Ventilation is an integral attribute of a modern private home. Fresh air has a positive effect on health and mental activity, gives the body vigor and energy. The cleanliness of country air in itself encourages the organization of a system for regulating the microclimate in the house.
Ventilation in a wooden house is designed to solve the same problems as in any other room - the removal of air supersaturated with carbon dioxide, the flow of oxygen, and ensuring a comfortable temperature and humidity regime. However, the process itself is affected by the characteristics of the material from which the building is constructed.
Content:
- How ventilation works
- Attic ventilation
- Natural air exchange
- Exhaust ventilation type
- Roof of a wooden house and ventilation features
- Air exchange in the bathroom
- Ventilation of a wooden house toilet
- Ventilation of the floor of a wooden house
- Walls of a wooden house and metabolic processes
- Modern house: ventilation scheme
- Natural ventilation: positive and negative sides
- Air exchange in the house
- Ventilation system: stages of creation
- Supply system: installation features
- Supply and exhaust air exchange system
- Video on ventilation in a wooden house
A wooden house in itself is already a dream. Its owners live in an environmentally flawless home. To make life even better, you need to take care of proper ventilation of all rooms in the house. A wooden house feels moisture more than a stone one. Ventilation in a wooden house is an important factor in the health of the people living in it and the durability of the structure. There are factors that contribute to the destruction of wood without proper ventilation:
- fungus;
- mold;
- humidity.
The hackneyed saying “wood breathes” should not be taken into account when deciding on the installation of a hood in a wooden house.
For closed combustion chambers
Modern houses made of laminated veneer lumber
The coaxial chimney looks like a pipe inside a pipe. The structure is delivered ready-made and can be assembled quickly and without problems. It is enough to know the outlet diameter and parameters - height, length.
The simplest is the coaxial chimney system. The pipe rises above the boiler and rotates 90°. There should be at least 20 cm from it to the ceiling. Then it is inserted through a hole in the wall, from the outside it should end at a distance of at least 30 cm from the wall.
The height from the ground level is also adjustable - the pipe outlet should not be lower than 20 cm from the ground, and the distance from the nearest wall - from the end of the pipe to the wall should be at least 60 cm.
How ventilation works
The air in a wooden house is special, but not because wood ventilates it, but because the material is natural and releases trace elements that create a natural smell. Wood can only absorb or release moisture. The microclimate is maintained only by the ventilation system.
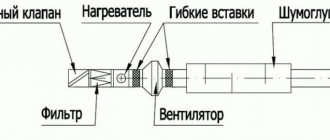
The ventilation device in its classic form involves its placement in the attic. The riser, floors, ceiling are the location of hidden air routes (air is supplied and taken in through them). Distribution boxes are responsible for supplying and removing air. The inside is lined with a material that insulates noise.
The ventilation unit itself has a removable panel for easy filter replacement. Silencers are installed near it. A passage is made in the load-bearing wall to install the outlet. Its tasks include taking air from the street for further supply to the premises of the house.
Silencers are connected to the ventilation unit. A passage is made in the roof and a fungus is installed with a pipe connected to it, which removes air from the installation. Air ducts (corrugated plastic pipes) are connected to the ceiling boxes. The flexible air duct is connected to the air intake and air outlet sockets. Valves and ventilation grilles are installed on the outside of the walls and commissioning work is carried out.
Fighting condensation
If there is a large temperature difference between inside and outside, exhaust air can condense on the pipe and flow down. To minimize condensation, the ducts are thermally insulated and placed in a common duct with the pipes of the heating boiler, stove or fireplace. Thermal insulation increases drafts.
Another way to combat condensation is to install a steam trap. Older ventilation systems used an “otter” seal to cool warm air before venting outside.
Pipes that are in the field of view are masked in the following ways:
- hidden behind suspended and suspended ceilings;
- placed in decorative boxes;
- built into furniture;
- Order a custom tube design.
Recently, systems consisting of a large number of small cross-section air ducts have become popular, in contrast to traditional mainline transport. They are connected to one large supply and exhaust device, located in the utility room and connected to the collector.
