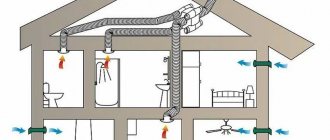
The dry lines of the scientific definition say that ventilation of a private house is a process of specially organized air exchange (from the Latin ventilatio - ventilation) in the residential and utility rooms of the building, in order to maintain the required sanitary and hygienic parameters of the air environment (air composition, its purity, temperature, humidity ). Ventilation is also called a set of technical means and measures that ensure controlled air circulation in a separate room and throughout the building.
The result of all these words is the same - in order to have fresh air in the house, it is necessary to install additional equipment, and what exactly - we asked the specialists of ATM Climate, a company that occupies one of the leading positions in the climate equipment market, to tell us.
General diagram of air exchange in the house Source socialmec.com
Proper arrangement of ventilation, both in apartment buildings and in private buildings, is the job of specialists, since here you will need to make a large number of calculations. At the same time, it would not hurt the owners of private houses to learn the basic principles of how ventilation works - this will help them at least in general terms understand what work will need to be done and how much it will cost.
Why is ventilation needed in a private house?
Air quality must fully ensure the comfortable state of the human body. This is unanimously stated by GOSTs and SNiPs, which regulate the microclimate parameters in premises. The most important factors of a comfortable microclimate include the following indicators of the air environment:
- cleanliness and degree of freshness of the air;
- air temperature and humidity.
To ensure that these indicators always remain within acceptable limits, a ventilation system is installed in a private house, the scheme of which is individually calculated for each individual case.
Ventilation has two main tasks:
- removal of air with a high content of dust and carbon dioxide into the external environment;
- an influx of clean, oxygen-rich air from the street.
8 reasons to install ventilation Source technosip.ru
Aeration
This is a type of natural ventilation. Here it is necessary to take into account the wind rose. This is necessary so that harmful substances from the waste stream in the workshops do not enter, for example, office premises. It is desirable that the ventilated building (room) be located on the windward side of the production workshops. Air exchange occurs through windows and skylights due to temperature differences and wind pressure. Optimal draft is created with special three-level vent designs. In warm weather, fresh flow enters through the lower transoms, and contaminated flow is removed through the upper ones.
Ventilation requirements - air flow rates
The basic indicators for designing a ventilation system are the incoming air flow rates and air exchange rates provided for by the relevant SNiPs:
On a note! The frequency of air exchange or ventilation is the ratio of the volume of air entering during one hour to the volume of the room. The multiplicity parameter characterizes the hourly number of air updates.
- The ventilation system must provide air supply in an amount no less than that required for comfortable stay of people in the room. For one person this is 30 m³/hour if the area of the room is more than 20 m² or 3 m³/hour for each square meter if the area allocated for one person is less than 20 m².
- For residential and associated premises with certain functionality, air flow is determined by the following standards:
- A minimum of 3 m³/hour must flow into the living room for each square meter of area.
- To the bathroom and toilet – 25 m³/hour.
- In a combined bathroom - over 50 m³/hour.
- For the kitchen - depending on the type of stove and the number of burners: electric and gas two-burner - 60 m³/hour; gas four-burner – 90 m³/hour.
A hood over a gas stove as one of the ventilation options in the kitchen in a private home Source deskgram.net
- The air exchange rate of a private house should be within the following limits:
- at least one volume per hour if there are always people in the room;
- at least one volume every 5 hours (0.2 volume/hour) for technical rooms.
Note! The given standards are calculated for indoor air temperature +18 °C and outdoor air temperature +5 °C.
Supply system
Its purpose is to “infuse” new flows from outside into the premises. General ventilation is installed where the temperature is above normal and there are relatively few harmful substances. Exhaust air is discharged outside through natural ventilation - through shafts through transoms. Along the way, flows with dirty particles are supported by air from outside, pumped by centrifugal or axial fans. Sometimes, if necessary, heaters are used with them, humidifying and heating the input flows. Their volume is regulated by means of special dampers and valves. There are two types of supply system:
- In the form of a monoblock. The simplest option: several air ducts and supply voltage are connected to one device. Maintenance is minimal. However, such equipment costs a lot.
