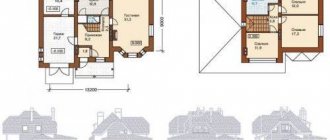
Due to the steady increase in energy prices and the high cost of gas connections, an increasing number of developers are thinking about building an energy-efficient house.
We have already told the readers of our website about what an energy-efficient house is and what technologies are used in its construction.
The time has come to understand how to calculate the economic feasibility of building such a house.
And FORUMHOUSE users will help us with this.
From our material you will learn:
- Which house is energy efficient and which is not.
- Is it possible to heat an energy-efficient house with electricity only?
- How to calculate the required thickness of insulation.
- Will building an energy efficient house pay off?
No. 1. Designing an energy-saving house
A home will be as economical as possible if it was designed taking into account all energy-saving technologies. Remodeling an already built house will be more difficult , more expensive, and it will be difficult to achieve the expected results. The project is developed by experienced specialists taking into account the customer’s requirements, but it must be remembered that the set of solutions used must, first of all, be cost-effective. An important point is taking into account the climatic features of the region .
As a rule, houses in which people live permanently are made energy-saving, so the first priority is to save heat, maximize the use of natural light, etc. The project should take into account individual requirements, but it is better if the passive house is as compact as possible, i.e. cheaper to maintain .
Different options can meet the same requirements . Joint decision-making by the best architects, designers and engineers made it possible to create a universal, energy-saving frame house (read more here). The unique design combines all economically advantageous offers:
- thanks to SIP panel technology, the structure is highly durable;
- decent level of thermal and noise insulation, as well as the absence of cold bridges;
- the construction does not require the usual expensive heating system;
- using frame panels, a house is built very quickly and has a long service life;
- The premises are compact, comfortable and convenient during their subsequent use.
As an alternative, you can use aerated concrete blocks to build load-bearing walls, insulating the structure on all sides and ultimately getting a large “thermos”. Wood is often used as the most environmentally friendly material.
What is energy efficiency
Energy-efficient houses have been built in European countries for a long time, but for our country such housing is still exotic.
Many developers are distrustful of the construction of such buildings, considering it an unjustified waste of money.
Let's figure out whether this is true and whether it is profitable to build an energy-efficient house in relation to the climatic conditions of most zones of Russia, including Moscow.
An energy-efficient (energy-passive) house is a building in which the costs associated with energy consumption are on average 30% less than in a conventional house. Energy efficiency of recent times could be determined by the coefficient of seasonal thermal energy use - E.
- E <= 110 kWh / m2 / year - this is an ordinary house;
- E <= 70 kWh/m2/year – energy efficient;
- E <= 15 kW*h/m2/year – passive.
When calculating the E coefficient, the following are taken into account: the ratio of the area of all external surfaces to the entire cubic capacity of the house, the thickness of the thermal insulation layer in the walls, roof and ceilings, the glazing area and the number of people living in the building.
In Europe, to determine the energy efficiency class, it is customary to use the EP coefficient, which determines the amount of electricity spent on heating, hot water supply, light, ventilation and the operation of household electrical appliances.
The starting point is EP = 1 and energy class D, i.e. standard. The modern classification of houses adopted in European countries looks like this:
- EP <= 0.25 – class A, passive house;
- 0.26 < EP <= 0.50 – class B, economical;
- 0.51 < EP <= 0.75 – class C, energy-saving house;
- 0.75 < EP <= 1 – class D, standard;
- 1.01< EP <= 1.25 – class E;
- 1.26 < EP <= 1.50 – class F;
- EP >1.51 – class G, the most energy-consuming.
In ordinary, insufficiently insulated housing with large heat losses through the building envelope, most of the energy (up to 70%) is spent on heating.
We can say that the owners of such a home heat the street.
Therefore, in European countries, no one will be surprised by the thickness of the insulation in the walls of 300-400 mm, and the outline of the building itself is made airtight.
The required level of air exchange in the house is maintained using a ventilation system, and not the mythical “breathing” of the walls.