Attic ventilation
Ventilation in a wooden house with an attic floor has its own characteristics. An attic is a residential attic space that is located above the main living spaces. Properly installed ventilation prevents the harmful effects of condensation on the roof structure. Proper air exchange in the attic prevents overheating of the attic in the summer and the formation of ice in the winter (and as a result, corrosion of the metal elements of the roof, wetting of the insulation, the appearance of moisture and mold).
Operating principle of a household recuperator
Most likely, any person will be interested in how heat is transferred from the outgoing flow to the incoming one. Let's consider the operating principle of a household recuperator. This is a small cassette installed in an air duct, the design of which is similar to a radiator and has a large area; this is the heart of the device - the heat exchanger. Passing through it, warm air gives up its heat to the heat exchanger. It heats up and transfers the resulting heat to the incoming flow.
To regulate heating, some devices have an incoming air heater installed. The heating is regulated by the user. If the device is not equipped with a heating element, the temperature of the supplied air is regulated by heating batteries.
Natural air exchange
Do-it-yourself hood in a wooden house is a labor-intensive process and requires certain knowledge. There are several types of ventilation. One of them is natural. Air is supposed to enter the home through cracks in window and door systems. For effective air outflow, care should be taken to ensure that the outflow tract is taken care of. For this purpose, air ducts are installed. Modern construction technologies greatly complicate the process of natural air entering the room. To create conditions for free circulation of air flows in the rooms of the house, holes are made in the door leaf (decorated with grilles). Strong exhaust is ensured by the large length of the air duct.
How not to make a mistake
The range of household heat exchangers is quite large and, although any such device is designed to perform one task - room ventilation, each device has its own differences, advantages, disadvantages, and each of them occupies its own niche, performing some task better than anyone else.
In order not to receive additional education in the field of domestic ventilation, the most effective solution is to contact the Fresh Air company, where experienced specialists will select the optimal equipment to perform the assigned tasks with an optimal quality-functionality-price ratio.
Exhaust ventilation type
The positive answer to the question of whether ventilation is needed in a wooden house is based on many years of experience in the construction and operation of private households. The organization of air flow is the basis of the principles of exhaust ventilation. Air intake must be ensured unobstructed. Natural supply ventilation supplies the house with air from the street. Main advantages:
- efficiency;
- simplicity of the ventilation system design;
- availability.
Exhaust ventilation in a private wooden house is provided for at the design stage. It is a central main line with branches that are designed to ensure the outflow of air from all rooms of the house. To increase operating efficiency, exhaust ventilation is equipped with fans mounted at the entrances of the ventilation ducts. The power of fans varies, so it is selected based on the volume of the room. The fans are economical; there are models with automatic operating modes.
Installing a window inlet valve
Window valves are mounted on the sash; it is quite easy to install this type of supply ventilation yourself in a private house. You will need the following tool:
- screwdriver;
- sharp knife;
- ruler no shorter than 35 cm.
window valve installation procedure
Work progress:
- We cut out the standard seal from the fixed frame in the place where the valve is intended to be installed.
- We install the seal that comes with the valve.
- We mark the location of the valve on the flap; it should coincide with the replaced area.
- We remove the seal section on the flap as well.
- We install valve plugs into the resulting gap. They must fit entirely into the slot so that the valve can subsequently be attached to them.
- The valve is glued to the double-sided tape and secured to the fasteners with self-tapping screws.
- A seal is inserted between the fasteners.
Now you can check the valve in action. The window inlet valve has several advantages:
- easy to install;
- during installation, all enclosing structures remain intact and intact;
- you can regulate the intensity of the inflow or completely block it.
And there is only one drawback: in severe frosts it can freeze. But there are branded models that do not have this drawback. You will have to pay more for them.
Another model of window valve is the handle valve. A very convenient device, the installation of which will have to be entrusted to a specialist.
