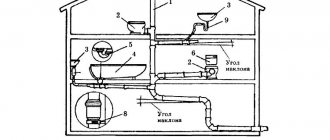
The durability of a private house made of any building material largely depends on regular ventilation of the space located under the lower ceiling. The ideal option is when underground ventilation in a private house is designed and implemented during the initial stage of construction. Then it is calculated and arranged correctly.
You will learn everything about the competent organization of a system designed to remove excess moisture from structures partially or completely buried in the ground in the following article.
We will talk about the important functions performed by ventilation. We will show you how to correctly position and install components designed to remove exhaust air and supply fresh air.
Causes of moisture
The problem of wood floors dying has been known to builders since time immemorial. In order to understand the condition of the floorboards and the presence of moisture under the boards, two methods were used:
- An obese, heavy man with a load in his hands was asked to walk along the edges of the floorboards in the room, furthest from the windows and doors. If the sagging of the boards was not accompanied by a squeak, the floors could be considered unhealthy;
- The second sign was considered to be the presence of a heavy “earthy spirit” or swampy smell, indicating high humidity and the presence of wood rotting products in the air. Even internal airing and ventilation did not help get rid of dampness;
- In the absence of ventilation, sections of the walls adjacent to the floor above the baseboards looked earthy, the whitewash or wallpaper changed color, often acquiring a reddish tint.
Today it is known that even the absence of the listed signs does not guarantee a normal level of humidity in the underground. The reasons why moisture accumulates under floorboards can be very different. From improper ventilation of the subfloor waterproofing, lack of vents through which air penetrates under the boards, to leaking water pipes or, even worse, sewer outlets.
For your information! Improper floor ventilation can also occur in apartments in multi-storey buildings, especially if these are rooms on the first or last floors of the building.
It does not save a room with improper ventilation, even if the walls and ceilings in the building are made of treated wood. The floor of a wooden house in the absence of ventilation is destroyed in the same way as in ordinary stone or frame buildings. The protective impregnation or coating penetrates just a few millimeters deep into the wood. If cracks form on the surface of wooden logs, beams or boards, even with impregnation, the fungus easily attacks the wood.
There is only one way out - to properly ventilate the floor. In this way, you can protect your home from many health problems, the origin of which we know nothing about.
Why is it necessary to provide underground ventilation? (+video)
Normal ventilation for this space is necessary to prevent high humidity. It can occur from autumn to spring due to:
- groundwater;
- melting wall, rain;
- condensate
If the subfloor is not ventilated, high humidity in it leads to the following problems:
- The appearance of mold.
- Dampness on the first floor.
- Acceleration of destruction of wooden elements (beams, joists).
A common situation: the house was built well, insulated, with a good heating system. But in winter the floor is damp for some reason. This happens precisely because the underground floor of the cottage is not ventilated, the humidity in it rises, and the floor boards become saturated with moisture - which is why it is already felt in the living quarters.
This situation is especially dangerous for a wooden house - because wood is most “afraid” of moisture, and most quickly deteriorates because of it.
Types of organization of air exchange in the subfloor of a house
From the above we can conclude: due to the described features, air exchange in the basement of a wooden house needs appropriate adjustment.
In addition, it would be useful to ventilate the floor in a private house. For this purpose, the floor structure is usually chosen to be floating.
Forced ventilation is more expensive, but also more effective. Its distinctive feature can be considered the use of special electrical appliances to increase the speed of air flow in the basement.
Typically, a forced ventilation system works in conjunction with natural ventilation.
The choice of ventilation scheme is carried out at the design stage of a wooden house. Its installation and installation must be carried out simultaneously with its construction.
This significantly reduces labor costs, because during construction, pipes for the required number of inlet and outlet channels can be immediately laid.
Then, after finishing the laying, drilling large-diameter holes in the concrete foundation is an extremely thankless task.
Features of natural air circulation
It is advisable to consider a natural ventilation system for the subfloor at the construction stage.
After the future ventilation scheme for the subfloor of a wooden house has been selected at the design stage, you can begin to implement the design solution. In any case, it is necessary to make mortgages for natural ventilation.
They are scraps, usually of plastic sewer pipes with a cross-section of 120 mm in diameter or can be square in shape. The length of these elements is equal to the thickness of the foundation walls.
