Foamed concrete is a modern promising material for low-rise construction; It is used primarily in the form of block modules of a certain size. The quality/price ratio for buildings made from it is significantly higher than for buildings made from other types of cellular concrete, not to mention stone and wood. The exception is expanded polystyrene concrete, but it has zero fire resistance. At the same time, you can build a house from foam blocks with your own hands, without resorting to special equipment and without having construction qualifications; Some idea of the range of possibilities for amateur “foam construction” is given in Fig. Therefore, the interest of individual developers in foamed concrete is completely justified and we will try, to the best of our ability, to cover the issues of constructing foam block (gas block) houses; There are more than enough inaccuracies in widely available sources.
Houses made of gas blocks and foam blocks
What is “foam” and what is “gas”
First of all, the meaning of the terms “foam concrete” and “aerated concrete” often changes places; sometimes clearly intentional. For example, under the guise of an aerated concrete house, construction from monolithic foam concrete is described, foam blocks are called gas blocks, and vice versa. The psychological basis for this is obvious: a gas block, is it made of gas? A house made of thin air? And foam concrete appeared more than 100 years earlier than aerated concrete. But both materials are foamed cellular concrete, and in general it is legitimate to call an aerated concrete block a foam block, just as a diesel engine, a carburetor engine and a gas turbine are internal combustion engines. Moreover, the name “foam concrete” and its derivatives were already used by the advent of aerated concrete; it was necessary to somehow name the new material, which was very different from its predecessor.
This implies a commercial factor: the cost of a foam concrete block is 3-5 times less than an aerated concrete block of the same size, and the quality of foam concrete buildings in terms of all parameters is 1.5-2 times worse. By describing to a potential buyer the advantages of aerated concrete under the name of foam concrete and then offering foam blocks, you can make a lot of money: you can make foam concrete using a homemade method in the garage, but the production of aerated concrete requires industrial conditions and complex technological equipment.
The differences between foam concrete and aerated concrete have already been described in sufficient detail. We will also have to mention them in this article, but for now, briefly: that very fragile and rough material that absorbs water like a sponge, gives it away just as easily and can withstand no more than 25 freezing/defrosting cycles - this is foam concrete. And aerated concrete is much stronger and more durable, it can be used to build up to 3-4 floors and lay reinforced concrete floor slabs on a box of aerated blocks. An aerated concrete block can float for days and months, but, once saturated with liquid moisture, it takes just as long to dry.
Note: the degree of absorption of water vapor from the air for foam concrete is up to 16% by weight, and for aerated concrete up to 5%. Both are quite acceptable for building structures.
We will further describe mainly how to build a house from aerated concrete, i.e. aerated concrete blocks; Monolithic aerated concrete cannot be made on a construction site. Therefore, consider “foam block” and “gas block” with their word forms later in the text as synonyms denoting the same class of products: building modules of standard sizes made of aerated concrete. Where we talk about foam concrete buildings, it will be indicated “foam concrete block”, etc., or it is specifically stated that in this case we mean foam concrete and not aerated concrete, for example. "regular foam concrete".
Types of building stone
Foam concrete building products are produced in several modifications and standard sizes . They are grouped into classes based on the purpose and density of the structure, which is expressed by the number of empty cavities per unit volume. With a smaller number of pores, the density and strength of the product, its thermal conductivity and grade are greater. Foam concrete blocks are marked with the letter D from 100 to 1200.
Classification of foam blocks:
- Structural from D1000 to D1200, for load-bearing structures with the highest strength and weight indicators, 600x300x200 mm.
- Combined, structural and thermal insulation from D600 to D900 for private housing construction in the form of load-bearing structures with energy-efficient thermal protection, 600x400x200 or 300x200x600 mm
- Thermal insulation from D100 to D500, very light products, used for independent thermal insulation and sound protection systems, as well as for partitions, block size 100x300x600 mm.
Important ! The weight of foam blocks solely depends on the brand, however, under the influence of atmospheric conditions, it inevitably grows, which must be taken into account when designing the foundation.
Read more about the types of foam concrete blocks here.
Development stages
A general idea of the process of building a house from foam concrete blocks is given by the video:
Video: DIY foam block house
Variations of technology are possible, depending on local conditions and own capabilities. Foam concrete (aerated concrete) is a material that is very tolerant of fairly strong deviations from the approved rules for working with it, which largely explains its popularity. The purpose of this publication is to give the reader an idea of the technological aspects and operations that must be followed and performed accurately so that the house will stand, remaining warm and comfortable, for at least 70 years, provided that the local geology and soil mechanics may change significantly during this time. In general, according to the data collected to date, the durability of buildings made of foam concrete/aerated concrete can exceed 150 years without major repairs.