Roof of a wooden house and ventilation features
One of the main problems that arise when operating a house is the so-called “dew point”. Natural cooling of the air heated in the house leads to condensation in attic structures, which causes gradual destruction of structures. To ventilate gable roofs, they resort to arranging natural ventilation by making holes. This system is not suitable for flat roofs. Supply ventilation can solve the problem. This type of ventilation involves mechanical air injection. A heater is required for the cold season. The air in the room should enter at a temperature of 18 degrees Celsius, and a filter should be installed to prevent dust from entering. The system is controlled automatically to prevent overheating.
Equipment for installing a ventilation system
For the installation of ventilation air ducts, various types of pipes are used - asbestos-cement, plastic or galvanized metal - square, less often round.
Option #1 – asbestos-cement structures
Asbestos-cement pipes are resistant to corrosion, withstand frost and moisture well, and have a long service life. Such pipes are of sufficient length to allow installation of the air duct without welding.
Asbestos cement pipes have many advantages, but care must be taken when transporting and installing them, as they are fragile and can break.
Option #2 – galvanized metal pipes
Galvanized pipes are light in weight and relatively low cost, they are resistant to corrosion and easy to install.
Galvanizing is suitable for wet areas where it will serve reliably and for a long time under suitable operating conditions, but if these are not maintained the zinc coating may become damaged.
Pipes made of galvanized steel are quite often used as an air duct when organizing a ventilation system with your own hands. Their main advantage is light weight and ease of installation.
Option #3 - plastic pipes
Most often, plastic pipes are used to organize ventilation. The smooth inner surface ensures good air flow.
Plastic air ducts do not require cleaning and do not rust, their service life is more than twenty years, and their price is noticeably lower than pipes made from other materials.
The main disadvantage of plastic structures is the high flammability of the material, so they cannot be installed in rooms where the temperature may rise to extreme levels.
Air exchange in the bathroom
Ventilation in the bathroom of a wooden house is designed to get rid of excess moisture (as a result - mold, rotting wood structures, rusting of metal structures). Proper ventilation will ensure:
- comfortable temperature conditions;
- normal humidity;
- influx of fresh air.
Ventilation can be made natural or forced. The second option is much more effective. The costs of electromechanical means of air injection will be recouped by the durability of the structure. The fan check valve solves the problem of the spread of unpleasant odors. Ventilation in a wooden house in the bathroom provides the owners with comfort and health safety, as well as extending the life of the bathroom and the house as a whole.
Other premises
A private home is every person’s dream. Many people strive to have their own corner. The kitchen of a private home is the place where the housewife spends most of her free time. She prepares various dishes there to please all family members. Often, when preparing food, various unpleasant odors arise that spread throughout the apartment, where other family members may be present. Ventilation is also necessary in the toilet of a private house.
Kitchen ventilation in a private house
Kitchen ventilation in a private house
Due to increased air humidity and heat in the kitchen, a person may develop various diseases. To eliminate such inconveniences, it is worth installing a ventilation system.
In principle, the system is quite simple. Natural ventilation can be used to create air circulation. It is worth opening windows and doors from time to time. Most houses in the private sector are wooden. In them, natural ventilation is created by creating artificial openings in walls and windows. This will be enough to create air flow.
Hood
Kitchen hood
The hood can be made of various materials. Aluminum is the most popular in this regard. You can install the hood yourself or seek help from specialists. To organize air exhaust, a fan is installed in the hood, which draws out all foreign odors from the kitchen.
Fans operating from a 220-volt network are mainly used for ventilation. It is quite possible to install one in a hood yourself. The main thing is to follow basic safety rules.
Ventilation in a private house in the bathroom
Ventilation in the bathroom
It is worth paying attention to the fact that checking and installing ventilation should be carried out before starting any repair work. Installation of grilles and radial fan - upon completion. Ventilation in the bathroom must ensure air exchange not lower than all SNiP standards
In addition, the ventilation should have a simple design for further maintenance, as well as a low noise level. It is imperative to monitor the quality of work performed. You can monitor this yourself, or you can entrust this matter to the designers who were involved in the development of the project. In this case, you don’t have to worry about the quality of workmanship.
