Natural gas fields
In nature, gas can be found in the following forms:
- Gas deposits in some rock layers. Deposits of gaseous hydrocarbons are usually concentrated at a depth of 1000 m. Contrary to popular belief, gas in such deposits is not located in volumetric voids, but mainly in small cracks, microscopic pores and channels of rocks, for example, sandstone. The composition of such gas is dominated by lower alkanes: methane and ethane. The largest natural gas reserves are concentrated in Russia (Urengoy field), most Gulf countries, the USA and Canada.
- Gas caps above oil and gas dissolved in oil. Such gaseous accumulations are called Associated Petroleum Gas (APG). Unlike “traditional” natural gas, APG contains, in addition to methane and ethane, a significant amount of propane, butane and other heavier hydrocarbons.
- Gas hydrate deposits. Gas hydrates are crystalline compounds that are formed by dissolving gaseous hydrocarbons in formation water under certain thermodynamic conditions - high pressures and relatively low temperatures. 1 volume of water, upon transition to the hydrate state, binds up to 220 volumes of gas. This form of natural gas storage was discovered in the second half of the 20th century. Gas hydrate deposits are located mainly in areas of permafrost, as well as at relatively shallow depths under the ocean floor.
It has been proven that a large amount of hydrocarbons are found in the Earth's mantle, but at present, due to technical inaccessibility, they are of no practical interest.
In addition to gas deposits in the bowels of the planet, it is necessary to mention that hydrocarbons are also found in space. In particular, methane is the third most abundant gas in the Universe after hydrogen and helium. In the form of methane ice, it enters the structure of planets and other cosmic bodies. However, such formations are not classified as natural gas deposits and cannot be extracted at the current level of technology development.
Chemical composition of natural gas
Spatial model of the methane molecule
The main component of natural gas is methane (CH4) - its content varies in the range of 70 - 98%. In addition to it, the composition may include heavier saturated hydrocarbons - homologues of methane:
- ethane
- propane
- butane
In addition to the hydrocarbon component, natural gas may contain inorganic gaseous compounds:
- hydrogen
- hydrogen sulfide
- carbon dioxide
- nitrogen
- inert gases (mainly helium)
Dangerous properties of natural gas
Each of us, from school age, begins to be told about the need to carefully handle fire and household gas. However, not everyone knows what the consequences of leakage of this substance are.
For example, there is a widespread misconception that a person can be poisoned by household gas. This is impossible, because The natural gas supplied to homes is itself non-toxic. Death from leakage occurs due to asphyxiation. When gas molecules used in everyday life enter the lungs, they block access to oxygen. And the person dies, no longer able to breathe.
Natural gas is explosive. Once you smell it (more precisely, the smell of odorant), you need to stop using all electrical appliances, including those operating offline, and also not use open fire. Be sure to open all doors and windows, then call the gas service. These are measures to prevent an explosion from occurring when a dangerous gas concentration in a room is reached (5 - 15% of the total air mass). It is impossible to determine the level of gas pollution on your own, so it is better to play it safe and follow the recommendations. And also remember that the highest concentration of the substance in the room will be at the top, because Natural gas is almost 2 times lighter than air.
You can prevent dangerous consequences from gas used in everyday life by installing a special gas analyzer that will warn of a leak. And, of course, have a working ventilation system that will not allow high gas concentrations in the room.
What types of gas tanks are there?
Gas holders are special containers designed for storing liquefied gas. Variable-volume tanks are widely used in industry, but in everyday life only gas tanks of constant volume should be used. This is due to security requirements. The operating gas pressure in the gas tank should be 16 atmospheres.
A gas holder is a device for storing liquefied gas; its specific characteristics for each home are determined in accordance with the technical conditions of the facility (+)
Such a tank looks like a cylinder, although sometimes spherical models are also found. The volume can vary within a very wide range - up to fifty thousand cubic meters, although such large volumes are not needed for a private home. There are gas holders for installation underground, but there are also above-ground models.
The choice largely depends on the nature of the gas used. For a summer cottage that is not used in winter, a ground-based gas holder is suitable. You can use a mobile gas tank.
