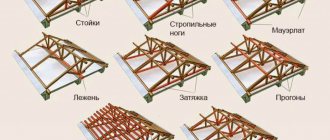
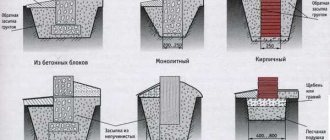
Shallow strip foundation
A shallow foundation saves both budget and time. And labor costs will be significantly less, since its construction does not require a deep pit. The following foundation is used for lightweight structures of small area:
- wooden houses
- aerated concrete structures or buildings constructed from aerated concrete and foam concrete blocks, the height of which does not exceed 2 floors
- monolithic buildings with permanent formwork
- small structures built of stone
The depth of the shallow foundation reaches half a meter.
What does the calculation consist of?
The most important thing is to enter verified and accurate information. Having made calculations with the same data, you cannot use the final conclusions in case of any changes. For example, if you change the design of the foundation, or enter erroneous soil characteristics, then you will need to recalculate everything again, since the previous figures will lose their relevance.
The following must be taken into account: the type, parameters and general appearance of the foundation, the depth at which the soil freezes, as well as the grade of concrete. How complete the entered data is, the more accurate the calculation of the total consumption of building materials will be.
Marking
Marking is carried out by marking on the ground both the external and internal boundaries of the future foundation. To do this, it is best to use pegs or reinforcement rods and ropes. But it will be more effective to use special devices, such as laser levels. Remember that large errors in markings will noticeably affect the appearance of the finished building.
To achieve ideal results you need:
- determine the axis of the structure being built
- use a plumb line to mark an angle, and from it, at an angle of 90 degrees, pull a rope to two more corners of the structure
- use a square to determine another angle
- check the angles, focusing on the diagonals. If the test gives positive results, pull a rope between them
- take on the internal markings, retreating from the external markings to the distance of the thickness of the future foundation
When you are finished with the markings, study the differences in the surface at the construction site and select the lowest point to measure the depth of the trench and eliminate the difference in the height of the foundation. If the building is planned to be small, then the depth of the pit can be 40 cm.
General information on the calculation results
- Total length of tape
- Tape sole area
- Outer side surface area
- Concrete volume
- Concrete weight
- Load on soil from foundation
- Minimum diameter of longitudinal reinforcement bars
- Minimum number of rows of reinforcement in the upper and lower chords
- Minimum diameter of transverse reinforcement bars (clamps)
- Spacing of transverse reinforcement bars (clamps)
- Amount of reinforcement overlap
- Total length of reinforcement
- Total weight of reinforcement
- Formwork board thickness
- Number of boards for formwork
— The length of the foundation in the center of the strip, taking into account the internal partitions.
— Area of support of the foundation on the soil. Corresponds to the dimensions of the required waterproofing.
— Corresponds to the area of the required insulation for the outside of the foundation.
— The volume of concrete required to pour the entire foundation with the given parameters. Since the volume of concrete ordered may differ slightly from the actual one, as well as due to compaction during pouring, it is necessary to order with a 10% reserve.
— The approximate weight of concrete based on average density is indicated.
— Distributed load over the entire support area.
— Minimum diameter according to SP 52-101-2003, taking into account the relative content of reinforcement from the cross-sectional area of the tape.
— A minimum number of rows of longitudinal rods in each belt to prevent deformation of the belt under the influence of compression and tension forces.
— Minimum diameter of transverse and vertical reinforcement bars (clamps) according to SP 52-101-2003.
— The pitch of the clamps necessary to prevent shifts of the reinforcement cage when pouring concrete.
— When fastening sections of rods with overlap.
— The length of all reinforcement for tying the frame, taking into account the overlap.
— Weight of the reinforcement cage.
— Design thickness of formwork boards in accordance with GOST R 52086-2003, for given foundation parameters and at a given support spacing.
— The amount of material for formwork of a given size.
Installation of strip foundation formwork
The formwork is usually made of planed boards approximately 40-50 mm thick. You can use slate for this purpose.
When erecting formwork, control verticality. The recommended height of the frame above the ground is 30 cm. This is necessary to build a small base. Asbestos concrete pipes are laid in the formwork to introduce sewerage and water supply into the building.
