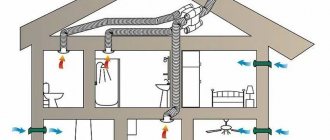
The dry lines of the scientific definition say that ventilation of a private house is a process of specially organized air exchange (from the Latin ventilatio - ventilation) in the residential and utility rooms of the building, in order to maintain the required sanitary and hygienic parameters of the air environment (air composition, its purity, temperature, humidity ). Ventilation is also called a set of technical means and measures that ensure controlled air circulation in a separate room and throughout the building.
The result of all these words is the same - in order to have fresh air in the house, it is necessary to install additional equipment, and what exactly - we asked the specialists of ATM Climate, a company that occupies one of the leading positions in the climate equipment market, to tell us.
General diagram of air exchange in the house Source socialmec.com
Proper arrangement of ventilation, both in apartment buildings and in private buildings, is the job of specialists, since here you will need to make a large number of calculations. At the same time, it would not hurt the owners of private houses to learn the basic principles of how ventilation works - this will help them at least in general terms understand what work will need to be done and how much it will cost.
Why is ventilation needed in a private house?
Air quality must fully ensure the comfortable state of the human body. This is unanimously stated by GOSTs and SNiPs, which regulate the microclimate parameters in premises. The most important factors of a comfortable microclimate include the following indicators of the air environment:
- cleanliness and degree of freshness of the air;
- air temperature and humidity.
To ensure that these indicators always remain within acceptable limits, a ventilation system is installed in a private house, the scheme of which is individually calculated for each individual case.
Ventilation has two main tasks:
- removal of air with a high content of dust and carbon dioxide into the external environment;
- an influx of clean, oxygen-rich air from the street.
8 reasons to install ventilation Source technosip.ru
Premises where the use of recirculation is prohibited
According to the regulatory document SNiP 41-01-2003, ventilation with air recirculation cannot be installed in premises:
- where air mass flow rates are determined based on the amount of harmful substances formed;
- where there are high concentrations of various fungi and pathogens;
- where there are harmful substances that sublimate upon direct contact with heated surfaces;
- which are classified as categories A and B;
- where work is carried out involving the use of harmful and flammable gases, as well as steam;
- which are classified as categories B1 and B2 and where harmful dust and aerosols can be released;
- where there are systems containing local suction of harmful substances and explosive mixtures; their airlock vestibules created.
Air recirculation is limited:
- within the same apartment, hotel room or single-family home
- outside the same room in public buildings
- outside one or more rooms in which equally harmful substances of hazard classes 1-4 are released, except for the rooms listed in the section above “Air recirculation is not allowed.”
Ventilation requirements - air flow rates
The basic indicators for designing a ventilation system are the incoming air flow rates and air exchange rates provided for by the relevant SNiPs:
On a note! The frequency of air exchange or ventilation is the ratio of the volume of air entering during one hour to the volume of the room. The multiplicity parameter characterizes the hourly number of air updates.
- The ventilation system must provide air supply in an amount no less than that required for comfortable stay of people in the room. For one person this is 30 m³/hour if the area of the room is more than 20 m² or 3 m³/hour for each square meter if the area allocated for one person is less than 20 m².
- For residential and associated premises with certain functionality, air flow is determined by the following standards:
- A minimum of 3 m³/hour must flow into the living room for each square meter of area.
- To the bathroom and toilet – 25 m³/hour.
- In a combined bathroom - over 50 m³/hour.
- For the kitchen - depending on the type of stove and the number of burners: electric and gas two-burner - 60 m³/hour; gas four-burner – 90 m³/hour.
A hood over a gas stove as one of the ventilation options in the kitchen in a private home Source deskgram.net
- The air exchange rate of a private house should be within the following limits:
- at least one volume per hour if there are always people in the room;
- at least one volume every 5 hours (0.2 volume/hour) for technical rooms.
Note! The given standards are calculated for indoor air temperature +18 °C and outdoor air temperature +5 °C.
Air distribution calculation
Before starting calculations, you need to understand the parameters of the air stream. First of all, it is assumed that there may be workplaces under a direct stream, because the boundaries of the zone can only be known after calculating the air distribution.
Moreover, in summer the temperature on the jet axis will be lower than the ambient air temperature, and in winter it will be higher. Thus, knowing the air exchange patterns, you need to determine which initial data to pay special attention to. Subsequently, based on them, choose one of the options for arranging air distributors.
Methods for calculating ventilation parameters
Accurate calculation of ventilation in a private home is performed using specialized software, to work with which you must at least know in what order and what data to use. Therefore, in order to do it once and wisely, you need to start with the development of an individual ventilation project for a private house.
But along with such calculations, there are methods of simple calculations that will make it possible to approximately estimate the necessary parameters.
- According to consumption standards.
According to SNiP, air consumption by one person (Vnorm) is approximately 60 m³/hour. This means that to calculate ventilation performance, the formula V=Vnorm*N is used, where N is the number of permanent residents of the house. But the problem with this approach is that residents may be in different rooms or congregate in one. For this reason, this approach is used only for air heating (air climate systems) with air circulation inside the house and with the addition of fresh air in the specified quantities. - According to the frequency of air renewal (calculation by area).
