The series of apartment buildings II-49 (P-49D) is a multi-storey panel building, which was developed by the design organization MNIITEP (Moscow Research Design Institute of Typology, Experimental Design). What are the features of such houses and apartment layouts with different numbers of rooms, we will discuss in this article. In addition, we will consider the issue of possible redevelopment.
The most disappointing thing about the apartments of the P-49 D series is the area, which in those years seemed not so small, but in our time does not meet the requirements of comfortable housing
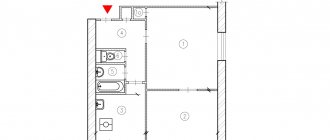
Features of apartment layouts II 49 (II 49p and II 49d)
The typical layout of sections provides for apartments with a number of rooms from one to four (sometimes 5-room apartments were added). The design of houses II-49 is not suitable for intra-apartment redevelopment due to the large number of transverse load-bearing wall panels. A positive point is that almost all the rooms in the apartments of this series are not adjacent.
The area of residential premises is increased due to large loggias, which are found in all apartments, except for one-room apartments.
Our specialists will provide qualified assistance in carrying out redevelopment in houses of series ii-49 (ii-49d and ii-49p). We have extensive experience in cooperation with all institutions on which decision-making depends.
Series II-49 was developed in the 60s as a replacement for the “main” series of five-story buildings K-7, the first buildings appeared in Novye Cheryomushki in 1965, and the end of construction of houses of the II-49 series occurred in 1985. The houses were mainly built in Moscow and the Moscow region, there are also buildings in Tolyatti and Crimea.
The thickness of the internal walls and ceilings in houses II-49 is 14 cm, external - 30 cm, the external walls are three-layer, with foam or fiberboard insulation. By the way, for the first time, various color schemes for facades were used using factory cladding of external panels with ceramic or glazed tiles.
There is only one elevator at the entrance, the garbage chute loading pocket is located between the floors. Ceiling height - 2.5 - 2.55 meters, gypsum concrete partitions.
Series II-49 combines two modifications II-49d and II-49p, among which II-49p should be highlighted - some houses in this series contain phenol, which is dangerous to life, and there are already “phenolic” II-49d in the metro area. Southwestern. The two modifications differ in that II-49p has an attic.
Layout options for residential section II-49:
How to fight?
Unfortunately, there are few options. The first is to sell and move out. But not everyone can afford this difficult procedure, especially considering the state of the secondary market in Moscow. Moreover, this is unethical: the “phenolic” background will have to be hidden, rewarding the new residents with the delights of life with toxic air. The second way is preventive. You can isolate the toxin by carefully covering the wall with plasterboard. Air filtration is facilitated by indoor plants and regular ventilation. This can reduce the risk of harmful consequences.
Technical characteristics of apartments of series II-49 (P-49D)
If we talk about the general technical characteristics of apartments in this series of houses, it is worth noting the following features:
- A small curved corridor with an average area of 7 square meters. m.
- The kitchen is small and rarely exceeds the parameters of 6-7 square meters. m.
- In one- and two-room apartments, most often all rooms have their own exit to the corridor.
- But in 3, 4 and 5-room apartments, one of the rooms is a passage. It can have either one exit to the adjacent space or two exits to adjacent rooms.
- A balcony or loggia is available only in three-room apartments and large apartments. Moreover, in those that are located in corner sections.
- The living room area ranges from 19-20 square meters. m.
- Bedroom area from 9 to 12 square meters. m.
Options for apartment layouts in houses of series II-49 (P-49D)
The layout of apartments II-49 in this series of houses is determined, first of all, by the location of the load-bearing walls. The number of rooms varies from 1 to 5. They are partially walk-through. And only in some projects, depending on the number of rooms, the layout was done in such a way that each space had its own exit to the corridor.
The plumbing unit was made separately, with the exception of only one-room apartments, where it was combined.
One-room
One-room Brezhnevka II-49 D layout with dimensions presented below has the following features:
- L-shaped curved corridor about 5 square meters. m.
