November 23, 2016 Stroyexpert Home page » Foundation » Types and types
Diagram of a slab foundation with stiffeners
The most important structural element of the future building, on which its strength, reliability and durability depends, is the foundation. There are many types of foundations used for private housing construction. One of the most reliable foundations for any type of soil, as well as at any level of groundwater, is a slab foundation with stiffeners.
Height of floating slab above surface
According to the standards SP 21.13330, a slab foundation can be buried to any distance, focusing on the groundwater level and soil composition.
However, the higher the slab is located above the surface, the longer the lifespan of the wall materials. For example, the maintainability of the lower crowns of a log house is much higher if they are located above the ground. Therefore, for timber and log buildings, slabs with stiffeners are usually used:
- cup-shaped - a slab is cast, after the concrete has gained strength, formwork is installed, reinforced concrete beams are made under the load-bearing walls
- inverted bowl - the outer formwork panels are higher, the inner ones remain under the concrete structure for the entire period of operation, the inner perimeter is filled with sand or polystyrene foam is laid to insulate the structure
On heaving soils, it is necessary to calculate the cross-section of the reinforcement, the mesh cells of the lower and upper chords. It is forbidden to rigidly connect foundations to a sidewalk or blind area with a floating slab. Various loads and uneven freezing of soils under these structures can lead to the opening of cracks in reinforced concrete.
In this case, the calculation is made for the tensile strength of the sole from prefabricated loads, the upper surface of the slab when heaving forces occur.
Attention: The lower mesh can be made from rods 10 – 16 mm, since prefabricated loads are always present. The bottom mesh is knitted from rods 8 - 14 mm, since swelling is partially balanced by the weight of the house
Thus, the slab foundation for outbuildings has a thickness of 10 cm. To support the cottage, a load-bearing capacity calculation will be required. The choice of thickness is influenced by the size of the protective layer of concrete and the minimum permissible distance between the reinforcing mesh.
Formation of the structure: formwork, mortgages, reinforcement
After waterproofing, they begin to install removable formwork for a slab with a height of 50 mm higher than the pouring mark. Boards, sheet materials or inventory panels are used for it. I use a level to set the formwork. In addition, the vertical is controlled, and supports are used for better stability.
Along with the arrangement of the formwork, sleeves for utility service entries are laid. The sleeves are closed with plugs and then wrapped with plastic film, so that concrete will not get into the pipes.
Then reinforcement is made to give the base the required strength parameter. The reinforcement is first installed on the ribs, placing 2-4 rods in them, which are connected transversely by the reinforcement, at such a distance that there is a protective layer of concrete of 50 mm on each side. The connection between the ribs and the slab is ensured using special bent elements.
A classic frame for the slab is formed from two horizontal grids - the rods are connected perpendicularly so that the formed cells have a size of 200x250 mm. The rods of one grid are placed on clamps made of plastic, and vertical rods of a certain length provide sufficient distance from the upper grid. The rods are fixed with wire, ties or polypropylene clamps.
The project specifies each reinforcement parameter, the type and diameter of the reinforcement used. All that remains is to carry out the work accurately, according to the drawing, in compliance with the technology.
Stages of arranging a slab foundation
In general, the arrangement of any foundation first requires preparation of the space.
It is important to remove the fertile soil layer from the area where the building is being constructed, since the substances and microorganisms contained in it can destroy the foundation of the structure. In this case, in addition to these works, it will be additionally necessary to dig trenches for arranging a concrete strip
The holes need to be made so deep that it is still possible to build a cushion of sand or crushed stone. In order for all the recesses to be accurate, it is necessary to make preliminary markings.
In the future, all construction work must strictly comply with the developed project. The construction of a slab base with ribs includes the following steps:
- Preparing the base. In this case, the soil is compacted.
- A layer of sand and crushed stone is poured.
- Waterproofing material is installed. This is necessary to protect the foundation from the effects of groundwater that can rise to the top.
- Installation of formwork.
- Construction of a frame from reinforcement, as well as reinforcing mesh.
- Pouring concrete solution.
This sequence of actions must be carried out in accordance with existing regulatory documentation in the field of construction. You need to take a closer look at the technological maps to ensure that all erected structures meet safety and reliability requirements.
Unlike a conventional foundation, slab foundations with stiffeners have a more complex structure and method of construction, so such work must be carried out based on state construction standards. The algorithm of actions may also include additional measures; the specified list is not the only correct one.