SNiP standards require at least one hourly air renewal. If, in this case, for the comfortable well-being of people in the room, one-time air circulation is not enough, use the formula V=K*S*H, where K is the air exchange rate, S is the total area of a private house, H is the height of the ceilings. The multiplicity index varies from 1 to 3. This approach is the most common, but is associated with a significantly larger volume of air supplied to and removed from the house than in the previous case.
SNiP requirements for air exchange rates in the table:
Source vodakanazer.ru
Exhaust areas
Exhaust ducts remove exhaust air, excess moisture, and odors to the street. Outflow areas for natural ventilation of a private house are equipped in the kitchen, bathroom, bathroom, and, if necessary, in other rooms. Air intake grilles are placed at a height of 0 to 25 cm from the ceiling.
A separate shaft is allocated for the kitchen hood, which is not taken into account in the general calculations (it is turned on temporarily). If there is only one channel, then the equipment is connected through a tee with a check valve. The blades open when the hood is turned off, then the room is ventilated. The mine is considered working, but its increased resistance is taken away in the calculations.
Several channels can be combined into one only with the installation of a fan above all connections; without it, odors will flow between rooms. For the same reason, individual inflow/outflow is organized in technical rooms (basement, garage, furnace room). The doors are closed hermetically so that the flows do not mix with the home air exchange.
Natural and forced ventilation
All ventilation systems are divided into two main types:
- Natural (convective or natural) ventilation. The circulation of air masses here occurs in the same way as in nature - under the influence of draft, which arises due to the difference in temperature, and therefore air pressure in the room and outside the house;
- An artificial (forced) air exchange system, which is carried out by air blowers such as fans or compressors.
Natural ventilation - operating principles and features
The operating principle of natural ventilation is convection - the movement of warm air currents to the upper part of the room and the replacement of departed air masses with cold street air that flows from below. In addition to the temperature difference, the speed of air circulation here is also affected by the wind speed.
Previously, leaks in windows and doors were used to allow air to enter the home. However, modern plastic windows do not have such micro-slits and ventilation valves have to be purposefully installed in the frame or walls. In turn, the “exhaust” air leaves the house through exhaust ducts located in the kitchen, toilet and other rooms.
The principle of operation of convection (natural) ventilation Source bolts-master.com
See also: Contacts of companies that specialize in ventilation and air conditioning.
Natural air exchange has the following advantages:
- economical, since no additional equipment is required to move air flows;
- energy independence;
- trouble-free operation;
- noiselessness.
The disadvantages include:
- low intensity of air exchange, not always able to fully combat the accumulation of unpleasant odors or the formation of condensation;
- poor circulation efficiency due to the dependence of draft on the height of the building and time of year;
- almost complete impossibility of regulating the intensity of air exchange (dampers can be used, but they can only reduce draft, which means they do not always help);
- in summer there is almost no air movement, since the temperatures inside and outside the house are almost equal;
- a large outflow of heat to the street, which significantly increases heating costs;
It is important! In winter, the traction force in the air channels increases, as the temperature difference between inside and outside becomes significant. This leads to an increase in heat loss up to 40% of the total heat loss of the entire house!
- When installing sealed double-glazed windows, the natural flow of air practically stops.
- the need to additionally install special supply valves in windows or external walls.
Ventilation valves - outside and inside the room Source ventazbuka.ru
Features of artificial ventilation
The circulation of air masses in the artificial ventilation system is carried out forcibly due to the operation of electromechanical equipment. Fresh air from the street enters the ventilation unit through the air intake, which distributes the air throughout the rooms of the residential building. Exhaust air is forcibly sucked out of the premises and discharged into the street through exhaust air ducts.
The forced circulation ventilation equipment includes the following elements:
- fan;
- air purification filter;
- silencer;
- air heater/heater;
- air valve.
Even in modern systems, a recuperator can be added to the listed equipment - a device that, by removing heat from the air exhausted to the outside, heats the incoming air.
When installing a ventilation network you will need:
- air vents;
- air intake grilles, diffusers, anemostats.
Ventilation system in a “smart home” Source restate.ru
Advantages of artificial ventilation:
- autonomous operation, independent of environmental conditions (temperature and pressure, building height);
- the ability to bring the parameters of the air supplied to the house to the required values to create a comfortable microclimate (dust removal, heating/cooling, humidification/dehumidification).
Disadvantages of forced ventilation:
- energy dependence of technical means and significant energy costs for heating a large volume of supply air, which provides the necessary air exchange rate, especially in winter;
- significant costs for purchasing equipment;
- the need for regular maintenance.
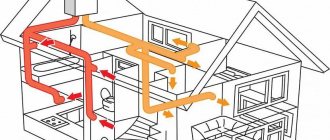
Mixed ventilation type
If there is no need to install forced ventilation in all rooms of the house, then you can consider the option of mixed ventilation. This is what is commonly called the combined use of natural circulation with the installation of mechanical hoods and fans. Typically, forced ventilation is used in the kitchen or bathrooms, and air exchange in other rooms occurs naturally.
