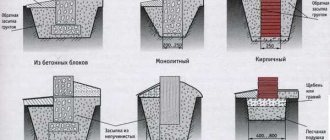
For some structures to be solid, the load-bearing foundation must be laid deep in the ground.
But the greater the weight of the tape, the more expensive the house construction will be. Therefore, at the stage of design calculations, it is necessary to take into account the initial conditions and use the regulated methodology.
We will tell you in the article what the width and depth of the strip foundation should be.
Optimal distance for various buildings
You cannot rely only on the size or purpose of buildings, since in addition to the weight of the house, the type of soil plays an important role.
The denser the underlying layers, the smaller the width of the tape can be made during construction.
For auxiliary and utility buildings, the width of the tape is allowed:
- Dense (rocky) soil, clay - 25 cm.
- Loam - 30 cm.
- Sand, sandy loam - 35 cm.
- Soft compacted sand - 40 cm.
- Very soft sand - 45 cm.
For one-story light houses (dacha, frame house):
- Dense (rocky) soil, clay - 30 cm.
- Loam - 35 cm.
- Sand, sandy loam - 40 cm.
- Soft compacted sand - 45 cm.
- Very soft sand - 50 cm.
For two-story cottages:
- Dense soil - 50 cm.
- Loam - 60 cm.
- Other types of soils do not have average indicators and require separate specialized calculations.
It must be borne in mind that average values are rarely suitable for specific situations, since there are always a lot of additional factors not taken into account in the tables.
The impact of these factors can radically change operating conditions and require a separate calculation, sometimes made using a completely different methodology.
What should be the height of the foundation above the ground?
The construction of most types of foundations for a frame or brick house requires the presence of an above-ground part. Its main purpose is to provide protection from precipitation and temperature fluctuations of the load-bearing part of the structure, which is located underground. How tall should it be? On the one hand, it is logical to increase the above-ground part in order to also protect the house itself, but on the other hand, doing this will be expensive from a financial point of view.
It is recommended to install a strip foundation made of blocks or bricks or slabs for a frame or stone house with an elevation from the ground surface of more than 30 cm. Such a device will visually clearly separate the building from the foundation and improve the integrity of the object when operating under the negative influence of the external environment.
This fact must be taken into account and the appropriate dimensions must be applied to the drawing of the house using reliable data for a specific region of development. To simplify the task, you can look at ready-made house designs that were built nearby. But it is still recommended to double-check the accuracy of the calculations.
We recommend watching a video about how deep to dig a strip base.
When building a frame house, they usually try to save on the foundation and make it from timber. However, to provide additional protection against freezing and heaving of the soil, the height is made much higher than when laying a foundation made of blocks. The maximum permissible length is 30-40% of the total length of the piles, depending on the presence of compressive and tensile stresses in the soil, so that the foundation is not flooded with water.
If you plan to build a house from timber or brick on a foundation made of blocks or a monolith, then the calculation must be carried out taking into account the factor of soil subsidence under heavy load. In such cases, it is necessary to provide a reserve of approximately 20-30% of the value taken taking into account the amount of precipitation. This will allow you to effectively deal with heaving and loose soils, as well as seasonal soil movements.
Price
The cost of a strip foundation consists of the costs of materials (including their transportation) and work. The lion's share of costs falls on concrete.
Based on average prices in 2022, the following cost figures can be given for typical examples: 30x60 cm - 3900 rubles/m, 40x80 cm - 4800 rubles/m. The cost of work is on average 30-40% of the cost of materials. This article can be significantly shortened when making a foundation with your own hands.
When ordering the manufacture of turnkey strip foundations, you can give the following approximate prices:
- with a house size of 4x6 m - 130,000-150,000 rubles (cost of work - 50,000-65,000 rubles);
- with a size of 6x8 m - 165,000-190,000 rubles (work - 70,000-80,000 rubles);
- with a size of 6x10 m - 220,000-250,000 rubles (work - 90,000-110,000 rubles);
- with a size of 9x9 m - 245,000-280,000 rubles (work - 100,000-125,000 rubles).
The cost of the foundation depends significantly on the depth and structure of the soil. On excessively hard soil, special earth-moving equipment must be used.
Calculation of the foundation depth of a one-story house
Trench under the base
The foundation for a one-story house must be laid at a depth that is below the freezing level of the soil. The drawing must take into account this criterion and is made taking it into account.