But if people live in a house or cottage all year round, you should definitely install an underground tank.
Gas tanks designed for installation underground are more in demand than above-ground models, since they provide a stable temperature for storing liquefied gas
Although it is easier to install an above-ground gas tank, there are more problems with its operation. Due to the influence of high and unstable temperatures, such devices are subject to more stringent safety requirements. The cost of above-ground installations is also usually higher than for underground counterparts.
As a rule, land-based models are installed where large gas consumption is not planned. The container will be emptied periodically, so you need to immediately think about whether to prefer a stationary or mobile option. Refueling of mobile models equipped with wheels for towing is carried out as follows:
If there is a need to use a ground model in winter, i.e. At lower temperatures, you will need to use an evaporator. This is an electrical device that provides safe heating of a gas container.
As a result, LPG quickly turns into a gaseous state and enters the system, providing sufficient pressure.
Underground gas tanks can reach volumes of 50 cubic meters, but for a private home you usually need a smaller container
Gas tanks designed for installation underground are considered more reliable and safe. However, their installation will require more time, cost and effort.
This is due to large-scale work. Installation above soil freezing is not allowed, and in many regions this figure is 1.5 m or even more.
The contents of the reservoir, located inside the soil, are almost completely at a temperature of 5-8°C. A special evaporator is not needed for this model.
For a specific site and project, a gas tank is selected in accordance with the technical conditions developed for an autonomous gas supply system. Typically, the organization tasked with completing the project will purchase the device itself, taking advantage of discounts that manufacturers provide to such customers.
The gas tank control system is installed on its top cover. The pressure gauge allows you to control the pressure inside the container, which should not exceed critical limits (+)
Independent searches and purchase of a gas holder usually do not give the owner of the site the opportunity to save, but increase the risk of purchasing a low-quality or unsuitable device.
On our website there is a series of articles devoted to the selection and installation of gas tanks.
We advise you to read:
- Types of gas tanks: classification basics + review of popular brands
- Turnkey gas tank: how to install a gas tank and install equipment
- The cost of installing a gas tank in a private house: prices for gasification work
In addition to gas holders, liquefied gas cylinders can also be used for autonomous gas supply. One such capacity is usually not enough; several are combined into a common network.
How does natural gas differ from liquefied gas?
Depending on the type of gas used in everyday life, it can be delivered to the consumer in two ways:
- Through a pipeline system directly connected to a gas stove or water heater. With this option, it comes immediately in a gaseous state and is suitable for use.
- Through the ground transport system. Some household and industrial gases are pre-placed in cylinders or special containers (gas holders). There they are in a liquefied state. Depending on the type of gas, the process of turning into a liquid may differ. To convert household gas back into a gaseous state, simply open the cylinder.
Natural gas is suitable for use almost immediately after its extraction. The absence of the need for additional transportation costs makes this type of fuel the cheapest and most convenient for use in everyday life. Depending on what gas is used: propane or butane, the methods of bringing it to a liquid state and placing it in a cylinder differ. There are also differences in the methods of transporting cylinders and safety precautions during their operation.
Depending on what kind of gas is used in residential buildings, it is necessary to ensure its delivery to the consumer, to correctly select, connect, configure and maintain equipment, as well as to take measures for the safe use of this gas.
Rules and regulations
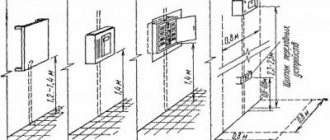
To determine the required distance from the gas pipe, after developing a residential building project, citizens of the Russian Federation apply for the appropriate permit (approval) from the local gas distribution organization. For a definite answer, you need to know the type of gas pipeline and what pressure is used when supplying it. If there is no data on the type of laying and the pressure in the pipes, it is impossible to give an unambiguous answer.
SNiP 42-01-2002 is one of the natural results of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On Technical Regulation” No. 184, adopted in December 2002. In November 2008, the Government of the Russian Federation adopted Resolution No. 858, according to which the current sets of rules were developed and approved. This SP was approved at the legislative level in an updated version and was named SP 62.13330.2011.