Mixed ventilation system Source linternaute.fr
Air recirculation is not allowed:
- from premises in the air of which there are pathogenic bacteria and fungi in concentrations exceeding those established by the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of Russia, or pronounced unpleasant odors
- from premises in which the maximum external air flow rate is determined by the mass of emitted harmful substances of the 1st and 2nd hazard classes
- from rooms in which there are harmful substances that sublimate upon contact with the heated surfaces of air heaters, if air purification is not provided in front of the air heater
- from premises of categories A and B (except for air and air-thermal curtains at external gates and doors)
- from 5-meter zones around equipment located in rooms of categories B1-B4, D and D, if explosive mixtures of flammable gases, vapors, aerosols with air can form in these areas
- from laboratory premises for research and production purposes, in which work can be carried out with harmful or flammable gases, vapors and aerosols
- from local suction systems for harmful substances and explosive mixtures with air
- from vestibule locks
Ventilation operating diagrams
In the practice of arranging ventilation devices, depending on the functions performed, four types of ventilation are defined:
- Supply ventilation in a private house - supplies air from the street to the room.
When double-glazed windows are installed in the house, the “micro-ventilation” mode or special valves are used. But the intensity of air supply depends on weather conditions and is not always able to provide a comfortable microclimate. For artificial ventilation, additional ventilation ducts and devices are installed that purify the street air and heat it to room temperature using an electric or water heater.
What does supply ventilation look like schematically in a private house Source bir.bilagyteco.ru.net
- Exhaust ventilation in a private house removes “exhaust” air from the house to the street.
If a high intensity of air exchange is not needed, then use natural ventilation through ready-made ventilation ducts. But due to the obvious shortcomings of natural ventilation, forced hoods with exhaust fans are more often installed. They are installed both in ventilation ducts and in the ceiling space.
The principle of operation of supply and exhaust ventilation Source mojdominfo.ru
- Supply and exhaust ventilation in the house - in this case, two parallel multidirectional air flows are organized. The first is the supply of oxygen-saturated air into the room, and the second is the removal of “exhaust” air outside.
- Air climate system (air heating) in the house - in this case, internal air circulation is arranged inside the house with supply air mixed into it and exhaust air removed from bathrooms and technical rooms.
The advantage of such a system is that significantly less fresh air is needed for the supply (60 m³/h per resident) and, accordingly, less air is removed through the hood together, which means less heat leaves the house in winter.In addition, it is easy to organize heating or cooling of the air circulating in the house, cleaning and humidifying it, i.e. You can do without a traditional hydronic split heating and air conditioning system. For this reason, such a comprehensive solution is often used in smart homes.
Ventilation system in a “smart home” Source restate.ru
Initial calculation data
The basis is taken from the data obtained from air exchange calculations, as well as the requirements of building codes.
Basic initial data for calculating air distribution:
- firstly, the selected air exchange scheme, and the air exchange determined for it Lin;
- secondly, the length, width and height of the room in meters;
- thirdly, the amount of air inflow L0 = Lin in m3/s;
- supply air temperature t0 = tin, °C;
- normalized air temperature twz of the blown zone, °C;
- normalized air speed Vwz in the ventilated area, m/s.
However, there are times when additional data is needed:
- concentration of harmful substances in the supply air in mg/m3;
- maximum permissible concentration (MPC) of a harmful substance in the work area Swz in mg/m3;
- amount of air removed by local suction, m3/s.
The calculation of air distribution occurs in the following sequence:
- The first step is to determine the scheme. When choosing, the size of the room, architectural features and regulatory requirements are taken into account.
- Finding the normalized difference in temperature and air speed.
- Determining the number of air distributors and their type.
- The pitch of the air distributors is determined.
- Determination of the excess temperature and air speed in the supply jet at the point at which the jet enters the work area.
- Comparison of calculated and standardized values.
- Acoustics check.
We provide a calculated example below.
In conclusion, we can only advise when choosing an air exchange scheme to take into account all possible factors. Using regulatory documents will only make your work easier. In addition, the design guidelines for certain rooms indicate recommended air distribution patterns. These data are obtained as a result of tests and detailed study.
Recuperator
When arranging supply and exhaust ventilation in private homes, significant savings come from the use of systems with heated supply air, called “supply and exhaust ventilation with recovery.”
Scheme of operation of ventilation with recuperation Source airclimat.ru
Recovery means the process of recycling heat from internal exhaust air with a temperature tb, which is emitted into the street during a cold period with a high temperature, to heat the supply external air. The process of heat recovery occurs in special heat recuperators: plate recuperators, rotating regenerators, as well as in heat exchangers installed separately in air flows with different temperatures (in exhaust and supply units) and connected by an intermediate coolant (glycol, ethylene glycol).
The last option is most relevant in the case when the supply and exhaust are spaced along the height of the building, for example, the supply unit is in the basement, and the exhaust unit is in the attic, however, the recovery efficiency of such systems will be significantly less (from 30 to 50% compared to the PPV in one building.
