The online mansard (gable) roof calculator will help you calculate the angles of inclination of the side and ridge slopes, the size and number of side and ridge rafters, the amount of sheathing, as well as the volume of required materials online. The most popular roofing materials, such as metal tiles, slate, ondulin, tiles made of ceramics, bitumen, cement and other materials, are entered into the calculation base in advance.
The design of attic roofs begins with the collection of typical loads and initial data (distance between load-bearing walls and partitions, approximate construction plan, snow, wind and special loads, requirements for insulation, type and weight of roofing, considerations of comfort and design).
Useful diagrams and tables when working with a mansard roof:
Information on the purpose of the calculator
The online attic roof calculator is designed to calculate the angles of inclination of ridge and side slopes, the number and cross-section of rafters, the volume of sheathing and other materials required for the construction of the roof. To design an attic floor, you should carefully read SNiP 2.08.01-89 “RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS”.
All calculations are performed in accordance with TKP 45-5.05-146-2009 and SNiP “Loads and Impacts”. A mansard (broken, sloping) roof consists of two slopes on each side, with different angles of inclination. Thereby forming a voluminous attic space called an attic or attic floor. A mansard roof can be added to an existing building, thereby adding additional living space without adding a full floor. This type of roofing dates back to the 17th century. There are many variations in the design of the attic floor, with the location of both residential and utility premises. You should carefully consider the choice of roofing materials, since the side slopes have quite steep slopes, which may require additional costs for roofing. You should also increase the amount of thermal insulation and the size of windows if a full-fledged living space is provided.
When filling out the data, pay attention to the additional information with the sign ❗
The following is a complete list of calculations performed with a brief description of each item. You can also ask your question using the comment form below.
Designer capabilities
The KALK.PRO service is a universal assistant for beginners and professional craftsmen, with the help of which you can make a truly reliable and safe design. However, it is necessary to understand that the program calculates the roof based on the entered data and does not take into account their correctness, except in exceptional cases when the structure is guaranteed to be unstable.
When building a roof (especially for the first time), we recommend paying attention to the following regulatory documents: SNiP 2.01.07-85 (SP 20.13330.2010) “Loads and impacts”, SNiP II-26-76 (SP 17.13330.2017) “ Roofs", TSN 31-308-97 "Roofs. Technical requirements and acceptance rules. Moscow region", SP 31-101-97 "Design and construction of roofs".
We currently provide calculations for the following roofing structures:
- roof is pitched;
- gable roof (gable, gable);
- hip roof;
- The roof is hipped (hipped).
We also have separate simplified calculators for calculating the rafter system of a gable and single-pitch roof - try it, maybe this is exactly what you need!
Among the main features of the designer, it is necessary to highlight (– only on KALK.PRO):
- Units. You can select the most convenient units of measurement (mm, cm, m, inches, feet), and the program will automatically convert all values in the calculator fields and calculation results.
- Roof type. When using a soft roof, it becomes possible to take into account the substrate in the form of OSB sheets.
- Roof parameters. You can specify the expected height of the structure, side outlet and overhang. In some roof calculators, the extreme position of the rafters (on the edge, against the wall) is also selected.
- Dimensions of the house. You can set the dimensions of the house: width, length of the house box and wall thickness (the latter affects the layout of the rafters, since the thickness of the gables is taken into account). The height of the walls is only needed to create a correct 3D model.
- Mauerlat. Only from us you get a separate calculation of the Mauerlat for the side and end slopes.
- Calculation of rafters. In addition to entering standard values for width/thickness and the distance between adjacent elements, for a more correct calculation of the rafter system, we can also specify the cutting depth.
- Insulation. The amount of insulation is automatically substituted into the results, the thickness of the material is taken equal to the thickness of the rafters and fills all the space between them.
- Vapor barrier. A block for entering the characteristics (width, length) of a waterproofing material with the ability to take into account overlaps from the sides and top.
- Lathing and counter-lattice. There is functionality for taking into account the parameters of the lathing and counter-lattice - you can enter the width/thickness of the board and the distance between them.
- OSB sheets. In the case of using a soft roof, the parameters of OSB sheets are taken into account in the calculations.