Place a plastic film between the concrete and the formwork; this will protect the formwork from contamination.
How is calculation done?
It can be produced in one of two ways
- You can take a ready-made program. There is a special online calculator that significantly speeds up any calculations. This is especially true when making ongoing changes.
- You can make the calculation manually. To do this, you should use a regular calculator - everything can be calculated very accurately, although you will have to spend time.
The type of base, as well as its design, must be determined first of all. For this purpose, geodetic surveys are carried out. With their help, they establish at what depth the groundwater lies, determine the characteristics of the soil and determine the level of its freezing.
It is also necessary to determine what load as a whole will act on the base.
Pouring a strip foundation with concrete
Fill the formwork with concrete gradually. The thickness of the layers is 15-20 cm; to avoid voids and increase overall strength, compact the layers with a special tool - a wooden tamper or an internal vibrator.
You can order ready-mixed concrete from a factory or make it yourself using a concrete mixer. The recommended proportion of cement, sand and crushed stone is: 1:3:5.
The layers should not differ in composition. In cold weather, you should use a concrete heater and frost-resistant additives; in hot weather, water the concrete.
Portland cement
When making concrete mass, cement is certainly used. Portland cement can be very different, there are many of its variations - not only the stability, the guaranteed strength of all building structures, but also their service life depends on the characteristics of this product, on its quantity that will be introduced into the batch. The calculator processes all received data in a complex, providing information about the required amount of cement.
If you calculate all this manually, then you need to take into account that in the total mass of the forming concrete, 1/9 of the part is occupied by Portland cement itself.
When mixing, it is recommended to take 3 parts sand, 5 parts cement and 1 part crushed stone. For one cubic meter of concrete you will need the following amount of cement:
- 200 kg brand M100;
- 280 kg brand M150;
- 330 kg brand M250;
- 380 kg brand M300;
- 420 kg brand M400;
- 530 kg brand M500.
Knowing this information, you can quite accurately determine the need for cement manually. But do not forget that the program will handle this faster and more accurately.
Stages of soil deformation in the classical form
Design and calculation of the foundation for a house, how to calculate and make a foundation with your own hands
Scheme of development of deformations and possible soil movements in the event of incorrect calculation of bearing capacity
In modern literature, it is customary to distinguish three main phases of soil deformation:
- Initial. This is the stage of soil compaction under the influence of external factors, which occurs due to the reduction of pores between soil particles under the sole. The phase is different in that now there is no shift of the foundation, because all tangential loads are equivalent and are compensated by the load. But the load always arises spontaneously, it is distributed unevenly. As a result, the deformation may be slight at one point and severe at another. As a result, foundation shifts occur.
- The second stage is the phase of shear of the base. As the load increases, the soil compresses more and more, covers new areas, and a significant shift of the sole occurs towards a higher load. The standard balance is disrupted, a dense ball of soil is formed under the sole, and empty space is formed on the sides. The foundation material tends to take up the vacated space due to natural gravitational forces, which is why cracks and breaks appear in the foundation, and then in the load-bearing walls of the house.
- The third phase is the destruction of the sole. Here the material of the sole sticks out from the dense ball of soil and immediately becomes deformed.
This situation occurs with those foundations that are laid above the limiting depth of soil freezing or above the groundwater horizons. A slightly different picture occurs with deeply laid foundations. In such cases, a dense layer of soil also forms under the sole, but it does not stick out to the surface due to the large overlap area of the sole. Therefore, such a foundation has better load-bearing capabilities than a shallow foundation.
Once the process of soil deformation begins, it is sometimes impossible to stop it. The only way out is to install special protective structures that can level the loads or minimize their impact.
Types of concrete structures.
How to calculate the volume of concrete for a foundation.
The foundation is the basis of any structure. Based on this, it is necessary to ensure that it is sufficiently reliable and durable.
From the very beginning you need to decide on the type of foundation. It depends:
- on the massiveness and area of the building;
- building materials from which it will be built;
- type of soil on the site;
- climatic conditions;
- soil freezing level;
- availability of groundwater.
Only after this can you calculate the volume of the foundation yourself. At the moment, there are three most common types of concrete foundations: strip (monolithic). slab, as well as from concrete pillars.