Pros and cons of the system
- PLUS OF THE SYSTEM:
A system with air recirculation allows you to reduce energy consumption for heating air (sometimes for cooling), since the thermal power of the heater or cooler is spent mainly on changing the temperature of only that part of the air that is taken from the street.
- DISADVANTAGES OF THE SYSTEM:
Cannot be used everywhere (see SNiP below)
When operating the system in cold climates, the disadvantage of the system is that the mixing of outside and recirculated air is not good enough.
Video description
For more information about recuperators, see the following video:
It is important! Including a recuperator in the supply and exhaust system allows you to save up to 70-90% of the heat of the exhausted room air.
Phases of operation of the recuperator in the supply and exhaust ventilation mode in the house Source moydomik.net
I “recently” had my ventilation checked, why should I check it again???
This question may be asked by many residents of multi-apartment residential buildings, to which they came with a (formal) check of natural ventilation, attaching a piece of paper or placing a match (highly not recommended for fire safety reasons) to the ventilation duct.
Practice shows that a piece of paper “sticking” to the grille of a ventilation duct cannot always indicate the serviceability of the ventilation system.
Let's look at the ventilation grille located in the kitchen area of a two-room apartment. The kitchen area is 6 m2, the grate is located at a height of 2.4 meters.
A new vent was installed in the cleaned and inspected duct approximately one year ago from this inspection.
Inspection of the ventilation grille, apparently nothing special
Judging by the traces of dirt on the grille, it can be assumed that the ventilation in the room was functioning until recently. An anemometer (a device for measuring air flow speed) shows a speed of 0.5 m/s, which is low for the winter period of the year, but there is still a slight draft. In this case, most likely, the attached piece of paper will stick to the ventilation grille.
If it were not for the readings of the device, then a piece of paper stuck to the grille of the ventilation duct would give reason to assume that the ventilation in the apartment is working properly.
Now let's take a closer look at the ventilation grille
dust on the ventilation grill after a year of operation
I emphasize that the grate was used for only one year in a kitchen area of 6 m2, in an ordinary two-room apartment (Khrushchev), with three people living in it.
Now let's see what's going on under the outer part of the grille
The mosquito net of the ventilation grill is clogged with dust
The photograph clearly shows that the mosquito net of the grill is approximately 70% clogged with dust. And this is just in one year.
You can also understand from the photograph why you cannot check ventilation using a lighter, match, candle, etc. The accumulation of dust and grease deposits can easily ignite, causing fire and fire.
The above example clearly shows the need to periodically check and clean at least the ventilation grilles!
Features of ventilation of premises of a private house
Any of the premises of a private house, residential and technical, need high-quality air exchange that corresponds to the functional purpose of the room. When arranging the ventilation system of a house, it is necessary to take these features into account.
Ventilation of the underground space
The underground floors of private buildings are characterized by the presence of damp, unventilated areas, which, in conditions of high levels of dampness, lack of sunlight and musty air, are a favorite place for the spread of various fungi. Rapidly growing colonies of microorganisms have a destructive effect on wood, concrete and metal structures.
To ventilate the subfloor of a private wooden house, ventilated openings are arranged in the basement along the entire perimeter of the foundation, creating natural circulation of air masses under the floor. The dimensions of basement ventilation openings for rectangular openings must be at least 100 mm, and for round ones - from 120 mm. The height of the holes is within 300 mm from the ground surface.
Example of underground (cellar) ventilation Source givewhereyoulivehamptons.org
If natural ventilation cannot cope with dampness and mustiness, mechanical means of forced circulation are brought to its aid - fan units located on opposite sides. The operating mode of the fans is determined in accordance with the task. They can work for half an hour several times a day or be turned on for a longer period.
Ventilation of upper floors
When using natural ventilation in two or three-story private houses, the biggest problem is the flights of stairs, which can be considered as large ventilation ducts. The already “exhausted” air from the first floor rises up the stairs, which means that in the building there will be a difference in temperature and humidity levels between the lower and upper floors.
Designers and builders solve this problem by blocking the access of air from the stairs to the floors, or by isolating each room separately. But the second option is practically not used due to its complexity, because in fact, here you will have to make separate ventilation in each room separately.
The nuance of ventilation of the upper floors
The second floor is difficult to ventilate well using natural flows - there is a small height difference for traction. If the level is separated by an entrance door, it is ventilated in the same way as the first. But, if the space is not blocked, then individual ventilation of each room is organized on the upper floor. Otherwise, “dirty” air from the first will be drawn to the second floor. This option is difficult to implement for natural traction. Therefore, multi-storey buildings are often equipped with mechanical ventilation.
Gone are the days when rooms were ventilated with wide open windows. After all, fresh air brought with it dust, noise and cold. Modern ventilation in a private house is invisible, it is only felt. Good sleep, lack of dampness and constant fresh air are worth implementing proper air exchange.