- Roofing materials. This block allows you to calculate metal tiles, corrugated sheets, ondulin and any other roofing material using known sheet parameters.
Our professional roofing calculators are used by many professionals - if you want to use them for commercial purposes, you can remove our watermark and upload your logo.
General information on the calculation results
1. Angle of inclination of side rafters
— The angle of inclination of the side (steeper) slope, layered rafters. The program will additionally tell you whether this angle is suitable for the selected roofing material.
2. Angle of inclination of ridge rafters
— The angle of inclination of the upper (flat, ridge slope), hanging rafters.
3. Roof surface area
— The total area of the entire roof surface, taking into account the length of the overhang. Corresponds to the amount of required roofing and under-roofing material
4. Quantity of roofing felt
— The amount of roofing material in rolls 1 meter wide and 15 meters long, taking into account overlap.
5. Attic floor area
— The area of the attic excluding the area under the side slopes.
6. Side rafter length
— Length of side slope rafters, layered rafters.
7. Ridge rafter length
— Length of ridge rafters, hanging rafters.
8. Recommended rafter section
— Recommended rafter cross-section taking into account the selected parameters and loads. By default, loads are indicated for the Moscow region.
9. Number and volume of rafters
— The total number and volume of rafters at a given pitch for the entire rafter system.
10. Number of rows of sheathing
— The total number of rows of sheathing according to given dimensions for the entire roof.
11. Uniform distance between sheathing boards
— Recommended distance between sheathing boards for using the material without trimming.
12. Number and volume of sheathing boards
— The total number and volume of boards for lathing the entire roof.
As a result of the calculations, we find out the angles of inclination of the side and ridge rafters, the surface area of the roof, the weight of the lumber and the number of rolls of roofing felt or other insulator.
The required dimensions of the rafter legs, their volume and weight will be shown in the form of a table. The same will be calculated for the sheathing and the distances between the sheathings will be calculated.
Selection of cross-section and sheathing thickness
The stage begins with choosing the type of sheathing: solid (selected for low slope slopes or low self-supporting abilities of the roofing) or loose (mounted on medium and steep slopes, optimal when working with rigid sheet materials). Next step by step:
- Based on the sum of the loads, the cross-section and thickness of the sheathing lumber is determined.
- The position of the first strip or the bottom edge of the sheet is determined.
- Taking into account the recommendations of roofing manufacturers, roof slope, rafter pitch and SNiP standards, the optimal sheathing pitch is selected.
- The need for strengthening of individual sections (if any) is clarified. Solid flooring or double boards are laid in the upper zone of slopes, under valleys, stairs or heavy objects.
- Manually or using programs, an approximate layout of the planks is calculated.
- A calculation of lumber and fasteners is carried out, the result is rounded up and the margin is increased by 5% (from 10% for a complex attic roof configuration).
Types of roofing materials
A variety of roofing types are used for roofing: flat and profile, rolled, soft, rigid, piece.
Let's look at the main types of roofing used in the construction of mansard roofs:
- Metal tiles
are cold-rolled galvanized steel sheets coated with a polymer coating. Metal tiles are used everywhere - as roofing for private houses, industrial buildings, garages, kiosks, and summer cottages. - Roofing sheeting.
The composition of the material is similar to metal tiles. It is most often used in the construction of industrial buildings, but due to its low cost it can be used for the construction of attics. - Ondulin.
One of the cheapest materials. Consists of cellulose fibers using bitumen and polymer additives. Painted with heat-resistant paint. It is rarely chosen as a roofing covering due to fading in the sun. - Soft tiles - shinglas.
It is made of fiberglass using bitumen, on top of which stone chips are applied, which resists sunlight and protects against fading. - Ceramic tiles
. One of the oldest types of roofing. To make it, clay is fired at high temperatures, as a result of which it acquires hardness and strength. - Sand-cement tiles.
The appearance is similar to clay tiles, but is cheaper to produce. It is made from a solution of cement and sand by pressing. The surface is smooth or textured. Used in the construction of private houses, cottages, dachas. - Slate roofing.
Extremely rare. It is characterized by a very high cost with the highest technical characteristics. Used in the construction of unique luxury houses and cottages. Such roofing can be found on ancient European castles.
