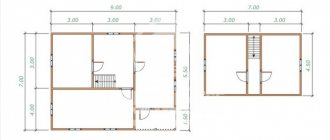
What is considered a semi-detached house by law?
The norms of the Russian town planning code define several types of low-rise residential development. One of these types of housing is blocked houses.
The main definitions and technical provisions relating to blocked residential development are given in the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation (Article No. 49, Part 2):
A blocked
residential building
is an apartment-type building consisting of two or more apartments, each of which has direct access to the adjacent plot. The building itself is considered a single house, although it consists of several, essentially autonomous residential blocks.
We will look at all the differences and rules for the development and operation of blocked houses a little later. Now let's move on to the background - how did this type of housing appear and why is it so in demand?
Advantages of constructing blocked buildings
The construction of a residential building for 8 families has a number of distinctive advantages:
- It is possible to build on areas with difficult terrain;
- The presence of blocks allows you to create a building project with various configurations;
- Formation of high density buildings;
- The length of communications is reduced;
- The outer perimeter of the external walls of the apartment is reduced, which leads to heat savings;
- Construction requires less land than custom construction;
- Since each apartment has an individual exit to the adjacent territory, this creates additional attractiveness for the buyer.
History of the format
This format of low-rise buildings first appeared in England and France, and received special development in the 17th – early 20th centuries.
Thus, the first street consisting entirely of interlocking buildings appeared in Paris in the early 1600s. In Britain, such development began to be widely used in urban planning after the great fire that occurred in London in 1666.
Since the late 18th and early 19th centuries, when Britain was undergoing massive urbanization, standard block housing has become prevalent in growing industrial centres. In conditions of large population concentrations and lack of space for the construction of individual households, this type of housing has become widely in demand.
Other obvious advantages of block development are:
- Significantly lower cost per square meter;
- Improved layouts, often larger area;
- More comfort compared to apartments, using some of the advantages of a country house (such as its own plot, separate entrance, etc.);
As a result, by the end of the 19th century, most cities in Great Britain began to consist of long rows of narrow streets lined with block-type houses.
Then, from England, semi-detached residential development “migrated” to other countries and territories associated with the British Empire: to the USA, India, Australia. Also, this type of residential buildings has become widespread in Scandinavia and Germany.
Design of blocked residential buildings and its features
Blocked houses, often called townhouses, have long become a familiar and widespread type of housing in Europe, but in our country they are not yet so common.
Recently, in this regard, there has been a tendency to increase the share of blocked houses in the Russian housing stock, which is explained by the high cost of real estate and the shortage of land for development in cities. Initially, back in the 90s of the last century, when townhouses began to appear in Russia, this housing option belonged to the concept of economy class, but in modern conditions the scope of ideas about blocked houses has expanded significantly. Nowadays you can still find townhouses that belong specifically to this category of housing, but you won’t surprise anyone with premium options, and all thanks to the development of construction technologies, which allows you to create block-type residential buildings at the highest level of comfort. Of course, all this becomes possible only with the right approach to the construction of this type of housing, first of all, this concerns the issue of developing designs for these houses. Accordingly, serious attention must be paid to the design of blocked residential buildings so that the resulting result does not upset apartment owners with its level of quality and does not create obstacles for them to have a normal and fulfilling life.
What are the differences between a blocked house and an apartment building?
Being essentially a low-rise building with several apartments, a semi-detached house can be quite difficult to distinguish from ordinary multi-apartment residential complexes. However, it has several major differences.
Thus, according to the law, a blocked building must meet the following requirements:
- The number of floors in the house should be no more than 3;
- The total number of blocks in the building should be from 1 to 10;
- Each of these residential blocks is designed for autonomous living of one family, and is a separate comfortable apartment;
- Neighboring apartments (blocks) are separated from each other by blank walls, without doorways;
- Residents of semi-detached houses do not have common property (i.e. common entrances, attics or basements, communication shafts, etc.);
- Each family has a separate exit to the local area, without a common corridor or entrance (front door).
The main difference between blocked buildings and a standard apartment building, from the point of view of Russian legislation, is the design of the local area. If all the land under a multi-apartment residential complex is registered as 1 plot, then in semi-detached buildings a separate plot of land is registered for each block.
There is also quite often confusion in the use of terms: what is “block housing”? Are they the same thing as "townhouses" or "duplexes"?
Registration stage:
4.1. Obtaining permission to put the facility into operation
To receive it, you must submit a corresponding application to the local government body (LSG) in person or through the MFC or electronically.
