The main purpose of the RCD is to disconnect the entire electrical network or its individual section from the power supply by opening the contacts. This ensures protection against electric shock and fire prevention. In modern electrical engineering, the use of these devices in many cases becomes mandatory, therefore, the question often arises of how to choose the right RCD. These protective devices are used not only in single-phase, but also in three-phase networks under various loads, therefore, their selection is made depending on the specific operating conditions.
Purpose of RCD and principle of operation
The main task of the RCD is to neutralize currents when various damage occurs in electrical installations. The residual current device is the most effective protective device. Unlike fuses or circuit breakers, RCDs are capable of breaking a circuit in a split second and saving a human life.
The danger is not only the possibility of direct electric shock. Sometimes simply touching the parts of live devices and devices is enough. Therefore, protective devices must operate in a timely manner. In order to correctly solve the problem of how to choose an RCD for a home, the conditions in which it will operate must be taken into account.
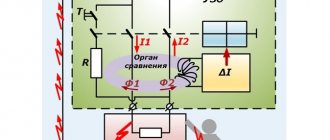
The operation of protective devices uses the phenomenon of electromagnetism. In this regard, the design of the RCD includes coils with a magnetic core connected to current-carrying wires that transmit electricity to the consumer. At the same time, a magnetic flux occurs, which is the arithmetic sum of the currents flowing through these conductors. In this case, the incoming currents have a positive value, and the outgoing currents have a negative value. In the absence of leaks and short circuits, they will be equal and add up to zero. This state of the circuit indicates the serviceability of the installed equipment.
In the event of a leak, a partial reverse flow of current occurs through the grounding conductors, which leads to an imbalance. The difference in differential currents causes the excitation of magnetic flux in the core. Its value will be proportional to the difference in electric current. When a certain threshold is reached, the device is triggered and turns off the power supply to consumers.
Electronics or electromechanics
Choosing an RCD - which one to prefer - electronic or electromechanical? There are two types of such devices on the market. The difference between them is the type of trigger mechanism. Electronic RCD is cheaper, but has a significant drawback: it only works if there is external power.
People who believe that if there is no food there is no danger are mistaken. If the neutral wire breaks, the light will not light up, but the power will remain in the phase. There is still a danger of current leakage and, accordingly, electric shock. Therefore, remember: electromechanical ones should be considered the best RCDs. They do not depend on external power.
You can distinguish one type of RCD from another by the following characteristics:
- marking. Electronics always have a triangle with the letter “A” on the diagram—current amplifier;
- using a battery. When a regular battery is connected to the device, the electromechanics are activated, but the electronics are not;
- using a magnet. An electromechanical RCD that is turned on will turn off if a magnet is brought near it.
It is worth choosing an electromechanic for a private home, where the quality of the wiring is usually worse than in an apartment, and the likelihood of a burnout or break of the neutral conductor is higher. Simply due to the fact that part of the wiring of a country house or cottage is always located on the street and is exposed to the external environment.
How to choose the right RCD
In order to select the best option for a residual current device, you need to know its basic parameters. Devices with different characteristics are used in specific conditions, which must be taken into account when choosing. The nature of leakage currents allows us to divide them into different types. This division depends on a smooth or sudden increase in current. RCDs with such characteristics are most widespread as they are most suitable for the widest operating conditions.
Triggering technology allows RCDs to be divided into electromechanical and electronic. In the first case, high-precision mechanisms are triggered as a result of leakage currents. These are the most reliable and expensive devices capable of operating under any conditions. Electronic devices are cheaper, however, for normal operation of the electronics, the use of external power is required. Their efficiency is significantly reduced when voltage surges occur. The response speed of RCDs allows their use in multi-level protection systems. This allows you to turn off all emergency sections individually.
There are other parameters that require knowledge of electrical engineering. Therefore, when choosing an RCD, it is best to seek help from qualified specialists. However, if the exact characteristics of the electrical network are known in advance, you can independently select the most suitable protective device. Among them, the most important are the following:
- Voltage. The RCD can be designed for a single-phase network with a voltage of 220 V or a three-phase network with a voltage of 380 V. The first option is usually used in apartments, and the second in private houses, dachas and cottages. If there are sections with one phase in three-phase wiring, then protective devices designed for 220 volts are used for them.
- Number of poles. In single-phase networks, two-pole RCDs are used, designed for one phase and zero, and in three-phase networks, four-pole devices are used, to which three phases and zero are connected.