Main stages of the device
For a foundation slab with downward stiffening ribs, it is necessary to remove not only the layer of fertile soil under the entire area of the building, but also to dig trenches under the concrete strip, taking into account the construction of a crushed stone-sand cushion. Before this, preliminary marking is carried out on the site.
Further work is carried out in strict accordance with the project:
- the base is compacted;
- crushed stone and sand are added;
- waterproofing is installed;
- formwork is installed;
- reinforcement frames and meshes are installed;
- concrete is poured.
The sequence of work and additional measures (insulation, output of communications, drainage, etc.) are indicated in the technical documentation. It is compiled taking into account individual conditions, state regulations and standards. You should also adhere to the instructions and recommendations set out in the technological maps.
Classification
There are three types of ribbed slab bases:
- with ribs pointing down (in this case, the monolithic slab rests on a frame in the form of a continuous strip);
- with ribs directed upward (a continuous strip of stiffening elements rests on a monolithic slab on top);
- combined version of the frame arrangement.
The ribs turned upward additionally serve as a base. They must be insulated. Utilities can be laid between them, as well as underfloor heating systems installed. The monolithic tape located on the top of the slab serves as a support not only for load-bearing walls, but also for the materials cladding the facade, as well as roof structures and ceilings.
A foundation with stiffening elements turned downward resembles a shallowly buried strip base, which is rigidly connected to a monolithic reinforced concrete slab laid above. The only difference is that the cross-section of the tape is trapezoidal rather than rectangular.
The technology for constructing a base with ribs pointing down is somewhat simpler than in the second option. The thing is that in this case there is no need to erect hanging formwork. Also, when pouring stiffeners, there is no need to monitor the level of the concrete mixture, which, according to the laws of physics, can begin to rise in the area of contact with the slab.
Design features
Essentially, this design is a combination of strip and slab base
The slab base in the form of a continuous monolithic structure under the house is itself quite strong. But in some cases it is necessary to give the structure additional rigidity. This is achieved through the use of stiffening ribs, which are located along the perimeter of the slab and sometimes stand at a certain pitch along the longitudinal side (if the slab is very long).
Important: among all types of foundations, it is the monolithic slab that ensures sufficient stability of a heavy building on any type of soil, since it has the largest supporting area.
Essentially, this design is a combination of strip and slab base. Imagine that a solid monolithic slab was placed on a monolithic strip or, conversely, a monolithic strip was installed on a solid slab base. This is what a slab foundation looks like, equipped with stiffening ribs.
In this case, the slab is a single monolith with a rib structure. This gives the entire structure additional strength, resistance to soil movement and rigidity.
Attention: stiffeners must be installed along the perimeter of the slab part and under all load-bearing walls of the building.
If the building area is large, then the ribs can be located not only across the long side, but also along it, thereby forming a lattice-like structure. The thickness of the slab structure and the height of the strip part are determined by calculations taking into account all loads and soil characteristics.
Stages of constructing a monolithic foundation with your own hands
Foundation layout diagram
- digging the foundation along strictly marked lines and with a calculated immersion depth;
- filling the base with a sand and gravel cushion;
- creation of a special pipe or drip drainage system along the perimeter of the future foundation or along the external contour of the foundation;
- It is recommended to create an expensive layer of footing in the sand cushion, which protects the basement from water ingress.
That's it, the preparatory work is completed. The pit is ready, a drainage system is provided, the load on the corners of the foundation, as well as the main load points, are correctly calculated. Now it's time to build the foundation itself. And this procedure also consists of a number of stages, because only then will everything work out as correctly and reliably as possible:
- Foundation reinforcement. Depending on the type of building and its mass, horizontal and vertical reinforcement can be considered popular. There is also corner reinforcement using seal welding, but this is popular in the construction of high-rise prefabricated buildings.
- Installation of wooden formwork. It should be slightly wet to ensure optimal adhesion to the concrete mortar. It is also taken into account that mesh formwork always protrudes beyond the width of the foundation. But this is not a problem, because all popular monolithic foundations are buried, so the external contours are subject to waterproofing. The arrangement of formwork is done depending on the type of soil and its characteristics, therefore it is selected individually in each case.
- The main stage is concreting. There are several options here. If it is possible to use several concrete mixers at once, then it is better to simultaneously pour concrete in layers. But if the budget does not allow this, then you can fill the fragments with concrete and connect them with reinforcement. But this technology is a little more expensive.
