The next stage of updating the real estate fund complex in the process of developing a metropolis with multi-storey buildings is associated with the design and construction of houses of type II-57.
These are very common buildings not only in the capital, but also in other cities, for example, in Troitsk, Tolyatti and so on.
Note that the main characteristic of this series is the modern technology for the production of external panels and butt joints, as well as a heating system that does not include radiators. In such houses, heating elements were installed under the window sills, but in later versions the designers returned to the radiator system.
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Alternative name: | II-57 |
| Construction regions: | The main areas for the construction of series II-57 houses in Moscow are Kuntsevo, Chertanovo, Teply Stan, Mozhaisky, Zelenograd, Ryazansky Prospekt, Golyanovo, Izmailovo, Konkovo, Kotlovka, Meshchansky, Academichesky, Vostryakovo, Butyrsky, Obruchevsky, Golovinsky. In addition, houses of this series were built in the cities of Troitsk, Likino-Dulevo, Kharkov, Togliatti, Naberezhnye Chelny |
| Construction technology: | panel |
| By construction period: | Brezhnevka |
| Years of construction: | 1963-1970: nine-story, 1971-1978: twelve-story |
| Demolition prospect: | Not subject to demolition |
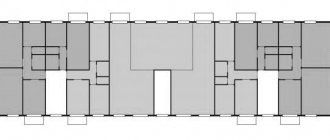
| Number of sections/entrances: | 2 or more |
| Number of floors: | 9, 12, several 17-story experimental buildings |
| Ceiling height: | 2.64 m |
| Balconies/loggias: | All floors have triangular or rectangular balconies. |
| Bathrooms: | The bathrooms are separate, the baths are standard, 170 cm long. |
| Stairs: | Double-flight staircases made of prefabricated reinforced concrete steps and platforms. |
| Garbage chute: | With loading valve on the interfloor platform |
| Elevators: | Two passenger elevators (load capacity 400 kg). In the 12-story version, one passenger (400 kg) and one cargo-passenger (630 kg) |
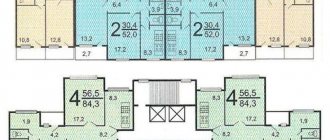
| Number of apartments per floor: | 4 |
| Apartment areas: | Shared/living/kitchen |
| 1-room apartment 34-35/17-18/8-9 | |
| 2-room apartment 45-46/29-30/6-7 | |
| 3-room apartment 61-62/41-42/6-7 |
| Ventilation: | Natural exhaust, ventilation units are located in the kitchen |
| Walls and cladding: | The external walls are three-layer expanded clay concrete panels 32 cm thick. |
| Internal load-bearing walls are reinforced concrete panels with a thickness of 16 cm. | |
| Interior partitions made of gypsum concrete 80 mm thick. Floors – reinforced concrete panels 14 cm thick. | |
| The houses are lined with ceramic or glazed small-sized tiles in yellow, blue, pink or light green colors. | |
| Roof type: | Flat, internal drainage with rainwater discharge onto the terrain at the base level. |
| Manufacturer: | DSK-3 |
| Designers: | MNIITEP |
| Advantages: | Separate bathrooms, many possibilities for redevelopment. Isolated rooms, built-in mezzanines and wardrobes. |
| Flaws: | Small kitchen areas; the 9-story version does not have freight elevators. |
Houses of the II-57 series can be recognized without problems. Here the facades have convex, paired balconies, but there are also modifications of buildings in which the balconies have a rectangular shape. In addition to houses with twelve floors, other versions of II-57 can be mentioned:
- houses with 9 floors – II-57-05;
- houses with 17 floors - II-57/17.
It is noteworthy that for the first time, the developers decided to install elevators for lifting goods in 12-story buildings. The experiments did not bypass 17-story buildings. Here, only prefabricated reinforced concrete frames were used as supports. Consequently, the buildings were called “house on chicken legs”. Note that since 2000, work has been carried out in the capital aimed at rehabilitating the buildings of the series in question. So far there is no talk of their demolition.
Description of the II-57 series
Panel houses of the II-57 series (often written P-57), designed by MNIITEP, became widespread in Moscow during the industrial development of the city with high-rise buildings.