Wooden houses are most often built:
- on a strip foundation: its walls are located under all the walls of the house. During pouring, the elements mentioned above are inserted into the foundation body to organize air passages in the foundation;
- on a columnar foundation: piles or pillars, for example, made of brick, are connected to each other along the perimeter of the house. The subfloor is supported in the same way on individual pillars. In this case, gaps are left between the rough and finished floors and between the floor and the walls, which serve for natural ventilation. Mortgages for supply channels are made in the outer plinth belt;
- on a solid concrete slab: in this case, ventilation ducts for the subfloor are installed in the baseboards of wall structures.
As a matter of fact, the channels that serve to pass air form the main part of the natural ventilation system of the underground space. From the material presented above, it becomes clear how to ventilate the basement.
You can do the work yourself. The easiest way to do this is at the stage of pouring the foundation and construction.
Forced air exchange system
It happens that the power of natural ventilation is not enough to effectively remove excess moisture from the subfloor. This is most common in homes that have large basements.
And here there is no way to do without installing forced ventilation.
For its proper operation, it is necessary to have supply ventilation ducts, which are located in the body of the foundation or base. In addition, vertical exhaust ducts must be installed to remove air from the subfloor.
They are also made from plastic pipes or boxes and must go outside through the roof. Such a system of channels will enhance the natural flow of air due to the temperature difference between the street and the basement. Exhaust air will be extracted continuously.
You can enhance the removal of exhaust air from the underground using fans that are installed in the supply ducts or in the exhaust manifolds. The use of such devices makes the ventilation system forced.
It remains to add that there are many types of forced ventilation. But these systems are rarely used in small private homes due to their high cost. Most often, in this case, a couple of fans in the basement will do the job.
What should be the vents in the foundation and how to position them
Ventilation holes in the foundation are made of round or square cross-section. If desired, it can be triangular or any other shape. If only they were large enough in area to effectively remove moisture from the subfloor.
Dimensions
The dimensions of ventilation holes in the foundation are regulated by SNiP (SNiP 31-01-2003). Paragraph 9.10 states that the area of the vents must be at least 1/400 of the total area of the subfloor. For example, if you have a house measuring 8*9 m, the underground area is 72 square meters. m. Then the total area of vents in the foundation should be 72/400 = 0.18 sq.m. or 18 sq. cm.
The same paragraph of the standard specifies the minimum ventilation area - it should not be less than 0.05 sq.m. If we translate into dimensions, it turns out that rectangular holes should not be less than 25*20 cm or 50*10 cm, and round ones should have a diameter of 25 cm.
Larger holes can be made
In multi-storey buildings this is done, but in private buildings such holes look too large. Usually they are made two times smaller, while increasing the number of vents so that the total area of the vents is not less than the recommended one.
How to position
Make vents in the foundation 15-20 cm below the top edge of the tape. If the base is low, a recess is made in front of the vent - a pit. But ventilation of the underground is required.
The vents in the base are placed evenly on all sides of the foundation opposite each other. This is necessary for the foundation ventilation to work properly. The wind, “flying” into one hole, will fly out into another, taking with it water vapor and radon.
The distance between two adjacent vents in the basement is about 2-3 m. If there are any partitions inside, at least one vent is needed for each “room”. It is also necessary to make vents in the partitions themselves to allow air masses to move and form a draft. This is exactly what we need. In order for movement to be more or less free, the area or number of holes in the internal partitions must be larger and better, if it is 2-3 times larger. You can make several holes the same size as in the base, or you can make one, but wide one. The second option, by the way, is preferable - the resulting passages can be used to service the underground.
If you don’t find a grate of a suitable diameter, you can do this
Vents in the foundation of any format must be covered with gratings to prevent living creatures from entering the underground. It is desirable that the grilles are metal and the holes are small. For mice, plastic is not a problem, and keeping them out is easier than dealing with them later.
This option improves ventilation conditions and protects against rodents
Forced ventilation: basic elements and design rules
Unlike natural ventilation, where air moves due to pressure differences, in forced ventilation, gas movement is created by electrical appliances. These are fans of various types, some of which are very technologically advanced. They maintain a given temperature and humidity regime, purify the incoming air, and also carry out recovery - transferring heat from heated air masses to cold ones.
In home basements, all these complex devices are not necessary. As a rule, the simplest manually operated devices are used. More advanced installations with control sensors are relevant for large vegetable stores, wine cellars and other objects where it is necessary to maintain certain conditions. For a private cellar, the main thing is efficiency and safety.