- Dismantling the formwork and checking the monolithic base for strength. This is the climax.
Types of slab foundation
There are several options for making a foundation slab. Most often it is a monolithic slab, the thickness of which is the same over the entire area. The advantages of such a base include ease of installation; the disadvantage is that the upper edge is close to the ground surface - in this case, the base of the walls may be exposed to moisture, which is harmful to building structures.
To ensure that the edge of the slab is located higher above the ground surface, you should not increase its thickness - this will significantly affect the cost of the foundation. A more practical option would be to install a slab with stiffeners.
The foundation is a monolithic slab with ribs up
The monolithic structure is a flat base with reinforcing ribs protruding above the surface - it looks like a strip foundation on top of a slab. The ribs are located around the perimeter and under future load-bearing walls inside, if this is provided for by the project.
A foundation slab with upward stiffening ribs allows the construction of a building with a basement or ground floor. In this case, the monolithic structure must be buried in the ground and grillage ribs of a suitable height must be designed. Subsequently, a layer of waterproofing is laid over the ribs and wall structures are mounted.
Slab foundation with ribs down
To increase the load-bearing capacity of the slab foundation without deepening it, a monolithic structure is made with stiffeners directed downwards.
There are two options for making a monolithic slab with downward stiffening ribs:
- Stiffening ribs are formed by trenches dug in the ground below the level of pouring the reinforced concrete slab. A reinforcing frame is installed in the pits for the ribs, made as a single unit with the frame of the slab itself, after which the concrete mixture is poured.
- A pit with a flat bottom is being prepared for the slab. Polymer slab insulation is laid on the waterproofed base - stiffening ribs will form in the spaces between the “islands” of the heat insulator and the walls of the pit. Before pouring the concrete mixture, a reinforcement cage is installed.
Stiffening ribs should be located under load-bearing walls and capital internal partitions. If the project does not include partitions, but it is necessary to increase the rigidity of the slab, the downward-facing ribs should be located parallel to the short side of the building in increments of up to 3 meters.
Laying a heat insulator, including extruded polystyrene foam, under the foundation slab not only allows you to install stiffeners of the required size, but also helps to insulate the foundation base and reduce the cost of heating the house. This type of foundation is called a “Swedish slab”. It is often supplemented with a water heating circuit.
Prefabricated slab base
Instead of a monolithic slab foundation, in some cases a precast concrete foundation is used. Finished structures are laid close to each other. But this option can only be used on rocky soils that are not prone to heaving. In other cases, the base may deform over time under uneven heaving loads due to the lack of a rigid connection between the slabs.
A foundation made of ready-made reinforced concrete slabs is used only in the case of the construction of outbuildings, bathhouses, and small light houses. A screed is made on top of the laid slabs. The technology for installing a prefabricated foundation requires the use of special equipment for transporting and laying slabs.
I decided to build a cottage, which foundation to choose?
Foundation slab
For economic and technical reasons, suburban construction often involves the use of surface foundations. This type of foundation is considered one of the simplest and cheapest for the construction of any low-rise buildings, including cottages. The surface foundation, in turn, is divided into three main types: a monolithic slab, a slab with stiffening ribs directed upwards, and ribs directed downwards.
Monolithic slab
This type of surface foundation is the most durable and at the same time simplest to construct. It is a monolithic slab usually 25-30 cm high. B25 grade cement is most often used here. To strengthen the concrete slab, a frame is built from reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm, in two layers: lower and upper. Utilities are laid under the slab before its construction, at the time of preparation of the foundation.
A surface foundation of this type allows you to build a cottage with a fairly large weight (not only from timber or foam concrete, but also, for example, from brick).
Slab with stiffening ribs directed upwards
The main difference between this type of foundation is the presence of stiffening ribs around the entire perimeter, under the load-bearing walls. The ribs are erected on top of the slab, along pre-made reinforcement outlets, for which formworks are constructed, as shown in the photo below.
Ribs are made to raise the house from the ground surface. This is done for architectural and functional reasons.
The advantage of this type of foundation is that utilities can be laid after the cement mortar has been poured and dried. Sand or polystyrene concrete can be poured into the resulting empty space between the ribs. Afterwards, a clean floor is installed (often a screed with underfloor heating pipes on top of 50mm polystyrene foam).