- There are 3 doors leading from the corridor. One of them is for the kitchen, the area of which varies around 6-7 square meters. m.
- The second door leads to the bathroom, which simultaneously houses a shower room and a toilet. That is, in this apartment the bathroom is combined and its area does not exceed 3.5 square meters. m.
- And finally, the third door leads to the living room of about 19 square meters. m.
Another feature is that there is no balcony or loggia, which is not entirely convenient from the point of view of use.
Two-room
The following is a two-room apartment layout P 49 D with dimensions:
- The corridor is curved, it is the most traditional for this type of house. The area ranges around 6-8 square meters. m.
- The bathroom is separate, located in a small branch from the main corridor in close proximity to the kitchen.
- The guest room has the same area as the one-room apartment. It is 18-19 square meters. m.
- The bedroom is small, about 9 sq. m.
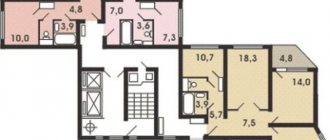
Three-room apartment
In P 49D, the 3-room layout with dimensions has the following features:
- The same L-shaped curved corridor of a small area, recognizable and typical for this type of house. Although, in some layouts a rectangular corridor was used with a dedicated narrow passage to the kitchen and bathroom areas.
- Separate bathroom located near the kitchen.
- The kitchen space is small, no more than 6 square meters. In addition, there is no balcony, which makes its operation very problematic, especially for a large family, for which a three-room apartment is designed.
- The living room is 19-20 sq. m. and has a separate entrance from the corridor. In some cases, there is a small specific entrance that forms an original “dressing room”. If you use certain design techniques, the space in a three-room apartment can be used ergonomically. A niche or shelves can be organized here.
- Most often, one bedroom had a separate entrance and was isolated. But the second one was located directly behind the guest room, as a result of which the living room was a passageway. The bedroom areas are small, not exceeding 10-12 square meters. m.
- Some layouts had a balcony. He usually led from the bedroom. In other types of premises there was no balcony at all.
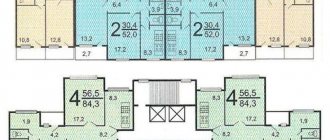
Four-room apartment
Brezhnevka II 49 D has the following layout features:
Curved corridor. There are only three main exits from it - to the kitchen, to the bedroom and to the guest room. And two more additional exits to the plumbing rooms.
The guest room is a walk-through room - its area is about 19 square meters. From it there are 2 additional doors leading to the bedroom. It is this specific arrangement of rooms that makes the guest room practically non-functional.
After all, it is difficult to arrange furniture here due to the fact that there is a window on one wall, an entrance to the corridor on another wall, and two exits to the bedroom on the third wall.
It is for this reason that most owners of such apartments face certain problems when organizing living space in a guest room. You can’t do without specific design techniques. Otherwise, the room will remain uncomfortable and will serve solely as a passage corridor.
All three bedrooms are standard and their area can range from 7.5 to 9.5 square meters. m.
In the vast majority of cases, a four-room apartment layout has a loggia or balcony, which is located in one of the bedrooms.
"Phoning" objects
A small amount of radiation radiation falls on the same concrete, since it contains crushed rocks - granite and basalt, and these, in turn, contain tiny particles of thorium and uranium. The period of their decay exceeds the lifespan of the Earth and amounts to 4.5 billion years. At the same time, they emit radon, which we will discuss in detail below. Fortunately, the volume of this inert gas is extremely small, which does not negate the precautions: frequent ventilation will prevent the gas from accumulating.
Now about serious sources. 137 Moscow enterprises, as well as an unknown number of military units, deal with radioactive industrial waste. They all store them in their own way, eventually sending them to a burial ground in the Sergiev Posad region. This is an exemplary storage facility with very high quality control. The nearest settlement (4 km from it), according to representatives of the Federal State Unitary Enterprise Radon, is not in danger. But not all Moscow radiation cemeteries are perfectly sealed and safe.
Main characteristics of the layout
The multi-section panel house with row and end sections of the II-49 series combines two modifications II-49D and II-49P. Series II-49 is designed for construction to replace the outdated K-7 series.