The normalized freezing depth is determined based on data obtained over the last 10 years for a specific region. The observation results are compared with GOST 25100, and then the line of transition of plastic frozen soil into solid soil is determined.
If there is no access to such data or they are lost, then for regions with a freezing depth of up to 2.5 m it is permissible to perform the calculation using the formula:
where Mt is a dimensionless coefficient, which is determined by the sum of all absolute temperature values below zero, according to SNiP 23-01. If there is no information on temperatures in regulatory documents, then you must contact the hydrometeorological center to obtain them;
d0 is a value depending on the type of soil in the area. You can take it from SP 22.13330.2011.
If the freezing depth exceeds 2.5 m, then thermal calculations must be carried out in accordance with SP 25.13330. Calculation of seasonal soil freezing is carried out using the formula:
where kh is a dimensionless coefficient that takes into account the thermal regime for external and internal foundation structures based on information about the heating of the building. Determined according to Table 1 or taken equal to 1.1 for unheated premises (with the exception of the northern regions, where negative temperatures prevail throughout the year).
Table 1. The value of the kh coefficient depending on the design features of the building
The data in Table 1 is valid for those cases when the distance between the wall and the edge of the foundation is less than half a meter, and if it is exceeded, the coefficients should be increased by 0.1. If the temperature falls within the interval between the table values, then take the value with the lower value.
The depth of laying the external or internal foundation for heated rooms with cold basements or technical rooms should be determined based on Table 2.
Table 2. Foundation depth depending on the type of soil for houses with an unheated basement
Calculation of the foundation depth for a house made of blocks or bricks with a basement is carried out using the following formula:
where hs is the thickness of the soil above the base as viewed from the basement;
hcf – basement floor thickness;
γcf – value of the specific gravity of the basement floor structure.
Watch the video on how to make your own base scale.
An example of independent calculation of the width of a strip foundation
To better understand how to calculate the width of a monolithic tape, you need to consider this with an example. Initially, you need to systematize the initial data necessary for the calculation.
- size of the house in plan – 10 m x 10 m. Building area – 100 m 2;
- inside the house there is a load-bearing wall in the middle;
- the walls are brick, 1 brick thick - 250 mm and 2.7 m high. The specific gravity of the brickwork is 1600 kg/m 3;
- slate roofing – 40 kg/m2;
- flooring made of reinforced concrete slabs - 500 kg/m2;
- soil freezing depth – 700 mm;
- groundwater level – 2.2 m;
- soil base – dry loam of medium density with a design resistance of 2 kg/cm2;
- snow load – 50 kg/m2;
- payload – 20 kg/m2.
Determination of the total load from the house on a strip monolithic foundation
Based on the available initial data, the total load on the foundation is calculated. The dimensions of the monolithic tape are also determined. It is necessary for developers to make calculations in the following order:
Roof
The roof is made of slate and has a gable roof. Taking into account the slope of the roof and its overhangs, a coefficient of 1.1 is used. The load from the roof will be: 100 m 2 x 1.1 x 40 kg/m 2 = 4000 kg.
Brick walls
To determine the load from the walls, knowing their thickness, you need to calculate their length. The length of the walls along the perimeter will be: (10 x 4) – (0.25 x 4) = 39 m. The deduction of the double thickness of the brickwork is made because the axes of the house plan are drawn in the middle of the thickness of the walls. The length of the internal load-bearing wall will be 10 - 0.25 = 9.75 m. The total length of the load-bearing walls will be equal to 48.75 running meters.
The volume of brickwork will be: 48.75 x 0.25 x 2.7 = 32.9 m3. The total load from the brick walls is: 32.9 x 1600 = 52,670 kg.
Flooring made of reinforced concrete slabs
The one-story house has ceilings on two levels. This is the ceiling of the basement and the ceiling in the house. The floor area is: 100 x 2 = 200 m 2. Accordingly, the load from the floor slabs will be equal to: 200 m 2 x 500 kg/m 2 = 100,000 kg.
Snow load
To calculate the snow load, take the total roof area of the house - 100 x 1.1 = 110 m2. The snow load will be: 110 m 2 x 50 kg/m 2 = 5,500 kg.
Payload
The rate of this load is calculated based on the average weight of technical equipment, internal communications, room decoration, furniture and other things. The specific weight of the payload ranges from 18 to 22 kg/m2.