- Team. Here you will have to independently calculate how many and where you need to install individual devices. This method requires the participation of experienced specialists. But the products themselves are more affordable.
Supply ventilation allows you to heat, dry or, conversely, humidify and cool air supplied from outside.
Methods for calculating ventilation parameters
Accurate calculation of ventilation in a private home is performed using specialized software, to work with which you must at least know in what order and what data to use. Therefore, in order to do it once and wisely, you need to start with the development of an individual ventilation project for a private house.
But along with such calculations, there are methods of simple calculations that will make it possible to approximately estimate the necessary parameters.
- According to consumption standards.
According to SNiP, air consumption by one person (Vnorm) is approximately 60 m³/hour. This means that to calculate ventilation performance, the formula V=Vnorm*N is used, where N is the number of permanent residents of the house. But the problem with this approach is that residents may be in different rooms or congregate in one. For this reason, this approach is used only for air heating (air climate systems) with air circulation inside the house and with the addition of fresh air in the specified quantities. - According to the frequency of air renewal (calculation by area).
SNiP standards require at least one hourly air renewal. If, in this case, for the comfortable well-being of people in the room, one-time air circulation is not enough, use the formula V=K*S*H, where K is the air exchange rate, S is the total area of a private house, H is the height of the ceilings. The multiplicity index varies from 1 to 3. This approach is the most common, but is associated with a significantly larger volume of air supplied to and removed from the house than in the previous case.
SNiP requirements for air exchange rates in the table:
Source vodakanazer.ru
Natural and forced ventilation
All ventilation systems are divided into two main types:
- Natural (convective or natural) ventilation. The circulation of air masses here occurs in the same way as in nature - under the influence of draft, which arises due to the difference in temperature, and therefore air pressure in the room and outside the house;
- An artificial (forced) air exchange system, which is carried out by air blowers such as fans or compressors.
Natural ventilation - operating principles and features
The operating principle of natural ventilation is convection - the movement of warm air currents to the upper part of the room and the replacement of departed air masses with cold street air that flows from below. In addition to the temperature difference, the speed of air circulation here is also affected by the wind speed.
Previously, leaks in windows and doors were used to allow air to enter the home. However, modern plastic windows do not have such micro-slits and ventilation valves have to be purposefully installed in the frame or walls. In turn, the “exhaust” air leaves the house through exhaust ducts located in the kitchen, toilet and other rooms.
The principle of operation of convection (natural) ventilation Source bolts-master.com
See also: Contacts of companies that specialize in ventilation and air conditioning.
Natural air exchange has the following advantages:
- economical, since no additional equipment is required to move air flows;
- energy independence;
- trouble-free operation;
- noiselessness.
The disadvantages include:
- low intensity of air exchange, not always able to fully combat the accumulation of unpleasant odors or the formation of condensation;
- poor circulation efficiency due to the dependence of draft on the height of the building and time of year;
- almost complete impossibility of regulating the intensity of air exchange (dampers can be used, but they can only reduce draft, which means they do not always help);
- in summer there is almost no air movement, since the temperatures inside and outside the house are almost equal;
- a large outflow of heat to the street, which significantly increases heating costs;
It is important! In winter, the traction force in the air channels increases, as the temperature difference between inside and outside becomes significant. This leads to an increase in heat loss up to 40% of the total heat loss of the entire house!
- When installing sealed double-glazed windows, the natural flow of air practically stops.
- the need to additionally install special supply valves in windows or external walls.
Ventilation valves - outside and inside the room Source ventazbuka.ru
Features of artificial ventilation
The circulation of air masses in the artificial ventilation system is carried out forcibly due to the operation of electromechanical equipment. Fresh air from the street enters the ventilation unit through the air intake, which distributes the air throughout the rooms of the residential building. Exhaust air is forcibly sucked out of the premises and discharged into the street through exhaust air ducts.
The forced circulation ventilation equipment includes the following elements:
- fan;
- air purification filter;
- silencer;
- air heater/heater;
- air valve.
Even in modern systems, a recuperator can be added to the listed equipment - a device that, by removing heat from the air exhausted to the outside, heats the incoming air.