Having started from a height of 9 floors, the II-57 series, in the process of creating modifications, grew to 12 and received, in addition to one of the passenger elevators, also a cargo-passenger elevator.
In addition, in a significant part of the houses in the series, innovative solutions were used - heating apartments using in-panel heaters (warm window sills), which, however, created difficulties in the operation and repair of the heating system.
Years of construction of all modifications of the series in Moscow and the Moscow region from 1964 to 1978.
The variants of the series are characterized by the presence of loggias and balconies of various shapes on all residential floors and separate layout of bathrooms.
Description
The next stage of industrialization in the development of cities with high-rise buildings was marked by the design and construction of houses of the II-57 series, which are quite common both in the metropolitan areas and in a number of other settlements: Togliatti, Kharkov, Troitsk, Naberezhnye Chelny, etc.
The main characteristics of the series were a new technology for the production of external panels and connecting their joints (assemblies), as well as a heating system without installing radiators; heating elements are placed under the window sills.
Over time, in some houses in the series, heating systems with such an unusual arrangement were replaced with standard ones - radiators.
Multi-section houses of this series are easily recognizable by their facades with convex paired balconies (although there are also modifications of houses with rectangular balconies). This series of 12-story buildings has several variations: II-57-05 (nine-story buildings) and II-57/17 (seventeen-story buildings), the main difference of which is the number of floors.
And it was in the 12-story version of this series that freight elevators were used for the first time.
Interestingly, the 17-story version of the houses was built using experimental technology - the buildings relied only on prefabricated reinforced concrete frames, so they began to be unofficially called “houses on chicken legs.” Since 2000, work has been actively carried out in Moscow to rehabilitate houses of series II-57 and they are not yet subject to demolition.
Design features of the series and facade finishing
The external panels of the building are made of three-layer expanded clay concrete 32 cm thick; The walls inside the house, which are load-bearing, are reinforced concrete panels with a thickness of 16 cm, and the interior partitions are made of gypsum concrete and have a thickness of 80 mm. Floor ceilings are made of reinforced concrete panels 14 cm thick.
The entire area under the building is occupied by a spacious technical basement, where engineering networks and communications are located.
Houses of series II-57 are lined with tiles (small-sized, glazed or ceramic) in yellow, blue, pink or light green colors on the façade. Heating, hot and cold water supply - central city networks.
The disadvantages of the series are considered to be poor sound insulation of inter-apartment walls and insufficient ventilation.
Features of apartment layouts
The standard layout of a 3-room apartment has built-in wardrobes and mezzanines. In addition, the advantages of standard houses of the II-57 series include isolated rooms and separate bathrooms. But the kitchens in the houses of the series remain small.
A positive aspect of the II-57 series was the reduction in the number of load-bearing walls - there were significantly more options for redevelopment.
Marine theme
According to the layout proposed by the customer, we lay the tiles, starting from the side of the bathtub. The wall cladding is standard - dark bottom and light top, the border of the transition is the decor in the form of “wet stones”. The theme of the collection is marine, there are panels on the bathroom, and “shells and starfish” hanging from the ceiling.
Let's start laying wall tiles
The first row of wall tiles comes from the bathtub
Laying Uralkeramika Island tiles in the bathroom
Laying tiles on a plumbing box
Wall decor above the bath
Specifications
- Alternative name: II-57
- Construction regions:
The main areas for the construction of series II-57 houses in Moscow are Kuntsevo, Chertanovo, Teply Stan, Mozhaisky, Zelenograd, Ryazansky Prospekt, Golyanovo, Izmailovo, Konkovo, Kotlovka, Meshchansky, Academichesky, Vostryakovo, Butyrsky, Obruchevsky, Golovinsky. In addition, houses of this series were built in the cities of Troitsk, Likino-Dulevo, Kharkov, Togliatti, Naberezhnye Chelny
- Construction technology: panel
- By construction period: Brezhnevka
- Years of construction: 1963-1970: nine-story, 1971-1978: twelve-story
- Prospect for demolition: Not subject to demolition
- Number of sections/entrances: 2 or more
- Number of floors: 9, 12, several 17-story experimental buildings
- Ceiling height: 2.64 m
- Balconies/loggias: All floors have triangular or rectangular balconies.