The payload is calculated on the basis of an average of 20 kg/m2. The weight will be: 100 m 2 x 20 kg/m 2 = 2000 kg.
In total, the total load on the foundation will be equal to: 4,000 + 52,670 + 100,000 +2,000 = 159,000 kg.
Calculation of the width of a monolithic tape
According to the above formula, the minimum area of the foundation base is determined:
(1.2 x 159,000 kg): 2 kg/cm 2 = 95,400 cm 2. That is, the minimum allowable area of the base of the house will be 10 m2.
The total supporting area of brick walls is determined by the product of the plan length of the load-bearing walls and their thickness: 48.75 m x 0.25 m = 12.18 m 2.
The result shows that the calculated support area is less than the minimum support area of the walls. Therefore, the width of the strip foundation should be equal to 250 mm + 100 mm = 350 mm.
Requirement for materials for the construction of a monolithic tape
Taking into account the thickness of soil freezing (0.7 m) and the depth of the groundwater level (2.2 m), the monolithic tape is made shallowly buried - 1 m.
To fill the formwork, concrete M 300 is used. The volume of need for concrete solution is equal to: 0.35 m x 1 m x 48.75 m = 17 m 3. . Taking into account unforeseen losses, the need for concrete will be 17.3 m 3.
The reinforcement frame consists of 4 longitudinal reinforcing bars of a periodic profile with a diameter of 12 mm. Since the transverse rods of the frame are made from the same rods, the total need for reinforcement will be: 50 m x 4 = 200 m.
From all of the above, we can conclude that it is quite possible for people who are more or less knowledgeable in the construction business to calculate the width, height and length of the strip foundation for their home.
Peculiarities
Advantages:
1. Increased load-bearing capacity. A monolithic slab creates a slight pressure on the ground due to the uniform distribution of the entire load, regardless of the thickness of the fill. An excellent option for a house made of timber, cellular concrete, even brick.
2. Spatial rigidity. This eliminates the possibility of subsidence in certain areas (for example, a tape) and the appearance of cracks in concrete, on walls or loose joints.
3. Versatility in application. A slab foundation is suitable for any soil, including those called problematic.
4. Simplified construction technology. The construction of a monolithic slab does not require extensive excavation work, which significantly saves time.
5. Possibility of high-quality insulation. Options - laying polystyrene foam under the base, introducing special additives into the solution.
6. Reduced concrete consumption. Although this is only true for cases of arranging a non-buried monolithic slab.
Flaws:
Many of them are relative, but they are worth noting.
1. Complexity of calculations. This concerns the thickness of the future slab. If we are talking about a building with a basement, then it is better to choose a different foundation option. Firstly, the cost of construction will increase sharply. Secondly, calculations for a monolithic slab will become significantly more complicated.
2. High costs. Here a lot depends on the specific scheme, but it is undeniable that with such construction savings are achieved on other materials. If the slab foundation is shallow and of small thickness, it can be impressive.
3. Labor intensity. The question is how well the construction work is organized. For example, using an “automixer” greatly simplifies the technology of pouring concrete mortar and saves time. The same applies to the accuracy of calculations of the thickness of a monolithic foundation.
4. Certain difficulties with individual projects. First of all, when implementing a scheme with a basement and during construction on relief soil.
Calculation of slab thickness
It is appropriate to provide only general instructions and recommendations, since much depends on the specifics of construction - the characteristics of the soil, the number of storeys of the house, the materials from which it is built, and a number of other nuances.
Initial data for calculating the thickness of the foundation:
- Soil type.
- Configuration of underground aquifers.
- Soil freezing level.
- The presence of a drainage system on the site and its layout (if installed).
- Total load on the foundation.
What is determined:
1. Thickness of concrete reinforcement elements (rod, mesh).
2. The size of the reinforcement cells and the interval between its layers in the monolith.
3. The distance of the rod from the upper and lower cut of the foundation.
The difference in this foundation parameter for buildings of the same type can be significant. For example, the thickness of a slab for a wooden house varies quite widely and depends precisely on the characteristics of the soil, although it is a relatively light structure of 1-2 floors.
*Dimensions – in “mm”.
- The cross-section of the rod is 12.
- 2 levels of reinforcement, the interval between which is 70.