Construction of a house made of foam blocks (gas blocks) includes the following steps:
- Surveys at the site of future construction;
- Choosing the type of foundation;
- Determining the feasibility of building on your own;
- Selection of material for the supporting structure (box);
- Design;
- Zero cycle and laying the foundation;
- Selecting a wall laying scheme;
- Construction of the box, including load-bearing partitions and ceilings, see below;
- Construction of the roof crossbar (supporting structure);
- Roof decking;
- Technological break for box shrinkage;
- Exterior finishing (cladding);
- Installation of interior partitions;
- Installation of floors, including heat and sound insulation;
- Installation of windows and doors;
- Interior finishing, including flooring.
Note: when they say “A house made of foam blocks in 6 (10, 15) days!”, this is, excuse me, a scam. Two or three people can actually install a box made of aerated concrete in a week. But - on an established foundation, which takes a year. And then a technical break is needed for dry shrinkage of the masonry, from 1 month. for aerated concrete and up to a year for foam concrete. The latter, in addition, needs breaks of 2-3 days after every 3-4 rows of masonry, so that the mortar sets and the next blocks do not slip.
Dismantling technology
Dismantling work on foam block walls is required mainly when the owner decides to redevelop it , for example, to increase the usable area in the house. This type of work is very labor-intensive and dusty. Performers are required to have professional skills and effective tools.
The owner of a building in which they plan to dismantle the walls must first obtain official permission from local authorities, BTI and other regulatory organizations, for example, the department of architecture.
It will also be necessary to resolve in advance the issue of disposal of building materials after disassembly. Before starting work, be sure to turn off all utility networks in the house , especially power lines and gas supplies. Work is carried out in protective clothing with personal protective equipment.
Manual disassembly of foam blocks is a very labor-intensive operation; at a professional level, such work is performed using diamond cutting. This technique guarantees high-quality wall removal, without noise or vibration effects on the main structures of the house.
Read more about this here.
Research
The purpose of this stage is to determine whether it is possible to build a house from foamed concrete and cellular concrete in general on this particular building site, or whether it is necessary to use another structural material. Foam concrete is lightweight; most of its structural grades, except D1000-D1200, are lighter than water and even wood. But they, unlike wood, are fragile: aerated concrete cracks from impact and long-term bending and shear loads, and foam concrete simply from any uneven load. Therefore, a foam (gas) concrete house, on the one hand, will lightly load the foundation and will do little to help it counteract the forces of frost heaving of the soil with its weight. On the other hand, a house made of foam blocks is not capable, like an elastic wooden one, of swaying together with the foundation in time with the seasonal movements of the soil. Eventually:
- On weak ones, with a load-bearing capacity of less than 1.7 kgf/sq. cm, but stable, slightly heaving and little watered soils (dry sand, sandy loam, crushed stones, gravelly soils, etc.) - it is possible and necessary to build from any foam concrete.
- Under the same conditions, but on medium heaving soils (loam, fine silty sand) with soil water standing no higher than 1.2 m, it is possible to build up to the 1st floor with an attic from non-autoclaved aerated concrete (see below), and 2nd floors and above from autoclave; preferably brand Η+Η.
- On highly heaving, high (over 0.9 m) watered and unstable soils (quicksands, wet sand, silty, peaty soils, etc.) - anything except any foam concrete, despite any promises. In such conditions, even a high pile foundation with a powerful concrete grillage will not save a foam concrete house from rapid soaking and deterioration.
Foundation
In any conditions suitable for construction from foam concrete, a house made from foam concrete will stand securely on a normally buried strip foundation, i.e. with a tape depth of 0.6 m or more below the standard freezing depth. Anti-heaving widening of the tape base is not contraindicated, but in this case it does not allow reducing the depth of the foundation: the weight of the fragile structure is insufficient. For the same reasons, it is undesirable to use slab surface foundations: Swedish slab and other similar structures.
On stable dry soils, in order to reduce the volume of excavation work, if the building is made of aerated concrete blocks, it is possible, according to the designer’s recommendations, to use a tape of incomplete burial, on the left in Fig. For the same purpose and also for an aerated concrete structure, but on medium-heaving soils with water up to 0.9 m, the TISE foundation is suitable, on the right.
Foundations of houses made of foam blocks/gas blocks
The foundation strip of a house made of foam blocks should pass not only along the perimeter, but also under all partitions, except in the case of a reinforced concrete basement floor, see below. If the house has a basement, the edges of the pit under it should be no closer than 1 m to the inner edge of the surrounding tape. The same condition must be met for the stove foundation in a stove-heated house.