Ventilation in the bathroom must ensure air exchange not lower than all SNiP standards. In addition, the ventilation should have a simple design for further maintenance, as well as a low noise level. It is imperative to monitor the quality of work performed. You can monitor this yourself, or you can entrust this matter to the designers who were involved in the development of the project. In this case, you don’t have to worry about the quality of performance.
Ventilation ducts
Ventilation ducts
If the ventilation duct is not located directly behind the wall, but across two or three rooms, then ventilation in the bathroom cannot be organized using such a simple method. In this situation, it is necessary to install a ventilation duct into the room. Here we are talking about ventilation ducts. There are several types of ventilation ducts:
1. Plastic box. It can have either a rectangular or circular cross-section. It conducts noise poorly, and the resistance to air flow is minimal, which is what is required in this situation. Special fasteners are used for installation.
2. Corrugated box. There can be two types - soft and hard. A product of this type is best used at short distances, as well as in difficult places for ventilation supply.
Ventilation of a wooden house toilet
Ventilation in the bathroom is an important part of ensuring comfortable living. The toilet will need to be artificially ventilated. The fan should enhance the system's performance. It is integrated into the overall ventilation system and enhances air exchange. Modern control systems (sensors) will allow you to control the operating mode of air exchange. The fumes are removed by a network of ventilation ducts. One fan installed in the attic can be common to the entire ventilation system. The following precautions must be taken into account:
- Only fireproof classes of fans are used in the air duct system;
- the air duct is secured using metal stands;
- use of non-combustible air duct materials;
- mandatory fire damper on the bathroom grill.
The fluttering of a burning match will indicate to you the operating status of the air duct system.
Roof outlets
At the exit from the roof, the exhaust pipes are combined into a common rectangular ventilation duct. The common duct can be replaced with separate short ventilation outlets, almost invisible on the roof.
To enhance traction, a special cap is installed above the pipe - a deflector. When there is a side wind or air currents rise from the ground upward, it creates a vacuum and works as an injector. The deflector protects the pipe from precipitation, birds, and other large objects from outside.
There are technical requirements for the height of the channel in relation to the ridge level that must be observed. This is necessary so that the top of the pipe is accessible for wind blowing from any side and there is always draft in the ventilation duct.
Ventilation of the floor of a wooden house
Wood is finicky to use. It is afraid of moisture. Lack of room ventilation will have a detrimental effect on the condition of the floor covering elements. You should not wait for a moment that will have a catastrophic effect on the condition of the house. A well-thought-out ventilation system will help keep the house in perfect condition. Proper underground ventilation in a wooden house can help with this. It is organized using air intakes (in the form of holes). Thanks to this ventilation scheme, the soil under the floor does not freeze.
Application of air conditioners
You can increase air circulation using an air conditioner.
The use of climate control systems is not always justified. Ventilation of the room shows high efficiency in maintaining a good microclimate and supplying fresh air. The air conditioner can be installed on the facade of a wooden house. Then systems that operate for heating and cooling will save on heating costs.
All split systems are equipped with two units that operate synchronously:
- The outdoor unit condenses refrigerant.
- The internal one is a radiator that heats the air around it.
There are air conditioner models that take in outside air. But its share is less than 5%. It makes no sense to buy such products, since they are overpriced and do not perform their functions.
Walls of a wooden house and metabolic processes
Wood is an excellent organic material for construction. Only moisture exchange in wooden structures has nothing to do with air exchange. We are talking about moisture regulation. Human skin also senses gas exchange through moisture exchange processes, but just like wood, the percentage of gas exchange here is negligible. A tree cannot provide the human body with air capable of supporting the normal functioning of the body by regulating the humidity regime.
The question arises - how to make a hood for ideal comfort in the house. The ideal option is a forced ventilation device. It is controlled, that is, manageable. And it is carried out with the help of mechanical devices that provide a comfortable indoor microclimate.
What should be the vents in the foundation and how to position them
Ventilation holes in the foundation are made of round or square cross-section. If desired, it can be triangular or any other shape. If only they were large enough in area to effectively remove moisture from the subfloor.