But before you buy cubic meters of insulation, you need to understand when additional insulation and the whole range of measures associated with building an energy-efficient house are economically justified.
No. 2. Architectural solutions for an energy-saving house
To achieve resource savings, you need to pay attention to the layout and appearance of your home. The home will be as energy efficient as possible if the following nuances are taken into account:
- correct location . The house can be located in the meridional or latitudinal direction and receive different solar radiation. It is better to build a northern house meridionally in order to increase the influx of sunlight by 30%. Southern houses, on the contrary, are better to be built in a latitudinal direction to reduce air conditioning costs;
- compactness , which in this case refers to the ratio of the internal and external area of the house. It should be minimal, and this is achieved by eliminating protruding rooms and architectural decorations such as bay windows. It turns out that the most economical house is a parallelepiped;
- thermal buffers, which separate living spaces from contact with the environment. Garages, verandas, loggias, basements and non-residential attics will be an excellent barrier to the penetration of cold air from outside into rooms;
- proper natural light. Thanks to simple architectural techniques, it is possible to illuminate the house with sunlight for 80% of the entire working time. Premises, where the family spends the most time (living room, dining room, children's room) better positioned on the south side, for the pantry, bathrooms, garage and other auxiliary rooms there is enough diffused light, so they can have windows on the north side. East facing windows in the bedroom In the morning they will provide you with a boost of energy, and in the evening the rays will not interfere with your rest. In summer, in such a bedroom it will be possible to do without artificial light altogether. As for window size, then the answer to the question depends on everyone’s priorities: saving on lighting or heating. Great welcome - installation solar tube. It has a diameter of 25-35 cm and a completely mirrored internal surface: receiving the sun's rays on the roof of the house, it retains their intensity at the entrance to the room, where they are dispersed through a diffuser. The light is so bright that once installed, users often reach for the switch when leaving the room;
- roofing _ Many architects recommend making roofs as simple as possible for an energy-efficient home. They often opt for a gable option, and the flatter it is, the more economical the house will be. Snow will be retained on a flat roof, which provides additional insulation in winter.
Summarizing
Now it is clear whether it is worth spending money on additional insulation of the building. Due to constantly rising energy prices, investing in energy efficient housing needs to be considered over the long term.
It is also necessary to take into account the development of construction technologies and the mass introduction of highly efficient types of insulation, more sophisticated components and designs of cottages, alternative energy sources and heating systems.
Currently, the cost of building energy-efficient housing in our country is 15-20% more than the construction of an ordinary cottage. But in European countries in the 90s this difference reached 30-35%, but now it is less than 8-10%.
Read on FORUMHOUSE about building energy-efficient housing and whether heating with electricity can be cheap. Get acquainted with the diary for calculating the payback from additional insulation of the house and the algorithm for calculating the optimal thickness of insulation. Find out how to calculate the economic feasibility of additional insulation.
In this video, watch how to build an energy efficient house. Find out what an energy-passive house is.
No. 3. Thermal insulation for an energy-efficient home
Even a house built taking into account all the architectural tricks requires proper insulation in order to be completely airtight and not release heat into the environment.
Thermal insulation of walls
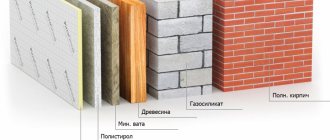
About 40% of the heat from the house escapes through the walls , so increased attention is paid to their insulation. The most common and simplest method of insulation is the organization of a multi-layer system. The external walls of the house are sheathed with insulation, which is often mineral wool or expanded polystyrene , a reinforcing mesh is mounted on top, and then a base and main layer of plaster.
A more expensive and advanced technology is a ventilated facade . The walls of the house are covered with mineral wool slabs, and facing panels made of stone, metal or other materials are mounted on a special frame. There remains a small gap between the insulation layer and the frame, which plays the role of a “thermal cushion”, prevents the thermal insulation from getting wet and maintains optimal conditions in the home.
In addition, in order to reduce heat loss through the walls, insulating compounds are used at the junction of the roof, taking into account future shrinkage and changes in the properties of some materials with increasing temperature.
