Houses of series 1–464 are a legacy of the Soviet past. The design documentation was developed by Moscow architects of the Giprostroyindustry Institute by 1957. And the very next year the first five-story building of the 1–464 series from the Khrushchev family was built. Houses 1-464 were built throughout the Soviet Union until 1963, and modified versions, for example, series 1-464A-20, until 1975.
The building of series 1–464 is a residential building consisting of end and row sections. As a rule, the number of entrance sections is 4. This is the most used layout option. The number of floors of large-panel residential buildings is 5 floors. At first they built 3- and 4-story versions, but for direct benefit they settled on a 5-level version.
During the construction of buildings of the 1–464 series, a structural scheme with longitudinal and transverse load-bearing walls was used. External walls are single or three-layer reinforced concrete panels with a thickness of 210 to 350 mm, depending on the climatic conditions of the construction region. The width of reinforced concrete panels with small pitches is 2600 and 3200 mm. They can be painted or covered with a layer of gravel. The balconies are installed on slabs of greater width.
Solid reinforced concrete slabs with a thickness of 100 mm are used as interfloor ceilings. Partitions are made of reinforced concrete with a solid section and a width of at least 120 mm. The layout of the house provides for combined bathrooms.
Houses series 1-511: apartment layout options
The flat roof has a soft roof made of roofing felt based on bitumen mastic. Drainage is carried out through an external drainage system. There is no technical floor in the house of series 1–464. Ceiling height 2500 mm.
The vital functions of the building are ensured by centralized water supply, sewerage and heating systems. Electricity and gas supply is provided from citywide electric and gas networks.
Ventilation of the interior space occurs naturally due to windows and a ventilation duct, according to the layout, located in the wall between the kitchen and toilet.
The combined bathroom is equipped with plumbing equipment, and the kitchen is equipped with a stove for cooking. An elevator and a garbage chute are not provided for by Project 1–464.
Home 1,464 episodes. Typical residential building series 1-464
The 1-464 series of houses is all-Union and was built throughout almost the entire former USSR, including Moscow and the Moscow region. Houses in this series can be recognized by the windows on the interfloor landing, which are identical to the double-leaf windows in the apartments. Houses of series 1-464 consist of a set of row and end sections, all apartments face one side, with the exception of corner ones. The type of stove in such houses is gas.
Photo of the house series 1-464
| Construction technology: | panel |
| By construction period: | Khrushchev buildings |
| Years of construction: | from 1958 to 1963 |
| Number of sections/entrances: | from 3 or more |
| Number of floors: | 5, in rarer cases 3-4 |
| Ceiling height: | 2.50 m. |
Main characteristics
The main material used for standard design houses is reinforced concrete panels. Houses were also built from block rooms and bricks.
The number of entrances is usually 3 or more. Houses of a standard design are among the top ones with multiple entrances in Minsk. For example, a residential building on 2nd lane. Bagration has 24 entrances, Odintsova, 36/1 - 25 entrances, and Yesenina, 6/1 - 26.
Many standard-design houses have vestibules, usually for 2 apartments. Many citizens use vestibules as places to store strollers or bicycles. Previously, most of them had special boxes - storage for vegetables.
The design of the houses provides for a garbage chute. Despite the fact that they are currently being preserved in Minsk, at the time when construction began, they were considered a luxury.
Series of panel houses of 5 floors. Typical apartment layouts Thu, Ap. 2011
Description and standard layouts of apartments. From Stalinist to modern ones.