Forced ventilation can be organized in various ways:
- install the fan in the exhaust duct;
- install 2 fans in two pipes at once;
- use a rotating diffuser-vane, which is attached to the top of the exhaust pipe and operates from the wind pressure;
- place an incandescent lamp inside the hood; when heated, the air will rise to the top faster, thus stimulating the evacuation of contaminated gases from the cellar.
Since the basement is a room with high humidity, when installing and operating electrical appliances, you must carefully monitor compliance with electrical safety rules. It is prohibited to use 220 V sockets. It is necessary to install a step-down transformer so that the supply voltage does not exceed 12 or 36 V. Accordingly, the electrical equipment must be designed for these loads.
Calculation of the required section
In many cases, a single-pipe hood turns out to be quite effective, so its installation (with subsequent testing) is technologically justified. Work on proper ventilation of the cellar begins with cross-section calculations. If you skip this step, then the pipe section will have to be chosen at random. You may simply not guess correctly, and then the air exchange will be disrupted.
Professional formula calculations for hooding include many variables; they are needed for complex forced ventilation systems, and are not always convenient. For the conditions of a small private cellar, a simplified calculation scheme is suitable. To correctly select the required pipe diameter, perform the following calculations:
- The cellar area is determined by multiplying its length and width.
Calculations for a small cellar Source metasold.com
- Calculate the total area of the ventilation openings, taking into account the fact that per 1 m² of area it is necessary to provide 26 cm² of exhaust duct (normative data). For example, with a room area of 6 m², we get 6x26 = 156 cm² - the total area of the channels (or one channel).
- The radius of the pipe is determined by the formula R=√S/π=√156/3.14=3.67 cm. Therefore, the cross-section will be 8 cm (the value of 7.34 cm is rounded up). For better functioning, the indicator is increased by 10-15%, that is, up to 9 cm.
The need to arrange air exchange in the house
A well-thought-out and correctly implemented ventilation scheme in the house acts as a guarantor and basis for the formation of comfortable living conditions.
Ventilation of premises, provided by various systems and additional devices or devices, is a mandatory process due to the following factors:
- the ability to regulate temperature conditions and create comfortable conditions;
- adjustment of humidity parameters necessary for normal life;
- saturation of all rooms with oxygen and removal of contaminated gas-air mixture;
- removal of unpleasant and specific odors or steam from target premises;
- preventing the deposition of condensate, which provokes the development of fungus and mold.
A high-quality and well-organized air exchange process in a residential building plays a big role and requires careful planning.
Why is floor ventilation needed?
Ventilation for wooden floors is necessary for one simple reason: wood without proper ventilation begins to gradually become damp and rot, that is, to collapse.
And the base, the so-called subfloor, on which the insulation will subsequently be laid, is made of wood. The gradual destruction of wood will inevitably lead to the fact that one day the floor will simply collapse. You will have to disassemble the entire structure and reassemble it, this time following all the rules. But there is a danger much greater than the collapse of the floor structure. These are fungi and mold that can multiply in underground dampness. Fungal spores can cause catastrophic damage to the health of people living in the house, causing serious illnesses. And if there is increased dampness in the house when the heating is turned off, this is a pretty serious cause for concern. So ventilation of a wooden floor is a necessary thing.
Additional humidity reduction
To ensure that the ventilation system does not have to be strengthened by increasing the total cross-section or installing fans, the following work must be carried out:
- Installation of an effective drainage system - removal of water from the foundation.
- Waterproofing the base of the house and the basement. There are many types of waterproofing: it can be rolled, built-up, coated, etc.
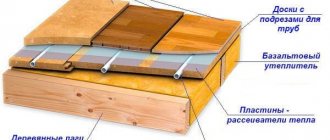
- Performing insulation. The best material in terms of economy and efficiency is EPS. This is a good heat insulator that does not allow water to pass through. It is not of interest to rodents and does not rot. EPS can also insulate the blind area.
The listed measures do not cancel, but simply supplement ventilation. Only in combination can you achieve ideal drainage of the space in the basement compartments.