Video description
For a clear overview of ventilation in a private house, watch the video:
Usually, the doors from the staircase to the floor must be closed for the normal functioning of natural ventilation
In the attic it is always necessary to install forced ventilation, since the standard natural draft is not provided due to the low height of the ventilation ducts.
Kitchen ventilation
To ventilate the kitchen, builders of a private house must provide a separate ventilation duct into which the exhaust air flow will be sucked.
The channel is mounted from galvanized steel sheets or other stainless materials. The surface of the channel should be smooth so that greasy fumes from the kitchen and soot from the stove do not settle on it. The inlet and outlet openings of the channel are protected by grilles.
As in the whole house, air circulation in the kitchen is carried out by natural and forced methods. Those. vents and windows are opened, or a hood is purchased. The latter option is clearly preferable, since the inability of natural ventilation to cope with the odors that appear during cooking is beyond doubt.
Channel planning and calculation
The cross-section of the air ducts depends on the ventilation system and the volume of air that needs to be served. The parameters can be taken from the table, taking the speed of natural draft to be 1-2 m/s, mechanical – 3-5 m/s:
Table 2 - selection of duct cross-section
An example of calculating the cross-section of an air duct:
450 m3/hour is discharged by four channels. Accordingly, for each there are 450/4 = 115 m3/hour. Using the table presented above, we find that at a speed of 2 m/s, a pipe Ø140 mm is sufficient.
Good natural traction occurs only in vertical shafts (a deviation of 30° up to a meter is allowed). Constrictions and cuts slow down the flow, while horizontal sections practically stop it. Mechanical advancement gives stable, uniform draft, where all the voiced nuances are simply taken into account when choosing the fan power.
Video description
An example of combining natural ventilation with a hood in the kitchen in the video:
Since a kitchen stove is a constant source of fairly strong odors, the area above the stove needs ventilation most of all, and it is above it that the natural ventilation outlet channel or an electromechanical hood is placed.
When installing ventilation in the gas stove area, first of all, it is necessary to compare the number of burners with the volume of kitchen air space. The standards require:
- for a kitchen space with a volume of more than 8 m³, it is allowed to install a stove with two burners;
- for a kitchen with a volume of 12 cubic meters - no more than three burners;
- for a kitchen of 15 cubic meters - 4 burners.
If this standard is observed, for high-quality air exchange in the kitchen with a gas stove, an air exchange rate of 140 m³/hour is sufficient, and with an electric stove – 110 m³/hour.
Bath ventilation
The air in the bathhouse has its own specific specifics - during bathing procedures the humidity reaches 100%, and when the bathhouse is not in use, everything depends on the quality of air exchange in the room. To comprehensively solve these issues, mixed ventilation is used.
An example of air movement in a bath Source elektroservis-rostov.ru
But since the mechanical part is needed only during the operation of the bathhouse, then, in fact, the most effective natural ventilation is made and fans are added to it. Thus, during operation, the power of the ventilated installation allows you to comfortably steam in the bathhouse, and during its downtime, natural ventilation ventilates the room.
Technically, this is expressed in the arrangement of one or two supply channels and an outlet on which a fan is installed (preferably with an adjustable number of blade revolutions).
It is important! When arranging a bathhouse, one should not forget about floor ventilation. To do this, the floor covering is assembled from boards with a gap of 5 mm between them.
Advantages and disadvantages of the design
The installation of ventilation of this type does not differ from the standard placement of similar household appliances, but their autonomy is much higher. They are not tied to the ventilation system, so the designers have developed a number of compact retractable hoods that use recirculation. They are called telescopic hoods. During operation, they carry out filtration by creating a strong lateral draft, sucking in all contaminants along with the air flow. After switching off, the system is recessed into the tabletop, very convenient and original.
Advantages
This type of device has slightly less performance and power, but this has allowed manufacturers to reduce their cost, which only pleases users. All components of the systems experience less load, so they can operate without accidents for much longer.
When such a system operates, there is no room for reverse thrust. The autonomous location allows for free installation of the stove - users place it where it is most convenient for them, regardless of the location of the entrance to the ventilation shaft. Recirculating hood Recirculating hood in the kitchen interior
Tips, recommendations, nuances
Often, owners of private houses are lenient when it comes to ventilation requirements for their own home, especially if they may entail additional costs. Here are some misconceptions regarding the use of technical means in residential premises.
- Installing an air conditioner will solve all ventilation problems.
The air conditioner is able to change air parameters, cool or heat the air, and dry it. But it does not create an air cycle. In a house with a working air conditioner, a comfortable temperature will be established, but after a couple of hours the body will feel a lack of oxygen and an excess of carbon dioxide.
Ventilation is always installed along with air conditioners Source anantaircon.podbean.com
- If you install an exhaust fan, this will be enough for good ventilation of the house..
If plastic sealed double-glazed windows and doors are installed, there is no air flow, which means there will be no exhaust/removal of air masses. After a few minutes of operation of the hood, a pressure will be established in the room that simply will not push air to the fan blades.
- Periodic ventilation or an open window for micro-ventilation will solve all problems.
