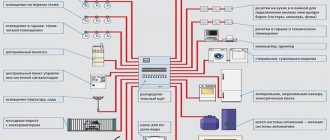
To properly organize the supply of electricity during construction or renovation, you need to know which wire to use for wiring in the house. It is better to entrust the installation of the power supply network to a specialist, but you can purchase materials yourself. To do this, you need to remember the basic rules for choosing a cable correctly.
What are electrical cables made of?
The main conductor of electric current is aluminum or copper conductors. The larger their diameter, the higher the cable's capabilities.
Aluminum wires are cheaper, but they are more likely to deteriorate and have a lower electrical conductivity coefficient.
Copper cable is durable, does not break at bends and is capable of carrying more current than aluminum cable with the same diameter.
It is recommended that all wiring in the house be of the same type. This is due to the fact that to connect products from different materials, a special adapter will be required so as not to create a galvanic couple. In this case, oxidation and destruction of the wires occurs, which can lead to a short circuit.
The main cores are covered in braids made of rubber, polyethylene or PVC. Often several of these insulated conductors are combined into a bundle, which in turn is covered with a protective sheath.
Cable core: what should it be like?
The main element in the design of a cable is its metal core or conductor through which current flows. Cable cores can be single-wire or multi-wire, that is, they can contain several thin wires twisted into a bundle. The more wires a cable core has, and the thinner they are, the more flexible the cable itself will be.
In most cases, a cable with a single wire core is used for fixed hidden wiring. But cables with multi-wire conductors are allowed for laying electrical wiring in an apartment only in an open way, since they do not have properties that satisfy modern fire safety requirements for a hidden type of installation.
For example, cable VVGng-LS or ng-LS. The four letters at the end mean: ng-LS – flame retardant with low smoke and gas emissions; ng-HF - do not propagate combustion and do not emit corrosive gaseous products during combustion and smoldering - halogens. Let's say this cable is laid under a suspended ceiling. If, purely hypothetically, a short circuit (short circuit) or severe overload of the cable occurs, no protection works, and this cable catches fire, then due to these properties it will simply smolder smokelessly until it burns out completely and the contact/short circuit is lost. PVA cable, in principle, in its insulation does not have such properties, and if it catches fire under the ceiling under the same circumstances, it will smoke heavily, emitting poisons, and since it is hidden, there is no way to extinguish it without getting poisoned.
These two types of cable will have almost the same technical characteristics. However, a stranded cable has a higher price and some installation features: it is necessary to solder the ends of the contacts or install cable lugs at the connection point.
Also, when selecting the required cable, it is important to take into account the number of cores themselves. It is best to use a multi-core cable, since to supply power to consumers you will need at least two wires: one for phase and one for neutral. If the house has a three-phase consumer, then you will need three phase and one zero. In addition, modern electrical installation rules dictate the presence of an additional grounding wire in single-phase and three-phase networks.
Note!
Modern electrical safety rules require grounding the load and, accordingly, installing special sockets for it, therefore, for single-phase wiring it is necessary to use a three-core cable, and for three-phase wiring, a five-core cable. That is, the cable, in addition to the phase conductor(s), must have a neutral and grounding.
Types of wiring
The choice of the required wire depends on the type of installation, because The installation method affects the requirements.
Open
Open cabling is the laying of cables directly along building structures. It is produced where there is no possibility or need to hide wiring in the wall or ceiling.
Since an openly laid cable is not protected by anything, it is necessary to protect it from mechanical damage. In addition, for safety reasons, it is recommended to use a wire with a core cross-section of at least 4 mm².
Hidden
To install hidden wiring, a groove is punched in the wall in which the cable is laid, and then it is sealed and covered with plaster. With this method of power supply, less stringent requirements are imposed on the wire, because it is isolated both from external influences and from the effects of overheating.
The requirements for the home electrical network are regulated by the PUE clause 7.1.34.