- The distance between the reinforcement and the sections of the concrete monolith is 50.
Calculation: 12 x 2 + 70 + 50 x 2 = 194.
Rounded - 20 cm. For example, this is the minimum thickness of a slab for a house made of aerated concrete. But subject to the construction of a shallow monolithic foundation on good, dense soil. That is why it is advisable to entrust all calculations to a professional.
The final stage of installation
After pouring the concrete strip into the foundation for the house, the formwork is removed after ten days. However, complete hardening occurs on the 30th day. Only after this they begin the next work.
Waterproofing
The monolithic slab has the ability to absorb water well. Therefore, in order to protect the foundation of the house, the slab is waterproofed. Before starting such work, it is necessary to assess how close groundwater passes to the soil surface and ensure that a drainage layer is installed underground. This will prevent premature destruction of the slab.
Waterproofing is carried out in different ways:
- Coating - in this case they use bitumen mastics, which are applied with a brush or roller. You can do this simple work yourself. However, due to the fact that the material must be applied twice, the foundation coating will take a long time. In addition, the mastic is short-lived: after ten years it will need to be re-treated.
- Roll - covering with rolls of roofing material, waterproofing using adhesive bitumen mastic or a melt gas burner. This insulation is used to protect the lower part of the tape from groundwater. The base is insulated from above in this way when brick walls are laid.
- Sprayed - applied using liquid rubber with preliminary cleaning of dirt and dust and priming of surfaces.
- Special plaster with hydrophobic components. The mesh is first secured to the surface with dowels.
- Penetrating waterproofing is a special cement-based solution that penetrates into the concrete and makes it waterproof.
- Shielding - using bentonite panels that are nailed to the foundation walls.
The most optimal solution is penetrating waterproofing. Its components increase the strength of the monolithic foundation strip.
Insulation
The unprotected base of the building is subject to cooling in winter. At the same time, the soil begins to freeze, which means additional costs for heating the house. The presence of insulation on the outside allows you to save 25% of heat.
Insulation materials used for the foundation of a brick house:
- Polystyrene foam – in the form of sheets. It is worth using such material with a thickness of at least 5 cm. Advantages: The low weight of the material simplifies the work.
- Does not absorb moisture.
- Keeps you warm.
- Not susceptible to fungus or mold.
- Extruded polystyrene foam or EPS. EPS and polystyrene foam are made from the same raw materials, but undergo different processing. The first one is heated strongly, which improves the characteristics of the material.
- Polyurethane foam or PPU is a liquid material, applied by spray. Features: Thanks to its consistency, it penetrates into cracks.
- Easily lays on the surface.
- Resistant to temperature changes.
- Not exposed to fungus and mold.
- Expanded clay – absorbs moisture well. Popular because of its low price and environmental friendliness.
- Mastics are liquid materials. Used as a basis for laying other materials.
The simplest and most reliable material is polystyrene foam. With this material it is easy to insulate the foundation from the outside yourself. The materials you will need are: primer, plaster, glue, mesh and dowels.
Having understood the technology and all the nuances of foundation installation, correctly calculated the required materials and carried out the work correctly, the owner of the house will receive a reliable structure that will last a very long time.
How to calculate everything correctly
The formula for calculating the base area is as follows: S>γn F/γc R0, where
- γn—reliability factor equal to 1.2.
- F is the load on the base, i.e. the total weight of the house, foundation, snow load, weight of property, people, etc., affecting the underlying soil layers.
- γc is the operating conditions coefficient. Depending on the type of soil, it ranges from 1 (clay) to 1.4 (sand).
- R0 is the conditional soil resistance. The tabular value is in the SNiP annexes for this type of soil.
As a result of this calculation, the total area of the tape will be obtained. To determine the base width (average), the resulting value S must be divided by the total length of the tape, including internal walls and other areas of the perimeter. The resulting value will show the estimated thickness of the tape base.
This value is the minimum. In practice, it is increased, sometimes several times.
It should be noted that the given formula is given only to familiarize yourself with the calculation methodology. In any case, this work must be performed by a competent and experienced specialist. Calculating the foundation is an important and responsible procedure, which has a large number of difficulties and specific issues.
An unprepared person cannot calculate such a project without making a number of gross mistakes, which could result in the destruction of the house. Alternatively, you can use an online calculator, which allows you to obtain the parameters of the tape using known data (soil type, calculated or tabulated resistance values, etc.).