The most affordable type of fuel has become widespread and has become a publicly available energy resource. Its widespread use has led to the urgent need to develop regulatory documents in which the permitted distances can be found.
Since 2010, SNiP registered by Rosstandart:
- are legislative documents, compliance with which is mandatory;
- checked by supervisory organizations designed to ensure the safety of such structures;
- may be the basis for a decision in a lawsuit;
- are recognized as a significant reason for imposing an administrative penalty upon violation.
SP 62.13330.2011 regulates the distances that must be observed depending on the type of laying of the main gas pipeline or its branches and the pressure of liquid fuel in the pipes.
If gas is supplied in cylinders, only the prescribed fire safety standards must be observed. More economical and volumetric transportation in pipes provides for differentiated requirements for different types of supplies and pressure levels during their implementation.
Types of gas pipelines
Gas pipelines are divided into:
- Trunk gas pipelines are designed to transport gas over long distances. At certain intervals, gas compressor stations are installed on the pipeline to maintain pressure in the pipeline. At the final point of the main gas pipeline there are gas distribution stations where the pressure is reduced to the level necessary to supply consumers.
- Gas distribution network pipelines are designed to deliver gas from gas distribution stations to the end consumer.
According to pressure in the line:
- Main: first class - at operating pressure over 2.5 to 10.0 MPa inclusive;
- second class - at operating pressure over 1.2 to 2.5 MPa inclusive
- low pressure - up to 0.005 MPa;
By gasket type:
- aboveground;
- underground;
- underwater.
Reserve gas pipelines are constructed for strategic reasons, to provide flexibility in loading gas carriers and to reduce the length of the transportation route.
Gas supply to residential buildings
The use of gas for heating residential buildings and heating water in the warm season has become possible due to the relatively low cost of this fossil.
After undergoing primary processing, it is cleared of mechanical impurities and chemical additives. Thanks to a wide network of gas pipelines, it can be obtained in any locality and delivered to every home.
Scope of application of natural gas in residential buildings:
- Cooking food
- Heating water in the absence of central hot water supply
- Heating in the cold season
Cooking food. Most homes have gas stoves for cooking. They gained popularity not so much from the price of the stoves, but from the cost of fuel, ease of connection, and uninterrupted supply.
The advantages of gas stoves include ease of operation and low cost of maintenance and repair.
Heating water. The use of natural fuel to heat water in homes became popular in the middle of the last century.
A huge advantage of these systems was the presence of an already supplied source of natural gas to apartments and houses.
A serviceable and adjusted column provided stable hot water for the needs of each consumer in the absence of a central hot water supply.
Heating. This type of gas use has found wide application in private homes where central heating is not practical.
Each consumer, having an existing gas supply system in their arsenal, installed a heating boiler for their needs.
Depending on the area of the house, a boiler was purchased and a heat distribution system was installed throughout the house.
The consumer himself chose the temperature in his home depending on weather conditions and, accordingly, gas consumption.
Security automation.
Designed to automatically shut off the gas supply in order to prevent accidents and incidents. Consequences of accidents
Based on thermocouple.
EMC with thermocouple assembly VPG “ASTRA”, the second picture shows an example of a valve.
As a result of heating the thermocouple by the igniter flame, it begins to generate electric current, which is supplied to the winding of the electromagnetic coil, while the core will attract the armature. As a result, the valve will be in the open state. When the igniter goes out, the thermocouple stops producing current, the core will not be able to hold the armature, as a result, under the action of the spring, the valve will close and the gas supply will stop.
Based on ionization electrode.
The operating principle is based on the property of the flame to conduct electric current.
Firstly, automatic shutdown of the gas supply when the burner flame goes out. Secondly, monitoring the state of the air-gas mixture and restoring the combustion process. Thirdly, the combination of ignition and control functions in one device.