Plate with stiffening ribs pointing downwards
The difference between this type of foundation and the previous one is that it does not require making a full-fledged foundation slab, because The entire load is carried by the ribs, or foundation strips, poured together with the slab. The slab in this case can be 100mm thick. It would be more correct to call it a screed here. The list of advantages includes the presence of a basement rise, in order to visually lift the house from the surface of the earth. When constructing such a foundation, prepare the base with a crushed stone layer of 15-20 cm and then form a layer of sand (to the height of the base). In this layer of sand, trenches are formed for the subsequent installation of foundation strips in them. The entire resulting surface is insulated with polystyrene foam, the film is laid out and the reinforcement is knitted. Once everything is ready, concrete is poured, and everything is poured at once, both the tapes and the slab itself (of course, depending on the size of the foundation). As in the first case, utilities are laid before pouring, at the time of preparing the crushed stone base.
The advantage of such a foundation over a foundation with ribs up is that here we save on the thickness of the slab and the reinforcement in this slab. But you must understand that this type of foundation is only intended if you decide to build a wooden or frame cottage. Stone and brick houses should be built on a full foundation slab - types 1 and 2.
In conclusion, it must be said that understanding the structure of the foundation slab, its types and features is an important component when building a country house. By contacting the architectural studio “Meta”, you are guaranteed to receive full consultation on all issues of interest and high-quality work
When can you choose a monolithic slab?
A monolithic slab with a grillage upwards can be chosen as a base for a future structure in the following cases:
- Based on the results of geological studies, a large number of problems were found in the soil. For example, too much humidity, bulk soil, the presence of gushing springs underground, flooding of the area with melt water, quicksand, moving soil, etc.
- It is planned to erect a complex architectural structure of large dimensions.
The foundation slab can be erected depending on the initial conditions under the following circumstances:
- Construction of a foundation without deepening the base. In this case, no preliminary work regarding digging pits is done; the foundation is erected directly on the cleaned surface.
- Shallow recessed base. In this case, the foundation is buried into the ground no more than half a meter. This involves digging a pit to fill the concrete solution.
- Monolithic slab, buried to a sufficiently large depth. In this case, a pit is dug to the point where soil freezing extends in winter. As a rule, the depth is about one and a half meters.
Concreting
The slab foundation is made of M300 concrete, which is characterized by high levels of compressive strength, mobility and water resistance.
The slab must be poured within one day. For this reason, concrete workers have to work day and night. The work project indicates the correct pattern for laying concrete.
In case of force majeure situations (failure to deliver concrete on time, breakdown of a concrete pump, etc.), it becomes necessary to install working concreting joints, which are sometimes specified in the project if the slab foundation has a large area.
The concrete mixture is laid horizontally, in layers directed in one direction. A concrete pump is used for this. Concrete is laid evenly distributed around the perimeter. It is allowed to raise individual protrusions above the pouring level by a maximum of 10 cm.
Redistribution and leveling of the mixture entering the formwork cannot be done with a vibrator, which is used to compact the concrete after redistribution.
Layers of concrete are laid one at a time before the previous layer begins to harden. If this happens, you cannot do without constructing a working seam. But to continue work it is necessary to wait until the concrete becomes stronger.
The drying speed of concrete depends on the method of cleaning the cement film:
- Washing – strength 0.3 MPa.
- Metal brushes – 1.5 MPa.
- Mechanical cleaning method (sandblasting) – 5 MPa.
Strength is determined in a construction laboratory.
In the absence of force majeure circumstances, the next layer of concrete is compacted using a vibrator. The device is immersed at least 5 cm into the previous layer. The vibrator must not be allowed to come into contact with embedded or reinforcing elements.
The relocation of the vibrating tool should be a distance equal to a maximum of 1.5 of its radius of action. In this case, the compacted area will intersect with the previously compacted one. Vibration is carried out until the concrete stops settling and a shiny cement paste appears on its surface.
All compacted layers must be up to 25 cm high. The foundation slab is poured at a time, and the ribs are poured layer by layer. Their depth parameter is up to 80 cm.
Features of the construction of slabs with downward stiffening ribs
When constructing a slab base with the protrusions downwards, it is necessary to remove not only the humus layer under the entire building, but also to develop a trench for the future monolithic strip, taking into account the addition of a sand cushion. To do this, mark the area with diagonal measurements to eliminate unnecessary work.