Dimensions
The dimensions of ventilation holes in the foundation are regulated by SNiP (SNiP 31-01-2003). Paragraph 9.10 states that the area of the vents must be at least 1/400 of the total area of the subfloor. For example, if you have a house measuring 8*9 m, the underground area is 72 square meters. m. Then the total area of vents in the foundation should be 72/400 = 0.18 sq.m. or 18 sq. cm.
The same paragraph of the standard specifies the minimum ventilation area - it should not be less than 0.05 sq.m. If we translate into dimensions, it turns out that rectangular holes should not be less than 25*20 cm or 50*10 cm, and round ones should have a diameter of 25 cm.
Larger holes can be made
In multi-storey buildings this is done, but in private buildings such holes look too large. Usually they are made two times smaller, while increasing the number of vents so that the total area of the vents is not less than the recommended one.
Do I need to close the vents for the winter?
In winter, frosty air entering the underground causes the floors in houses on the ground floor to become very cold.
To avoid this, some owners close the ventilation holes in the winter. As a result, the underground will be warmer, and the floors on the first floor will not be so cold.
However, closed vents will lead to increased humidity and mold growth. Therefore, stopping ventilation for the winter is not correct.
To prevent the floor from cooling too much, it needs to be insulated. It is correct to do this at the construction stage, because in an already inhabited house you will have to open up the floors for insulation.
If you do not close the vents for the winter, be sure to make sure that they are not covered with snowdrifts. In this case, the ventilation will not work (after all, the holes are closed), and the humidity inside will increase (due to snow falling into the underground, which will melt there).
Care in spring and autumn
In the spring, the main thing is to pay more attention to the conditions of the underground. Melt water can penetrate inside, leading to increased humidity
If the vents were closed for the winter, it is important to open them as quickly as possible in the spring: with the onset of warming. In the fall - check if the ventilation grilles are in place (or install them if they are not)
During this period, small rodents begin to look for warm places for the winter, and uncovered openings will allow them to get inside your home
In the fall, check if the ventilation grilles are in place (or install them if they are not). During this period, small rodents begin to look for warm places to hibernate, and uncovered openings will allow them to get inside your home.
Natural
No electrical equipment required. Exhaust ducts are simply laid throughout the house, which are connected to the general house exhaust duct. It is important to do them with a minimum number of turns and bends. This allows air masses to escape freely.
The indoor atmosphere changes naturally due to changes in pressure, temperature and convection currents. In winter, warm air rushes upward, entering the surrounding space outside through the pipes of the exhaust system, and enters the room through microcracks, cracks, the front door, open vents or windows. The concept of natural ventilation also includes the organization of air flow through supply valves of various designs.
Kinds
All types of ventilation are divided into several types, depending on its purpose, complexity of arrangement and principle of operation. But the principle of operation of any of them will be based on the laws of physics on the movement of air masses. Cold air goes down and warm air rises.
Natural supply ventilation
The simplest, vent system in the foundation or basement. It is installed during the construction of a house and consists of small holes in the upper part of the basement.
If the basement is located below ground level, then the hood is equipped with plastic or asbestos-cement pipes with a diameter of 10-15 cm. They are brought above the surface to a height of 30 cm and covered with grates to prevent debris and rodents. This method is natural and depends on fluctuations in street temperature, wind strength, and humidity.
When calculating its throughput, 1/400 of the total area of the basement is taken - this way we get the total area of all vents.
The holes should be located on the leeward side, least susceptible to precipitation. Houses with a complex foundation shape and located in low-lying areas can have up to one hole every 3-4 meters. We close the vents with gratings on the outside.
This inexpensive option is well suited for ventilation of garages and non-residential basements or as an additional means to the main ventilation system.
Natural exhaust ventilation
Supply and exhaust type. For proper operation, you will need to install two pipes for ventilation, and the supply and exhaust ventilation device looks like this.