Selection of conductor cross-section by power and length
The length of the conductor determines the voltage supplied to the end point. A situation may arise when the voltage at the point of consumption is insufficient to operate electrical appliances.
In household electrical communications, these losses are neglected and a cable is used ten to fifteen centimeters longer than necessary. This surplus is spent on switching. When connected to a distribution board, the reserve is increased, taking into account the need to connect circuit breakers.
Cable laid in a closed way Source kadetbrand.ru
When laying long lines, one should take into account the inevitable voltage drop. Everyone has their own resistance, which is influenced by three main factors:
- Length measured in meters. As this indicator increases, losses increase.
- Cross section, measured in square millimeters. If this parameter is increased, the voltage drop decreases.
- The resistance of the conductor material, the value of which is taken from the reference data. They show the reference resistance of a wire with a cross-section of one millimeter and a length of one meter.
The product of resistance and current numerically represents the voltage drop. This value should not exceed five percent. If it exceeds this figure, then it is necessary to take a conductor with a larger cross-section.
Difference between cable and wire
The wire is a lightweight structure consisting of 1-3 insulated cores. It is less secure than cable and has a simpler internal structure.
A cable is a wire of a more complex structure. In addition to several cores separated from each other, it has a double layer of insulation, a gasket, a screen and is recommended for use in residential areas.
Rules for choosing a cable for wiring in the house
The selected cable must comply with the following rules:
- Ensure the required level of electrical and fire safety.
- Provide the ability to simultaneously turn on several household appliances and lighting.
- Allow quick and convenient installation.
Initially, the rules of the PUE, clause 7.1.34, allowed the use of only cables with copper conductors in residential premises, except for houses whose construction began before 2001. However, later these requirements were excluded.
However, when choosing home electrical wiring, you must remember that to combine aluminum and copper conductors, you need special adapter clamps that prevent contact of dissimilar metals.
When choosing means for home electrical wiring, it is necessary to determine the material of the cores and their cross-section. When purchasing, first of all, check the labeling and availability of certificates. The quality of the cable products offered does not always meet the standards, so it is better to purchase them from reputable manufacturers.
Marking
The wires are marked on the braid. The letter designation is followed by a series of numbers.
If the cable brand begins with the letter A (for example, AVVG), then its cores are made of aluminum. Otherwise, the conductors are copper. The following letters indicate the material from which the outer and inner braids are made:
- B (Вр) - polyvinyl chloride;
- P (Ps) - polyethylene;
- C - lead.
The numbers indicate the number of cores and the cross-sectional area of each of them.
For example, the name of the most common cable for internal wiring VVG-0.66 kV 3x1.5 means the presence of 3 cores with a cross-section of 1.5 mm² each, enclosed in a polyvinyl chloride sheath, with the same external insulation.
The designation 0.66 kV indicates that the product is used in networks up to 660 V.
If the marking has the letters “ozh”, the conductors are single-wire, i.e. whole.
Section calculation
To determine the required wire cross-section, you should estimate the maximum load of the electrical network. This can be done by knowing the power consumption of the connected devices. It is indicated in the instructions, passports or on the housing of the devices themselves.
Pivot table
There are tables that allow you to determine the required cross-section using several parameters at once - current, power, conductor material, and so on. They are more convenient to use and one of them is located below. It indicates the cross-section of the wire in terms of current and power, and also takes into account the installation method.
Wire cross-section by current and power - table for copper and aluminum conductors Source tvz2.ru
Cables for underground input
To supply electricity to a detached house, a cable is often laid by digging a trench in the ground. The following must be taken into account:
- The cross-section of the conductors must provide a general house load for both devices plugged into sockets and for lighting. The thickness of the cores in this case is at least 6 mm².
- For underground input, you need a shielded cable, which is designed for installation in a trench. Otherwise, use a metal pipe (corrugation) of the PND type.
- When calculating the depth of the trench, soil freezing must be taken into account.
- Sometimes rodents damage wiring.