Location of the slab on the foundation
For long-term operation of the building, it is necessary to waterproof the foundation. Before pouring concrete, the crushed stone-sand mixture must be treated with a special cement mortar no more than 4 cm thick. A bitumen primer is placed on top of this layer, followed by laying waterproofing. To prevent damage to the waterproofing during other work, a 4 cm thick cement-sand screed is poured on top.
The next step in building a foundation with projections down is to install the formwork under the top layer of the base. The bottom layer is installed before the sand cushion is compacted. Formwork panels can be made either by yourself or purchased in special stores. It is possible to use scrap materials. In the video you will see how to properly install the foundation slab formwork.
The future ribbed slab must be reinforced according to the calculations made. Depending on the load taken, reinforcement of different diameters and its quantity are laid under the walls. For better load perception and stability of the foundation, it is necessary to connect the frames of the ribs and slabs together.
The last stage in the construction of a slab foundation with downward stiffening ribs is pouring concrete into the formwork. Filling must be done in one step, otherwise it may affect the integrity of the slab, which will lead to the appearance of minor cracks in the protective layer of concrete.
Monolithic slab foundation with grillage
Construction of a monolithic foundation for a private house
Slab foundation for a bathhouse: technology for pouring a monolithic slab
How to set the foundation level
The cost of work includes:
- Geodetic works
- Digging a foundation pit (30 -40 centimeters deep)
- Laying the bottom of the pit with geotextiles
- Construction of a sand-crushed stone cushion with layer-by-layer compaction (20 cm sand, 10 cm crushed stone)
- Installation of formwork from boards
- Installation of windows for utility networks and laying of pipes
- Double reinforcement with a pitch of 250x250mm
- Pouring concrete M300
- Foundation waterproofing
Location of the slab on the foundation
A slab-type foundation does not require deepening - its ability to “float” and resist the forces of frost heaving is fully manifested precisely when laid on the surface.
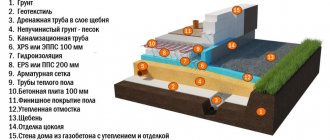
Foundation layers from bottom to top:
- Compacted soil is the bottom of the prepared pit.
- Pillow - made of sand or a mixture of sand and gravel, crushed stone. It is filled in layers, leveled and compacted. The cushion dampens ground vibrations and reduces the intensity of the impact of loads from below on the foundation.
- Geotextiles. Dornit fabric protects the pillow from silting and reinforces it. Geotextiles can additionally be laid at the bottom of the pit, between layers of sand and crushed stone to increase the strength of the pie.
- Footing. A thin leveling layer of concrete on top of the cushion helps to properly waterproof the foundation and correctly install the reinforcing frame.
- Waterproofing. Waterproof material protects the reinforced concrete foundation slab from the penetration of moisture from the soil. Waterproofing of a monolithic foundation slab is traditionally performed from two or more layers of rolled bitumen material.
- Concrete slab. Actually, the foundation itself, the thickness of which depends on the magnitude of the loads on the foundation.
- Reinforcement frame. Reinforcement increases the strength of a monolithic structure, takes on tensile-compressive loads, preventing cracking of concrete.
Slab base with ribs up
This arrangement option helps to save materials, however, not by reducing the thickness of the slab, but by reducing the cost of constructing the base. The disadvantages of such a base also appear during its manufacturing process:
- Since it is better to pour the slab simultaneously with the stiffening elements, it is necessary to construct hanging formwork for them, which is quite difficult and expensive in itself.
- In addition, the formwork must not only be suspended at a certain distance from the bottom of the pit, but also be rigidly fixed so that during pouring the solution does not push it up and violate the geometry of the foundation.
- Also, during pouring, problems may arise when the concrete in the slab tries to equalize the level of concrete in the tape (based on the principle of communicating vessels), pulling the solution towards itself. In other words, when pouring the tape, the volume of concrete will be forced into the already poured concrete slab solution.
Advice: so that squeezing out the concrete mixture does not interfere with pouring, it is worth preparing a thick solution, pouring it carefully and not using a vibrator.
- Laying communications does not require the use of special channels.
- Saving money on the construction of a basement.
- Repairs to utility networks under the house can be carried out without opening the slab.
Stages of manufacturing a monolithic slab
To put all the pieces of the puzzle into one picture, I suggest you understand everything step by step. The technology for constructing a monolithic slab foundation is very difficult. It will be difficult for beginners in this matter to think about specific formulations. But if you have set yourself such a goal, then do not deviate from it.