Vents in the tape under a foam block building should be made at least every 1.2 mm. It is convenient to use pieces of 70-80 mm asbestos-cement pipes for this. Their protruding ends are covered with fine steel mesh or, better, fiberglass mesh. Underfloor insulation - any kind, for example, filling with expanded clay.
Which manufacturer's aerated concrete block is better?
Aerated concrete is used to reduce construction costs. This material has a low price which may be negatively impacted by shipping. It is not profitable to transport a high-quality and inexpensive block for several hundred kilometers. For this reason, builders use products from factories located as close as possible to the construction site. Given the choice, which manufacturers' aerated concrete blocks are better? The VyborExperta.ru team found answers to this question:
- Ytong - building material with the best geometry and range;
- Aeroc – an impeccable balance between price and quality;
- Sibit is the best material for those who build beyond the Urals;
- Bonolit – for complex architectural projects;
- StoneLight is a high-quality building material for budget construction.
All manufacturers presented in our review have earned an impeccable reputation. The products of factories with innovative equipment and a strict quality control system deserve the title of the best in their category.
Is it worth it yourself?
It is quite possible to install a box made of foam blocks without experience in construction work. When building brickwork, stumbling blocks for beginners and the features of laying foam blocks that eliminate them are as follows:
- Proper mixing of masonry mortar. Glue for aerated blocks is sold dry ready-made; all you have to do is mix it with water according to the instructions on the package. The achievable quality of buildings made from foam concrete blocks is such that if you get M50 instead of M150 mortar, then this will have little effect on the reliability of the structure.
Manual adhesive dispenser for aerated concreteApplying masonry mortar so that the seam comes out at a uniform thickness (12 mm). Using an inexpensive device - a manual glue dispenser (dispenser), see fig. on the right, when laying aerated blocks, this problem is solved automatically. And the transverse dimensions of foam concrete blocks vary by (+/–) 3mm. Taking into account the mandatory reinforcement of joints for this type of material, see below, it is easier to maintain the thickness of the masonry joint in the standard.
- Raising (raising) corners and laying bricks exactly in a row. As we will see later, it is possible to ensure the verticality of the corners and the evenness of the rows of foam block masonry without having strong working skills. It is also not necessary to bring the corners up 3-4 belts and then fill the rows, as when laying bricks. The large size and lightness of foam blocks allow you to build from them almost like from cubes.
- Precise cutting of bricks into halves, quarters, three-quarters. All types of foam concrete can be easily processed with ordinary steel cutting tools: sawed, drilled, etc.
It remains to figure out the financial feasibility of independent construction from foam (gas) concrete. The price of a block of simple foam concrete 600x300x300 per piece is currently (April 2016) 30-42 rubles. depending on the region; foam concrete ceramic fiber blocks (see below) 600x300x200 are approximately twice as large. Non-autoclaved aerated concrete blocks of the same size cost approx. 120 RUR/piece; autoclave class H+H – approx. 210 RUR/piece or approx. 3500 rub./cubic. m; on a pallet - 2 cubic meters. m. Real savings when purchasing pallets are less, because theoretically, there are 27.8 blocks of 600x300x200 in a cube, and suppliers, taking into account shrinkage and shrinkage and the size of the pallet, count 24-26 blocks per cube.
For a house 6x9 m you will need approximately 1000 blocks 600x300x200; in money - up to approx. 200 thousand rubles. in case of using “cool” H+H. Building a turnkey house from foam blocks will cost approx. 18,000 rub./sq. m; for our area - approx. at 972 thousand rubles.
And keep in mind that turnkey delivery means separated communications, without plumbing, gas, heating, stationary electrical appliances, and readiness for final finishing, without external cladding. Having gone through the sites and exchanges of craftsmen and calculated, we find that if you just install the box with the roof on a ready-made foundation yourself, and order the rest of the arrangement, up to the housewarming, in parts as needed, then the entire construction will cost approx. for 250-300 thousand rubles. cheaper than a turnkey order with subsequent “finishing”. Let us remind you that this is if you purchase aerated blocks of the highest quality category. In general, if we are not afraid to build, we should build.
Material selection
Foam- which is foam-
Foamed concrete, which is foam concrete, is produced using organic blowing agents introduced directly into the batch. The pores of foam concrete blocks are long, sinuous, interconnected, irregular in shape, pos. 1 in Fig. On a pallet, blocks of simple foam concrete can be recognized immediately: the dimensions are apparently inaccurate (additional deviation - 1% of the corresponding size), the color is uneven, the surface is conchoidal, pos. 2. Block size – 600x300x300.