- Rated current. This is also the throughput current of the RCD, which depends on the number and power of connected electrical appliances and equipment. Therefore, this indicator for a general (input) protective device must be calculated for all installed consumers. For linear RCDs, the total power is calculated based on the number of devices on a particular line. The RCD ratings set by the manufacturers are 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 63, 80, 100 A.
- RCD leakage current. The value upon reaching which it turns off. It also varies in ratings of 10, 30, 100, 300 and 500 mA. For ordinary apartments, a 30 mA device is best suited. With a lower current rating, the device will constantly respond to even minor fluctuations in the network and turn off the power.
- Type of leakage current. The symbols AC, A, B, S and G are marked on the body of the device. For example, AC reacts only to alternating leakage current, and B - to direct and alternating currents. The rest of the markings also correspond to certain parameters, including the device shutdown time delay.
Design features of devices
The residual current device is not too complicated and consists of only four main working elements, such as:
- differential current transformer;
- a special mechanism responsible for breaking the connected circuit;
- electromagnetic type relay;
- test node.
Opposite windings - zero and phase - are connected to the transformer device. When the network operates in normal standard mode, conductors in the area of the transformer core control magnetic fluxes, which are initially in the opposite direction.
Based on the type of design, residual current devices are divided into electromechanical and electronic. Products of the first type are a simplified type of safety module, and are triggered immediately upon initial detection of a current leak, regardless of what voltage is currently available in the network.
The main working component of an electromechanical device is a toroidal core with windings. When a leak appears in the area of responsibility of the device, voltage appears in the secondary winding level to activate the relay. This process causes the mechanism to shut down the network
For correct operation, the device does not require an external power source. It has good operational stability, since it does not have any electronic parts in its design that can be damaged or burned when the network is overloaded or as a result of sudden power surges.
It is quite cheap and is sold in almost any store that sells an assortment for household needs or the construction of electrical networks. It works reliably and for a long time, without requiring complex additional maintenance.
An RCD that has been triggered to open the network cannot be turned on immediately. First you need to find the area of the problem and fix it. Only then is it permissible to return the device to working condition
The electronic type RCD is a more modern control module and is equipped with sensitive microcircuits that respond to any changes that occur in the network. It works even if the mains voltage drops, since the transformer element “notices” only the difference in current flow.
The main working element is an electronic board located inside with a special amplifier. For correct functioning, it certainly needs power supplied from an external network. If the system has a base voltage of 220 V, the protective device immediately reacts to the leak and opens.
Despite a more advanced design device, electronic protection devices are not always able to perform their functions. For example, when the neutral wire in the network burns out, they may not work
The electronic device is very sensitive and as a result of constant voltage fluctuations it can fail and lose its protective functions, and this will not be noticeable outwardly.
In order not to suffer due to this situation, experts strongly recommend that users monthly check the RCD for functionality by pressing the “Test” button located on the device body.
What types of RCDs are there?
The main classification of residual current devices is based on their operating current. For example, fire protection devices respond to currents of 100, 300 and 500 mA. They protect wiring from fire in the event of insulation failure and short circuit. Typically, an introductory RCD is installed behind the electric meter and provides protection for the entire facility. For people, electric current becomes dangerous at 50 mA. Therefore, devices that protect against fire are not able to protect a person from electric shock. For these purposes, devices are used that turn off the network when the current reaches a value of 10 or 30 mA.
Protective devices differ in the number of poles and can be used in single- or three-phase networks. Each type of device has a different way of functioning. The markings on the body of the device must be correctly deciphered and you need to know exactly what it means:
- AC is a category of RCD used only in alternating current networks. Accordingly, the device responds only to alternating current.
- A - protective devices of this category operate not only with alternating current, but also with direct current.
- B – has more advanced functions and responds to three types of current. In addition to direct and alternating current, the device turns off with rectified differential current.
- S – selective devices with the possibility of time delay when switching off.
- G – are also selective devices, but with a shorter time delay.
RCDs are also classified according to their technical design. This allows you to select a RCD of better quality. Most often, electromechanical devices are used that do not have their own power supply. They operate and shut down when a differential current appears.
Another type refers to electronic protective devices that require connection to an external power source. In this regard, the reliability of protection decreases, so such RCDs are used less frequently. When the auxiliary power is turned off, they turn off the network automatically, and when the power is restored, the network also turns on automatically. Some device designs do not provide for automatic switching on of the circuit when the power supply is restored.