If the house is built on a soil foundation that does not drain water well, in addition to the ventilation system, drainage and storm drainage are required. The drainage system will collect water from the soil and upper layers of soil, the storm drain will collect and drain precipitation
When installing a system according to a forced scheme, the costs for installation, maintenance and service will be higher than when organizing a natural type. It should be taken into account that in winter condensation can form on the walls of the ventilation pipes themselves, and in cold weather the cross-section can become completely clogged.
To avoid this, pipes can be thermally insulated with penofol. At the bottom turn of the pipe, you can come up with a condensate collector - for example, drill a hole or install a tee instead of an angle.
How to make perfume
Vents are formed at the foundation manufacturing stage. If we are talking about a strip monolithic foundation, then the embedded parts are laid and secured after installing the reinforcing frame. To organize round vents, plastic or asbestos-cement pipes are laid. Their edges are brought flush with the outer edge of the formwork and secured well. If plastic pipes are used, sand is poured into them and the edges are closed with plugs. This is necessary so that the mass of concrete does not flatten them when pouring. These mortgages are not removed after the formwork is removed.
Installed plastic pipes for vents in the basement
Rectangular vents are formed from boards, knocking down a box of the required size. It is also installed in formwork, but after the concrete has set, the wood is removed.
If the base is built of brick, you can periodically trim the bricks or install a half instead of a whole. In concrete block plinths, take several pieces with two large holes and make them through. Installed instead of one of the “normal” ones. If the foundation and plinth are built from reinforced concrete blocks, vents are made at the joints.
The formwork was removed
Vents are organized in approximately the same way in columnar and pile (screw, bored, TISE) foundations. When the gaps between the supports are covered with the selected material, the required number of holes is left, the total area of which is equal to 1/400 of the area of the subfloor.
This way you can insert a pipe for an vent into a base made of blocks
An example of the formation of a vent in a wooden house made of logs. Vents in a brick plinth. Cover with a fine mesh grille.
Do-it-yourself forced ventilation in the cellar
In fact, forced ventilation differs from natural ventilation only in that fans are installed inside the pipes (ventilation ducts), which provide more intense air flow and removal (Figure 4).
Principle of operation
The principle of operation of forced ventilation is quite simple. In the simplest version, the fan is installed only on the exhaust pipe. This creates more active air movement through the inlet.
In large rooms, it makes sense to install both exhaust and supply fans. In this case, it will be difficult to cope on your own and it is better to contact a specialist who will help you determine the appropriate pipe diameter and fan power.
Equipment
Since forced ventilation is considered more reliable and modern, additional equipment will be required to install it. Of course, first of all you need to prepare the required number of channels of suitable diameter. After this, you should buy fans of the appropriate size and power.
Figure 4. Basic elements of forced ventilation
It is also necessary to provide waterproofing of devices from moisture, which may enter the room from the outside or seep through the walls.
DIY system installation
Forced ventilation is a little more difficult to install than natural ventilation. So that you can carry out the installation yourself, we recommend using our step-by-step instructions.
Forced exhaust in the cellar is installed as follows:
- Holes are drilled in the walls or ceiling for laying channels, or voids that were previously left for this purpose during the construction phase are used.
- Pipes are laid in the holes. You can use metal, plastic or cement products.
- The supply and exhaust pipes are installed in opposite corners of the room and at different levels, as is the case with natural ventilation.
- A fan is mounted inside each pipe and dampers are installed so that the intensity of ventilation can be adjusted if necessary.
The upper parts of the pipes protruding to the surface must be covered with canopies. In the case of natural ventilation, this requirement is more of a recommendation, while for the forced type it must be observed, since rainwater can damage the fans and the entire system will be disrupted.
The video shows how best to arrange natural ventilation in the basement.
How to install an air duct?
Most often, 2 air ducts are used to organize a supply and exhaust ventilation system. To make the circulation of air masses more uniform, take pipes of the same diameter. To speed up air removal, you can install an exhaust pipe with a slightly larger cross-section.
Install the air ducts at the greatest possible distance from each other on opposite walls. Along the route of the pipes, it is necessary to minimize the number of bends.
The exhaust pipe is mounted in one of the corners and its lower end should be near the ceiling so that all the warm air going up is removed through it. The air duct can be combined with a kitchen exhaust ventilation system and brought to the roof one and a half meters above the ridge.
The street air duct must be insulated, we wrote about this above. The most aesthetic option is to put another pipe on the pipe, but of a larger size, and lay any insulation in the resulting space. It is better to install a special ventilation deflector on the head of the pipe, which helps to increase traction.