To clarify the data obtained, you should double-check the results obtained on other similar resources.
Common mistakes and ways to avoid them
Laying a sand cushion without compaction. This leads to uneven subsidence of the pillars and deformation of the strip part. It is necessary to compact the soil under the pillow and the pillow itself.- Unevenness of the trench bottom is allowed. As a result, the thickness of the concrete pour is uneven and it dries unevenly. To avoid this, you should use construction laser levels when laying a trench.
- Dig trenches and leave them for several days . As a result, the earth crumbles from the walls and creates differences at the bottom. You need to dig and fill the holes in one day.
Features of a columnar strip foundation
Such a foundation is an attempt to combine the advantages of column and strip foundations in one design and eliminate their disadvantages as much as possible. I must say that this is a very successful experiment because it brings a number of advantages to this type of fund:
- Significant reduction in the volume of earthworks.
- Possibility of construction on medium and strongly curved soils, including peat soils.
- There is no need to make sandstone or sand cushions for the entire foundation.
- No drainage system required.
- Reduces consumption of concrete, reinforcement and working time.
- Heat losses are reduced and vibration insulation of the building is improved.
Pillars
The main problem in our climate is the large difference between summer and winter temperatures, when the freezing of water in the ground in winter leads to high loads on the floor of the building.
One way to protect the foundation is to bury it deeper than the freezing level of the soil at the construction site. For example, for the Moscow region, depending on the type of soil, this value averages 1.4 meters.
If piles are used, then only they are installed at this depth. Also evaluate the difference in the intensity of work and the number of cubic meters of land that you extracted yourself.
Strip foundation
The strip foundation (crane) in this design serves as a load-bearing element that absorbs and distributes the load from the walls.
As a rule, it does not come into contact with the ground, as it is located at a distance of 10-20 cm. If the belt is installed in the floor, for example if a flatter device has been chosen, it should be taken into account that it is also affected by the load from the floor due to temperature fluctuations .
To ensure that the belt does not pull away from the posts, it is necessary to provide such a design if it can also move during vertical movements, i.e. when working as a piston. The rods should be smooth without expansion at the bottom.
Materials
The supports can be made from a variety of materials, from round wood to reinforced concrete. The shape is also round, square, hollow and polygonal.
If this is an independent building with minimal external attraction of forces and mechanisms, then a round concrete pillar is optimal.
Video description
When and how to make a sand cushion under the foundation, see the following video:
It is important! It is strongly recommended to place the foundation pad not only directly under the foundation structure itself, but also beyond the projection area of its base.
- Combined method . This option combines insulation of the foundation, installation of sand bedding and installation of a drainage system. To artificially reduce the depth of foundation laying, this technique is the most effective. The following figure illustrates the scheme of such a combination of techniques.
Scheme for insulating a strip foundation using an additional sand cushion Source readmehouse.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in the calculation, installation and repair of turnkey foundations.
Depth of slab foundation
Due to the fact that it is prohibited to fill monolithic structures on the arable layer, the black soil is removed from the pit entirely. The depth of the layer is usually 40 cm, which is covered with non-metallic material that does not contain clay. Features of the shallow slab technology are as follows:
The maximum construction budget is observed for a slab buried below the freezing mark. This option is justified exclusively for buildings with a basement. The outer perimeter of the underground walls will have to be completely insulated, the cavities will have to be filled with non-metallic material, having previously laid wall or ring drainage.
Attention: Taking into account the removal of the fertile layer and its replacement with non-metallic material, a foundation 30 - 40 cm thick is buried into the ground by 10 - 20 cm maximum. Therefore, you will need either a brick base or monolithic beams under the load-bearing walls, which perform the same function of increasing the distance between the ground and wall materials.
Pile type devices.
The use of a pile or pillar structure is most suitable for soil with a fragile or excessively heaving surface.
The columnar foundation design, which includes wide support soles with a drilling device, is very popular.
Such a foundation has one main drawback - its construction requires the use of specialized equipment. The design is well suited for the construction of one-story buildings and all kinds of extensions.