- Bathrooms: Separate bathrooms, bathtubs are standard, 170 cm long.
- Stairs: Double-flight stairs made of prefabricated reinforced concrete steps and landings.
- Garbage chute: With loading valve on the interfloor platform
- Elevators: Two passenger elevators (load capacity 400 kg). In the 12-story version, one passenger (400 kg) and one cargo-passenger (630 kg)
- Number of apartments per floor: 4
- Apartment areas:
Shared/living/kitchen 1-room apartment 34-35/17-18/8-9 2-room apartment 45-46/29-30/6-7 3-room apartment 61-62/41-42/6-7
- Ventilation: Natural exhaust, ventilation units are located in the kitchen
- Walls and cladding:
The external walls are three-layer expanded clay concrete panels 32 cm thick. The internal load-bearing walls are reinforced concrete panels 16 cm thick. Interior partitions made of gypsum concrete 80 mm thick. The ceilings are reinforced concrete panels 14 cm thick. The houses are lined with ceramic or glazed small-sized tiles in yellow, blue, pink or light green colors.
- Roof type: Flat, internal drainage with rainwater discharge onto the terrain at the base level.
- Manufacturer: DSK-3
- Designers: MNIITEP
- Advantages: Separate bathrooms, many possibilities for redevelopment. Isolated rooms, built-in mezzanines and wardrobes.
- Disadvantages: Small kitchen areas; the 9-story version does not have freight elevators.
Apartment layout
Typically, each floor contained one two-room and one-room apartment, and 2 three rubles each.
If we consider the standard layout of a three-room apartment, then there are built-in mezzanines and wardrobes. It is also worth noting isolated rooms, as well as a separate bathroom. As for kitchens, in the II-57 series of houses they are small. And due to the fact that there are fewer load-bearing walls, new opportunities for redevelopment have emerged.
House type:
panel.
Planning solution:
consists of row sections with 1, 2 and 3 room apartments.
Number of floors:
12 floors.
Ceiling height:
2.64 m.
Technical premises:
technical underground for the placement of utilities.
Elevators:
two passenger lifts with a lifting capacity of 400 kg.
Building structures:
external walls - three-layer panels 320 mm thick;
internal - concrete 160 mm thick; partitions - gypsum concrete 80 mm; ceilings - concrete panels 140 mm thick. Ventilation:
natural exhaust in the kitchen and bathroom.
Water supply:
cold and hot water from the city network.
Garbage disposal:
garbage chute with loading valve on the interfloor landing.
II-57
The construction of panel houses of the II-57 series, the author of which is MNIITEP (you can often find this series designated as P-57), began in 1963. The first was the 9-story version (II-57-A/09). The first floors were residential and non-residential, and in the latter version there are 10-story versions of the buildings.
Photos of houses series II-57-09
Soon the series became 12-story (II-57A/12), and in these houses, for the first time for mass construction, a freight-passenger elevator appeared in the entrances. In addition, the series was the first to use the principle of heating using heaters placed inside the panels (warm window sills).
Houses series II-57-12
The series also has a 17-story modification (II-57/17), but not many such houses were built.
A distinctive feature of this modification is the design of the building with open columnar supports (on legs) and the presence of a technical (second) floor above them.
Photo of the house series house series II-57-17
It is also rare to find variants II-57-05 and II-57-07. In addition, the parts of the series mastered in production were used to create various residential and non-residential buildings.
Mass construction of the series was completed in 1970 in connection with the development of production of the P-3 series, but some modifications were built until 1979. In total, more than 350 houses of this series were built in Moscow.
There are two elevators in the entrances of buildings II-57 (two passenger elevators in a nine-story building and a passenger and freight elevator in higher versions). The series is characterized by the presence of balconies on all floors and separate layout of bathrooms.
- Apartments in a series of 1, 2, and 3 rooms.
- A one-room apartment has 34-35 m2 of total area and 17-18 m2 of living area.
- For a 2-room apartment, the total area is 45-46 m2 and about 30 m2 of living area.
- A three-room apartment with a total area of about 62 m2 has a living area of 41-42 m2.
- The kitchens in all apartments are small, ranging from 6 to 9 m2, with one-room apartments having the largest area.