Mechanical ventilation ducts passing through the basement should be insulated so that due to the temperature difference between the air passing through them and the air mass inside, condensation does not form on the pipes
The supply air duct is mounted in the opposite corner of the subfloor, and its open end should be as close to the ground as possible. The supply opening must be lower than the exhaust opening. In the same way, a pipe can be run through a house.
If the supply air duct is ducted through the roof, its intake opening should be located below the exhaust pipe. The outer edge of the draft pipe is raised on the roof to 20-25 cm.
Also, the supply pipe can be installed near the wall of the house outside. In this case, the hole should ideally be raised above the ground by 80cm. Inside, dampers are installed in each air duct to regulate the intensity of air movement.
The following article will introduce you to the rules for installing a ventilation system in the attic of a private house, covering in detail the principles of the device and the nuances of the structure.
Features of designing a ventilation system
To understand how to make ventilation in a house, you need to carefully study standard designs and be sure to take into account a set of important factors:
- the internal volume of the entire room, and the number of people living in the house;
- the need to arrange ventilation for the subfloor, attic and other rooms;
- free flow of air exchange processes in all rooms of the home;
- using filters to purify clean air coming from the street;
- use of equipment for additional heating or cooling;
- installation of a check valve to prevent the return of waste material.
Additional devices for optimizing air exchange are used quite often and can increase the efficiency of ventilation in a private home.
Briefly about the main thing
Ventilation is as important a part of the cellar arrangement as hydro- and thermal insulation. A poorly designed ventilation system will not cope with the job, which will result in spoilage of supplies. Air circulation for underground ventilation is organized in two ways: natural and forced (mechanical).
The choice of a suitable system (pipe diameter) largely depends on the area of the room. You should not install one pipe in a spacious cellar (or basement); two channels will provide the required level of air circulation. If natural circulation is weak, it is made combined or completely forced, installing one or two fans.
DIY basement ventilation device in a private house
The basement space in a private house is often used for household needs. To avoid dampness and condensation on the walls, it is necessary to have ventilation in the basement of a private house. You can create simple ventilation with your own hands by punching holes on opposite sides of the base. Cover them with bars so that rodents cannot get into the basement.
Design and principle of operation of a supply and exhaust ventilation unit.More efficient basement ventilation can be done using pipes. For installation you will need two pipes (8-15 cm in diameter), grilles, canopies that protect against precipitation, and thermal insulation. One end of the supply pipe is installed in a wall hole at a distance of 25-35 cm from the basement floor. The upper end of the pipe is led out through the base and placed along the wall. The length of the outer part of the pipe should be 50-60 cm. For a more aesthetic appearance, the pipe can be made invisible.
The supply pipe must be installed in a hole under the basement ceiling. If the basement is used to store products, then it is recommended to place the pipe in close proximity to them. The pipe from the basement is led out through all the ceilings and ends at a height of 40-60 cm from the roof. It should be noted that in private houses, condensate in the ventilation that forms in the exhaust pipe will flow into the basement. Therefore, a container is placed in the basement to collect condensate. Pipes for ventilation can be used plastic or asbestos cement.
A ventilation scheme for a private house that you can create yourself.
On the Internet you can find various ventilation schemes in a private house. It is much easier to do the installation according to the diagram yourself. The video will tell you about options for installing ventilation systems in the basement of a private house.
Materials for the system design
For the arrangement of supply and exhaust ventilation air ducts, 3 types of pipes are used:
- Asbestos-cement ones are durable, resistant to corrosion and withstand frost well. They are of sufficient length, so during installation you can do without connections;
- Galvanized steel - resistant to corrosion, easy to install, and light weight. However, the price for metal components of ventilation systems is usually higher than for plastic and asbestos-cement ones;
- Plastic ones have a smooth inner surface, which ensures easy and fast air flow. Plastic pipes do not rust, they do not need to be cleaned, and their service life exceeds a couple of decades. One of their drawbacks is flammability.
The determining factor in the effectiveness of the ventilation system is the proportionality of the cross-section of the installed air duct to the area of the room in which it is installed. Heating engineers recommend adhering to the following norm when making calculations: 26 cm2 of section is required for 1 m2 of subfloor.