The principle of operation of a ventilated facade
Roof thermal insulation
About 20% of the heat escapes through the roof. To insulate the roof, the same materials are used as for the walls. Mineral wool and expanded polystyrene are widely used today . Architects advise making roof insulation no thinner than 200 mm, regardless of the type of material. It is important to calculate the load on the foundation, supporting structures and roof so that the integrity of the structure is not compromised.
Thermal insulation of window openings
Windows account for 20% of heat loss in a home. Although modern double-glazed windows protect the house from drafts and isolate the room from external influences better than old wooden windows, they are not ideal.
More progressive options for an energy-efficient home are:
- selective glasses, which work on the principle of the earth's atmosphere. They let in short-wave radiation but do not release heat rays, creating a “greenhouse effect.” Selective glasses are of I- and K-type. On I-glass The coating is applied in a vacuum to the finished material. On K-glass The coating is applied during the manufacturing process using a chemical reaction. I-glasses are considered more efficient, since they retain 90% of heat, while K-glasses retain 70%;
- selective glass with inert gas minimizes heat loss through windows. The thermal conductivity of the inert gas used is lower than that of air, so the house almost does not lose heat through them.
Thermal insulation of floor and foundation
10% of heat is lost through the foundation and floor of the first floor. The floor is insulated with the same materials as the walls, but other options can be used: self-leveling thermal insulation mixtures, foam concrete and aerated concrete, granular concrete with a record thermal conductivity of 0.1 W/(m°C). You can insulate not the floor, but the ceiling of the basement, if such is provided for in the project.
It is better to insulate the foundation from the outside, which will help protect it not only from freezing, but also from other negative factors, incl. influence of groundwater, temperature changes, etc. To insulate the foundation, sprayed polyurethane, expanded clay and foam are used.
Construction technology
If you want to build a passive house with your own hands, you will have to devote a lot of time to this. During construction, it is important to understand the essence that energy-saving technologies for a private home include. There are a lot of options for using materials for construction and thermal insulation.
Before you start building a passive house yourself, it is recommended to order a project for such a house from professionals. They will be able to calculate all the nuances of the design and indicate the necessary materials that are suitable specifically for the selected plot of land.
If you want to build a passive house, the following technologies are used in its construction:
- warm walls;
- warm floor;
- foundation insulation;
- roof waterproofing;
- use of SIP panels for walls, floors and roofs.
You can use the following algorithm of actions:
- after the passive house project has been completed, the actual installation work begins;
- Initially, a foundation is built and its insulation is carried out. Materials for this are selected individually. A good option for insulating the foundation is foam glass. A mesh is being installed for the liquid floor heating system. After this, they begin to assemble the frame of the house;
- start building the roof. For insulation and waterproofing when laying the roof covering, insulating material and a waterproofing film are mounted to the frame;
- carry out complete waterproofing of walls and floors;
- start finishing the facade;
- install windows and doors;
- The final stage of construction is the finishing of the façade of the house.
No. 4. Heat recovery
Heat leaves the house not only through the walls and roof, but also through the ventilation system. To reduce heating costs, supply and exhaust ventilation with recovery is used.
A recuperator is a heat exchanger that is built into the ventilation system. The principle of its operation is as follows. The heated air leaves the room through the ventilation ducts, gives off its heat to the recuperator, coming into contact with it. Cold fresh air from the street, passing through the recuperator, heats up and enters the house at room temperature. As a result, households receive clean fresh air, but do not lose heat.
Such a ventilation system can be used together with natural ventilation: air will enter the room forcibly and leave due to natural draft. There is one more trick. The air intake cabinet can be located 10 meters away from the house, and the air duct is laid underground at a freezing depth . In this case, even before the recuperator, the air will be cooled in the summer and heated in the winter due to the soil temperature.
Window
It is known that significant heat losses occur due to the installation of leaky windows.
Therefore, today, high-quality glazing (for example, triple-glazed windows filled with inert gas) is used as the main energy-saving measure in construction.
Another effective technology has also appeared on the market - the “thermal mirror”.