Classification according to operating principle
All protective devices offered today on the market of related electrical equipment and accessories differ from each other in the type of operation. AC modules are installed in systems designed to protect household appliances from surges or slowly rising voltages and are triggered by alternating current.
Products A detect a constant pulsating current that increases in steps and react precisely to it. They are usually installed in homes for individual protection against extremes and combustion of washing machines, televisions and dishwashers. They have a structurally complex structure and are much more expensive than other elements of this class.
The most suitable place to locate an RCD in a residential building is an area close to a power source. Experts recommend placing the device directly next to the common meter
Units B are not suitable for homes or other residential areas. Their area of operation is enterprises and production workshops with a large amount of electronic equipment.
Selective devices S and G are triggered 1-4 seconds after a leak is detected. They are usually implemented in networks where several protective devices are present on one power line.
How to choose an RCD based on power
Unlike circuit breakers that protect against overloads and short circuits, residual current devices are designed to protect against current leakage. The reason is faulty insulation of electrical appliances or contact of live parts with the housing. In these cases, the RCD is instantly turned off, the line is de-energized, and consumers are protected from electric shock.
In order to calculate the RCD by power, you need to know the total number of consumers connected to a given line. In the case when the question of how to select an RCD and a circuit breaker based on power is being decided, both protective devices must have appropriate values to ensure their normal operation. If the installation of circuit breakers is not provided for by the project, in this case the total power consumed by electrical appliances is calculated. As a rule, this value in a standard apartment in a multi-storey building does not exceed 25A.
When installing RCDs in private houses, it is recommended to divide all consumers into groups connected to separate lines extended to each floor, outbuildings, external lighting, etc. If the RCD has less power than the existing consumers, it will constantly turn off due to overloads. That is, the device will actually not work normally and will not be able to protect the line. Sockets with RCDs built into them, designed for a current consumption of 5A, will help partially solve this problem.
General tips for selection and installation
In addition to the criteria for selecting an RCD, there are general useful recommendations when purchasing and installing this equipment.
They will help you avoid making mistakes and immediately purchase a model suitable for a specific apartment or house.
Ignoring wiring installation rules and the absence of an RCD in the power supply circuit can lead to a fire throughout the house
Selection tips are as follows:
- It is recommended to take RCDs, which, when triggered, turn off not only the phase, but also the “zero”;
- There should be no grounded electrical appliances within the circuit controlled by the device;
- the device must operate during short-term voltage drops of 50% of the nominal voltage, which can occur in the first moments of a short circuit;
- RCD terminals must be made of slightly oxidized material and equipped with a reliable wire fixation system;
- preference when purchasing should be given to devices with short circuit and overload protection functions;
- The second level RCD need not be installed on safe groups of equipment, for example, on ceiling lighting sources;
- It is recommended to install devices with a threshold current flow of 10 mA on shower stalls and Jacuzzis;
- You should pay attention to the possibility of connecting aluminum wires to the device - some devices do not work correctly with them.
You can install the correctly selected RCD yourself. This process is not much different from installing a socket or switch.
It is important to carefully consider the wiring diagram and do as indicated on it.
Detailed information about the rules and diagrams for connecting RCDs in an apartment and house is presented in this article.
How to calculate RCD
In order to calculate the protective device and solve the problem of how to choose an RCD based on power, the table of parameters will help you do this as quickly and accurately as possible. It is necessary to use two technical characteristics - leakage current and maximum current - to obtain the desired result. The calculations use a mains voltage of 220 V, with a frequency of 50 Hz.
Calculation and selection of the maximum current rating of the RCD is quite simple. It is necessary to establish the value of the total electrical power of devices and equipment turned on simultaneously. For example, if this indicator is 6000 watts, then the calculated current value will be equal to: I = P/U. Substituting the required values into the formula, we get the result: 6000W/220V = 27A. The closest RCD from the standard range of rated currents will be 32A.
If the RCD is calculated based on leakage current, in this case a simplified scheme is used, according to which various types of protective devices are selected in accordance with the operating conditions of the objects:
- In ordinary residential premises - at 30 mA.
- In bathrooms, kitchens and other rooms with high humidity and higher requirements for electrical safety - 10 mA.
- At large facilities with electrical networks over 1000 m in length or at the input - 100 mA.
Quite often there is a need to select an RCD for a group of machines, the calculation of which is carried out according to certain rules. The installation of these devices in the circuit is carried out sequentially; the machines can be installed both before and after the RCD. The current values of the circuit breakers must be lower than in the RCD, but not less than the actual current consumption. Correct calculation of RCDs and circuit breakers shows that in the event of overloads and short circuits, the circuit breaker will protect not only the line itself, but also the residual current device installed on it.