A house built on such an excellent and stable foundation will be worth much more when it is subsequently sold than a house whose foundation does not consist of a monolithic slab. So:
- A large number of assistants or professional builders dig a pit of a certain depth.
- The entire depression is filled with a sand cushion.
- As mentioned above, a special drainage system will be laid around the foundation in order to protect it and future basement areas from flooding.
- A layer of so-called concrete is made on the sand cushion, which is made in order to place material there that will protect against water ingress.
- Then the main part of the work happens: the reinforcement and foundation slab come into play. After pouring this slab, some of the reinforcement will stick out from it. Thanks to this, future walls will be firmly connected to the slab.
- Then follows a mandatory process, without which it is not possible to make a monolithic foundation. You need to make a strong frame from the reinforcement, the distance between the rods of which should be 25-30 cm. The reinforcement should cover the formwork, do not forget this.
- Clean and slightly wet formwork must be installed to make the walls more durable. The aligned beams together with the bolts finally secure the formwork.
- The climax comes, namely concreting. The average thickness of one layer of concrete is 15 cm. After pouring it, you need to level and properly compact the uncured mixture. We do this until the first water appears on it. Thanks to the leveling bar, which must be moved along the formwork, the gradually cooling concrete will finally assume a level position.
- The last, final stage. This is like an indicator of the work done. Only when the entire concreting process is completed and the concrete has hardened does dismantling of the formwork begin. After this, the monolithic slab is considered complete.
And after this the question arises: are you really ready to sacrifice your family budget for expensive equipment, good equipment? If yes, then we have no right to restrain you. The main thing is to do this consciously, after consulting with your family. We can rejoice in the fact that your house will have the fate of a long-liver - this foundation will stand firmly for about 150 years.
Slab foundation with stiffeners: features and pouring order
A foundation slab is an almost universal solution for building a private house. It is reliable, durable, and holds up well on difficult soils. One drawback is that a large solid slab requires a lot of concrete and reinforcement. To save materials without losing strength, use a slab foundation with stiffeners. Find out why it is good and how to fill it correctly.
Price
Thickness 200 mm Thickness 250 mm Thickness 300 mm
| from 3200 RUR/m2 | from 3800 RUR/m2 | from 4200 RUR/m2 |
The cost of work includes:
|
A slab foundation with stiffeners is a “lightweight” version of a conventional flat slab. Thanks to the presence of reinforcing ribs, the thickness of the slab part can be reduced by 2–2.5 times without reducing the strength of the structure. This saves concrete, but requires more complex foundation work and increases the consumption of reinforcement.
Design and types of slabs with stiffeners
There are three types of such foundation:
- with stiffening ribs upward (concrete “ribbon” poured on top of a flat slab);
- with ribs down (with a strip part under the slab);
- combined (ribs are directed both up and down).
The first type is described in detail in the article “Do-it-yourself slab foundation with a grillage.” Here we will consider the second type - a slab with stiffening ribs directed downward. First, about its design.
Stiffening ribs are protrusions resembling a concrete strip (up to 80 cm deep), but not with a rectangular, but with a trapezoidal cross-section. This shape reduces the soil pressure on the foundation (the loads in this case are tangential). The ribs are located under the slab along the perimeter of the house and inside the perimeter:
- under load-bearing walls;
- along the slab at a certain distance from each other;
- along and across the foundation (like a lattice).
The depth, shape, number, location of the ribs and thickness of the slab part are designed based on the design of the house and geodetic conditions on the site.
Pros, cons and scope of application of the “ribbed” slab
Thanks to the stiffening ribs on the bottom side, the slab foundation receives additional advantages:
- concrete consumption is reduced;
- the stability of the foundation to deforming loads increases;
- the working surface of the slab remains smooth and can be used as a subfloor;
- protruding ribs improve the adhesion of the slab to the ground and reduce the likelihood of its horizontal movements.
The disadvantage of the “ribbed” slab is the complexity of its arrangement. Under it you need to make a foundation pit with trenches and “two-story” formwork. Reinforcement also becomes more complicated
With all this, it is very important to make the foundation monolithic (fill it in one go) and strictly follow the project. If the ribs are positioned or reinforced incorrectly, the strength of the structure will decrease dramatically.