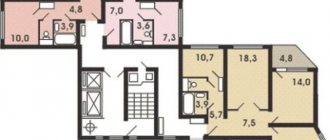
Redevelopment option for a three-room apartment of the P-57 series
Category:
Paired balconies at obtuse angles, as well as triangular structures (in some versions the balconies are still straight).
There are 3 modifications of this series depending on the number of floors:
- II-57 - 12 floors;
- II-57-05 - 9 floors;
- I-241 - 10 floors, without convex loggias;
- II-57/17 - 17 floors.
The 9-story and 12-story buildings were designed 5 years apart. The 12-story version featured a freight elevator for the first time, while the 9-story version only had a passenger elevator. The house has separate bathrooms, there is an underground - technical floor. The disadvantages of the II-57 series include small kitchens.
Among the features of this series:
- warm window sills (heating system without radiators);
- a small number of load-bearing walls inside the apartment, which means there is room for redevelopment;
- panel joints that were new for that time;
- For the first time, a freight elevator appears in houses in series.
The designers abandoned warm window sills, and most houses were built without them. The houses are not on the list for demolition.
Examples of floor plans in houses II-57
- The ceiling height in living rooms is 255-265 cm.
- External walls are three-layer panels made of expanded clay concrete, 32 cm thick. Internal load-bearing walls are reinforced concrete panels, 16 cm thick. Partitions (non-load-bearing walls) made of gypsum concrete, Floors are assembled from reinforced concrete panels, 14 cm thick.
- The advantages of the series are separate bathrooms with a full-size bathtub (with rare exceptions, a plumbing cabin was installed), and the possibility of redevelopment.
- Disadvantages include kitchens that are modest in size, as well as the original design of the heating system, which was replaced during a major overhaul with a system with an open arrangement of radiators and risers.
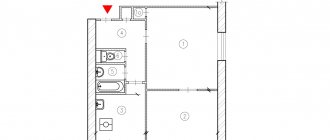
Redevelopment of a 3-room apartment in a panel house of series II-57
The construction activities of the redevelopment project included:
- Construction of an opening in the load-bearing wall between the kitchen (4) and living room (3);
- Moving the toilet;
- Expansion of the bathroom to the area of the restroom;
- Dismantling built-in furniture;
- Dismantling the partition between the corridor (7) and the living room (3);
- Glazing of the loggia;
- Replacement and relocation of engineering equipment in the bathroom.
Plan of a three-room apartment in a panel house of series II-57 after redevelopment
Usually, when redeveloping a wet area in a panel house, a combined bathroom is installed, but this example is interesting because the area of the bathroom has expanded to the area of the restroom, and the toilet itself with the transfer of the toilet bowl has been placed in the area of the corridor. A passage was made from the living room (3), by dismantling the partition that separated it from the corridor.
At the same time, an opening was made in the load-bearing wall between this room and the kitchen. The last step in this redevelopment was the glazing of the loggia. Among the “smaller” ones, we can note the dismantling of built-in furniture in the corridors of the apartment.
New plumbing
After leveling the walls with plaster, we move on to laying out the plumbing pipes. The customer’s wish was to minimize the dimensions of the sanitary cabinet in the bathroom. To do this, we try to fit the entire revision to the right of the cast-iron riser, although it became quite cramped, everything fit. Access to the shut-off valves on the heated towel rail is quite convenient.
Plastering interior walls
We assemble the entire revision very compactly in order to gain useful space
Comb
Hidden piping for bathtub and sink
If possible, we “recess” polypropylene pipes into the wall; we hide the sewer pipe from the bathtub in a small box. The bathroom is ready for tiling. Before laying the tiles, we lay the electrical cable to the socket, fan and mirror.
Preparing a place for a cast iron bath
Connecting and checking the water heated towel rail
Location in Moscow and Moscow region
- In Moscow, series II-57 houses were built mainly in the following areas: Chertanovo, Teply Stan, Meshchansky, Mozhaisky, Zelenograd, Ryazansky Prospekt, Kuntsevo, Golyanovo, Izmailovo, Konkovo, Butyrsky, Obruchevsky, Kotlovka, Academichesky, Vostryakovo, Golovinsky and others.
- In the Moscow region, houses of series II-57 were built in the cities of Troitsk, Likino-Dulevo and others.