When installing a ventilation network you will need:
- air vents;
- air intake grilles, diffusers, anemostats.
Ventilation system in a “smart home” Source restate.ru
Advantages of artificial ventilation:
- autonomous operation, independent of environmental conditions (temperature and pressure, building height);
- the ability to bring the parameters of the air supplied to the house to the required values to create a comfortable microclimate (dust removal, heating/cooling, humidification/dehumidification).
Disadvantages of forced ventilation:
- energy dependence of technical means and significant energy costs for heating a large volume of supply air, which provides the necessary air exchange rate, especially in winter;
- significant costs for purchasing equipment;
- the need for regular maintenance.
Mixed ventilation type
If there is no need to install forced ventilation in all rooms of the house, then you can consider the option of mixed ventilation. This is what is commonly called the combined use of natural circulation with the installation of mechanical hoods and fans. Typically, forced ventilation is used in the kitchen or bathrooms, and air exchange in other rooms occurs naturally.
Mixed ventilation system Source linternaute.fr
home_and_garden
Stylish and comfortable home
Like a Hedgehog in the Fog: Cooling outdoor terraces and verandas
Winter, it seems, does not plan to indulge in frosts in our area and is more like early spring (the same one about which they usually write “it was the 40th day of winter”). However, last year’s summer was compactly grouped in May, and then turned into a months-long autumn with little snow.
According to statistics, those who expected warmth last year will want the heat to stop this year. This means that there will again be air conditioners (and their victims with runny noses), fans, cool showers, a swimming pool and other bodies of water. With traditional schemes in enclosed spaces everything is clear, but what if you need to create coolness in an open space, terraces or verandas? Installing fans or air conditioners every three meters is quite an expensive option.
Remember your feelings from walking through the fog on a summer morning, when it was already hot around you, and you walked into a hollow with fog and felt a comfortable coolness. This is due to the fact that fog particles, as they evaporate, “take” with them the temperature of the surrounding air. A way to make staying in the heat more comfortable is based on this principle - using fog cooling. A couple of years ago we enjoyed similar beauty on the mini-terrace of the Garden and Flower Festival in Muzeon:
Manufacturers and sellers promise that with the help of such systems it is possible to achieve a temperature reduction of 10-15 degrees.
This is how the open verandas of restaurants in the USA are cooled, and in Saudi Arabia the huge square of Medina and the Jamarat Bridge leading to Mecca are cooled with fogs, and we also have similar solutions.
When I began to study the issue of implementation methods, it turned out that there are options:
1. You can order an inexpensive kit on Ali. True, there is a high chance of “getting” into a set where the pumps are weak, the fittings are not small enough and the feeling is created not of fog, but of fine rain. Accordingly, it is necessary to ensure that high-pressure pumps are offered, close to industrial ones, which create not humidity, but precisely fog.
2. You can order the system in Italy or the USA, I think it’s a little cheaper than buying in Russia and somewhat more reliable / quieter than in China.
3. Look at Italian or American systems here in Russia in a specialized company.
4. Well, DIY has not been canceled either, the solution scheme is not rocket science, so a handy craftsman, having gained a couple of bumps during experiments, will be able to implement it himself.
Additional advantages of high-quality ready-made options: The system does not drip, thanks to nozzles with a built-in anti-drip valve and a drain valve that relieves excess pressure when the system is not in use.
But whether it’s worth buying a system, if we don’t have much of a summer, depends on the willingness to “be patient a little.” I remember that many opposed the installation of air conditioners in apartments for a long time, but one very hot (smoky) summer was enough for the most persistent opponents to begin to give up with the words - “It won’t be superfluous. ". I admit that in case of hot weather, many will think about a similar option for their terraces/gazebos/verandas/patios. let it stand, and let the automation activate it according to a given program.
From myself, using an everyday example, I will say that if I have a choice, then among the street cafes I will choose the one where it will be comfortable to sit on the veranda, and not where I will have to sweat, get under the air conditioning or hide in the back of the room. So, as a competitive advantage, an outdoor cooling system is a must-have in hot weather.
This is what the diagram for an open veranda or terrace looks like:
Equipment.