The following documents must be attached to the application:
- title documents for the land plot;
- urban planning plan of the land plot submitted to obtain a building permit;
- building permit;
- act of acceptance of a capital construction project (in the case of construction or reconstruction on the basis of a construction contract);
- an act confirming the compliance of the parameters of the constructed capital construction facility with the design documentation, including the requirements for energy efficiency and the requirements for equipping the capital construction facility with metering devices for energy resources used, and signed by the person carrying out the construction (the person carrying out the construction, and the developer or technical customer in the case of construction, reconstruction on the basis of a construction contract, as well as by the person exercising construction control, in the case of construction control on the basis of a contract);
- documents confirming the compliance of the constructed or reconstructed capital construction facility with technical conditions and signed by representatives of organizations operating engineering support networks (if any);
- a diagram showing the location of the constructed or reconstructed capital construction project, the location of engineering and technical support networks within the boundaries of the land plot and the planning organization of the land plot and signed by the person carrying out the construction (the person carrying out the construction, and the developer or technical customer in the case of construction, reconstruction on based on a construction contract), with the exception of cases of construction or reconstruction of a linear facility;
- the conclusion of the state construction supervision body on the compliance of the constructed or reconstructed capital construction project with the requirements of design documentation, including the requirements of energy efficiency and the requirements for equipping the capital construction project with metering devices for the energy resources used, the conclusion of the federal executive body authorized to carry out federal state environmental supervision;
- technical plan of a capital construction project, which is prepared by a cadastral engineer for each block of a residential building separately, indicating the cadastral number of the land plot on which this block is located.
Regulatory framework
The procedure for operating semi-detached housing, as well as construction and technical standards, are determined by the following legal acts:
- Housing legislation of the Russian Federation. It contains the basic concepts and definitions of block houses, and their operational and technical characteristics;
- Town Planning Code (Article No. 49). Contains a precise and comprehensive definition of semi-detached development;
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 220, dated 2015, establishing the procedure for purchasing blocked housing on the primary market;
- Federal Law No. 161, as well as Order of the Ministry of Construction No. 223, defining the rules for the provision of land plots for the construction of combined residential buildings;
- Land Code of the Russian Federation (Article No. 35), which regulates the procedure for legal registration of plots intended for block development;
- Letter from the Ministry of Economic Development stipulating the procedure for placing interconnected buildings on one plot of land.
In accordance with these legal acts, a full range of legal registration of blocked development is carried out, starting from the allocation of land for construction, and ending with the purchase and registration of finished housing.
Preparatory stage:
Before starting construction work, you need to carry out several preparatory procedures:
2.1. Preparation of project documentation
Preparation of design documentation for a residential building in a blocked development is mandatory.
The project is ordered by the owner (owners) of the land plot from the design organization and prepared by it on the basis of the following documents:
- urban planning plan of the land plot;
- results of engineering surveys (if they are missing, the contract for the preparation of design documentation must provide for the task of performing engineering surveys);
- technical conditions (if the functioning of the designed capital construction facility cannot be ensured without connecting (technological connection) such a facility to engineering support networks).
2.2. Taking into account building codes and regulations during design
When designing and constructing a residential building in a blocked development, it is necessary to comply with the construction, sanitary and fire safety standards and rules contained in the Land Code, Town Planning Code, SNiPs (building codes and rules governing construction, engineering and architectural surveys and town planning activities).
Of all the many SNiPs for individual housing construction, the following are important:
- SP 11-111-99 - development, coordination, approval, composition of design and planning documentation for the development of low-rise housing construction areas;
- SP 30-102-99 – planning and development of low-rise housing construction areas;
- SNiP 30-02-97 – planning and development of territories of gardening dacha associations of citizens, buildings and structures;
- SNiP 21-01-97; – Fire safety of buildings and structures;
- SP 55.13330.2016 - Code of rules. Single-apartment residential houses (or SNiP 31-02-2001).