Ionization electrodes are certainly used in gas burner flame control sensors. Their main task is, first of all, to signal to the control unit that combustion has stopped and the need to shut off the gas supply. In general, these devices are used to control flame continuity in industrial furnaces, home heating boilers, gas water heaters and kitchen stoves. They are often duplicated by photosensors and thermocouples, but in the simplest thermal apparatus, the ionization electrode is the only means of controlling the ignition of the gas and the continuity of its combustion.
Main reasons for triggering:
- incorrect proportion of the gas-air mixture formed in the igniter;
- carbon deposits or contamination on the ionization electrode;
- insufficient flame flow power;
- reduction in insulation resistance due to the accumulation of conductive dust in the igniter.
Advantages of ionization electrodes.
Undoubtedly, this is the instantaneous response speed when the flame goes out. In contrast, thermocouple sensors generate a signal only after a few seconds, which they require to cool down. In addition, ionization electrodes are inexpensive because they have a very simple design: a metal rod, an insulating sleeve and a connector. Moreover, they are very easy to operate and maintain, which consists of cleaning the rod from carbon deposits.
Disadvantages of ionization control sensors.
First of all, they are unreliable when working with gas fuel containing large proportions of hydrogen or carbon monoxide. That is, an insufficient number of free ions and electrons is generated in the flame, which makes it impossible to maintain a stable current. In addition, this method may not be suitable when working in dusty conditions.
Gas water heater device
A geyser is a unit for heating cold water to the required temperature in a single apartment or house using gas.
The column consists of the following parts:
- gas-burner
- heat exchanger
- chimney
- automation unit
- ignition unit
The automation unit ensures the safe operation of the gas appliance.
To turn on the column in water heating mode, the following conditions must be met: the presence of water in the water supply system and sufficient pressure, the presence of draft in the chimney to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning during its operation, and sufficient pressure in the gas supply system.
What gas is used in residential buildings, and at what pressure
Before being supplied to the house, gas is cleaned and supplemented with certain components, which increases the level of safety of its use. Then the methane, through many kilometers of pipelines, reaches the gas distribution station. The pressure level in the pipelines is very high and reaches 11.8 MPa.
The gas produced from the fields has no odor. To avoid emergency situations, odorants are added to methane. They have a sharp, specific smell. In the event of a leak, consumers will be able to recognize it and report it to the appropriate services.
The gas supplied to apartments has the following components:
- propane
- methane;
- water vapor;
- carbon dioxide;
- hydrogen sulfide;
- ethyl mercaptan and ethanethiol - for a pungent odor.
Natural gas (methane) is widely used today. It can be extracted using the traditional method (mining) and by processing organic waste (so-called biogas). The pipeline delivers methane directly to citizens’ homes.
The most widely used gas at present is liquefied gas (propane-butane mixture). It is stored in cylinders and tanks at a pressure of 16 atmospheres. Residents of houses without a central gas supply system purchase methane cylinders weighing up to 40 kg, with a capacity of up to 50-80 liters.
Houses connected to the gas supply system receive liquefied fuel from underground tanks.
Depending on the time of year, different gas is supplied to consumers. It differs in its composition. This is explained by the evaporation temperature of its various components.
The uniform blue color of gas used in residential buildings indicates good quality fuel. Its use in the home is safe and will not cause unnecessary waste.
If gas combustion is accompanied by the appearance of bright yellow or red tongues, this will indicate an excess of air and other harmful components. Fuel with excess impurities is characterized by reduced heat productivity, which increases its consumption and the amount to be paid for consumed resources. Using contaminated gas is dangerous for your home. May shorten the operating life of the equipment.
For the needs of the population at gas distribution stations, the methane pressure is reduced to 1.2 MPa. This indicator is sufficient for heating the house and cooking. The fuel also undergoes additional cleaning. After which it goes through the gas pipeline to citizens.
Types of domestic gas
Compared to other energy sources, gas has many advantages: it ignites quickly, does not emit soot and smoke during combustion, and practically does not contain harmful components and solid impurities. The combustion process of blue fuel is easy to control.