Cooling the veranda of the restaurant vtumane.ru https://v-tumane.ru/prodazha/ohlazhdenie-tumanom It can be seen that it comes with a timer and remote control. You can install the operating program from your smartphone and turn it on and off remotely.
So far, all the fogs that I have seen have been “frozen.” Here is another lovely nymph in the fog:
Festival of gardens and flowers in Muzeon.
The Imperial Garden Revive, author: Tatyana Goltsova To cool the air, it is more effective to place nozzles on top:
Cold air sinks down and cuts off the heat.
And for outdoor picnics they install a system with fans:
Afisha Picnic, 2016.
Also vtumane.ru You can simply install fans, but there are practically no thermodynamic reactions with energy absorption, only air will be driven around.
This is the summer theme today. Does anyone have experience using it? What do you think?
Ventilation operating diagrams
In the practice of arranging ventilation devices, depending on the functions performed, four types of ventilation are defined:
- Supply ventilation in a private house - supplies air from the street to the room.
When double-glazed windows are installed in the house, the “micro-ventilation” mode or special valves are used. But the intensity of air supply depends on weather conditions and is not always able to provide a comfortable microclimate. For artificial ventilation, additional ventilation ducts and devices are installed that purify the street air and heat it to room temperature using an electric or water heater.
What does supply ventilation look like schematically in a private house Source bir.bilagyteco.ru.net
- Exhaust ventilation in a private house removes “exhaust” air from the house to the street.
If a high intensity of air exchange is not needed, then use natural ventilation through ready-made ventilation ducts. But due to the obvious shortcomings of natural ventilation, forced hoods with exhaust fans are more often installed. They are installed both in ventilation ducts and in the ceiling space.
The principle of operation of supply and exhaust ventilation Source mojdominfo.ru
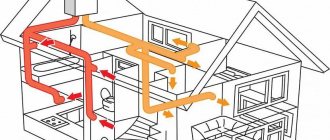
- Supply and exhaust ventilation in the house - in this case, two parallel multidirectional air flows are organized. The first is the supply of oxygen-saturated air into the room, and the second is the removal of “exhaust” air outside.
- Air climate system (air heating) in the house - in this case, internal air circulation is arranged inside the house with supply air mixed into it and exhaust air removed from bathrooms and technical rooms.
The advantage of such a system is that significantly less fresh air is needed for the supply (60 m³/h per resident) and, accordingly, less air is removed through the hood together, which means less heat leaves the house in winter.In addition, it is easy to organize heating or cooling of the air circulating in the house, cleaning and humidifying it, i.e. You can do without a traditional hydronic split heating and air conditioning system. For this reason, such a comprehensive solution is often used in smart homes.
Ventilation system in a “smart home” Source restate.ru
How to heat air using recirculation?
The principle of operation of the device due to recycling:
- The air flow comes from outside into the duct. Part of it, using a special system, is removed back outside the room, and the remainder ends up in the mixing compartment (read separately about the specifics of installing ventilation outlets that lead the air flow outside).
- In the compartment, fresh air enriched with oxygen is mixed with exhaust air, that is, that which was already in the room. Mixing, the air masses are warmed up and sent to the heater or air conditioner, and then into the room.
Recuperator
When arranging supply and exhaust ventilation in private homes, significant savings come from the use of systems with heated supply air, called “supply and exhaust ventilation with recovery.”
Scheme of operation of ventilation with recuperation Source airclimat.ru
Recovery means the process of recycling heat from internal exhaust air with a temperature tb, which is emitted into the street during a cold period with a high temperature, to heat the supply external air. The process of heat recovery occurs in special heat recuperators: plate recuperators, rotating regenerators, as well as in heat exchangers installed separately in air flows with different temperatures (in exhaust and supply units) and connected by an intermediate coolant (glycol, ethylene glycol).
The last option is most relevant in the case when the supply and exhaust are spaced along the height of the building, for example, the supply unit is in the basement, and the exhaust unit is in the attic, however, the recovery efficiency of such systems will be significantly less (from 30 to 50% compared to the PPV in one building.
Local exhaust
This refers to the use of special suction systems that capture and remove harmful flows from the workplace. For example, dust, gases from welding machines. In essence, a local exhaust hood is an air shower, which is “obliged” to remove waste streams, supply fresh ones and, at the same time, lower the temperature in the work area. Such systems are relevant, for example, for melting furnaces.