Types and structures of building blocks made of foam concrete and aerated concrete
However, simple foam concrete is not such a bad material. Firstly, as mentioned above, although it greedily absorbs liquid moisture, it is no less willing to part with it. For a seasonal home, this is a useful feature; especially if we are talking about a commercial cottage, inhabited from warm to warm. In early spring, it will be enough to heat such a house with a stove that produces strong thermal (IR) radiation for 3-6 hours to make it comfortable. Stove - even a homemade potbelly stove or, better, an economical surface burning stove, for example. famous bubafonya.
Concrete foamed with organic matter can withstand up to 25 freezing cycles, which is bad in the current unstable climate. However, if a box made of it is surrounded by a simple ventilated façade (see below), then if frost strikes after a thaw, excess moisture from the pores will evaporate faster than the wall freezes.
In addition, simple foam concrete is made using a cement-sand mixture. There is no point in using surrogates (lime + industrial ashes or slags): the blocks will crumble during transportation. Therefore, a box made of simple foam concrete gains strength over time; quite good buildings from it are known, which are almost 100 years old.
The main disadvantage of simple foam concrete is its high fragility. Blocks made of foam fiber reinforced concrete and foam fiber ceramic concrete (foam fiber blocks, ceramic fiber blocks, fiber blocks) are largely devoid of it. They can be recognized by their more regular shape, precise dimensions and some regularity in the location of surface pores and poses. 3. In relation to liquid moisture, fiber blocks behave in the same way as foam concrete blocks, but are stronger, and can be used to build 2 floors. A significant drawback is that the market is flooded with lime-ash surrogates, which provide a building service life of up to 40 years; often – 20-25 years.
Foam-, which is gas-
Foaming of the mixture for aerated concrete blocks is carried out with hydrogen obtained as a result of a chemical reaction. The pores of the gas blocks are round, not communicating, pos. 4. Curing of aerated concrete can be carried out in a free atmosphere or under excess pressure in an autoclave; Accordingly, a distinction is made between non-autoclaved and autoclaved aerated concrete. The most commonly used is non-autoclave; it is almost half the price, but its characteristics satisfy most of the requests of private developers. The bulk is cement-sandy (slightly grayish color, item 5) or surrogate (color up to dazzling white, item 6).
Regardless of the composition of the bulk and the method of hardening, gas blocks can withstand at least 50 freezing cycles; most often – 100 cycles. Depending on the purpose, aerated concrete is produced in grades (numbers indicate density in kg/cubic m):
- Up to D400 – insulating. Weight load is not standardized; Simply, they don’t hold it.
- D400-D600 – structural and insulating. Weight class - B2.5, i.e. You can build up to 2 floors.
- D800 and higher, up to D1200 – structural. In private construction they are used to a limited extent in special cases, for example, see below.
Note: fire resistance of all types of aerated concrete is A1, i.e. Let's allow short-term heating up to 300 degrees.
The standard size of an aerated concrete block is also 600x300x300, but due to the real needs of construction, there are more variety of “non-standard” ones on the market. The most popular size is 600x300x200. Such blocks can be used to build walls 400 mm thick, which is enough so that additional insulation is not required in the middle zone. The heat and sound insulating properties of aerated concrete are very high, see table. below. The nature of moisture absorption is discussed above; Here we emphasize: it is impossible to leave the outer surfaces of an aerated concrete house unfinished or otherwise unprotected from the effects of precipitation and capillary moisture, the house will become damp and it will be very difficult to dry it.
Table: parameters of thermal and sound insulation of aerated concrete
The accuracy of maintaining the dimensions of aerated blocks is 1 mm; dry shrinkage of non-autoclaved aerated concrete up to 1 mm per 1 m of stack height within a month. Autoclaved surrogate aerated concrete shrinks by only 0.1 mm/m within a week. High-quality surrogate aerated concrete ensures the service life of buildings up to 70 years, so in this case the surrogate is not so bad. However, there are also surrogates for 20-25 years, so you need to take lime-ash aerated concrete from a trusted manufacturer.
Note: it is better for inexperienced builders to overpay approx. 5% and take aerated concrete blocks with locks, pos. 6. Maintaining the evenness of the rows and ensuring proper structural strength will be much easier.
H+H
For H+H aerated concrete, pore sizes are standardized (1-3 mm) and the degree of porosity is 85%. Therefore, it holds bending and shear loads much better. You can recognize H+H aerated concrete by its smooth surface, without visible porosity, pos. 1 in Fig. It is better to lay the lower chord from aerated concrete H+H grades 900 and above (see below), but its most preferable use is trough-shaped blocks for pouring the upper support belt (also see below), pos. 2. H+H gas blocks are often sold under the names wall or structural. And one more thing: recognizing H+H gas blocks by the presence of grips and a lock, as is sometimes written, is incorrect. H+H aerated blocks are also available as smooth ones, while blocks made of non-autoclaved aerated concrete can have grips and locks.