Cable laid over the air
Often, to organize power supply in outbuildings, sheds, garages, and local areas, the cable is pulled through the air. If the wiring distance is more than 25 m, install additional support.
When laying a cable through the air, it is important to protect it from external influences: ultraviolet radiation, temperature changes, and precipitation. These factors negatively affect the most commonly used PVC braid, causing it to crack. To extend the service life of the cable when laid overhead, it is enclosed in a corrugated metal or polyethylene pipe.
Which wire is better to choose for wiring in a private house?
Taking into account modern loads on the electrical network due to the inclusion of powerful household appliances, it is recommended to use a multi-core copper cable when installing or replacing wiring.
For sockets, VVG 3x2.5 is most often used. Even when all household devices are turned on simultaneously, it can withstand a load of 27 A with a power of 5.9 kW.
Lighting requires less energy consumption, so electric current is supplied to the switches using VVG 3x1.5.
A wooden house must have an increased level of fire safety. According to the rules of the PUE, in this case the cable is laid in metal pipes. It is unacceptable to use a plastic box.
terms of Use
Manufacturers set certain conditions under which the VVG cable can be laid and operated.
- Installation and installation can be carried out at a temperature not lower than -15C.
- Operation within the range from -50C to +50C.
- In unusual situations, the temperature can rise to +70C. And in case of emergency (short-term) up to +80C.
- Humidity – up to 98%.
- The bending radius is at least 7.5 times the diameter of the cable itself.
- Service life (guaranteed) – up to 30 years. Practice shows that this period, with proper operation, can be twice as long.
- Installation can be carried out by air. But if the installation altitude is higher than 4300 m above sea level, then special overpasses will have to be used for installation.
- In industrial premises where there is high corrosive activity, installation must be carried out in special boxes.
Which wires are not suitable?
PVA wire cannot be used in residential premises, despite its low cost, for the following reasons:
- Its conductors are multi-wire, so when connecting the segments you will have to tin and solder each conductor. Because of this, installation takes a long time.
- Multiple wires cannot be laid in the same groove, unlike other cables. Each line will have to be grooved separately.
Products branded PVVP and ShVVP also cannot cope with modern loads. For apartment wiring, the PUNP cable is outdated.
Useful tips
Tips for purchasing electrical cables:
- Carefully inspect the appearance of the cable. Even small bends, dents, or scratches can cause wiring to malfunction.
- The lack of packaging and its poor appearance may indicate poor quality storage of the cable. It is better to refuse such a purchase.
- In order to save money, the lighting can be made with aluminum wires, and a cable with copper conductors can be connected to the sockets.
- To reduce the reserve cross-sectional area to 30%, it is recommended to leave terminals in the apartment panel for connecting additional lines if necessary (for example, purchasing energy-intensive equipment).
The costs of properly installing the electrical network are fully compensated by the durability and reliability of the wiring.
KG
Cable with general rubber insulation and rubber insulation of each core. The wires are copper, high flexibility, there are from 1 to 6 wires inside. Maximum voltage – 660 V, frequency – 400 Hz. The cable is expensive, so many people prefer VVG. The KG is well suited for connecting very powerful equipment, such as welding machines, generators and other portable devices. Modification – KGng.
SIP
This is a separate category of power cables. SIP is a self-supporting insulated wire, the cores are made only of aluminum, there is no belt insulating layer. Possible core cross-section is from 16 to 150 sq. mm. The markings for this type of cable are specific. So, for example, SIP-1 is a cable with three cores, one of which is neutral and at the same time load-bearing.
The cable insulation is made of cross-linked polyethylene, so it can withstand severe mechanical stress, exposure to sunlight and high humidity. SIP is excellent for ground-based electrification of private houses. Installation must be carried out using special fittings.
TsASBp
Aluminum cores, one or more wires. The cable features paper insulation and a lead alloy sheath and can withstand up to 10 kV. Can be used on sloping areas.
APvPu
Cable with aluminum cores and cross-linked polyethylene sheath, suitable for installation in damp soil.