The issue of ventilation will not be fully resolved, since there remain fairly large periods of time during which it will not be possible to ventilate the house, for example, at night. If in the summer this is a solvable issue, then micro-ventilation in the winter is fraught with drafts that will quickly cool the room, preventing it from being ventilated.
- Using equipment with a heater will allow it to be operated at the lowest temperatures
As a rule, equipment with recovery has restrictions on the minimum outdoor air temperature. This is due to the capabilities of the recuperator and the limit is -25…-30 oC. If the temperature drops, the condensate from the exhaust air will freeze on the recuperator, so at ultra-low temperatures an electric preheater or a water preheater with antifreeze liquid is used. (The range of these installations is presented on our website)
Positive and negative points
Although filter hoods have a low capacity, they have many advantages.
These include:
- ease of installation and operation;
- unlimited choice of placement of the stove, because a ventilation shaft is not needed for this;
- easy care.
These exhaust devices also have disadvantages. This is a small efficiency - up to 70%, the need for frequent replacement of disposable filters - 3-4 times in 24 months. The hood does not affect the humidity level in the room in any way. The electric drive of the device when turned on creates a certain noise.
Small, compact hoods are becoming increasingly popular because they save space. This design can be installed anywhere
Hoods of the latest releases, as a rule, can operate both in air mass removal mode and as recirculation mode. Such a device must have a connection to the ventilation shaft.
Since a stand-alone hood does not provide fresh air, it is necessary to ventilate the room after turning it off.
Supply valves
The need to use valves is caused by the complete tightness of modern window structures, which prevents the penetration of street air into the house through the gaps between the frame and the frame, as happened previously with ordinary wooden windows. Even if in a small volume, there was still an influx. The entrance doors, which did not have several sealing contours, as they do today, cracks under the window sills and other “leaks” also contributed. Of course, you can let fresh air into the house by setting the tilt-and-turn window sash to ventilation mode, but do not forget that you will have to do this constantly - both in winter and summer, regardless of the weather. Just like through an open window, rain moisture, dust and noise easily penetrate into the resulting gap (sound insulation is reduced by almost half) and blow noticeably, and in winter a cold zone appears around the perimeter of the sash and ice may even appear on the frame. In addition, when there is a gust of wind, the window “whistles” and slams strongly, loosening the hinges and creating serious acoustic discomfort. One more nuance: a window with slot ventilation is a real gift for a burglar.
All these problems can be solved by equipping windows with ventilation valves. Models of different brands differ in performance, installation method, type of control and adjustment capabilities.
An example of such devices is the REHAU AEROVENT+ ventilation valves, which are three slotted holes made with a milling cutter in the upper part of the rebate and closed on both sides with covers.
The slots can have different sizes, and the total length of the valves ranges from 275 to 700 mm. The outer cover is equipped with a mosquito net and a self-regulating damper curtain: it covers the channels in the event of strong wind pressure or large thermal differences, thereby limiting excess inflow. The inner cover is designed to direct the stream of outside air upward, under the ceiling. There it quickly mixes with the warm air of the room, acquires a comfortable room temperature and replaces the exhaust air completely imperceptibly for humans - without “icy blows” and drafts. The valve operates on natural draft, without requiring user participation in the process, and it can be equipped with a window with any profile thickness, not only at the manufacturing stage, but also when it is already installed in the opening.
The slot holes in the vestibule are covered with a special lid
The REHAU AEROVENT+ cover has an acoustic foam insert
To determine the maximum performance of the valve, a pressure difference of 10 Pa is used: for AEROVENT+ this figure is 30 m³/h, which is the sanitary standard for fresh air supply per person
When equipping a window with a ventilation valve, the temperature in the room decreases by no more than 1–2⁰С. Its influence on the soundproofing properties of the structure is also minimal: the noise level increases by only 1–2 dBA, to which the human ear is immune. , an acoustic foam insert can be placed in the device cover
which will serve as an additional barrier to noise.
REHAU has developed GLASSOVENT valves (AR75) especially for large houses. They are designed to ventilate several rooms at once (maximum length of products is 2.5 m) and reach a productivity of 113 m³/h per linear meter of device. The model provides both manual and electric control and a four-stage adjustment system. The valve is located between the end of the glass unit and the sash profile, so in the case of a previously installed window, the unit will need to be replaced. The equipment of the devices includes hollow (heat-insulated) dampers, as well as highly efficient electrostatic fine filters Pollux.
Since with the installation of a ventilation valve it is no longer necessary to open and close the shutters many times a day, the load on the fittings and seals is removed, which eliminates the need for frequent window adjustments and ultimately significantly extends its service life
Design of a wall supply valve
Instead of window valves, you can use wall valves, and in rooms without windows (pantry, dressing room) they are generally the only option.
The devices are a tube with a diameter of 40 to 160 mm and a length of 200 to 1000 mm, at the outer end of which there is a protective grille or cap, and at the inner end there is a compact block with a valve mechanism. They are mounted in a through hole in the wall in the window area (if there is one), the main thing is that the supply stream quickly mixes with the warm air rising from the radiator. There are valves that require installation under the window sill or directly behind the heating radiator. The products are equipped with heat and sound insulating liners, filters, temperature and humidity sensors with automatic adjustment of flow intensity.