There are two main types of gas used in domestic settings:
- Natural. A gaseous substance that is pumped into storage facilities and supplied to residential buildings through an extensive pipeline system. It consists predominantly of methane and does not change its physical state from the moment of extraction to delivery to the direct consumer.
- Liquefied. A propane-butane mixture obtained during oil refining. It is a liquid placed in special tanks for storage or transportation to places where the use of pipes is impossible or economically impractical.
Through centralized heating and gas supply systems, natural gas is supplied to residential premises, extracted from the bowels of the earth and previously purified from a number of impurities. This type of fuel is considered the cheapest, most accessible and convenient for apartment buildings.
Natural gas brings comfort and warmth to your home, allows you to efficiently heat the room and quickly prepare food. It is a universal energy carrier that releases a large amount of heat during combustion.
But the liquefied propane-butane mixture is characterized by a high heat of combustion, but at the same time it is much more explosive. Liquid gas cylinders need to be transported, set up and connected correctly. When using them, it is extremely important to observe special safety precautions. Often, cylinders or gas tanks are installed in private homes and summer cottages.
Since methane is half the weight of air, it accumulates at the top during leaks. The propane-butane mixture, on the contrary, goes down. This must be taken into account in emergency situations.
Composition and pressure of gas in pipelines
Before ending up in the main pipelines leading to residential buildings, natural gas undergoes preliminary processing and several degrees of purification. During the procedures, the necessary impurities are added to the fuel, making the composition as effective and safe as possible for use.
Following from the place of production to heating systems and kitchen stoves, gas travels tens of thousands of kilometers along underground, underwater, onshore or surface pipelines. In terms of device complexity, they can be single- or multi-stage
The main share of the fuel mixture is methane. Depending on the mining region, its content varies from 80 to 98% of the total volume. It is the amount of methane that serves as an indicator of the quality of the energy carrier.
Domestic gas also contains:
- carbon dioxide;
- propane;
- ethane;
- butane;
- hydrogen sulfide;
- helium.
In addition, the fuel may contain a small amount of water and nitrogen vapor. Properties and characteristics are almost entirely determined by methane, but can change under the influence of the quantitative and qualitative composition of the mixture.
In the gas pipeline systems through which fuel circulates, very high pressure is created - above 2.5 MPa and up to 10 MPa. Under such pressure, gas moves over long distances and between populated areas.
Since such an indicator is unacceptable for domestic consumption, when it arrives at gas distribution stations it is significantly reduced by carrying out additional methane purification. Thus, gas is transported to consumers under pressure up to 5 kPa (low pressure), from 5 kPa to 0.3 MPa (medium pressure range) and 0.3 MPa to 1.2 MPa (high pressure range). We examined gas pipeline pressure standards in more detail in the following material.
Causes of the specific smell of gas
Methane itself, in its pure form, does not have a characteristic odor or color. What is added to household gas to give it its characteristic smell? It is possible to detect a leak using the sense of smell due to the fact that a small amount of substances with a strong unpleasant odor are mixed into the gas.
These substances are called odorants. They give the fuel mixture a specific smell of rotten hay, rotten eggs or rotten cabbage, which warns of danger and a possible gas leak in the room. Odorants do not make the gas more toxic. In small concentrations, these substances are not hazardous to health, evaporate easily and are of a warning nature. If concentration limits are exceeded, substances may cause headache, nausea
Sulfur-containing organic compounds are used as odorants, most often ethyl mercaptan or ethanethiol. They are sprayed into the structure of the fuel mixture using special installations during processing.
Paperwork and equipment selection
But before you face the installation, you will need to run around to different authorities and collect a package of documents. Prepare a passport, title documentation for the land plot and the building located on it. You also need to write and submit an application to the gas service in which you express your desire to gasify your house. After this, you will receive a technical specifications form, which is filled out by the developers. And only then can you start drawing up a project.
In the photo - gasification of a private house
You will need to enter into the following agreements:
- on carrying out work and drawing up technical documentation;
- on gasification and installation of relevant equipment;
- act of putting gas equipment into operation;
- for the supply and payment of natural gas.