| Stalinka 1954-1961 | 1955-1960 | 1955-1960 | 1954-1961 | |
| 2-, 3-story brick houses | 4-, 5-story brick houses | 4-story brick houses | ||
| Khrushchev 1958-1967 | 1960-1967 | 1963-1967 | 1958-1964 | 1959-1960 |
| 5-storey panel houses | 5-storey panel houses | 4-, 5-story brick houses | 4-, 5-storey block houses | |
| 1964-1967 | 1964-1967 | |||
| 5-story brick houses | 5-storey block houses | |||
| Brezhnevka 1966-1975 | 1966-1973 | 1966-1970 | 1967-1977 | 1966-1967 |
| 5-storey panel houses | 5-storey panel houses | 5-story brick houses | 5-storey panel houses (for small families) | |
| 1967-1970 | ||||
| 5-storey panel houses (block rooms) | ||||
| Standard 1968-1999 | 1970-1976 | 1968-1977 | 1970-1977 | |
| 9-storey panel houses | 9-storey panel houses | 9-story brick houses | 5-storey panel houses (block rooms) | |
| 1977-1998 | 1973-1975 | 1972-1977 | ||
| 9-storey panel houses (for small families) | 9-storey panel houses (for small families) | 9-storey panel houses (block rooms) | ||
| 1973-1985 | ||||
| 12-story panel houses | ||||
| Improved | 1976-1983 | 1977-1985 | 1976-1994 | 1977-1996 |
| 16-storey panel houses | 9-storey panel houses | 9-storey panel houses | 9-storey panel houses | |
| 9-storey panel houses | 12-story panel houses | |||
| 1983-1998 |
Elevators
The era of standard-design houses has made elevators an integral part of the life of millions of Belarusians. SNiP 1971 provided for the mandatory presence of an elevator in houses with more than 5 floors.
- For houses up to 9 floors inclusive - 1 passenger elevator with a load capacity of 320 kg.
- For houses with 10-12 floors - 2 passenger elevators.
- For houses with 13-16 storeys - 1 passenger and 1 cargo (up to 500 kg), or 2 passenger and 1 cargo, depending on the number of apartments on the floor.
Nowadays, many buildings have replaced elevators with modern ones.
Article on the topic
Improved project houses in Minsk: history, layout features, advantages and disadvantages
Series 1-464 drawings. Modifications of a series of standard panel houses 1-464
Due to the low cost of construction and the use of locally produced building structures and materials, the 1-464 series has gained great popularity.
Architects and builders, remembering the need for urgent liquidation of barracks, left the idea of comfortable housing to the next generations and revived the 1-464 series and modified it as needed.
The type of all houses in the series is large-panel
For the most part, these are 4-5 storey buildings, with the absolute majority of five-story buildings.
Height of living quarters from 254 to 262 cm
Modifications of the series can be divided into two generations and versions with increased number of floors.
The first generation of residential buildings of the 1-464 series with modifications.
The first generation was built from 1958 to the end of the 60s
Basically, the versions differ in the composition of apartments, number of floors and the presence of non-residential premises: 1-464(A)-(1, 2, 5, 6, 13, 27, 28) 1-464(A)-(3, 4, 7, 1 -464A-(9, 10, 11, 12) 1-464A-(14, 15, 16, 18)
1 -464A-(9, 10, 11, 12) 1-464A-(14, 15, 16, 18)
Photos and layout of early versions of the 1-464 series
And modifications on this basis: 1-464A-13 - a 5-story, 4-section house with 64 apartments and 40 rooms for small families; 1-464A-27 - a 5-story, 4-section building with 64 apartments with a store on the ground floor; 1-464A-28 - a 5-story, 4-section building with 72 apartments with non-residential premises at the ends of the house; 1-464A-30 - a 5-story, 5-section building with 100 apartments (one-room apartments - 75, two-room apartments - 25).
House version 1-464A-30 and apartment layout
The second generation of all-Union five-story buildings
The second generation of houses with up to five floors was built from the early 70s to the end of the 80s, and even rare two-story options appeared.
Apartments now have four-room apartments, and bathrooms are more likely to be separate.
Typical designs of five-story buildings 1-464A-(14, 15, 16, 17, 18) 1-464A-(58, 59, 60) - the same in expanded clay concrete structures; 1-464A-(55,56,57) 1-464A-E77 - with a store on the ground floor. 1-464A-17a - option with consumer service premises on the ground floor. The series was continued by subsequent modifications: 1-464D-(101, 102, 103, 104, 105)
The second generation of the series not only became widespread throughout the USSR, but also increased in height. There are versions that finally have an elevator and a garbage chute, ranging in height from 9 to 16 floors.
The first nine-story building was project 1-464A-20.
Later versions were built: 1-464D-(86, 87) 1-464D-(101, 102, 103, 104, 105)
Nine-story buildings of series 1-464 and their layout
A 9-floor “tower” 1-464D-89 appeared, intended for local cooperative construction.
Nine-story single-section tower 1-464D-89
House 1-464D-80 had only one-room apartments for small families.
There are only one-room apartments in this house
Houses of version 1-464D-E54 have grown to 14 floors, and the record of 16 floors belongs to 1-464D-E104 and 1-464D-E193.