Valve Vents TwinFresh RA-50-2, price 9040 rub.
Valve Blauberg Fresher 50, price 15,000 rub.
Vents 102 valve with solar battery, price RUB 5,400.
Sill valve
Another option for supply valves is window sill valves.
The products are about 400 mm wide and are installed directly behind the edge of the window sill above the radiator. The air intake duct runs under the window structure and is covered from the outside by ebb, so that when viewed from the street the device does not reveal itself in any way. The valves do not reduce the soundproofing properties of the window, do not violate its integrity and do not require making holes in the walls. The products are heat and sound insulated, equipped with a filter and allow you to regulate the volume of incoming air by smoothly moving the damper.
Design and principle of operation of a car heater
The interior is heated using engine coolant. It takes heat from a running engine and, passing through the radiator, transfers it into the car interior.
The design of a car heater, better known as a “stove,” consists of several main elements:
- radiator;
- pipes for coolant circulation;
- fluid flow regulator;
- air ducts;
- dampers;
- fan
The heating radiator is located behind the dashboard. Two tubes are attached to the device that transfer coolant inside. Its circulation throughout the car and heating of the interior is ensured by a pump.
As soon as the motor heats up, it takes away the heat emanating from it. Next, the heated liquid enters the stove radiator, heating it like a battery. At the same time, the heater fan circulates cold air. Heat exchange occurs again in the system: heated air passes further into the cabin, and colder masses cool the radiator and antifreeze. The coolant then flows back to the engine and the cycle repeats.
Inside the cabin, the driver regulates the direction of the heated flows by switching the dampers. The heat can be directed onto the motorist's face or feet, or onto the car's windshield.
If the ventilation system is bad
If there are disturbances in the air inflow or outflow, then:
Carbon dioxide will accumulate in the room
Consequences: feeling of stuffiness, increased fatigue, lethargy, loss of concentration. It’s also difficult to get a good night’s sleep in a stuffy room.
Humidity balance may be disrupted
If the air stagnates, moisture can accumulate in it. Poor ventilation is a common cause of dampness and mold.
Pollution accumulates in the air
Dust, animal hair, mold spores, anthropotoxins, harmful chemical emissions from furniture (for example, formaldehyde) - all this “enriches” the air in conditions of poor ventilation and ultimately enters our body through the lungs.
THE OPERATION OF THE VENTILATION SYSTEM AFFECTS THE WELL-BEING OF A PERSON IN THE ROOM, HIS PERFORMANCE, CONCENTRATION AND QUALITY OF SLEEP.
Therefore, it is important to choose high-quality ventilation that will cope with the needs for air exchange and provide a comfortable microclimate
Where is the power button
The location of the recirculation button varies depending on the model of your car, but there are two generally accepted symbols (icons) that make them easy to find.
The buttons look like this:
- Turn on recirculation. The button depicts a car, inside of which there is a reverse arrow, similar to a U-turn sign.
- Turning on the fence from the outside. It is located next to the button described above and looks the same, except that the arrow is directed from the environment to the interior of the car.
Unfortunately, these designations are not typical for all models. For example, on VAZ cars the recirculation button looks like a circle of three lines and is located to the left of the temperature control. Or it may look like arrows arranged in a circle.
For those whose car is equipped with climate control, the question of using or not using this mode largely disappears, since climate control takes care of the cleanliness and temperature of the air.
The principle of recycling is applicable not only to cars, but is also actively used at home and in industrial areas.
For example, built-in hoods in the kitchen, which work on the same principle as described above, do not allow you to connect to a stationary ventilation pipe, but purify the air used through integrated filters.
What does supply ventilation consist of?
- Air intake grille. Through it, street air enters the system. Performs a barrier function and prevents the absorption of debris. Can be equipped with a mesh to improve protection.
- Ducts are key components of the system. Through a network of ventilation ducts, fresh air enters the premises. The main characteristics are: cross-sectional area, shape (round or rectangular) and rigidity (there are rigid, semi-flexible and flexible air ducts).
- The air valve serves to shut off the ventilation duct when the system is turned off. Models with manual and automatic control are available on the market. The design may use a check valve that allows air to flow in only one direction.
- The air filter is installed in all ventilation systems and serves to protect serviced premises and equipment from dust, fluff, insects and other pollutants.
- The fan is the basis of any artificial ventilation system. There are 2 types of fans used: axial and radial (centrifugal).
- The throttle valve regulates the volume and speed of flow. Installed on main branches - peripheral sections of air ducts.
- Air distributors (grills and diffusers) are installed at the outlet of the ventilation duct and serve to uniformly distribute air throughout the serviced room.
- The noise suppressor reduces the sound effect of operating fans.
- The automation system is used to control the elements of the ventilation system. Allows you to regulate the fan speed and air temperature, and controls the safety of the system.