H+H aerated concrete blocks and its structure
Rating of manufacturers of aerated concrete blocks
In the production of gas silicate, natural materials are used - cement, sand, lime. Aluminum powder is responsible for gas formation. Hardening is carried out using different technologies, so the quality of aerated blocks can vary greatly. Vyborexperta.ru conducted a market analysis, tested building materials using instrumental methods, and compared the range of different factories. When compiling the rating of manufacturers of aerated concrete blocks, reviews of property owners, opinions of builders and designers were taken into account.
Experts analyzed the following characteristics:
- Technology - the autoclave production method allows you to create more durable foam blocks than non-autoclave technology;
- Brand - the range of the best factories includes materials of the D200-D600 brand. Different densities allow you to buy building materials for laying load-bearing walls, partitions and insulation;
- Compressive strength - depends on the density and hardening technologies used. Affects the durability of structures and the ability to withstand high loads;
- Frost resistance - leading companies produce products of the F50-F100 brand;
- Varieties - several types of gas blocks are produced: wall, for partitions, U-shaped. Building materials have different shapes and sizes;
- Geometry – stable geometry simplifies masonry, reduces the consumption of glue and plaster;
- Availability on the market.
Not all companies producing wall building materials offer good quality aerated concrete. Weak assortment, low technical characteristics, mechanical defects, unstable dimensions, flaws in geometry - manufacturers of such materials were excluded from our rating.
The best vibrating plates
Project and zero
The design of a house made of foam blocks should be entrusted to specialists or you should use their services to link a standard project to the area. The reasons are the same combination of the lightness of foam concrete with its fragility. Errors that stone and wood, as they say, will not even notice, can make a foam block house initially unsuitable for habitation.
But it is also possible to save a bit on the project if you master one of the entry-level computer programs for construction design, for example. VisiCon and FloorPlan 3D + House-3D. The result will be a technically competent sketch, from which a specialist will understand what you want. This will reduce the design time and the number of consultations during the project approval process, and ultimately its cost.
It is also better to order a foundation for a house made of foam blocks, even if you have built a little before: its supporting surface should be as flat and horizontal as possible. Just in case, let’s mention: the formwork should be without cracks and not absorb a lot of moisture. The last 1-2 layers of the tape are filled with a more fluid solution, with an increased water-cement ratio (WC). Immediately after the tape has set, its supporting surface is ironed: dry cement is rubbed into the still wet concrete. The horizontal unevenness of a fully established foundation should not exceed 3 mm.
Project documentation
The design of a house is its basis. The convenience and comfort of living, as well as the cost of the work itself, will depend on how competently the project for the construction of a house with foam blocks is completed.
Modern technologies make it possible to realize the most ambitious plans. You can erect a building of any configuration, shape, size, using both a standard solution and an individual, exclusive design.
Turnkey house projects, taking into account design styles, interior design, and operational requirements, make it possible to adapt the house not only for seasonal, but also for year-round use.
Also, the project pays special attention to the development of sections of water supply and energy supply engineering systems that must withstand daily loads and comply with mandatory standards and safety regulations.
At the moment, both a standard project for building a house and an individual plan of any number of floors and scale are in demand, allowing the most daring design ideas to come to life. And competent planning at the preparation stage will help to significantly reduce costs, including materials.
Typical project of a two-story house of a high price category
Wall masonry
Gas blocks are placed only with special glue; seam thickness – 2-3 mm. Experienced craftsmen apply the glue manually and disperse it with a notched trowel, but for a beginner it is advisable to use a dispenser, see above. Before applying the glue, the surface under it is moistened with a plaster brush. Watering and wiping off excess water with a rag is incorrect, unnecessarily troublesome and increases water consumption.
Foam concrete blocks can be laid either on glue or on ordinary cement-sand mortar with a standard joint thickness of 10-13 mm. But practice shows that ordinary masonry mortar is better. Foam concrete absorbs water too greedily, especially in summer, and the inaccuracy in the dimensions of foam concrete blocks is greater than the permissible thickness of the adhesive joint. The lower strength of the cement-sand joint does not matter, because the blocks themselves are weaker.
Insulation
The foundation of a house made of foam blocks/gas blocks with a reinforced concrete basement floor
Waterproofing between the foundation and the masonry is the most vulnerable point of a house made of foam blocks, because... Here, capillary damming between the foundation and the masonry and dampening of the wall are very likely. The likelihood of accumulation of capillary moisture in the base joint of the masonry is significantly reduced by non-layered waterproofing materials: linkrom, steklorubit, stekloizol. You cannot lay roofing felt on the foundation for laying foam blocks at all.