- Series: II-49
- House type: block
- Manufacturer: DSK-1 and ZhBI-2
- Years of construction: 1965-1985
- Number of floors: 9
- Number of rooms in apartments: 1, 2, 3, 4
- Height of living quarters: 2.64 m
- Number of apartments per floor: 4
- Number of sections (entrances): from 2 or more
- Elevators: passenger lifting capacity 400 kg
- Stairs: two-flight of prefabricated reinforced concrete steps and landings
- Ventilation: natural exhaust through ventilation units in the bathroom
- Garbage disposal: garbage chute with loading valve on the interfloor landing
- Technical premises: technical underground for placing engineering structures
- Bathtubs: standard, 170 cm long
- Bathrooms: separate
- External walls: expanded clay concrete panels 300 mm thick
- Internal walls: concrete 140 mm
- Partitions: gypsum concrete 80 mm
- Floors: concrete panels 140 mm thick
- In Moscow, houses of the standard series II-49 (2-49) were built mainly in the areas: Teply Stan, Yasenevo, Belyaevo, Cheryomushki, Orekhovo, Academichesky and others.
Options for redevelopment of apartments in houses of series II-49 (P-49D)
As you can see, the dimensions are not very impressive. In addition, there is a specific layout of rooms, which is determined by the peculiarities of the construction of the house and the presence of load-bearing walls inside the living space. It is for this reason that many owners who purchase such housing think about the processes of redevelopment in such housing. Especially often in II 49, redevelopment of a 4-room apartment is of interest to homeowners.
And this happens for the reason that the hall is the least functional room, although it should serve as a gathering place for the whole family.
But despite this, even in a one-room apartment, in some cases, the owners try to arrange the space a little differently, in accordance with their needs and needs. Therefore, let's look at all the possible options on how to change functionality and purpose of the internal space:
- You can create an opening in the load-bearing wall between the kitchen and the guest room in a one-room or two-room layout.
- In some cases, a sliding door is made between the corridor and the main room or bedroom, demolishing part of the partition. This is done so as not to occupy part of the space of the corridor or room with the swinging door leaf.
- In addition to creating additional openings, there are redevelopments in which, on the contrary, interior openings are laid and moved to another place. So, for example, P-49 D, a 2-room layout with small dimensions can be done as follows. An opening is made from the living room to the bedroom and is made between two adjacent bedrooms with a common wall.
True, this option is well suited when you need to divide two bedrooms between two same-sex children. And the parents arrange a sleeping place for themselves in the guest room.
In some cases, when the rooms face different facades of the building, two distant rooms can be separated by a small corridor. True, in this case, the area of one of them will be significantly reduced. But it turns out to be 3 full-fledged isolated rooms. Moreover, a small storage room can be organized in the corridor.
This is suitable for series II 49, so this redevelopment of a 3-room apartment is done when there are children of different sexes in the family and everyone wants to have their own corner.
Mustard gas in Kuzminki. "Forest of Heat"
The Kuzminsky forest park is familiar to every Muscovite. Lake, pond, peaceful views of Central Russian nature. The pastoral picture is broken by one fact: in the south-eastern part of the Kuzminki park, from 1918 to 1962, there was a Heat Forest test site. The Red Army inherited a colossal amount of chemical weapons from the tsarist government. Since 1918, military chemists have conducted large-scale exercises with infantry and cavalry, testing the properties of combat gases. Experiments on people and animals were carried out in the Heat Forest. The bunker of the main laboratory, where mustard gas was tested on soldiers, is perfectly preserved. Chemical maneuvers were personally supervised by Tukhachevsky. Here, in 1926, a combat form of anthrax was tested on goats. A total of six thousand experiments were carried out. In 1937, hundreds of barrels and cylinders of chemicals were buried at the landfill. Part of the deadly cargo was dumped into the lake. Now these barrels are reliably detected by metal detectors. In August 2022, sappers from the Ministry of Emergency Situations worked in the park: a hurricane broke down trees in several places, exposing buried chemical shells.