Its essence is as follows: a transparent polymer membrane with a low-emissivity coating is stretched between ordinary glasses inside a double-glazed window.
Its thickness is 0.075 mm.
By delaying thermal radiation, the “thermal mirror” practically does not reduce the ability of the structure to transmit light.
Vacuum double-glazed windows are another innovation.
Between two 4 mm thick glasses there remains a gap of about 0.5 or 0.7 mm, from which air is subsequently pumped out.
The design of glass that generates electric current is also known.
The glass is coated with a special polymer composition, thanks to which it works like a solar battery.
No. 5. Smart House
To make life more comfortable and at the same time save resources, you can equip your home with smart systems and equipment , thanks to which it is already possible today:
- set the temperature in each room;
- automatically lower the temperature in the room if there is no one in it;
- turn the lights on and off depending on the presence of a person in the room;
- adjust the light level;
- automatically turn ventilation on and off depending on the air condition;
- automatically open and close windows to allow cold or warm air into the house;
- automatically open and close blinds to create the required level of lighting in the room.
Energy saving when installing doors
To achieve a comprehensive effect from measures to improve the energy efficiency of a building, it is necessary to take care of the doors.
The following events are possible:
- thermal insulation. A metal door especially needs it. Various materials can be used as a heat insulator, but stone wool is most often used. At the same time, it acts as a fire retardant, as it has a high melting point;
- seals. The use of seals along the door contour allows you to avoid the formation of “cold bridges” and drafts, due to which heat loss occurs;
- returners. To reduce heat loss when people pass through the entrance doors, it is recommended to equip all door panels with closers. These are levers that return the door to a closed state without human intervention. Thanks to them, you will not encounter a situation where someone forgot to close the door to the house or entrance. In addition, closers will eliminate noise when the sash slams;
- vestibule. It is recommended to use double doors or make vestibules. This way you can protect yourself from heat loss and heat penetration into the room. In this case, an air gap is formed between the two doors, which also serves as a heat insulator.
No. 6. Heating and hot water supply
Solar systems
The most economical and environmentally friendly way to heat a room and heat water is to use solar energy. This is possible thanks to solar collectors installed on the roof of the house. Such devices are easily connected to the heating and hot water supply system of the house, and the principle of their operation is as follows . The system consists of the collector itself, a heat exchange circuit, an accumulator tank and a control station. A coolant (liquid) circulates in the collector, which is heated by the energy of the sun and transfers heat through a heat exchanger to the water in the storage tank. The latter, due to its good thermal insulation, is able to retain hot water for a long time. This system can be equipped with a backup heater, which heats the water to the required temperature in case of cloudy weather or insufficient sunshine.
Collectors can be flat and vacuum . Flat ones are a box covered with glass, inside it there is a layer with tubes through which the coolant circulates. Such collectors are more durable, but today they are being replaced by vacuum ones. The latter consist of many tubes, inside of which there is another tube or several with coolant. There is a vacuum between the outer and inner tubes, which serves as a heat insulator. Vacuum collectors are more efficient, even in winter and in cloudy weather, and are repairable. The service life of collectors is about 30 years or more.
Heat pumps
Heat pumps use low-grade environmental heat to heat a house , incl. air, subsoil and even secondary heat, for example from a central heating pipeline. Such devices consist of an evaporator, a condenser, an expansion valve and a compressor. All of them are connected by a closed pipeline and operate based on the Carnot principle. Simply put, a heat pump is similar in operation to a refrigerator, only it functions in reverse. If in the 80s of the last century heat pumps were rare and even a luxury, today in Sweden, for example, 70% of houses are heated in this way.
Condensing boilers
Conventional gas boilers operate on a fairly simple principle and consume a lot of fuel. In traditional gas boilers, after burning the gas and heating the heat exchanger, the flue gases escape into the chimney, although they carry a fairly high potential. Condensing boilers, using a second heat exchanger, remove heat from condensed air vapor, due to which the efficiency of the installation can even exceed 100%, which fits into the concept of an energy-saving house.