Like a flat floating slab, a slab foundation with stiffeners is suitable for building a house on the following sites:
- with heaving soils;
- with high groundwater levels;
- with soils of low bearing capacity.
It can be used in better conditions, but in such cases cheaper solutions are usually chosen.
Basic requirements for burial depth
The slabs are divided according to their depth, which can be:
- Normal (deep), which is laid lower than the soil freezing mark. They are used for the construction of houses with basements or ground floors.
- Shallow (surface or floating), buried to a maximum of 50 cm. The base has the ability to simultaneously move with the movement of the soil.
- Non-buried, which is laid at ground level. It is built after removing the top part of the soil, the thickness of which is equal to the thickness of the sand layer from which the foundation cushion is made.
The depth of laying a slab foundation is influenced by the following indicators:
- Arrangement of the basement.
- Loads that act on the structure.
- The depth of the foundation of the adjacent house or the depth to which communications are laid.
- The topography of the area where construction is taking place.
- To what depth does the soil freeze (this takes into account its type).
Before building a house, geological studies are carried out, the purpose of which is to identify the strength and physical properties of soils, the nature of bedding, possible voids, as well as soil layers that can liquefy and slide over time.
Hydrogeological studies of a construction site make it possible to determine whether there is high water on it, at what depth the aquifers lie and whether the groundwater is aggressive.
When choosing the depth of the foundation, you need to be sure that low-strength layers of small thickness do not pass under the slab, which, if present, are removed. Instead, a thick sand cushion or a deep foundation is used. In order not to spend money on dewatering equipment, the slab is laid higher than the groundwater level.
If the bearing capacity and deformability of the soil are low, it is better to use a pile foundation.
When laying the foundation, you need to take into account the location of groundwater and the freezing point of the soil. When the soil freezes, it increases its volume, and when it thaws, noticeable sediment appears. In areas with water-saturated soil, snow melting is accompanied by the formation of ice of varying thickness. When it begins to melt, the bearing capacity of the soil sharply decreases and deformations begin in it.
If you correctly calculate the depth to which the foundation will be laid, these problems will not be terrible. Reducing this depth is possible with:
- Arrangement of permanent thermal protection of the base.
- Conducting circular soil drainage.
- Complete or incomplete replacement of heaving or non-heaving soils at the construction site.
- Protect the base by coating and gluing roll materials to the horizontal and vertical sides of the base.
Advantages and disadvantages of ribbed foundation slabs
The design of the slab foundation allows it to work as a single whole - this is very important in weak and heaving soils. Such a foundation absorbs all deformations from heaving soil, and these deformations are not transferred to the main structures of the building - walls, floors, roofing, which avoids the appearance of cracks from uneven settlement of the building.
This differs from a strip foundation, which cannot withstand the uneven deformation of heaving soil. Therefore, this type is very popular at large depths of soil freezing, weak soil, in swampy areas, and at high groundwater levels. There are several main types of slab foundations:
- slab foundation with stiffening ribs upward;
- slab foundation with downward stiffening ribs.
Foundation slab with down/up ribs
A foundation slab with ribs up is used quite often, and concrete ribs in this case act as a plinth and at the same time serve as structural reinforcing elements. A foundation slab with downward stiffening ribs is used in private housing construction and allows saving concrete by reducing the thickness of the slab in its horizontal part.
The service life of a house depends on the correct choice of foundation type and compliance with all requirements during its construction and operation. Foundation slabs are used for buildings with heavy loads. Therefore, the consumption of materials for such a base increases. To save money, there are slab foundations with stiffeners that replace a shallow strip foundation.
In this type of foundation, stiffeners must be placed around the perimeter and under the load-bearing walls. If the building has a large area, then they are made along and across the long sides of the house.
In buildings that have an elongated shape (the length is much greater than the width), additional ribs are constructed along the dominant side.
The design and construction technology of this foundation implies the presence of both positive and negative aspects. Despite the widespread use of slab ribbed foundations, it has quite a few disadvantages:
- The disadvantage is the mandatory installation of special channels for laying communications in casings or capsules. Their early construction will allow the necessary communications to be laid without opening the foundation. If the structure of the house has a basement, then it is possible to lay communications along the floor.
- Two-story formwork structure. The bottom layer is trapezoidal, and the top is regular rectangular.
- A complex reinforcement scheme, which is determined only by calculation.