Ecologist Lev Fedorov argued: “This is a gigantic amount of chemical weapons, these are hundreds of tons of toxic substances. In combat conditions, this would be enough to destroy a city.” When leaving the test site in 1962, the military did not even dismantle the testing dugouts and cages for experimental animals. Not to mention special chambers and stone buildings. All this, although noticeably dilapidated, still stands today. Fragments of ceramic vessels for sarin, lewisite and mustard gas can be found. The barrels have long lost their tightness. The markings are barely visible. The contents flow to the ground unhindered. In some places, half-rotten “Danger to Life” signs still stand, and gas masks are scattered.
The abolished Institute of Experimental Veterinary Medicine was also located there. The animal burial ground at the institute has been mothballed, but its tightness raises questions. If released into groundwater, anthrax spores may rise to the surface.
How can the “Forest of Heat” be dangerous? On the one hand, mustard gas and lewisite have probably lost their combat properties. But this is not guaranteed. The barrels smell of garlic, which means the poisons are breaking down. Let us remember that a person who inhales mustard gas becomes covered with ulcers, goes blind and dies from pulmonary edema. On the other hand, the maximum concentration of arsenic in soil was exceeded 550 times. The main danger is unpredictability: what awaits a person who comes into contact with decaying biological-chemical weapons?
On the map of the General Staff of the USSR Armed Forces in 1968, the training ground is marked as a pioneer camp
Source: retromap.ru
Layout and construction of houses of series II-49
The most common event in this series is the creation of an opening between the kitchen and the room and the expansion of the bathroom into the corridor area. We must remember that II-49 uses three types of wall panels:
- – long,
- – average,
- – short.
Accordingly, the load-bearing capacity stems from the size of these panels. The long one has the largest one, and the short one has the lowest one.
The short panel is located in the apartment corridors where the corner of the elevator shaft is located.
Accordingly, if you have such an apartment, then it is very difficult to get approval for an opening in a load-bearing wall from the author of the house project (MNIITEP). It is reasonable to plan the opening in a “short panel” starting from the fifth floor and above.
In the case of a long one, you can count on a positive solution on the second floor. On the first floors everything is always extremely difficult.
Also, the possibility of constructing an opening is strongly influenced by the accuracy and precision of builders during the construction of a building, namely, the quality of installation of wall panels and floor slabs, since in the calculations of bearing capacity both the quality and location of the interpanel seam are taken into account.
If the interpanel seam is narrow, correctly caulked with cement-sand mortar and located directly along the axis of the wall panel, that is, the wall panel rests equally well on the floor slabs of the kitchen and room, then the calculation will be good and the load-bearing capacity is high, and in this case the chances of coordinating the opening increase .
The second point is the dimensions of the opening and the indentations from the outer wall of the house.
The owners try to press the opening as close as possible to the front wall in order to use the remaining kitchen space more functionally, but the author of the house project has a different opinion.
The opening should be no more than 90-100 with a distance of at least a meter from the facade wall. (Often 120 or 130).
Also, the decision to coordinate the opening is influenced by the condition of the wall panels above and below, namely the presence or absence of openings in them.
If the panel is in the design condition (that is, no openings were made in them), there is a chance that your opening will be approved. If done, then the dimensions of the opening and the distance from the outer wall panel are important, as well as the type of reinforcement of the opening. All this will be taken into account by the engineer when calculating your opening.
With all the complexity of the survey, calculations, etc. a positive decision is made more often than negative ones, that is, more openings are allowed than prohibited.
Cleaned and Uncleaned Radioactive Repositories
In the middle of the 20th century, numerous enterprises operated in Moscow that used radioactive substances, in particular uranium ores. Political reasons forced scientists to work in emergency mode. As a result, waste was disposed of carelessly, burying by-products wherever necessary. The radiation pollution standards were different, and the waste was shamelessly rolled into roads, poured into ravines, or simply placed in the ground. This is how, for example, the famous burial ground near the river arose. Likhoborka, liquidated by Radon seven years ago. Back in the 1950s, radioactive substances were literally transported there on carts (as Ivan Schwartz wrote in the article “Nuclear dump is our home” for Kommersant in 1997). However, not all landfills are known.