Short description
- Houses of the II-57 series have become widespread in Moscow and are typical representatives of the second wave of industrialization in construction.
- The nine- and twelve-story versions of the II-57 series went into construction with a gap of only five years. What’s noteworthy is that the twelve-story version now has a freight elevator.
- Houses of series II-57 have characteristic twin balconies (or even quadruple ones) convex at obtuse angles, making them relatively easily recognizable. However, there are versions with both straight and triangular balconies.
- The series featured new external panels at that time, a radiator-free heating system (warm window sills), and new panel joints. From a planning point of view, the II-57 series does not have many load-bearing walls, so relatively many redevelopment options can be implemented inside the apartment.
- The series happily ceased to exist in 1978, giving way to the P-30 and P-3, which inherited from it freight elevators, expanded clay concrete exterior panels, and a “vest” layout.
House characteristics
| Planning solution: | Multi-section panel residential building with row and end sections. The house has 1, 2, 3 room apartments. |
| Number of storeys: | 12 |
| Height of living quarters: | 2.64 m |
| Technical buildings: | Technical underground for placement of engineering structures. |
| Elevators: | Two passenger with a carrying capacity of 400 kg. |
| Building construction: | External walls are three-layer panels (320 mm). Internal concrete (160 mm). Gypsum concrete partitions (80 mm). Floors - concrete panels (140 mm). |
| Heating: | Central, water. |
| Ventilation: | Natural exhaust through ventilation units in the kitchen. |
| Water supply: | Cold and hot water from the city network. |
| Garbage removal: | Garbage chute with loading valve on the interfloor landing. |
| Additional information: | The buildings have characteristic twin (or quadruple) balconies convex at obtuse angles, making them relatively easily recognizable. The I-57 series has become widespread in Moscow and a number of other cities. |
Residential buildings of the II-57 series have become widespread both in Moscow and in the Moscow region and are typical representatives of the second wave of industrialization in the construction of residential buildings. The II-57 series has nine-story and twelve-story versions, which went into construction with a gap of only five years. It should be clarified that in the twelve-story version, a 630 kg freight elevator appeared for the first time. Construction of nine-story houses took place from 1964 to 1970, and houses with twelve floors were built from 1071 to 1078.
The house of series II-57 has paired balconies convex at obtuse angles, which is why they became easily recognizable. However, you can find versions of this series that have straight or triangular balconies. The external walls are made of expanded clay concrete panels, having three layers and a total thickness of 32 cm. The internal walls are load-bearing, made of reinforced concrete panels, the thickness of which is 16 cm. The partitions are 8 cm gypsum concrete. The ceilings are made of reinforced concrete panels 14 cm thick. The walls are lined with glazed small-sized or ceramic tiles. Colors are usually pink, yellow, light green, blue. The roof is flat with a drain located inside.
The II-57 series used the latest exterior panels at that time, new panel joints and warm window sills (radiatorless heating system). In building II-57, the layout does not have many load-bearing walls, so inside the apartments, if desired, many different redevelopment options can be implemented. There are two sections in the house. A technical underground is provided under the entire building for the placement of engineering structures. There are two passenger elevators installed in the entrances, the lifting capacity of which is 400 kg. Houses with twelve floors have one passenger and one cargo-passenger floor. There are four apartments per floor. Between the floors there is a garbage chute with a loading valve. Double-flight staircases are made of prefabricated reinforced concrete platforms and steps.
In the house of series II-57, the layout includes balconies on all floors. Bathrooms in all apartments are separate. The bathtubs are standard, the length of which is 170 cm. Natural ventilation passes through ventilation blocks in the kitchen. The ceiling height in residential building II-57 is 2.64 meters.
You purchased an apartment in a residential building of series II-57, and now for a comfortable stay you need repairs. Contact us and our qualified specialists will immediately begin to improve your apartment. Our craftsmen and designers know this series of houses well and will do an excellent job renovating apartment II-57, making all your dreams come true. We will certainly give you answers to all the questions that interest you regarding the repair. Our designers will create the most unimaginable design ideas that you would like to see in your home. Our goal is to ensure that the repair of II-57 is completed to the best of its ability and that the client is left with only positive emotions. We want you to feel comfortable and warm in your apartment.