Note! During computational work, all necessary parameters should be carefully measured. Even a small inaccuracy can have a very sad effect on the outcome of your efforts.
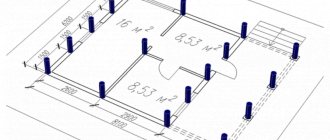
Base on stilts.
Pile foundation is an oriented group of supports that are buried in the ground. A simple and economical basis. When erecting it using the drilling method, concrete is poured into pre-drilled round holes.
In this case, the cubic capacity is the sum of two geometric figures. The first figure is the sole, in the form of a wide and low parallelepiped. The second figure is a pillar, in the form of a tall and narrow parallelepiped.
Calculation of the pile foundation.
This value is multiplied by the number of pillar supports in the base, which are located along the perimeter every 2 m.
For example, for a building 6×6 m with the number of pillar supports 20 (4 in the corners and 16 intermediate), the base of which is 0.5×0.5×0.2 m, and the pillar supports 0.3×0.3×0, 8 m, the base volume will be 20 × 0.5 × 0.5 × 0.2 = 1 m3. For pillar supports this value is 20×0.3×0.3×0.8=1.44 m3. Accordingly, the cubic capacity of the fill is 1+1.44=2.44 m3.
For an example of calculating a pile-tape foundation, look at the video:
What kind of fittings are there?
The fittings are produced mainly from steel. It can be smooth and profiled - with a specially shaped ribbing. The ribbed one is used to distribute the load, the smooth one serves only to give the structure its shape. That is, the main emphasis should be on the quality of the ribbed rod.
Reinforcement can be smooth or ribbed
Not so long ago, plastic reinforcement for foundations appeared on the market. She is actively promoting. But few experts (sellers don’t count) advise using it. If we analyze the properties of one and another type of reinforcement, then in reality all the advantages and disadvantages look something like this:
- Conductive steel - no plastic. It cannot be said unequivocally that conductivity is a poor quality. It can be used, for example, for grounding.
- Plastic fittings are 4-5 times lighter and are produced in coils. This is a fact, but it really only affects the cost of transportation. Since there is no difference in the mass of the reinforced concrete structure, the rod weighs 50 kg or 10.
- Steel rods can be bent directly on the construction site. This cannot be done with polymer products. If necessary, bent sections will be produced at the factory according to your order. It is impossible to do this on the site yourself.
Plastic fittings - a new product on the market
- Plastic is chemically neutral and does not collapse when moisture gets into concrete. This is true. But if the rules are followed (at least 50 mm of concrete from the bars to the surface), the steel reinforcement lasts for decades and does not collapse.
- Steel begins to melt at 600o. Plastics soften at 200-300oC.
- Plastics have better strength characteristics. Not certainly in that way. They stretch more under static loads. If you make a slab foundation reinforced with plastic reinforcement, it will sag after a while: their elongation coefficient is 10-11 times greater than that of steel. It’s the same with a strip foundation: the strip can sag.
In general, it turns out the following: it is better not to use plastic reinforcement for foundations. The idea is too risky.
Bored base with a monolithic grillage.
The volume of the base in this case is the sum of the cubic capacity of the supporting elements and the grillage slab. A complex structure is divided into numerous simple figures, for which the volume is calculated separately.
The volume of the supporting elements is the product of the area of its base and the height from the base to the lower edge of the monolithic grillage. And the area of the round base is ¼ of the product of twice the diameter and the number π (3.14).
How to calculate the volume of the foundation in m3 calculator.
Example for 20 supports with a cross section of 0.4 m, recessed by 2.5 m and a grillage element 10x12x0.3 m:
The volume of supports is made as 20x(¼x 3.14x0.4x0.4)x2.5=6.28 m3;
The cubic capacity of the grillage element is 10×12x0.3=36 m3; In total there will be 36+6.28=42.28 m3.
Construction of the base is a complex and multi-stage process. The full process of calculating consumable building materials involves many nuances that an experienced engineer can do.
How to calculate the volume of a house foundation in m3.
Here are simplified foundation calculation models to help the homeowner who must adequately spend his money on the construction processes.