How to calculate the rafter system
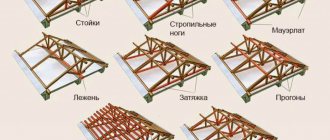
Before calculating the rafter system, let’s highlight its main system-forming elements:
- Rafters;
- Racks;
- Mauerlat;
- Struts;
- Lathing;
- Skate;
- Roof;
- Connection elements.
You should also remember a few rules:
- To construct the frame components, it is necessary to use beams with a cross section of 100*100 mm.
- Wood moisture content should be no more than 15%.
- Wooden elements must be treated with an antiseptic.
CAREFULLY! The service life of both the roof itself and the entire building depends on how correctly the calculations of all elements, including rafters, are made.
To calculate all elements, the first step is to determine the permanent and temporary loads to which the rafter system is subjected.
These include: the dead weight of the roof and natural phenomena in the form of wind, rain and snow. Depending on this and the choice of appropriate roofing material, the angle of inclination of the slopes is calculated.
After determining the level of the required slope of the slopes, the total load on the rafters is calculated. To do this, sum up the weight of the rafters, sheathing and roofing to calculate the weight of the element per 1 square meter.
The resulting value is multiplied by a multiplying factor of 1.1 -1.4. The resulting load figure, depending on the roofing material and insulation, ranges from 35 to 50 kg. per 1 sq.m.
This is a constant load value, to which periodic loads in the form of snow or wind are added.
To determine these loads, use the appropriate maps for individual regions. Snow load can vary from 80 to 150 kg per sq.m.
It should be multiplied by 0.7 if the roof slope is from 25 to 60 degrees. This value determines whether double rafters and continuous sheathing should be installed.
After calculating the load on the roof area and per square meter, the cross-section of the rafters is calculated. The number of rafters is determined by the length of the roof span and ranges from 70 to 120 m, depending on the length of the slopes.
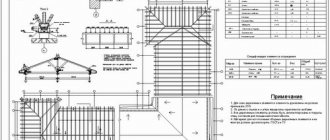
Development of a rafter plan
The process of developing a rafter plan includes procedures such as:
- Construction of modular axes linked to the thickness of the building’s load-bearing walls. In this case, on the plan itself, the projection of the crowning cornice is shown on the outer wall using a contour line.
- Ventilation and pipelines must also be indicated on the plan; their location must certainly be taken into account when arranging elements in the rafter system design.
- Based on the selected roof structure, a plan is developed. In this case, the walls and the fastening of the rafters in the ridge must be taken into account directly on the sketch.
Using such a sketch allows you to draw a plan of the rafter system, with the mauerlats, longitudinal struts and racks, a rafter beam, and rafter legs indicated on it.
Rafter system
The selection of a suitable distance between adjacent rafters is carried out based on:
- from the weight of the material chosen for roofing,
- scaffolding that will be used in this case,
- The pitch of the rafters can be changed due to the need to pass ventilation pipes or a chimney through them.
Also, ventilation and pipes can be passed through by interrupting the legs of the rafters, for which their ends are supported on special wooden jumpers, which are located between the adjacent rafters, and secured using a special rafter cut.
If we are talking about gable roofs, then the dormer windows should be located on the gables, which, in turn, are located on the ends, which cannot but increase the efficiency of attic ventilation in the summer.
In cases where the space under the roof is planned to be used for the construction of an attic floor, this should also be shown in the drawing in the form of upper beams that will serve as support for the rafters.
Also, we should not forget that the layout of the rafters should be developed simultaneously with the plan for the various designs of sections of the building. And both of these plans must necessarily be united by the presence of a common connection.
The drawing must take into account the data of all distances between the modular axes of the proposed structure, since all indicators of the thickness of future walls are associated with them.
Directly in the plan itself, the distances between the chimney, ventilation and racks must be indicated.
In addition, the plan should display callouts indicating all the required cross-sectional values and lengths of all available parts.
The rafter system can be called one of the most significant elements in the entire roofing structure, and, in particular, the safety of the roof, its reliability and service life depend on how correctly it is designed. That is why you should not undertake to draw up a rafter plan without having the necessary skills and abilities. You should still entrust this work to qualified specialists who already have the necessary experience in this field.