Photos of high-rise buildings series 1-464 in the Moscow region
In the Siberian region, SibZNIIEP developed and built its own modifications of the 1-464 series, of which there are about a dozen.
Series 1-464 9 floors. 1-464
1-464 - a series of residential low-rise buildings was developed by the Giprostroyindustry Institute in 1957 and did not become the cheapest in terms of cost, although it took second place in terms of this indicator.
Most often, five and four-story versions of houses of this series were built in the USSR. At the peak of the construction of the 1-464 series, almost two hundred house-building factories were involved in the production of panels throughout the country.
Photos of houses in series 1-464
The series was modified to suit the climatic conditions and production capabilities of various regions of the country and was overgrown with modifications.
In 1963, on its basis, the TsNIIEP Housing Institute developed an improved series 1-464A, which can be considered the second stage in the development of all-Union five-story buildings. Construction of improved versions of the series continued until 1978, taking into account regional long-term construction projects.
Moscow did not become a construction site for the 1-464 series, but its improved analogue with increased apartment areas, which received the 1605-AM index, was actively developing the capital
In the 70s, the series received modifications 1-464D with increased number of floors, elevators and garbage chutes. The modification, in the same way as the parent series, received options from houses for small-family living to single-entry towers for cooperative construction. The number of floors of various modifications ranged from 9 to 16, and the last houses in the series were commissioned by builders already in the 80s.
Photos of modifications of series 1-464 houses with elevators
In the basic elevator-free version, the houses of series 1-464 had 1, 2, and 3 room apartments with combined bathrooms, low ceilings (249 cm) and mediocre thermal insulation of external walls. Later, versions with external panels of expanded clay concrete appeared, which somewhat improved the situation and the ceiling height increased to 160 cm.
One-room apartments of small-family modifications had a kitchen even less than 5 square meters. meters, in the rest of the series it did not exceed 6.3 square meters. m., which was typical for Khrushchev.
The proportions of many rooms leave much to be desired, since the living spaces have an elongated shape with a window at the end. The practice of having to hang carpets on the walls arose due to the critically poor sound insulation of the apartments in the series. The cramped hallway and compact bathroom made the accommodation also not the most comfortable.
For adaptation to modern living conditions and redevelopment of houses, series 1-464 is also of little use due to the presence of load-bearing walls inside the apartment. There is a chance to change something only for bathroom partitions and a few non-load-bearing walls.
In Moscow, five-story buildings of the 1605-AM series are gradually being demolished, since their design is outdated not only physically, but also morally.
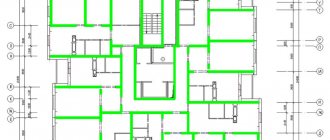
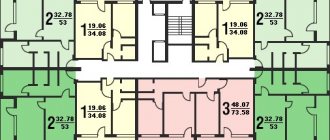
Floor plans of buildings series 1-464 of various modifications
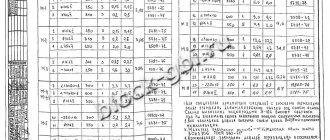
The total/living area of apartments in houses of series 1-464 is: 1 sq. m. 30/18 sq. m.; 2 sq.m. 31-45/18-35 sq. m; 3 k. sq. 54-59/39-45 sq. m. Some versions of the houses have four-room apartments in the end sections.
Redevelopment of a two-room apartment 464 series. Options for redevelopment of apartments series 1-464
Description of series 1-464
The design institute "Giprostroyindustry" lacked quite a bit to develop a frame-panel residential building with the lowest cost, but the triple place of honor led to the massive construction of the series and its modifications throughout the USSR. In total, during the years of construction from 1958 to 1963, more than 3,000 houses were commissioned for occupancy.
The number of floors in the series started from three, but most often five-story buildings were built. Houses of this series were mainly built in the Moscow region, and it was modification 1-464A, created in 1961, that became the most widespread.
Being massive, the series was continued in a large number of modifications. The last houses in the series were built in the late 80s.
In Moscow, houses were built in the Moscow version of the 1-464 series, which received its own name 1605-AM/5 and improved characteristics.