Read more…
2.2.1. Sanitary and fire safety standards and recommendations for interior spaces:
According to the requirements of SP 55.13330.2016, a house, including a block in a block house, must include one or more rooms, as well as auxiliary premises:
- kitchens, including kitchen niches and (or) kitchen-dining rooms;
- baths and (or) showers;
- toilet or combined bathroom.
| Minimum width of interior spaces, m | |
| kitchen and kitchen area in the kitchen-dining room | 1,7 |
| front | 1,4 |
| interior corridors | 0,85 |
| bathroom | 1,5 |
| toilet, with a length of 1.2 m (door opening outwards) or 1.5 m (door opening inwards) | 0,8 |
| Minimum height of internal premises, m | |
| living rooms and kitchen in climatic subregions IA, IB, IG, ID and IIA (according to SP 131.13330) | 2,7 |
| living rooms and kitchen in other climatic subregions | 2,5 |
| rooms, kitchen and other rooms in the attic or with sloping ceilings or walls | 2,3 |
| corridors and when installing mezzanines | 2,1 |
| Minimum area of internal premises, sq. m | |
| area of the main living space (living room, hall) - | 12 |
| bedroom - | 8 |
| kitchen or dining room-kitchen - | 6 |
| combined bathroom - | 4 |
| toilet - | 0,96 |
| bathroom - | 1,8 |
| hallway (if available) — | 1,8 |
In addition, built-in, built-in-attached and attached auxiliary premises can be arranged:
- utility rooms (storerooms);
- Built in furniture;
- auxiliary room for generator heating and (or) power supply;
- parking space at the house in accordance with SP 113.13330
- swimming pool in accordance with the requirements of SP 31-113-2004
- steam room, bathhouse or sauna in accordance with SanPiN 2.1.2.3150.
2.2.2. Sanitary and fire safety requirements for internal engineering networks
Technical conditions for connecting engineering and transport infrastructure in the adjacent environment are carried out in accordance with SP 42.13330.
2.2.3. Basic requirements for structural elements
The foundations and supporting structures of a residential building in a blocked development must be designed and constructed in such a way that during the construction process and in the design operating conditions, the possibility of destruction or damage to structures and unacceptable deterioration in the operational properties of structures leading to the need to cease operation of the house is excluded. When designing a roof, you should be guided by the provisions of SP 17.13330.
The structures and foundations of the house must ensure reliability during their service life in accordance with the requirements of GOST 27751 and be designed to withstand standard loads and impacts in accordance with SP 20.13330.
The foundations of the house must be designed taking into account the physical and mechanical characteristics of soils in accordance with SP 22.13330 (for permafrost soils in accordance with SP 25.13330), the characteristics of the hydrogeological regime at the development site, as well as the degree of aggressiveness of soils and groundwater in relation to foundations and underground utility networks. Foundations must ensure the necessary uniformity of settlement of the foundations under the elements of the house. Pile foundations should be designed in accordance with SP 24.13330.
Blocks in a block building should be separated by blind fire walls with a fire resistance rating of at least REI 45 and a fire hazard class of at least K1. Blocked houses of structural fire hazard classes C2 and C3 must additionally, in accordance with SP 4.13130, be divided by blind fire walls of the 1st type with a fire resistance limit of at least REI 150 and a fire hazard class of at least K0 into fire compartments with a floor area of no more than 600 m2, including includes one or more residential blocks.
When designing and constructing houses of blocked development, measures must be taken to prevent the spread of fire from one residential autonomous block to another and to other fire compartments, bypassing fire barriers. To do this, fire walls must cross all house structures made of flammable materials.
Each residential autonomous block of a blocked building must have at least one emergency exit to the outside, including to a type 3 staircase in accordance with SP 1.13130.
A residential building in a blocked building must be designed, constructed and equipped in such a way as to prevent the risk of injury to residents when moving in and around the house, when entering and exiting it, as well as when using indoor equipment.
2.3. Obtaining a building permit.
To obtain a construction permit, the owner of the land plot or his official representative must apply for a construction permit to the local government body (LGU) in person or through the MFC or electronically.
The following documents must be attached to the application:
- title documents for the land plot;
- urban planning plan of the land plot, issued no earlier than 3 years before the date of submission of the application for a building permit;
- materials contained in the design documentation:
- explanatory note;
- a diagram of the planning organization of the land plot, made in accordance with the information specified in the urban planning plan of the land plot, indicating the location of the capital construction project, entrances and passages to it, the boundaries of public easements, archaeological heritage sites;
- a diagram of the planning organization of the land plot, confirming the location of the linear object within the red lines approved as part of the territory planning documentation in relation to linear objects;
More details
The development of the SPZU is carried out in accordance with the norms of the Land Use and Development Rules (LRU) of the zone to which the original land plot belongs, and in accordance with the requirements set out in a number of regulatory documents:
- SP 30-102-99 “Planning and development of low-rise construction areas”;
- SP 42.13330.2016 “Urban planning. Planning and development of urban and rural settlements”;
- SNiP 31-02-2001 “Single-apartment residential houses”;
- “Regulations on the composition of sections of project documentation and requirements for their content” Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 87 dated February 16, 2008.