The main structural components of the installation system are listed above. Additionally, the supply ventilation unit can be equipped with a recuperator, air humidification, dehumidification and cooling system.
Right choice
How to make ventilation? If you are just planning to build a house, be sure to determine the state of the environment. A polluted atmosphere does not contribute well to a favorable microclimate in your home. In such cases, it is worth making ventilation with additional cleaning filters and special equipment in the system. Passing through them, the air can not only be purified, but also cooled.
The next important factor when choosing ventilation is the material from which the house is built. In recent years, modern building blocks and wall insulation have been mainly used for construction. Their introduction into the construction process necessitates the presence of special mixed-type ventilation devices.
Specifications
The heat recuperator consists of a housing, which is covered with heat and sound insulating materials and is made of sheet steel. The device body is quite durable and can withstand weight and vibration loads. The housing has inflow and outflow openings, and air movement through the device is ensured by two fans, usually of an axial or centrifugal type. The need to install them is due to a significant slowdown in natural air circulation, which is caused by the high aerodynamic resistance of the recuperator. To prevent the suction of fallen leaves, small birds or mechanical debris, an air intake grille is installed on the inlet located on the street side. The same opening, but on the room side, is also equipped with a grille or diffuser that evenly distributes air flows. When installing branched systems, air ducts are mounted to the openings.
In addition, the inlets of both flows are equipped with fine filters that protect the system from dust and grease droplets. This protects the heat exchanger channels from clogging and significantly extends the service life of the equipment. However, the installation of filters is complicated by the need to constantly monitor their condition, clean them, and, if necessary, replace them. Otherwise, a clogged filter will act as a natural barrier to air flow, causing resistance to increase and the fan to break.
In addition to fans and filters, recuperators include heating elements, which can be water or electric. Each heater is equipped with a temperature relay and is capable of automatically turning on if the heat leaving the house cannot cope with heating the incoming air. The power of the heaters is selected in strict accordance with the volume of the room and the operating performance of the ventilation system. However, in some devices, heating elements only protect the heat exchanger from freezing and do not affect the temperature of the incoming air.
Water heater elements are more economical. This is explained by the fact that the coolant that moves along the copper coil enters it from the heating system of the house. The coil heats the plates, which, in turn, give off heat to the air flow. The water heater regulation system is represented by a three-way valve that opens and closes the water supply, a throttle valve that reduces or increases its speed, and a mixing unit that regulates the temperature. Water heaters are installed in an air duct system with a rectangular or square cross-section.
Electric heaters are often installed on air ducts with a round cross-section, and they use a spiral as a heating element. For correct and efficient operation of the spiral heater, the air flow speed must be greater than or equal to 2 m/s, the air temperature must be 0-30 degrees, and the humidity of the passing masses must not exceed 80%. All electric heaters are equipped with an operation timer and a thermal relay that turns off the device if it overheats.
In addition to the standard set of elements, at the consumer’s request, air ionizers and humidifiers are installed in recuperators, and the most modern models are equipped with an electronic control unit and a function for programming the operating mode, depending on external and internal conditions. The instrument panels have an aesthetic appearance, allowing the heat exchangers to fit seamlessly into the ventilation system and not disturb the harmony of the room.
How is the supply ventilation system automated?
Automation regularly checks temperature, air humidity and other functional indicators. The complex consists of sensors, ventilation control panels and actuators. How it works? Parameters are monitored by sensors whose signals are sent to centralized controllers. These devices, if necessary, transmit signals to actuators.
Example: the temperature drops - the heater starts. The CO2 level has increased - the air supply unit is activated.
To control the standard level of air exchange and ensure stable indicators of air inflow and outlet, automation of the ventilation system is required.
Advantages of automatic control:
- reduction in staff costs;
- automatic startup and shutdown of equipment during abnormal and emergency events;
- reducing energy consumption by optimizing operation;
- Thanks to automation, it is possible to protect the ventilation system from power failures and short circuits.
Things to consider
When installing a modern ventilation system in a house, it is necessary to take into account the main criteria by which the equipment is selected. These include:
- maximum possible power of the ventilation unit;
- working pressure value;
- noise level.
The speed of circulation and replacement of exhaust air flows depends on the cross-section of the air ducts and their location. To ensure its high value, it is necessary to create a system of ventilation ducts of the same diameter and ensure a minimum number of turns.
When building a house
When building a private house from scratch, you need to pay increased attention to the ventilation system. At the stage of wall construction, it is necessary to carry out calculations using the formula described above and, based on the data obtained, create a ventilation system
Conclusion
Now you know what forced ventilation is, its structure, what it is needed for, principles of operation, types, pros and cons of the system. The cleanliness of the air in the apartment largely depends on the supply ventilation system. When choosing equipment, you need to take into account the location of the building, the area of the room and the number of rooms, exhaust power and other factors.
If the installation is installed at a commercial or industrial facility, it should be equipped with an automation system to control microclimate indicators. It is better to entrust the installation of fresh air ventilation in an apartment, house or factory to professionals, for example, specialists from the engineering company Qwent.