- The need for high-quality waterproofing with a continuous seam to protect the foundation from the effects of the aquatic environment.
- Cannot be reused.
- The difficulty of determining future walls due to the common foundation pit for the entire house.
With so many negative sides to a slab foundation, there are a number of advantages that make the choice of ribbed slabs obvious:
- Due to the arrangement of the stiffener, the thickness of the slab is reduced to 10 cm, which reduces the cost of construction.
- The main advantage of using a slab foundation with downward stiffening ribs is the smooth surface of the floor in the basement. This will minimize the finishing work of the basement.
- Possibility of erecting a foundation on heaving soils and at high groundwater levels.
- The disadvantage is the mandatory installation of special channels for laying communications in casings or capsules. Their early construction will allow the necessary communications to be laid without opening the foundation. If the structure of the house has a basement, then it is possible to lay communications along the floor.
- Two-story formwork structure. The bottom layer is trapezoidal, and the top is regular rectangular.
- A complex reinforcement scheme, which is determined only by calculation.
- The need for high-quality waterproofing with a continuous seam to protect the foundation from the effects of the aquatic environment.
- Cannot be reused.
- The difficulty of determining future walls due to the common foundation pit for the entire house.
Scope of use
Such foundation designs can be used on soils of any complexity.
Such foundation designs can be used on soils of any complexity, but it is especially advisable to choose this type of foundation in the following cases:
- On soft soils, a slab structure with stiffening ribs will be a good alternative to a deep strip foundation.
- In the northern regions, due to the large depth of freezing, the cost of installing a deeply buried strip structure increases significantly, so it is better to use a slab with increased rigidity.
- Also, such structures are indispensable on bulk soils.
It is worth knowing: when groundwater is deep, as well as when building on rocky, dense soils, installing a foundation slab is not practical from an economic point of view.
How to calculate a monolithic slab foundation
To calculate the foundation slab, you need to use the services of experts. At the design stage, all features of the site should be taken into account. Most math calculations should be done by experts, but light calculations can be done on your own.
So, if you need to build a garage, shed or bathhouse, then it is enough to determine the thickness of the foundation slab. If the parameters are too small, the structure will not be able to cope with bending loads, and if the thickness is excessive, unjustified costs will appear.
Calculation of optimal slab thickness
Calculating the thickness of a slab foundation with your own hands according to step-by-step instructions is carried out after a thorough assessment of the soil at the construction site. For this task, it is better to invite specialists with professional drilling equipment. They will help determine the composition and thickness of the layers, find the location of groundwater and carry out further calculations.
Each soil has its own bearing capacity, which is measured in kilopascals (kPa). The distributed pressure from the mass of the future building should not exceed the load-bearing capacity of the slab.
Calculation of the reinforcing frame and the amount of materials for its manufacture
If you need to reinforce slabs with a thickness of 150 mm, you will need a single-tier knitted mesh with a diameter of 12-16 mm, which is fixed in the central part. If 200 mm structures are used, the reinforced elements are secured in 2 tiers with two meshes with a pitch of 200-300 mm.
For more reliable fixation, the pitch of the rods should be tightened and the mesh should be tied at the points of intersection of the rods using steel wire.
To get accurate parameters, you should use functional online calculators.
Calculation of the thickness of the slab and reinforcing frame
When installing a slab foundation with your own hands, it is important to correctly calculate the thickness of the slab. A base that is too thin will not withstand the load. Pouring an excessively thick slab will lead to unnecessary financial expenses.
Please note: each centimeter of slab thickness is 1 cubic meter of concrete mixture per 10 square meters. m area.
The calculation should be entrusted to professionals or a special program should be used. The value is calculated based on the type of soil and loads on the foundation. Therefore, it is necessary to have geological exploration data on the site and a ready-made construction project. The standard thickness of a slab foundation is 200-300 mm.
The reinforcing frame for slabs up to 150 mm thick is made of one layer of mesh, located along the central horizontal axis. For slabs of 200-300 mm, two parallel layers of mesh are required, installed with a distance of 30-50 mm from the bottom and top of the future slab. The diameter of the reinforcement is 12-16 mm, the installation pitch of the rods is 200-300 mm.
Under load-bearing walls, the installation spacing of the rods is reduced due to the sparser arrangement of the elements in the central part of the slab.
It is most convenient to calculate the number of reinforcing bars and clamps for their fastening using a specialized calculator.