The most practical option for laying the exhaust part of the ventilation system in the cellar is an assembly made of polymer pipes. In addition to the affordable price, the opportunity to build a pipeline with your own hands is also attractive.
There is the following formula for calculating the required pipe diameter:
(S cellar × 26) ÷ 13.
That is, if the underground area is 9 m2, then a pipe with a diameter of 18 cm will be required: (9 × 26) = 208 ÷ 13 = 18 cm. For single-pipe ventilation, the diameter should be even larger, for example, 20 cm.
Types of ventilation holes in the basement
The classification of ventilation by type depends on the purpose and method of arrangement. The principle of their operation is based on the law of physics, according to which the flow of warm air tends to rise, and cold air flows down.
Natural supply
Created during the construction of a house, they represent small openings in the upper part of the basement. Refers to the simplest way to provide air exchange in the cellar.
To make an exhaust hood in a basement located below ground level, openings in the wall are equipped with asbestos-cement or plastic pipes with a cross-section of 10–15 cm. They are removed above the ground on the leeward side, at a distance of 30 cm from the surface. The vents are covered from the outside with bars to protect the room from rodents and foreign objects.
Attention
A natural supply system is used to provide ventilation for non-residential basements, garages, or for additional air exchange.
Natural exhaust
Correct operation of natural exhaust ventilation occurs due to the installation of two pipes:
- The first serves to remove warm air and is located in the upper part of the basement. To avoid exposure to adverse environmental conditions (precipitation, frost, etc.), the outer part of the pipe is insulated and a canopy is installed.
- The second pipe is designed to deliver fresh air flows into the cellar. It is placed at a distance of 30–40 cm from the floor, leading the other end of the pipe to the street, covering it with a grill. To maximize the efficiency of natural ventilation, install two or more supply pipes (depending on the area of the cellar) on opposite sides of the room. Due to the temperature difference in the basement and outside, air movement is ensured.
here
We offer a video on how to make natural ventilation in the basement:
Forced
This is a system of supply and exhaust fans and ducts that work synchronously and pump air, providing convection. Used in the following cases:
- the basement area consists of several rooms isolated from each other;
- The basement occupies more than 40 sq. m. m area;
- increased humidity in the basement when the exhaust duct freezes in winter, disrupting the movement of air masses;
- impossibility of installing high ventilation pipes;
- in the basement it is planned to place a cafe, steam room, workshop, garage, gym;
- It is impossible to use natural supply ventilation.
separate publication
Supply and exhaust with heat recovery
It is installed in the basement for permanent residence, where heat and waterproofing are carried out, floors and walls are insulated. Under such conditions, a forced ventilation system is not enough, so supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recovery is installed.
The device is an exhaust pipe that takes in and supplies already heated air, passed through a ceramic recuperator. Additionally, humidity and temperature sensors and dust filters are installed. Installation is complex, so it is performed by professionals.
Which ventilation scheme should I choose?
So, we have figured out whether an underfloor ventilation system is needed, and now it remains to decide which scheme to choose for specific conditions. There are several important points to consider when choosing a system. The operation of ventilation largely depends on the type of climate in a particular area, average street temperature, etc.
When installing natural ventilation, the main rule must be observed: the supply openings are located below the exhaust openings. The greater the altitude distance between them, the more efficient the system is.
Natural ventilation is more effective in winter, since it is at this time that a large difference is recorded between the temperature inside the underground and outside, which ensures good circulation of air masses.
However, with an even greater drop in temperature, there is a possibility of an excessive increase in air exchange, which is also not particularly good, as it can lead to freezing of structures. Therefore, if the temperature drops significantly, the vents must be closed.
In summer, the difference in temperatures inside the underground and outside is minimized, so air circulation may stop. Therefore, natural ventilation, even with a supply and exhaust system, is not the best option for hot regions. A combined ventilation system with pipes should be installed here.
If the house has supply and exhaust ventilation, it makes sense to connect the exhaust from the basement to the general circuit. This way, the outflow of air will be stimulated in any weather.
To install a combined ventilation system for a small underground area, it will be enough to install one pipe. In order for it to provide both output and reception of air masses, it needs to be divided vertically into 2 channels.
Such ventilation pipes are sold in hardware stores. Each channel has its own valve to adjust the flow intensity. The functioning of such ventilation is checked quite simply: you need to attach a sheet of paper to the outlet holes one by one.