Biogas as fuel
If a lot of organic agricultural waste accumulates, then you can build a bioreactor to produce biogas . In it, biomass is processed by anaerobic bacteria, resulting in the formation of biogas, consisting of 60% methane, 35% carbon dioxide and 5% other impurities. After the cleaning process, it can be used for heating and hot water supply at home. The processed waste is converted into excellent fertilizer that can be used in the fields.
Energy balance
An important characteristic of eco-housing is the balance between transmission or ventilation heat loss and its formation together with energy from the sun, heating and internal heat sources. To achieve this, the following components
:
- compactness
of the building; - thermal insulation
of the heated area; - supply of thermal energy from the sun
, through window openings facing south with a deviation of up to 30 degrees and no darkening.
When calculating, the angle of incidence of light from the sun at different times of the year is taken into account. Source stroyka.uz
To reduce the cost of energy resources, you should use household appliances with high levels of energy efficiency. The ideal passive housing is a thermos house with no heating. Water can be heated using a solar collector or a heat pump.
See also: Catalog of popular house projects from construction companies presented at the Low-Rise Country exhibition.
No. 7. Electricity sources
An energy-efficient home should use electricity as economically as possible and, preferably, obtain it from renewable sources. Today, a lot of technologies have been implemented for this.
Wind generator
Wind energy can be converted into electricity not only by large wind turbines, but also by compact “home” wind turbines . In windy areas, such installations can fully supply a small house with electricity; in regions with low wind speeds, it is better to use them together with solar panels.
The force of the wind moves the blades of the windmill, which causes the rotor of the electricity generator to rotate. The generator produces an alternating unstable current, which is rectified in the controller. There the batteries are charged, which, in turn, are connected to inverters, where the DC voltage is converted into alternating voltage used by the consumer.
Windmills can have a horizontal or vertical axis of rotation. With one-time costs, they solve the problem of energy independence for a long time.
Solar battery
The use of sunlight to generate electricity is not so common, but in the near future the situation risks changing dramatically. The principle of operation of a solar battery is very simple: a pn junction is used to convert sunlight into electricity. The directed movement of electrons, provoked by solar energy, is electricity.
The designs and materials used are constantly being improved, and the amount of electricity directly depends on the illumination. So far, various modifications of silicon solar batteries , but new polymer film batteries, which are still in the development stage, are becoming an alternative.
Energy Saving
The resulting electricity must be used wisely. The following solutions will be useful for this:
- usage LED lamps, which are two times more economical than fluorescent ones and almost 10 times more economical than ordinary “Ilyich light bulbs”;
- use of energy-saving equipment of class A, A+, A++, etc. Although initially it is slightly more expensive than the same devices with higher power consumption, in the future the savings will be significant;
- the use of presence sensors so that the lights in the rooms do not burn in vain, and other smart systems mentioned above;
- if you had to use electricity for heating , then it is better to replace conventional radiators with more advanced systems. These are thermal panels that consume half as much electricity as traditional systems, which is achieved through the use of a heat-storing coating. Similar savings are provided by monolithic quartz modules , the operating principle of which is based on the ability of quartz sand to accumulate and retain heat. Another option is film radiant electric heaters . They are mounted on the ceiling, and infrared radiation heats the floor and objects in the room, thereby achieving an optimal microclimate in the room and saving electricity.
Economic feasibility of additional insulation
The main indicator of the economic efficiency of additional insulation of a house is the payback period of the insulation system.
The experience of a user with the nickname Andrey A.A ,
who compared heating costs in the permanent residence mode of an insulated and non-insulated house. For the purity of the experiment, we take the following data as the initial conditions:
- heating with main gas;
- heat loss through the enclosing structures – 300 kW/h/(sq.m.*year);
- the house has a service life of 33 years.
Andrey A.A.
To begin with, I calculated the annual heating costs in permanent residence mode without additional insulation. After my calculations, the cost of heating an uninsulated house of 120 sq.m., with its heat loss of 300 kW/h/(sq.m.*year), amounted to 32 thousand rubles. per year (provided that the price for 1 m3 of gas until 2030 will be 7.5 rubles).