All apartments in the series have balconies, but all apartments have shared bathrooms. There was no elevator or garbage chute.
| Area m² | general | residential | kitchen |
| 1 sq.m. | 30-31 | 18 | 5.1 — 6.3 |
| 2 sq.m. | 32-46 | 27-35 | 5.6-6.3 |
| 3 k. sq. | 55-58 | 39-45 | 5.6-6.3 |
Ceiling height 250 - 260 cm.
Building materials:
The external walls are made of one or three layers of reinforced concrete, with a thickness of 21 to 35 cm, which depended on climatic conditions.
Internal walls are reinforced concrete 12 cm thick
The floors are solid reinforced concrete slabs 10 cm thick.
The advantage of the series is improved strength and durability of the structure, balconies.
The shortcomings of the series, characteristic of all five-story buildings, received a new interpretation. Added to these were mediocre thermal insulation of external walls, combined bathrooms in all apartments, and poor sound insulation inside the house contributed to the development of the fashion for hanging and laying carpets wherever possible. In addition, it is almost impossible to talk about changing the layout of the apartments - almost all the walls are load-bearing.
Communications
Heating
- central water supply, cold water supply - centralized, sewerage - centralized. Hot water supply is centralized or local (gas water heaters), in the latter case, chimneys are provided in the design of the house. Ventilation is natural in the kitchen and bathroom; ventilation ducts are located in the wall between the bathroom and the kitchen.
The apartments are equipped with a bathroom and a gas stove; in the absence of gas supply, an electric one.
There is no elevator or garbage chute.
The houses contain one-, two- and three-room apartments. There are 4 apartments on the landing. In corner sections the set of apartments is 1-1-2-3 or 1-2-2-2, in ordinary sections 1-2-3-3 or 2-2-2-3.
Redevelopment 464 series 3 room. Redevelopment of a three-ruble ruble in a standard socket: 7 schemes (free)
What can be done with a typical apartment of 80 sq. m without significant redevelopment? For example, find a place for an additional bedroom, arrange a dressing room, or move the kitchen to the hallway.
Typical layout
Apartments in houses of the P-111M standard series are quite spacious - a three-ruble ruble occupies 80 square meters. m. Living room 22 sq. m and a wide corridor is separated by a non-load-bearing wall, which can be moved to make a redevelopment. And the symmetrical bedrooms are 12 square meters. m are limited by load-bearing walls, so they cannot be changed. The kitchen area allows for different layouts, even with an island and breakfast bar. In addition, in some cases the opening can be moved to a load-bearing wall in the living room.
Option 1
The initial layout of the apartment is quite good, so you can limit yourself to a successful arrangement of furniture. In the living room we will provide a sofa area and a work desk by the window, in the kitchen there will be a corner set with all the necessary equipment. We use the far rooms as a bedroom and a nursery, in each of which we will install a closet along the wall adjacent to the bathroom. And we use the width of the corridor to accommodate a very spacious storage system.
Option 2
In this version, the living room area was sacrificed for more convenient access to the kitchen and bathroom. A closet was built into the living room wall on one side and a wide work desk for two on the other. A linear set in the kitchen allows you to install a large dining table for six people. Smaller rooms will turn into a nursery and a bedroom with a standard set of furniture.
Option 3
One of the standard layout options involves entering the kitchen from the living room. This will make both rooms more spacious. This will allow you to install a bar counter and a longer corner set in the kitchen, and build in a wardrobe for outerwear in place of the corridor. The wall between the living room and the corridor can be demolished, leaving only a small partition, for example, with an imitation of a fireplace. From the hall side you can hide a mini-dressing room behind it.
Option 4
This option is very similar to the previous one, but they did not build a dressing room here, limiting themselves to only a system of cabinets of different widths opposite each other. In addition, a dining table was installed on the balcony next to the kitchen. And instead of an office, there was a room for two children. To fit everything necessary into 12 squares, we chose a bunk bed and a wide wall-length desk by the window, which ends with shelves for books and toys.
Option 5
The area of the living room and the width of the corridor make it possible to move the wall between them and turn a three-room apartment into a four-room apartment. The living room will be open and dark, so you can install a window in the wall or make it out of glass blocks. We will allocate smaller living rooms for a bedroom and a nursery for the older child. And the 14-meter children's room next to the living room will be shared by two younger (or same-sex) children. We will install two desks for them by the window, and divide the two beds with a shelving unit.