We also recommend watching:
- Original design of house roofs
- Gable mansard roof - construction technology
- Do-it-yourself roofing
- Certificate of acceptance of roofing and technical condition
How to correctly calculate the angle of inclination
The main factors influencing the slope of the roof during its installation are:
- Natural factors - climatic conditions where construction is planned (wind and snow loads);
- Characteristics of roofing material.
The most optimal roof slope is an angle of 20-30 degrees. In snowy latitudes, it is recommended to make a slope of at least 45 degrees.
In this case, the snow will easily fall off the roof. Since the design of the attic roof is gable or broken gable, we will consider the slope angle in this aspect.
The geometric shape of a gable roof is an isosceles triangle, therefore, to calculate the height of the ridge depending on the slope of the slopes, you should use the trigonometric formula for a right triangle.
IMPORTANT! The structure of a sloping mansard roof is distinguished by the presence of edges on the slopes, and the lower plane of the slope descends to the base of the roof at a steeper angle.
Therefore, there are two slopes here - the upper one, built in accordance with generally accepted standards; the lower one is steep, depending on the size of the house and the usable attic space.
The angle of inclination of the lower plane is most often 70 - 80 degrees.
It is convenient to install attic windows in a roof located at such a slope, which, due to their location, will be reliably protected from precipitation.
How to calculate the area of a sloping roof
When we are dealing with a regular gable roof, its surface is represented as two rectangles, the area of which can be calculated by multiplying the length by the width. Multiplying the value by 2 we get the total area of the roof plane.
How to calculate a mansard roof? In the case of defining an attic sloping roof, the situation is more complicated due to the fact that in such a device, in addition to the slope divided into two parts, there may be additional elements (windows, balconies, terraces, exits to the roof).
In this case, you should divide the roof surface into its component elements and calculate their area separately. The sum of all areas of the elements obtained in this case will be the roof area
For example:
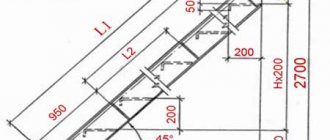
With the length of the base of the house being 10 m and the width of the base being 8 m, it is planned to build an attic space with a usable width of 5 m, a height to the edges of the slopes of 2.5 m and a height in the middle to the ridge of 3.5 m.
The width of the roof overhang is planned to be 50 cm.
The length of the side rafters is 3.42 m, the length of the ridge rafters is 2.69 m.
Now you need to calculate the area of the upper and lower faces.
Multiply the length of the side rafters by the length of the roof base. It turns out 34.2 sq. m. The sum of the two lower edges is 68.4 sq.m.
When multiplying the length of the ridge rafters by the length of the roof, we get 26.9 square meters. Fold the two top edges. We get 53.8 sq.m.
Accordingly, the total roof area is 122.2 square meters.
Services for calculating the required parameters
To simplify and verify the calculation, it is recommended to use:
- Professional programs such as Archikad, 3D Max, KZ-Cottage or ArCon (the latter is suitable for people without experience or construction education).
- Google SketchUp, Home Plan Pro, VisiCon and their analogues.
- Construction calculators and online services (stroy-calc.ru, stroysvoimirukami.ru, zhitov.ru, zamer-doma.ru).
Professional programs and applications allow you to create projects in 3-D projection and evaluate the expected appearance of the attic. The time spent on them always pays off - ordinary drawings do not give a full idea of the bulkiness and influence of the attic roof on the design of the house.
Construction calculators require accurate initial data and are most often used when designing power structures and pie, choosing the optimal option and calculating materials.
Video tutorial on how to design a mansard roof in Archicad 16:
Roofing calculation
We need to calculate the roof area to accurately calculate the required amount of roofing material.
In order to calculate the required material, you should know the dimensions of the material, as well as the method of fastening it together.
Let's look at the most common ones:
- Ceramic tiles. Consumption per 1 sq.m. about 10 pcs.;
- Metal tiles. The length can be any, width - from 1190 mm;
- Profiled sheeting. Any length, width - from 750 to 1100 mm;
- Ondulin. Length 2000 -2400 mm. Width 950 – 1250 mm
- Soft roofing shinglas. Length from 317 mm. Width 1000 mm.
You should buy roofing material with a reserve of 7-8% of the total area.