Moscow panel and block houses series II-57
The second wave of mass panel housing construction in the USSR consisted of such similar and such different types of houses that sometimes you are surprised: it seems like a newer model, but this solution and this have already been encountered.
This is not surprising: the development of types followed strict technical specifications, where unification and economic indicators played a role not least.
Series II-57 is a typical representative of such solutions. About 17 modifications are known in Moscow alone. These DSK-3 houses were built (developed by the same MNIITEP) from 1964 to 1978, while the nine-story version was completed in 1970, and the twelve-story version began in 1971.
In addition to Moscow, there are houses in this series in some cities of the Moscow region, for example, in Troitsk, as well as other cities of the former USSR: Ryazan, Kharkov, etc.
It is clear that the 12-story building now has two elevators, one of which is freight. But in nine-story buildings of recent years of production, I personally saw panels for two elevators, although in fact there is only one (two were installed infrequently, because it is expensive + SNiPs allow it).
The openings are blocked and plastered. Externally, II-57 can be recognized by its triangular balconies: single (at the edges of the building), double and quadruple (although there are versions with straight balconies more familiar from other series). But at the ends of the building there may or may not have been balconies (early versions). And on Zvezdny Boulevard there is II-57 (the first, by the way, with electric stoves), which has just windows at the ends.
This series resembles the older II-49: the same location and number of apartments, a large number of load-bearing walls and small kitchens (6-9 sq.m.).
The layout is different in some places. For example, in three-room apartments, two rooms and the kitchen face the entrance, and the remaining one faces the opposite side, while two rooms have balconies (this is the most common layout). Garbage chutes on the interfloor areas (however, this is also the case in the later P-30 (which replaced II-57) - P-46-P-47-P-55 everywhere).
What is new for mass house-building is the presence of the so-called. “warm window sills” (lack of conventional heating devices), modern external panels and the type of their connection.
The numbers say this: the thickness of the three-layer external panels is 320 mm, internal load-bearing walls are 160 mm, partitions are 80 mm, ceilings are 140 mm, the stated ceiling height is 2.64 m, in fact 2.55-2.64 m.
Interesting Facts. On the basis of II-57, 17-story buildings were built on Prospekt Mira and Smolensky Boulevard. Their layout was noticeably different from the 9-12-story versions.
In addition, they were also distinguished by the fact that the houses stood on stilts, which was popularly called “Houses on (chicken) legs.”
There were plans to build a 16-story building in Troparevo, but something went wrong (c) But a 13-story building was built. And also “on legs”.
They called it a separate series I-286, at the same time making the first floor non-residential and wider by one step (i.e. by one room in the section). In fairness, I will say that ordinary II-57-12 were sometimes in fact 13-story buildings: the first floor was farmed out to shops and was often built on a stylobate or simply stilts.
Houses are still very liquid on the secondary real estate market.
Layout features
In 12-story modifications, instead of two passenger elevators, there are passenger and freight-passenger elevators. Apartments are heated using “warm window sills” - in-panel heaters, which creates certain difficulties during major renovations.
All apartments, including those on the ground floor, have loggias and a separate bathroom with a full-size bath. The standard ceiling height is 2.64 m.
The layout of the apartments of series II-57 is quite successful due to its good area. In one-room apartments it is 34-35 m2, in two-room apartments – 45-46 m2, in three-room apartments – 61-62 m2. The kitchen area is the largest in one-room apartments (8-9 m2), and in the rest it does not exceed 6-7 m2.
The peculiarity of three-room apartments is the swing nature of the rooms, which even in the initial version are isolated.
"ZHILEKSPERTIZA" offers:
- development of design and technical documentation for redevelopment of any complexity;
- registration of permission from the Moscow Housing Inspectorate for redevelopment (including previously completed) apartments and non-residential premises;
- assistance in drawing up the Certificate of Completed Reconstruction;
- introducing changes related to redevelopment into the BTI floor plan, technical and cadastral plan;
- making changes to the Unified State Register;
- identifying options for minimizing costs associated with redevelopment;
- free consultations on technical and legal feasibility of reconstruction;
- clarification of the legal consequences associated with the redevelopment work and further operation of the redesigned premises;
- settlement of controversial issues with city services.
Full list of services here: Go