However, a radical way to protect a house made of foam blocks from midges is a reinforced concrete basement floor made of hollow-core slabs, see Fig. on right. They are not cheap, and you will have to rent a truck crane, but the walls can be erected from non-autoclaved aerated concrete blocks, which will most likely provide savings that cover the costs, and there will be no need to worry about rotting of the wooden floor. And you will be able to save a lot on the foundation, because... There is no longer any need to run the tape under all the partitions.
First row
If the lower floor is made of wood, the problem of the first masonry belt arises: it must be well adhered to the foundation. It is unrealistic to bring the supporting surface of the foundation to the horizon with an accuracy of half a glue joint of 1-1.5 mm, so the first row of gas blocks has to be laid on a simple mortar. However, the low weight and lower adhesion of aerated concrete to the cement-sand mortar reduce the adhesion of the box to the foundation.
Without the skill of a mason, you can bring the adhesion of the walls to the foundation to an acceptable level by laying out the first row of half-thick aerated concrete blocks D900-D1200, pos. 1 in Fig. below. Both seams of this belt, both lower and upper, are reinforced with fiberglass mesh (see below); The top seam is already glued. If you know how to lay bricks, then the best solution is the first 3-4 rows of good, smooth working red brick, then a row of working gas blocks in a cement-sand mortar, and then everything is done with glue.
Initial stages of construction of walls made of foam blocks/gas blocks
How to lay blocks
There are several ways to lay foam blocks. Some do not even adhere to the “cornerstone principle”: the laying of the row goes from the middle to the corners. Experts argue a lot about this, but it is better for a beginner not to enter into the discussion: the cornerstones (lighthouse) stones should be laid from 2 solid blocks, laid in an L-shape. Beacons along the cord and level are set into the horizon by tapping with a rubber hammer, the contour is outlined with a mooring cord, the row blocks are placed dry along it in advance, pos. 2, and now you can quickly and accurately lay them out along the dock.
There are 3 points here. First, dry blocks are placed on the butt so as not to be confused with those already placed on glue and not to leave a dry block in the wall. The seam is thin, you can even overlook it. The second is that a whole number of blocks rarely fit in a row. So, it is highly advisable to place sawn blocks away from corners and openings, i.e. closer to the middle of solid sections of the wall, which in amateur practice is ignored rather than respected. Third, the amount of ligation between rows (see below) for aerated concrete blocks is permissible up to 5 cm. But experienced masons avoid such a “tolerance”, and beginners are strongly recommended to adhere to full ligation, i.e. half the length of the block; for blocks 600 mm - 300 mm.
Note: for those who are completely inexperienced, a simple device made of 4 boards, pos. 3.
Schemes for laying walls made of foam blocks/gas blocks
Dressing schemes
In most cases, walls made of foam blocks are erected using glue in the same way as half-brick masonry, pos. a) in Fig. on the right, with ligation of seams only between rows. It is advisable to carry out masonry with ordinary mortar from blocks of whole and half thickness, which will also provide bandaging in rows, pos. b). Scheme c) is used in difficult climatic conditions; diagram d) in the same place with a number of storeys greater than 1-1.5. A smaller joint thickness corresponds to glued masonry; large - on cement-sand mortar.
Seam reinforcement
The seams of masonry made of foam blocks must be reinforced: every 4th along the entire length, and the seams under and above the openings - to the distance of the length of the support of the lintels, see Fig. below. The minimum permissible placement of jumpers in a wall made of aerated blocks is 150 mm, but it is better to give it for the full length of the block, i.e. in 600 mm; in extreme cases - half a block, 300 mm. In all cases, the length of the support will be one and a half blocks, so that the load from the jumper is better spread to the sides.
Reinforcement scheme for masonry made of foam blocks/gas blocks
The least labor-intensive way to reinforce the seams of masonry made of foam blocks is with a steel or fiberglass mesh with meshes of 40-60 mm and a total thickness equal to the thickness of the seam. The latter will cost approx. 1.5 times more expensive than steel, but will distribute the load better. The mesh is placed dry on the previous row, pos. 1 on next Fig., fill the cells with solution to the length of the block, apply the solution also to the end of the previous block in the row, place the next block, etc. Due to the high fragility and low load-bearing capacity of foam concrete blocks, it is strongly recommended to reinforce the seams of their walls only with fiberglass mesh, the total thickness of which is then taken to be half the thickness of the seam, pos. 2.
Reinforcement of masonry from aerated blocks and foam blocks
The greatest strength of the masonry is ensured by reinforcing the seams (8-10) mm with reinforcing bars, also steel or fiberglass, in grooves; for a house more than 8x10 m in plan with a service life of over 30 years, this is the only acceptable option. They cut foam concrete with a manual wall chaser, see fig. on right; The work is not particularly dusty or hard. From the outward-facing edge of the groove to the edge of the block there must be at least 70 mm, and between the inner edges of the groove - from 150 mm. Before laying the reinforcement, the grooves are carefully swept out with a hard brush.