Option 6
The layout in this version is approximately the same. But if the children are older, then they can be given more freedom and their bedrooms located in the back of the apartment. The layout of the children's rooms is absolutely symmetrical - in addition to the bed, each one has a wardrobe, a desk by the window and a couple of shelves next to it. We will build another closet into a specially built niche in the living room. We will dedicate an entire wall in the bedroom for a storage system. In a four-meter bathroom, we will replace the standard bathtub with a corner hydromassage one.
Option 7
The most difficult option both to implement and to coordinate is moving the kitchen into the living room. This will allow you to create full four rooms without sacrificing the feeling of spaciousness. Formally, the set is located in a non-residential area - in the corridor. In the combined kitchen-living room there will be a dining area with a large dining table. This layout will allow you to build a wardrobe for outerwear in the hallway and another one for seasonal items in the hallway. The bathroom will expand due to the corridor, and now it will become a master bathroom in the bedroom. In the back rooms you can arrange two children's rooms or a bedroom if three generations of a family live in the apartment at once.
If you want to see more of this in your feed, like it. Subscribe to the channel and learn the latest trends in interior design.
Author: Pavel Shelyagin.
pros
- Increased kitchen size compared to previous types of projects.
- Regularly shaped corridors provide space for a built-in wardrobe. Today, deep sliding wardrobes are perfectly built in there.
- The bathroom is separate, and the bathroom has enough space to install a washing machine and washbasin.
- Most layouts have a loggia with an area of about 4 m2. Many buyers convert it into an office or children's playroom.
- Apartments on the ground floors of standard-design buildings are in greater demand than similar options for “Khrushchev” or “Brezhnevka” buildings, since these floors are usually high. Also, apartments on the 1st floor with loggias often have a cellar.
- The widespread presence of elevators has made it comfortable to live on high floors, which suffer less from the noise of the local area, can have a panoramic view, and are better ventilated.
1-464d-83.
Series I-464 (1-464) - a series of large-panel residential buildings, developed by the Giprostroyindustry Institute in 1958, developed and improved by TsNIIEP housing (project authors N.P. Rozanov, V.G. Kocheshkov, A.G. Rosenfeld, Polozov I.P.) The series is based on a structural scheme with transverse (steps of 2.6 and 3.2 meters) and longitudinal (spans of 5.76 meters) load-bearing walls. Houses of the I-464 series are available in every district of Novosibirsk. Houses of the I-464 series were produced by the Sibakademstroy trust and the House-Building Plant No. 1 (DSK-1) of Glavnovosibirskstroy.
I-464 is the most popular Novosibirsk series. From the details of this series, four-, five- and nine-story residential buildings, which became the most widespread, were built, residential buildings with a height of 12 floors, residential buildings with a height of 2-3 floors and even public buildings (for example, building 63 on Mira Street, in which Clinic No. 21 is located).
The first houses of the I-464 series were built in 1961 in the “B” microdistrict of Akademgorodok and on Gogol Street, the first nine-story house DSK-1 was installed in 1967 on the Zatulinsky residential area. In 1972, DSK-1 became the general contractor for the construction of all houses of the I-464 series, produced until the mid-1990s.
Nine-story buildings
Nine-story buildings of the I-464D series are the most common high-rise buildings in Novosibirsk. DSK-1 Glavnovosibirskstroy mastered the production of the widest range of houses and block sections: ordinary, end, corner and rotary (at different angles) block sections, houses with passages and driveways, houses with built-in and attached shops.
Links
- Typical series of residential buildings in Novosibirsk: options for redevelopment, layouts
- N.P. Rozanov, Large-panel housing construction, Moscow, Stroyizdat, 1982, 224 pp. with illustration.
- V.A. Kossakovsky, Pioneer of industrial housing construction, Moscow, Stroyizdat, 1980, 80 pp. with illustrations.
| Residential buildings | Since 1957, after the adoption of a law that provided for the elimination of excesses in the design of houses, buildings of a new type began to be erected in the USSR. Popularly, such houses were called “Khrushchevka” (derived from the name of the General Secretary of the CPSU Central Committee N.S. Khrushchev). Such houses received a second name - Khrushcheby, mainly because of the inconvenient and disproportionate layout of the rooms, narrow corridors and landings, thin walls and, as a result, terrible sound insulation. In this article we will talk about what the typical Khrushchev series are, and we will try to highlight the main pros and cons of these buildings. We will provide the planning features in the form of descriptions and photos. |