The construction of a blocked residential building must be carried out on a single original plot of land or on several adjacent land plots for blocked residential development, and therefore permitting documentation for construction is issued taking into account the specific situation.
Blocked house - is it private or shared?
This is one of the most common questions that causes confusion and uncertainty among all those who are planning to buy a townhouse or duplex, or have already purchased. What is private in such houses and what is common?
There is simply no answer to this question. Due to the “youth” of this housing format on the Russian market and the large number of regulatory documents, many of them provide vague definitions, or even completely contradict each other.
Filling out the technical plan of the building
the pathfinder said: ↑ I agree that nothing, except an extract from the household register for a residential building Click to expand. I was always surprised by such statements.
you carefully read what should be included in the household book IP said: ↑ I have a building (residential building), it has a cad.
number. According to the court, this building was divided into three parts (each with a separate entrance and its own plot of land). Addresses were assigned to parts (residential buildings). I need to register three, now at home. As I understand from your message, this is possible by converting a residential building with a cad. number.Click to expand.
Anastasia25ru said: ↑ did the same TP. House with two apartments. Spoiler (Move your mouse over the Spoiler to expand the contents) Expand Spoiler Collapse Spoiler one of which was allocated as a unit, received an agreement on the transfer of PART of the residential building to citizens, made a technical passport for PART of the residential building, and the customer also gave filming of the entire house, for TP this was enough.
According to the technical passport and topographic survey, it was coordinated by its part; the plan was made for the formation of a RESIDENTIAL HOUSE by transforming a RESIDENTIAL HOUSE with a cadastral number (it is registered in the objects from which it is formed). and only on paper (this cannot be indicated in xml - otherwise it will not pass the test) registered the previously assigned cad. apartment number. TP passed. The client handed it over to the ward himself and last week received a passport for a RESIDENTIAL HOUSE, not for part of a residential building, I indicated this part only in the conclusion of the cadastral engineer.
To be honest, I don’t quite understand the meaning of such registration of residential buildings, because... This is not a residential building, but part of a residential building, in general it’s some kind of absurdity, but this is the only way to get a passport for this kind of object. Our CP said that it seems that a TP form is being developed just for registering such objects.
Click to expand. I just have to wonder, will the second half of this house then go through a staging (TRANSFORMATION?) amazing position, and will they then also share the slate roof?
Sample (example) of a technical plan of a building (residential building)
Rostov region Government of the Russian Federation President of the Russian Federation Roszemkadastr Rosimushchestvo Roskartography Roskomzem Roskomnadzor Rosleskhoz Rosnedvizhimost Rospotrebnadzor Rosregistration Rosreestr Rosstandart Rosstat Rosstroy Rostekhnadzor Rostekhregulirovaniya Rostov-on-Don City Duma Council of Ministers of the USSR Special Construction of Russia Court for intellectual rights Courts of general jurisdiction Federal State Budgetary Institution "FKP Rosreestr" Federal Migration Federal Notary Chamber service Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation Federal Arbitration Courts Branch of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "FKP Rosreestr" for the subject of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation FSSP Results per page: 10 20 50 You can find the technical plan in PDF format at the bottom of the page Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 We offer: “Hot” documents
- 16.03.18 11.11.15 26.10.15 26.10.15 10.10.15 02.10.15 01.10.15 30.09.15 28.09.15 27.09.15 20.09.15 10.09.15 01.09.15 28.08.15 27.08.15 16.08.15 16.08.15 16.08.15 05.08.15 02.08.15 21.07.15 14.07.15 14.07.15 13.07.15 13.07.15 13.07.15 10.07.15 09.07.15 02.07.15 01.07.15 30.06.15 26.06.15 24.06.15 22.06.15 20.06.15 17.06.15 17.06.15 16.06.15 08.06.15 05.06.15 30.05.15 26.05.15 25.05.15 23.05.15 22.05.15 22.05.15 22.05.15 22.05.15 22.05.15 20.05.15
We recommend reading: Who is entitled to a subsidy for utility bills in Oryol?