Working with a manual wall chaser on aerated concrete
At the corners of the groove and the reinforcing bars in it should bend smoothly. The branches of the reinforcement frame in the middle of the walls are made T-shaped from solid rods, pos. 3 in Fig. higher. If the wall branches less than 0.8-1.2 m from the corner, the reinforcement is branched into the overlay; the bends of the outgoing branches should be facing the corner, pos. 4. The grooves with laid reinforcement are sealed flush with cement-sand mortar, pos. 5, and laying on the glue continues after it has set.
Note: what is in pos. 6 – gross error in reinforcing foam block masonry. Such reinforcement will only prevent lateral displacement of the blocks, but will not help the wall bear bending and shear loads.
Methods for determining the quality of foam blocks
There are several ways to determine the quality of foam blocks visually, as they say “by eye”. Thus, the following quality parameters of foam blocks can be assessed:
- the homogeneity of the structure of foam blocks must be uniform throughout the entire mass of the block;
- air bubbles in the structure of the foam block should be small (no more than 1 mm);
- the shape of the air bubbles should be spherical;
- the air bubbles should be approximately the same, not interconnected;
- The color of the foam block should be gray, the color of cement, uniform throughout the entire block. If the foam block is light gray in color, it means that the proportions between cement and sand in the solution are not met;
- The foam block should not contain cracks. The presence of cracks indicates the existence of tension inside the block, as a consequence of the improper drying process of the block;
- there should be no streaks on the foam block or uneven color of the blocks;
- the foam block should not have traces of grease from iron molds;
- high-quality foam blocks do not sink in water;
- good foam blocks do not wobble if they are placed on top of each other;
- a high-quality foam block cannot be broken by hand;
- high-quality foam blocks have the same geometric dimensions.
Load-bearing partitions
A light and fragile box made of foam blocks by itself will not bear the weight loads from the upper structure of the building and lateral winds. Therefore, the strength diagrams of houses made of foam blocks almost always include connections of general rigidity - load-bearing partitions are 1.5-2 times thinner than the walls.
Take a look at the top row of diagrams in Fig. In the design of your house, you will almost certainly find partitions that correspond to one of these, the most common, spatial power schemes for houses made of foam blocks. Such partitions are erected simultaneously with the walls, and cut into them by 1/3 of the wall thickness, as shown in the middle in Fig. The methods of branching seam reinforcement described above are intended specifically for load-bearing partitions. A well-designed project for a house made of foam blocks must indicate which partitions need to be cut into the walls and reinforced along with them.
Installation of partitions in a house made of foam blocks/gas blocks
Brick partitions in a house made of foam blocks cannot be load-bearing and do not cut into the walls. Their seams are reinforced with single branches, only for connection with the load-bearing wall (below in the figure). In this case, the reinforcement ties are taken only from fiberglass; they should fit seam to seam. Sticking the reinforcement of a brick partition into the body of a foam block is unacceptable!
Note: non-strengthening brick partitions may be needed in a house made of foam concrete blocks for hanging something on the walls, because... simple foam concrete is not capable of bearing concentrated loads. Otherwise, you will have to determine in advance exactly where the TV, shelves, kitchen cabinet, etc. will hang, and during the construction process, lay through anchors in those places. But then, suddenly you need to reweigh something, you will have to rearrange the anchors and at the same time spoil the finishing of the adjacent room.
Along the way, more about partitions
Partitions made of foam blocks (gas blocks) may be needed to partition a city apartment without filling out a lot of documents for redevelopment. And when buying an apartment with an open plan, it is simply necessary to install them. In this case, we offer a video about the construction of lightweight partitions from aerated blocks:
Video: construction of a light partition from aerated blocks
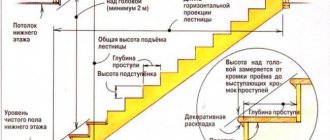
Dimensions: length, width, height
When building with your own hands, it is important to choose the right size of foam blocks . For load-bearing walls, blocks with a length of 600 or 625 mm, a width (thickness) of 300, 400 or 500 mm, and a height of 200, 250 or 300 mm should be used. If you need to determine which specific block is best to build a house from, you need to know not only the standard sizes offered on the market, but also the thickness of your external walls (which were discussed just above). Which block to choose if the wall thickness is 400 mm? Knowing the standard dimensions, we choose either masonry in one block of 400 mm, or in two blocks of 200 mm.