A special feature of local air exchange is the possibility of using mobile mobile systems. Minimum flow speed 1 m/sec.
Video description
For more information about recuperators, see the following video:
It is important! Including a recuperator in the supply and exhaust system allows you to save up to 70-90% of the heat of the exhausted room air.
Phases of operation of the recuperator in the supply and exhaust ventilation mode in the house Source moydomik.net
Exhaust air exchange
This is the exact opposite of the supply system. The main purpose here is the prompt removal of the contaminated stream. Exhaust ventilation is either general or local. In the first case, the entire room is covered, in the second - a specific workplace. Flows from outside enter the workshops through transoms, vents, and windows. This method of air exchange is usually used in warehouses and utility rooms, i.e., where there is no accumulation of harmful substances hazardous to health.
Features of ventilation of premises of a private house
Any of the premises of a private house, residential and technical, need high-quality air exchange that corresponds to the functional purpose of the room. When arranging the ventilation system of a house, it is necessary to take these features into account.
Ventilation of the underground space
The underground floors of private buildings are characterized by the presence of damp, unventilated areas, which, in conditions of high levels of dampness, lack of sunlight and musty air, are a favorite place for the spread of various fungi. Rapidly growing colonies of microorganisms have a destructive effect on wood, concrete and metal structures.
To ventilate the subfloor of a private wooden house, ventilated openings are arranged in the basement along the entire perimeter of the foundation, creating natural circulation of air masses under the floor. The dimensions of basement ventilation openings for rectangular openings must be at least 100 mm, and for round ones - from 120 mm. The height of the holes is within 300 mm from the ground surface.
Example of underground (cellar) ventilation Source givewhereyoulivehamptons.org
If natural ventilation cannot cope with dampness and mustiness, mechanical means of forced circulation are brought to its aid - fan units located on opposite sides. The operating mode of the fans is determined in accordance with the task. They can work for half an hour several times a day or be turned on for a longer period.
Ventilation of upper floors
When using natural ventilation in two or three-story private houses, the biggest problem is the flights of stairs, which can be considered as large ventilation ducts. The already “exhausted” air from the first floor rises up the stairs, which means that in the building there will be a difference in temperature and humidity levels between the lower and upper floors.
Designers and builders solve this problem by blocking the access of air from the stairs to the floors, or by isolating each room separately. But the second option is practically not used due to its complexity, because in fact, here you will have to make separate ventilation in each room separately.
Video description
For a clear overview of ventilation in a private house, watch the video:
Usually, the doors from the staircase to the floor must be closed for the normal functioning of natural ventilation
In the attic it is always necessary to install forced ventilation, since the standard natural draft is not provided due to the low height of the ventilation ducts.
Kitchen ventilation
To ventilate the kitchen, builders of a private house must provide a separate ventilation duct into which the exhaust air flow will be sucked.
The channel is mounted from galvanized steel sheets or other stainless materials. The surface of the channel should be smooth so that greasy fumes from the kitchen and soot from the stove do not settle on it. The inlet and outlet openings of the channel are protected by grilles.
As in the whole house, air circulation in the kitchen is carried out by natural and forced methods. Those. vents and windows are opened, or a hood is purchased. The latter option is clearly preferable, since the inability of natural ventilation to cope with the odors that appear during cooking is beyond doubt.
Technical advantages of plastic
As already mentioned, service life is one of the most important criteria by which people prefer plastic.
Along with a long service life, air ducts made of this material:
- They are lighter in weight than other materials from which the ventilation system segments are made.
- They are not afraid of slight sagging - up to 4% is acceptable.
- They are easy to install because they can be easily cut with a hacksaw or grinder.
- Reinforced thermal insulation is not required in the roof area.
- The inside has very smooth walls, which makes air circulation through such pipes more active and easier.
You can often see that the owner installs ventilation from the most ordinary PVC sewer pipes. They are cheaper, provide excellent sealing, and a wide range of fittings, tees, revisions, etc. gives them the opportunity to install a ventilation system of any degree of complexity.