News
- 14.03.2018 13.03.2018 25.02.2016
Control
The regional government carries out various programs within the framework of managing houses with different statuses. One of them is the capital repair program. Its task is to provide the necessary assistance to residential buildings that are in disrepair and in need of repair.
Since houses with combined development do not belong to the category of multi-apartment buildings, therefore they are not included in such programs.
The repair and maintenance of this type of house is carried out by the residents of individual blocks themselves.
Recognition of the emergency or other condition of a blocked building is carried out by the BTI, as well as housing services. As for the management of such a house, it is worth relying on the process of managing a private residential building, according to which the owner himself bears responsibility.
In general, it can be noted that houses of combined development are residential buildings with several owners who have the right only to a separate block and a separate plot with a separate exit.
Blocked buildings are an excellent replacement for apartment buildings, where problems with sewerage systems and insufficient living space often arise.
IMPORTANT! Buildings of this type make it possible to equip them to suit your individual tastes, while improving the quality of your life.
It is also worth noting that there is no clear legislative framework that would regulate the procedure for management, registration, and also deal with various issues relating to these buildings. However, many codes and laws contain specific information about the type of property that is blocked.
Sample technical plan in 2022
According to the law, if a technical plan is prepared in electronic form, a printed copy is not required. Good to know: A technical plan of a premises can be completed without a cadastral or technical passport if a floor plan or new measurements with outlines are available. Dear CLIENTS! The information in this article contains general information, but each case is unique.
You can get a free consultation from our engineers using one of our phones - call: 8 (499) 322-05-14 - Moscow (our address) 8 St. Petersburg (our address) All consultations are free.
Status
The status of these houses is associated with many misconceptions. Inclusion in the cadastral register of each individual part of the blocked building as a separate unit. This is considered an error. According to the Town Planning Code (Article 49), houses of combined development have separate parts and are considered a single whole.
Each separate block in which citizens live is not a separate independent dwelling.
The right to an owned apartment or a certain part of a building can be transferred into personal ownership.
Blocked buildings are classified as a type of apartment building. According to regulatory documents, a residential premises is classified as multi-apartment if it has two or more apartments with one exit to a public area.
That is, each apartment has access to a common area. As for buildings of combined development, each of its individual blocks has its own access, first to a separate territory, and then to a public street.
From the above it follows that the entire house or part of the combined housing with the adjacent land area must be registered in the cadastral register. In this case, the procedure for registering ownership rights is carried out by a family representative.
The Housing Code of Russia does not give an exact definition of this type of house, so work is underway on draft standards that will accurately outline the concepts of apartment and block houses.
ATTENTION! Such houses cannot be inherited entirely. The heirs receive personal ownership of only a separate part of the block building.
Advantages and disadvantages
By choosing housing of this type you can get a certain advantage, namely:
- Cost savings. When building such a house, you can significantly save on construction and significantly reduce the building area. Such housing is much cheaper. At the same time, the house turns out to be completely functional.
- Savings on utilities . Two residential blocks have one common riser.
However, there are also some disadvantages. The main disadvantage of blocked houses is the small space. There are problems with parking spaces for cars, as well as corners for garbage collection.
Cadastral Engineers Forum
It is proposed to change the VRI of the specified chargers to something like “maintenance of an apartment building.”
The mayor's office, when issuing permission for reconstruction, did not make such demands. The owners are categorically against replacing the VRI, because it does not correspond to reality and brings with it additional troubles. In fact, this is a one-story house of blocked development with independent access to its own land plots, and the territorial zone where the object in question is located (Zh-1) does not provide for “multi-apartment” VRI.
Please express your opinion and give advice on this issue.
Thank you!
- ,
- ,
- 0
- 3 February 2022, 10:10
Good afternoon Colleagues, we are faced with such a non-standard situation for us: there is a house, according to the certificate the concept of “residential building” appears, in the extract it appears the concept of “apartment building”, the type of permitted use of the land plot is the operation and maintenance of a residential building. The customer carried out the reconstruction, a reconstruction permit was issued for a residential building.
According to the extract: on the KU there is an apartment building, as well as 3 apartments.
Let me clarify that in our region, construction permits for individual housing construction are issued by the local administration, and for apartment buildings - by the regional administration. Those. I cannot currently perform TP due to contradictions between the extract and the certificate. A woman, her daughter and son live in these apartments. Ownership registered 166/189 - mother, 23/189 - daughter.
The property is completely owned by the mother.
The customer also wanted to leave the division, but it turns out not into apartments, but into blocks.