Partitions can be made from foam blocks 325 or 600 mm long, 250 mm high, 80, 90, 100, 120 or 150 mm thick.
In addition, U-shaped elements are available in 500 mm length, 250 mm height and 200, 250, 300 or 375 mm thickness with a central or offset channel. Such blocks are suitable for lintels and reinforcing belts.
Topside
A building made of foam blocks must bear the weight and climatic and meteorological loads of at least the roof and, possibly, the weight of the reinforced concrete floor. In the first case, the Mauerlat needs a reliable support capable of distributing tangential loads along the load-bearing wall, and in the second, the weight load must be distributed over as large an area as possible. For both purposes, the box of a house made of foam blocks is completed by an upper load-bearing belt made of reinforced concrete, on the right in the figure; Its diagram is also shown on the left. Concrete grade – from M200. The load-bearing belt is spaced further from the outer edge of the wall than from the inner edge, because shear loads from the roof are directed predominantly outward. The best material for the top chord of foam block masonry, as mentioned above, is H+H blocks with a longitudinal recess.
Upper load-bearing belt of a house made of foam blocks (gas blocks)
At pos. 3 and 4 – errors when making the upper load-bearing belt. Here and there it is not monolithic and therefore is not able to distribute loads. And the one at pos. 3 will also load the wall vertically in shear, which is completely unacceptable for foam concrete and aerated concrete.
About beams
The upper (attic) floor, in contrast to the basement floor, in houses made of foam concrete is preferably wooden in all respects. And its beams, in turn, are best made as composites (3 boards from 150x40 with inserts), as in Fig. Stacked beams resist torsion better and, accordingly, transfer less lateral loads to the wall.
Wooden floor beams in a house made of foam blocks/gas blocks
Facing and something else
The remaining stages of work on building a house from foam blocks do not have any significant features compared to other buildings, except for laying communications, installing windows with doors and external cladding; optionally with insulation. The first is made easier by the fact that ordinary tools with ordinary steel working parts are used, and pipes and wires are easy to hide in walls.
The fastening of anchor plates of window and door frames must extend into the foam concrete wall by at least 150 mm, and the anchors themselves must be spaced at intervals of no more than 650 mm. That is, to install a single metal-plastic window, you will need to purchase 2 more anchors for the long sides; double - 4 more, etc.
With external cladding the matter is more complicated. Foam and aerated concrete must be protected from liquid atmospheric moisture, otherwise the house will become damp. Here it is necessary to observe the principle: the vapor permeability of the cladding should be greater than that of foam concrete, but the latter is already high. One of the possible options is cladding with siding, metal siding or blockhouse - a type of metal siding that imitates a log house. The cells of the sheathing can be filled with mineral wool or ecowool, but in no case with foam plastic or other dense insulation!
Correct and incorrect cladding of a house made of foam blocks/aerated blocks with bricks
Another, most effective option is a ventilated facade made of facing bricks; Foam concrete itself is an excellent insulation material. A diagram of the design of a ventilated facade of a house made of foam blocks is shown on the left in the figure, and on the right it is shown how not to do it. What's the right way? In the following way:
- Anchor plates should only be placed flat in horizontal joints of the masonry and be steel with deformation bending. The resilient plastic anchors will become stiff and break within a few years, and the entire cladding will need to be redone.
- The anchors should, as in the case of a brick partition, go seam to seam. Embedding anchors in weak foam concrete means helping the wall to quickly crack and begin to crumble.
- The cladding should form an overhang of 30 mm over the base. If there is a shelf there, then instead of a dropper (tearpiece) you will get a collection of condensation just where it is easiest for it to seep into the wall.
Optimal wall thickness of a small country house and mansion for year-round use
When designing any structures, it is important to correctly calculate the thickness of the walls. For a year-round home, it is determined taking into account heat conservation, and the main parameters are determined by SNiP 02/23/2003. To calculate the thickness, use a simple formula:
В=RoxKt, where Ro is the minimum permissible thermal resistance of the wall of a residential building (degreesq.m/W), Kt is the thermal conductivity coefficient (W/degrees).
The Ro value is set separately for each region of the Russian Federation, taking into account climatic conditions . So for Moscow it should reach 3.13 degrees square meters/W, and in the northern regions – 5.2-5.5 degrees square meters/W.
The thermal conductivity of foam concrete depends on its density. For 500 kg/m3 Kt = 0.158 W/degrees, and for 700 kg/m3 – 0.17 W/degrees. Calculations show that in the Moscow region it is enough to have a wall made of foam concrete 50 cm thick, and for the northern regions - 76-82 cm.
This calculation does not have to be done for a dacha if you will live there only in the summer and heat preservation is not a determining factor. For a summer house, it is quite enough to have external walls 200-300 mm thick.