Winter ventilation issue
In an effort to avoid cooling the floor covering, owners of private houses close the vents inside the basement during the winter cold. At the same time, the soil under the house does not freeze, maintaining a positive temperature. Moisture continues to evaporate, albeit not in such quantities.
When the ventilation openings are closed, condensation collects in the underground space, settling on the supporting structures. It should be remembered that you need to keep the floor warm by properly insulating it. Closed ventilation holes will not save the floor in the house from cooling, while ventilating the floor even in winter will not significantly affect heat loss. In this case, the moisture released by the earth will be effectively removed.
Operation of the underground throughout the year
Perhaps, a detailed examination of the temperature and humidity conditions inside and outside the basement space of the house does not apply to houses with a special underground ventilation device through air intakes located under the baseboards. This is a complex system of holes of different sizes, through which air exchange should occur between the rooms and the underground space. The advantage of this design is that the ground under the house does not freeze, and the foundation of the house does not freeze either.
If the builders made do with a simpler design, when open windows (so-called “vents”) from the underground to the street serve as air intakes, then homeowners should pay attention to the following information:
- These ventilation holes are made mainly on the leeward side and on the opposite side in order to create natural draft. To do this, it is necessary to know which wind direction is dominant in a given area.
- It is imperative to ensure that in the summer the ventilation openings are free - not cluttered with things from the inside and not overgrown with weeds from the outside.
- If ventilation is not good enough, it should be increased. This can be done by cutting holes in the base using diamond drilling or by increasing traction in existing ones. For this purpose, a tin pipe is connected to the hole, protected from precipitation and the penetration of rodents. The higher you make it, the better it will perform its function.
- An option to increase the draft of the underground ventilation holes: insert into them on one side of the house several forced-action fans connected to electricity and turn them on several times a day for 20-30 minutes.
- In winter, however, the ventilation holes should be closed, otherwise the frosty air will cool not only the floor, which is uncomfortable for household members, but also the ground and wooden structures. And such a sharp change in temperature can subsequently lead to moisture condensation in the room when it gets warmer.
- When it gets cold, broods of small rodents (mice and rats) look for a warm shelter, and the subfloor of the house just meets their needs. Since mice are destroyers of wooden structures and carriers of diseases, their presence is dangerous for the residents of the house. Therefore, it is necessary to protect the basement space of the house from them. To do this, either hollow bricks are inserted into the windows, which will need to be “sewn up” for the winter, or gratings with 5x5 mm cells are installed on them, and for the winter they are replaced with special plugs made of wood or clay.
- If the ventilation holes are left open during the winter, care should be taken to ensure that melt water does not penetrate into the subfloor through them in the spring or during a thaw. A melting snowdrift located at the window level poses a danger to the underground space, since the presence of moisture is detrimental to the entire structure of the house. To prevent this from happening, snow must be thrown 1.5 meters from the house.
- After the snow melts and the thaw sets in, the plugs from the vents will need to be removed and the underground ventilated.
Regulatory requirements for air exchange
The presence of ventilation must be provided for at the design stage of the house itself. The study of building codes (SNiP) is recommended for both independent builders and customers of construction crews.
Not all migrant workers can be trusted; most have to be carefully monitored.
SNiP number 41-01-2003, which regulates the rules for the design of ventilation and heating systems, sets standards for air circulation speed both in the building itself and in its individual rooms:
- for living rooms, living rooms, bedrooms, the norm is 30 m 3 / hour;
- for kitchens and bathrooms where humidity is high, the norm is from 50 to 70 m 3 /hour;
- for utility rooms the norm is 15 m 3 /hour.
Regardless of the type of ventilation system, it must provide the required volume.
The designer's task is to select the type that suits the needs. You also need to immediately decide on the equipment and calculate the area of the air ducts if they are planned for use.
Air conditioners against natural air exchange
Can air conditioners replace the natural circulation of air masses in a room?
Any, even the most expensive, climate systems are significantly inferior to simple ventilation. Want to think fast to keep you productive? Ventilate the room more often, and even better, do not skimp on the ventilation system, since, for example, in winter it is not always possible to open the window for a long time.
All split systems have two blocks that operate synchronously:
- External is a compressor that condenses the refrigerant;
- The internal one is a radiator that heats the air that circulates around it forcibly.
The air, which will subsequently be cooled, is also taken indoors. This means that the split system cools and passes through the same air masses.