In some cases, if you do not dare to have an autonomous gas supply, you will have to stretch pipes through your neighbors’ plots, and then you will need written permission from them. It is necessary for specialists to come to you and inspect the chimney in the house, and at the end they are required to issue a certificate. You will also have to visit the local architectural and planning department. The head of this organization is also required to issue a permit for gasification of the site.
It has already been said that absolutely all materials, especially pipes, taps, hoses, must have the appropriate certificates. Without such documentation, all these elements cannot be put into operation. Blue fuel flows through pipes with a diameter of 150 mm and a wall thickness of 5 mm. Basically, elements made of low-carbon or low-alloy steel are selected. In principle, both seamless and welded structures can be used. Naturally, the gas main is assembled from a fairly large number of pipes. They are connected by gas welding. There are also very serious requirements for the quality of electrodes and they cannot be neglected.
Photo of the gas main of a private house
But the list of necessary materials does not end there; you will also need a number of small parts - tees, crosses, couplings, adapters, angles and plugs. They are usually made from cast iron or steel. To properly fix all threaded elements, you should choose the right tool. For example, maximum grip on the part is provided by wrenches with notches and parallel jaws. Is it worth mentioning the boiler, water heater, stove and other equipment?
Why is household gas dangerous?
Whatever gas enters residential buildings, through the main gas pipeline or from a cylinder, if handled incorrectly, it can be deadly.
Explosive situations arise at the moment of critical increases in methane concentration (more than 15% of the total volume of air in the room). At temperatures above 650 °C, spontaneous combustion is possible.
The natural gas supplied to homes contains almost no toxic substances. But in everyday life there are many cases when, as a result of a leak, serious harm to the body is caused or even death occurs. The main reason for this is carbon dioxide, which enters the room and displaces oxygen from the surrounding space, causing suffocation.
Another negative feature of methane is its high fire and explosion hazard. The level of risk is determined by many additional factors, in particular pressure and ambient temperature.
If there is a leak, the gas mixes with air, forming an explosive mixture. The source of ignition in hallways, apartments and houses can be a small spark, a flame from a cigarette, lighter, match, or any device that uses electrical impulses.
Electrical equipment and devices powered by batteries and accumulators pose a particular danger in closed, gas-filled rooms. With a high percentage of methane, even a turned-on mobile phone and laptop can cause an explosion or fire.
The explosions are so strong that they almost completely destroy housing. Therefore, if you hear a characteristic smell in the apartment, it is advisable not to use electrical appliances and turn off the electricity in the switchboard.
How to protect yourself when using gas appliances
Fuel and equipment must be used according to certain rules:
- Every year, gas service employees must check gas appliances and the in-house gas supply system.
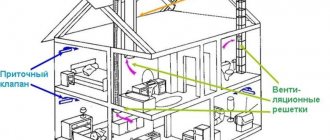
- Periodically monitor the draft level in the kitchen or in another room where gas equipment is installed. If an insufficient level of ventilation is detected, the shaft will need to be cleaned.
- In winter, do not close the ventilation.
- After finishing using the gas, turn off the valves and taps of the pipelines located near the equipment.
- While equipment is operating on methane, it must not be left uncontrolled.
- If you smell gas, you should follow the recommendations presented above.
- A gas analyzer can be mounted on the ceiling above gas appliances. If a fuel leak occurs, residents will be notified by an audible signal.
The above recommendations will help users avoid accidents.
Not allowed:
- move gas equipment on your own initiative and install it yourself;
- allow preschool children to use gas stoves and other equipment without parental control.
How to calculate paint consumption for painting walls
An important element of successful finishing work is the optimal consumption of materials. Unused interior decoration scraps often go unused and eventually deteriorate and are thrown into the trash.
The entire process of calculating paint for painting walls includes:
- Carrying out the necessary measurements of the surface to be painted;
- Sequential arithmetic calculation;
- Accounting for specific adjustments.
To measure the area of each wall, it is necessary to measure their height and width. After this, you should measure the dimensions of window and door openings to deduct from the total painting area. If you plan to paint the window sills, add the baseboard area to the overall size.