In an interview with Moskovsky Komsomolets in 2014, Mikhail Ivlev, director of radioecology at FSUE Radon, admitted that the most problematic place in Moscow in terms of radiation is the Kolomna slope. In the 1950s, the development of thorium bombs was carried out at the polymetallic plant (on Kashirskoye Highway). (The plant produced thorium and uranium from 1934 to 1972.) All waste from this painstaking work was simply dumped onto the slope. Now from time to time they are washed away by rain. There is an opinion that there is a burial ground on the territory of the enterprise itself. On the outskirts of Kolomenskoye you can find shallow pits, carelessly fenced off with yellow and white tape (the waste was removed, but not conscientiously). In 2022, volunteers recorded an activity of 1.3 microsieverts per hour, in some places up to 14.03, and also found rock fragments with an activity of 19.3 microsieverts per hour. The upper limit of human radiation per hour is 0.57 microsieverts.
What not to do
- Relying on the “standard” requirements for the opening, first cut the opening and make repairs, and then try to coordinate it. This situation is suitable only for those who have already bought an apartment with redevelopment, or the redevelopment was done many years ago and “there is nowhere to go.”
- To coordinate previously completed openings, the engineer needs to open the plaster layer of the opening, view the type of reinforcement and the quality of the work performed, open the floor and screed to the floor slab to inspect the presence of reinforcement frame support plates.
- Open the end of the wall panel from the corridor side to the floor slab. Open the plaster layer from the side of the room and kitchen at a distance of approximately 130-140 cm from the floor level to conduct an ultrasonic examination of the quality of concrete.
- In 90 percent of cases, reinforcement frames do not meet the requirements of the designer. And you will be lucky if the opening “passes” according to the calculations. In this case, the owners will only have to make local repairs, having first properly strengthened the opening.
Subscribe
to our pages on social networks to follow the latest company news and know everything about redevelopments:
Instagram
YouTube
Facebook
Problem areas II-49
Given the low cost of apartments in this series and good standard planning solutions for comfortable modification of apartments, there are also standard problem areas
- Seams of joints of external panels. Over time, due to the weathering of the solution from the joints of the panels, atmospheric moisture enters, which leads to the appearance of mold and freezing in the cold season at the ends of the wall panels adjacent to the facade.
- Plumbing cabins. Since most of the houses in this series were built in the 70s, due to the formation of a large amount of dust between the walls of the plumbing cabin and the ceiling and walls of the apartment and the maintenance of constant humidity in these places, fungus often forms in these places, which is practically impossible to remove without dismantling the old plumbing cabin and subsequent cleaning and antiseptic treatment of all adjacent surfaces.
When dismantling a plumbing cabin, the next problem area emerges - old rusty pipes.
Particular attention should be paid to the heated towel rail pipe. Threaded connections leak when there is any vibration or when pipes are touched. Therefore, the best solution before dismantling the plumbing cabin would be to temporarily turn off the hot and cold water supply risers. And at the end of the dismantling work, invite a plumber-welder from the management company, who will replace the rusty risers and bends with new pipes and install new modern shut-off valves.
Do not forget, after completing the work and turning on the hot and cold water supply, check all new connections for leaks, and also install a special plug on the drain hole of the sewer riser, since water flowing from the upper floors can leak into your apartment and flood the floors below.
- The next problem is typical for any old panel series - good audibility. Moreover, both the neighbors located above and below, and the neighbors located on the same staircase with you.
- When planning redevelopment work, be sure to include in the expense item the work on soundproofing the walls adjacent to the neighboring apartments, and be sure to soundproof the floor, so as not to disturb the downstream neighbors with noise. The height of the room will not allow you to soundproof the ceiling.
- Old garbage chutes with all the spicy aromas in the hallways
- Old elevators, lack of freight ones
- Small flights of stairs for lifting large furniture and other loads