Now let’s calculate how much you can save if you properly insulate your house.
Andrey A.A.
According to my calculations, additional insulation will reduce the heat loss of my home by approximately 1.6 times. Hence, with heating costs equal to 1.1 million rubles for 33 years (32 thousand rubles per year x 33 years), after insulation you can save 1.1-1.1/1.6 = 400 thousand on energy costs . rub.
To get 100% economic benefit from additional insulation, it is necessary that the amount spent on additional insulation does not exceed half the amount saved on energy costs.
Those. for this example, insulation costs should not exceed 200 thousand rubles.
Also interesting is the approach to calculating the profitability of additional insulation from a forum member with the nickname mfcn
:
– Consider the following hypothetical conditions:
- in the house +20°C, outside -5°C;
- heating period – 180 days;
- house - with a single-layer frame, costing 8,000 rubles/m3, insulated with mineral wool at 1,500 rubles/m3;
- installation cost – 1000 rubles/m3 of insulation;
- frame pitch – 600 mm, thickness – 50 mm.
Based on these data, a cubic meter of insulation costs 3,000 rubles.
No. 8. Water supply and sewerage
Ideally, an energy-efficient house should receive water from a well located under the house. But when the water lies at great depths or its quality does not meet the requirements, such a solution has to be abandoned.
It is better to pass household wastewater through a recuperator and remove heat from it. To treat wastewater, you can use a septic tank , where the transformation will be carried out by anaerobic bacteria. The resulting compost is a good fertilizer.
To save water, it would be a good idea to reduce the volume of water drained. In addition, a system can be implemented where the water used in the bathtub and sink is used to flush the toilet.
8(499)490-60-60
High-cost measures that increase the energy efficiency of water supply include:
- launch of automatic water control and accounting systems;
- implementation of treatment facilities with recycling equipment and the possibility of recycling water for technical purposes;
- replacement of sectional water heating systems with plate ones.
Before saving - water supply system inspection
No. 9. What to build an energy-saving house from
Of course, it is better to use the most natural and natural raw materials, the production of which does not require numerous processing stages. These are wood and stone . It is better to give preference to materials that are produced in the region, because this way, transportation costs are reduced. In Europe, passive houses began to be built from the products of processing inorganic waste. These are concrete, glass and metal.
If you once pay attention to studying energy-saving technologies, think through the design of an eco-house and invest in it, in subsequent years the costs of its maintenance will be minimal or even tend to zero.
The article was written for the site.
Tags: Heating boiler, House projects, Lighting systems, Construction, Electricity
conclusions
- Investing in solar panels is a smart decision. This type of investment is similar to investing in energy efficiency measures to reduce heat loss in your home. Any appliance that consumes less energy will immediately start making you money by saving energy. The cost of additional insulation in your home begins to immediately bring you savings on air conditioning and heating. By now, many already know that investing in energy efficiency measures is a very smart investment. We have tried to show that investing in solar panels is similar.
- Don't forget that in addition to saving money from installing solar panels, you are contributing to the fight against environmental pollution and global warming. This happens due to the fact that you reduce energy consumption from traditional, environmentally polluting, fuel-based power plants.
- Solar panels increase the value of your home. And in some cases they increase its attractiveness among buyers, because even if the increase in the value of the house is less than your costs for a solar power plant on the roof of your house, it will be easier to sell such an “advanced” house.
conclusions
Whether it is profitable to build a house or whether it is better to buy it depends on many factors. If you manage to buy a new house in excellent condition, which the previous owners built not for sale, but for themselves, putting their souls into it, but due to circumstances decided to sell, then such an acquisition can definitely be called a bargain purchase, especially if the cost of housing was relatively affordable. Building a house can also be considered profitable if you approach this process wisely.
A comparison table will help you decide whether it is better to buy a plot of land and build a house or purchase a ready-made building.
| Solution | Advantages | Flaws |
| Build it yourself |
|
|
| Buy a ready-made house |
|
|