The variety of connecting solutions provides excellent ground for those who are planning to install a high-quality and at the same time budget ventilation system from round plastic sewer pipesBut whatever the shape of the air duct pipes, the ventilation system must always fit within the framework of SNiP, which stipulates how any ventilation system should be equipped.
Video description
An example of combining natural ventilation with a hood in the kitchen in the video:
Since a kitchen stove is a constant source of fairly strong odors, the area above the stove needs ventilation most of all, and it is above it that the natural ventilation outlet channel or an electromechanical hood is placed.
When installing ventilation in the gas stove area, first of all, it is necessary to compare the number of burners with the volume of kitchen air space. The standards require:
- for a kitchen space with a volume of more than 8 m³, it is allowed to install a stove with two burners;
- for a kitchen with a volume of 12 cubic meters - no more than three burners;
- for a kitchen of 15 cubic meters - 4 burners.
If this standard is observed, for high-quality air exchange in the kitchen with a gas stove, an air exchange rate of 140 m³/hour is sufficient, and with an electric stove – 110 m³/hour.
Bath ventilation
The air in the bathhouse has its own specific specifics - during bathing procedures the humidity reaches 100%, and when the bathhouse is not in use, everything depends on the quality of air exchange in the room. To comprehensively solve these issues, mixed ventilation is used.
An example of air movement in a bath Source elektroservis-rostov.ru
But since the mechanical part is needed only during the operation of the bathhouse, then, in fact, the most effective natural ventilation is made and fans are added to it. Thus, during operation, the power of the ventilated installation allows you to comfortably steam in the bathhouse, and during its downtime, natural ventilation ventilates the room.
Technically, this is expressed in the arrangement of one or two supply channels and an outlet on which a fan is installed (preferably with an adjustable number of blade revolutions).
It is important! When arranging a bathhouse, one should not forget about floor ventilation. To do this, the floor covering is assembled from boards with a gap of 5 mm between them.
Tips, recommendations, nuances
Often, owners of private houses are lenient when it comes to ventilation requirements for their own home, especially if they may entail additional costs. Here are some misconceptions regarding the use of technical means in residential premises.
- Installing an air conditioner will solve all ventilation problems.
The air conditioner is able to change air parameters, cool or heat the air, and dry it. But it does not create an air cycle. In a house with a working air conditioner, a comfortable temperature will be established, but after a couple of hours the body will feel a lack of oxygen and an excess of carbon dioxide.
Ventilation is always installed along with air conditioners Source anantaircon.podbean.com
- If you install an exhaust fan, this will be enough for good ventilation of the house..
If plastic sealed double-glazed windows and doors are installed, there is no air flow, which means there will be no exhaust/removal of air masses. After a few minutes of operation of the hood, a pressure will be established in the room that simply will not push air to the fan blades.
- Periodic ventilation or an open window for micro-ventilation will solve all problems.
The issue of ventilation will not be fully resolved, since there remain fairly large periods of time during which it will not be possible to ventilate the house, for example, at night. If in the summer this is a solvable issue, then micro-ventilation in the winter is fraught with drafts that will quickly cool the room, preventing it from being ventilated.
- Using equipment with a heater will allow it to be operated at the lowest temperatures
As a rule, equipment with recovery has restrictions on the minimum outdoor air temperature. This is due to the capabilities of the recuperator and the limit is -25…-30 oC. If the temperature drops, the condensate from the exhaust air will freeze on the recuperator, so at ultra-low temperatures an electric preheater or a water preheater with antifreeze liquid is used. (The range of these installations is presented on our website)
Warming the veranda
Without any special details (since you can read about high-quality insulation here), but just for the sake of a reminder. The veranda will be warm if you work with high-quality insulation materials. This could be polystyrene foam or mineral wool, foaming joints, eliminating drafts and minimizing cold bridges, which seriously change the temperature. You can familiarize yourself with the material - do-it-yourself winter garden.
Also, if you are turning an ordinary veranda into a winter one, you need to take care of the windows, because they are the ones who will stop the cold from penetrating inside.
You can install new windows, or you can simply repair old ones, which we suggest reading about in a good article about window restoration and creating high-quality double-glazed windows.