination device
The principle of natural ventilation works here with increased air exchange using electric fans installed at different points. There are 2 popular options:
- Exhaust air is discharged through a vertical channel, and inflow is carried out using bellows. fans.
- The fan is placed on the exhaust shaft, and the inflow is installed through valves in the wall.
An example of a combined option is a kitchen hood or a fan in the toilet. Using such devices, vapors, unpleasant cooking odors, etc. are sucked out during the cooking process.
Breathers, built directly into the thickness of the walls, provide a mechanized supply of clean air. In the cold season, it is also heated with the help of heating elements.
Other solutions
The market does not stand still, and today new solutions are being offered. For example, there are recuperation systems that immediately, through one hole in the wall, remove exhaust air and supply fresh air. This is an ideal solution if you have taken care of ventilation after renovation or if you need to solve the problem only in some rooms. The main thing is that these rooms have at least one wall facing the street.
There is a device that removes exhaust air through one hole and takes in fresh air. At the same time, it also heats/cools it
There is only one drawback of this method of organizing ventilation in a house or apartment - the price of such equipment. The cost of one such device is more than $400.
Step-by-step action plan
To carry out all the work yourself, you need to have a minimum of technical skills and know the sequence of such work.
Preparation
Information plus calculations are the basis for preparing the installation of ventilation systems:
- Calculation of the air exchange rate in the house for each room.
- Drawing (diagram) of the movement of air masses. Approximate location of the vent. channels.
- Air duct diagrams are drawn taking into account the design of the room, trying to provide the possibility of hiding air ducts under suspended ceilings, bulkheads, etc.
Detailing
After the scheme has taken on a harmonious appearance and all the design nuances have been taken into account, they begin a detailed plan, drawing up an estimate, incl. choosing an equipment manufacturer:
- The cross-section of the air ducts is calculated and taken into account so that the movement of air is silent.
- Entering parameters into the diagram.
- Drawing up a list of necessary elements.
- The resistance of each section is calculated, fans are selected, and the noise level produced by them is taken into account.
- The cost of all ventilation components is calculated. systems.
In conclusion, a final, clean version with full detail is drawn up. We must not forget about the units for passage of channels through ceilings/walls, consumables (insulating materials, ventilation grilles, fasteners, diffusers, etc.). In the end, all the “little things” add up to a very significant amount of costs, but they are also necessary.
Materials and tools
You will definitely need:
- Hammer.
- Pipes of various configurations, diameters, textures and lengths.
- Connecting elements.
- Adapters, elbows, tees.
- Ventilation grilles moves.
- Holders, hanging elements.
Installation and configuration
Procedure:
- Markings are made on the walls to indicate where the vents will go. channels.
- A diagram of the air ducts is drawn along the ceiling.
- If the system is forced, note where the equipment will be mounted.
- The channels are assembled and mounted on hangers.
- Connect the pipes to a single vent. installation.
- Cover the holes with gratings.
- The equipment is connected to electricity and the entire installation is tested.
Video: ventilation in a private house
Useful tips and misconceptions
Experts advise:
- In brick and block buildings, the ventilation system is installed simultaneously with construction.
- It is convenient to use cardboard templates when creating air ducts of the same diameter.
- Internal walls vent. It is better to lay out the channel from solid brick and seal all joints tightly.
- It is better to install asbestos-cement pipes on the roof and cement them to the main structure.
It is believed that for complete ventilation it is enough to install an air conditioner, but it only affects the temperature in the room. It does not solve the problem of supplying clean, oxygen-rich air.
Windows installed in micro-ventilation mode do not solve the problem of lack of good ventilation. This principle is good in the warm season, but in winter the air in the room will quickly cool down without having time to be saturated with oxygen and remove unpleasant odors.