- The first pipe is located under the very ceiling of the basement and is intended for the outflow of warm air. We place the exhaust pipe as high as possible, preferably at the level of the roof ridge. This is necessary to ensure good traction. The part of the pipe that is located in the open air must be insulated to prevent freezing in winter and covered with a canopy from precipitation.
- The second pipe for the supply of fresh air is located at a height of 30-40 centimeters from the floor level, and its entrance is located on the street a meter above the ground and covered with a grill. Convection will occur due to the temperature difference between the street and basement air. Such a system will work most effectively when the supply channels are spaced on different sides of the basement.
All natural exhaust ventilation systems have one drawback - their dependence on weather conditions and prevailing winds. It will not work if the temperature in the basement and outside are equal.
Forced
It is used if natural supply ventilation cannot cope or there is no physical opportunity to use it. Typically used in the following cases:
- The basement area is from 40 m2 or has several rooms isolated from each other;
- High room humidity, when condensate in the exhaust duct freezes in winter and impairs the permeability of air masses;
- The architecture of the house does not provide for high ventilation pipes;
- A sauna, cafe, gym, workshop or other source of unpleasant odors is installed in the basement.
The forced supply and exhaust ventilation device has a system of channels and fans that circulate air.
The main condition is to force the air to constantly circulate, which is ensured by the synchronous operation of exhaust and supply fans. Their number is calculated depending on the volume of the cellar or basement and the throughput of the air ducts.
Supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recovery
For a basement floor in which permanent residence is planned, it is not enough to simply install a forced ventilation system. The room must be insulated and waterproofed. The issue of heating and heating is also resolved.
Increasingly, supply and exhaust with heat recovery is being built into such schemes.
Well-heated air enters the exhaust pipe, and in order not to release ready-made calories into the atmosphere, the air is passed through a special ceramic recuperator. When heated, it gives off heat to fresh air. The air flows do not intersect. The efficiency of such a device is 50-90% depending on the design of the heat exchanger. All heat recuperators are very reliable, do not require additional maintenance and can last for decades.
Equipped with moisture traps, dust filters, sensors that monitor humidity and air temperature. For a residential premises, these indicators lie in the range of 50-65% relative humidity and 18-220C. Such systems are most often found in “smart homes”, and their installation is complex and should only be carried out by professionals.
Should you close the vents for the winter or not?
There are two points of view on whether to close the ventilation holes in the underground for the winter or not. If they are left open, moisture will not accumulate. And this is good, but in return we get a cold floor and increased heating costs. The solution is enhanced floor insulation so that ventilation does not affect its temperature and does not require increased heating.
If the vents are closed for the winter, moisture accumulates in the soil. Warm, moist air from the house enters the floor, falling on cold surfaces, and in winter these are the walls of the basement, the moisture condenses and flows into the ground. This means that later, in the summer, it will evaporate from there, increasing the humidity in the basement.
Additional humidity reduction
To ensure that the ventilation system does not have to be strengthened by increasing the total cross-section or installing fans, the following work must be carried out:
- Installation of an effective drainage system - removal of water from the foundation.
- Waterproofing the base of the house and the basement. There are many types of waterproofing: it can be rolled, built-up, coated, etc.
- Performing insulation. The best material in terms of economy and efficiency is EPS. This is a good heat insulator that does not allow water to pass through. It is not of interest to rodents and does not rot. EPS can also insulate the blind area.
The listed measures do not cancel, but simply supplement ventilation. Only in combination can you achieve ideal drainage of the space in the basement compartments.
If the house is built on a soil foundation that does not drain water well, in addition to the ventilation system, drainage and storm drainage are required. The drainage system will collect water from the soil and upper layers of soil, the storm drain will collect and drain precipitation
When installing a system according to a forced scheme, the costs for installation, maintenance and service will be higher than when organizing a natural type. It should be taken into account that in winter condensation can form on the walls of the ventilation pipes themselves, and in cold weather the cross-section can become completely clogged.
To avoid this, pipes can be thermally insulated with penofol. At the bottom turn of the pipe, you can come up with a condensate collector - for example, drill a hole or install a tee instead of an angle.