When building a foundation for a brick house with your own hands, which has a pile structure. The following instructions must be followed:
- First, you should clean and mark the area. Check the compliance of the base angles with the specified values;
- Determine the places where the supports will be located;
- Remove soil from the marked areas;
- Drill wells;
- Carry out the manufacture of a frame from reinforcement. Its height should exceed the ground level by 30 cm;
- Pour the sand and gravel mixture into the well recesses;
- Install the frame into the holes for the wells and fill it with concrete mortar.
It will take 4 weeks for the base to harden. When pouring a base of piles, the use of formwork will be required. The material can be simple boards or plywood covering.
Calculation of the amount of concrete, wire and reinforcement
Having decided on the size of the foundation, we need to calculate how much reinforcement, wire and concrete we will need.
With the last one everything is simple. The volume of concrete is equal to the volume of the foundation, which we already found when we calculated the load on the ground.
But what metal to use for reinforcement has not yet been decided. It all depends on the type of base.
Reinforcement in strip base
For this type of foundation, only two reinforcement belts and reinforcement up to 12 mm thick are used.
Horizontal longitudinal reinforcement bars are subject to greater loads than vertical or transverse ones. Therefore, ribbed reinforcement is placed horizontally, and smooth reinforcement is placed vertically.
The length of the ribbed reinforcement can be easily calculated by multiplying the total length of the base by the number of rows of rods. If the foundation is narrow (40 cm), two longitudinal rods for each belt are sufficient. Otherwise, the amount of reinforcement in the belt will have to be increased.
Transverse rods are installed every 0.5 m, retreating 5-10 cm from the edge of the foundation. We determine the number of connections by dividing the entire length of the foundation by 0.5 (the step between intersections) and adding 1.
To find the length of smooth reinforcement required for one intersection, we use the formula:
(ShF - 2*ot)*2 + (VF - 2*ot)*P, where ShF and VF are the width and height of the foundation, from is the offset from the edge of the foundation, P is the number of rows of reinforcement in the belt.
the amount of smooth reinforcement required for the foundation
The cost of binding wire for the foundation is the product of the wire consumption for one bundle (30 cm), the number of bundles at one intersection (equal to the number of rows of reinforcement multiplied by 4) and the number of connections.
Reinforcement in slab foundation
For a slab base, ribbed reinforcement with a thickness of 10 mm or more is used, laying it in a grid, in increments of 20 cm.
That is, for two reinforcement belts you will need:
2*(ShF*(DF/0.2+1) + DF*(SF/0.2+1)) m reinforcement, where ShF is the width, DF is the length of the foundation.
connect the intersection of the upper grid with the corresponding intersection of the lower one
Taking into account the thickness of the slab and the distance of the frame from the surface of the slab, we determine the amount of reinforcement required to connect the belts using the formula:
((DF/0.2+1)*(SF/0.2+1))*(TP-2*from), where TP is the thickness of the slab, from is the distance from the surface.
how much reinforcement is needed for a slab foundation
The length of the knitting wire is calculated based on the formula:
(DF/0.2+1)*(SF/0.2+1)*4*0.3
Materials used
When constructing a strip foundation, the main material is concrete , which, in fact, is what the foundation itself consists of.
Strength characteristics and resistance to operational influences depend on concrete. In order for the concrete base to be durable, it must correspond to a grade of at least M300. For self-production, a mixture of cement, sand and crushed stone is used in a ratio of 1:3:5.
For a prefabricated strip foundation, reinforced concrete slabs FL 12.12 or FL14.12, as well as FBS blocks measuring 0.8-2.5 m can be used.
Concrete must be reinforced with steel rods . According to the specifications for the project, the frame is based on corrugated steel reinforcement of class AIII (A500) with a diameter of 12 to 16 mm. For vertical linking, smooth reinforcement with a diameter of 10-12 mm is used. The frame is tied together with steel binding wire.
An important element is the cushion under the concrete tape. It is made from layers of sand and crushed stone or gravel of the middle fraction. For waterproofing, bitumen or bitumen mastic, roofing felt, and thick polyethylene film are used.
Insulation can be provided by bulk, tile, sheet or roll thermal insulation materials. The most commonly used are expanded clay, expanded polystyrene (foam), polyurethane foam, mineral wool, glass wool.
In addition to the main materials, the consumption of auxiliary materials should be taken into account . To install the formwork, you will need an edged board with a width of at least 20 cm and a thickness of at least 15 mm. You can use plywood, plastic or metal sheets. To strengthen the formwork you need timber.