Selecting a difavtomat letter
When the washing machine starts, the starting current increases several times compared to the rated current. The difavtomat should turn off, but if you select it correctly, this does not happen. To understand the process, you need to analyze the time-current characteristic of the difavtomat. From it you can determine the speed and operating time of the electromagnetic release.
Protection devices are divided into three categories, according to which it is possible to determine how many times the electric current must be greater than the rated current in order for the machine to operate at lightning speed. This is what the lettering on the automatic machine says:
B16 means that it reacts instantly when the nominal value is exceeded by 3-5 times (48-80 A);- C16 means that the excess is 5-10 nominal (80-160 A);
- D16, respectively, 10-20 ratings (160-320 A).
It follows that in order to avoid false positives, it is better to use a difavtomat with the letter C, in this case C16 with Iut 30 mA.
In addition, there is such a characteristic as the rated breaking capacity. This is the maximum short circuit current that the automatic circuit breaker can turn off without loss of functionality. In new houses it is recommended to use circuit breakers with a value of 6000 A, in rural houses with old wiring 4500 A.
Which RCD should be installed at the entrance to the apartment?
In modern high-rise buildings it is prohibited to use three-phase wiring, so many owners are wondering how to choose an RCD for an apartment. Meanwhile, there is nothing complicated here, since for single-phase wiring a two-pole device marked AC is used. Based on the leakage current, the RCD for the apartment is selected at the rate of 30 mA. Devices with a lower shutdown threshold may cause false alarms.
How many RCDs should I install in an apartment? It all depends on the total power of consumers. If it is too large, it is recommended to split the home network into separate lines and install a protective device on each of them. Additionally, a general RCD is installed at the entrance to the apartment to protect against fire if the insulation is damaged.
Often false alarms occur due to old electrical wiring. If these processes occur systematically, it may require complete replacement.
Rated and differential current
The characteristics of this device will always indicate designations of approximately this type: 25/10 mA, 40/30 mA, etc. These are the parameters of the rated and differential current at which the device operates. The rated current is expressed in amperes (A), this is the total value of all currents that can pass through the device in normal operation, indefinitely.
Let's give an example. A group of consumers - sockets and lighting of one living room - is powered from a separate 16 A circuit breaker. According to the standard, the circuit breaker can withstand a load of 1.13 of the rated value for an indefinitely long time, and of 1.45 of the rated value for up to 1 hour.
This standard does not apply to protective devices, so if several powerful consumers are plugged into the sockets, whose total current is, say, 17 A for several hours, the machine will not turn off, but the RCD may fail.
The differential current, expressed in milliamps (thousandths of an ampere), is the leakage current at which the RCCB must operate. To protect people from electric shock, devices with a differential current limit of 10-30 mA are used. As fire protection - an RCD with a limit of 100 mA.
Connection to a three-phase network
Three-phase 380V power is used in factories and small workshops. They power machine tools, various furnaces and asynchronous motors (elevators). Installing an RCD in a three-phase network is no fundamentally different from a single-phase one. The difference lies only in the number of pins on the protective device. The three-pole RCD has 8 contacts for connecting cables. Four incoming L1, L2, L3 and N and 4 outgoing with similar markings.
Three-pole RCD
When connecting, there may be confusion in the wires. To understand the color and letter markings, it is enough to know the simple relationships from the table.
| Russian designations | European designations | ||
| Phase A | Yellow | L1 | Brown |
| Phase B | Green | L2 | Black |
| Phase C | Red | L3 | Grey |
| Neutral wire | Blue (cyan) | N | Blue (cyan) |
| Ground wire | P.E. | Green-yellow | |
Introductory three-phase RCD + separate group
The device is installed after the introductory three-pole circuit breaker. Three power supply conductors pass through it. Then they go directly to the RCD. Connection is carried out taking into account the markings. Terminal L1 at the output of the machine is connected to L1 on the protective device, L2 to L2, and so on.
After the introductory three-phase RCD, the wires go to the group circuit breakers. The zero core is connected to the common N bus. Ideally it is blue. Then the phase wires from the machines are connected to single-pole group RCDs and distributed to consumers.
Input protective device + three-phase meter
The scheme is similar to the previous one. However, in this case a three-phase electricity meter is added. It has 8 pins designed to connect 3 phases and zero. The metering device is mounted at the output of the input machine. After the meter there is a three-phase RCD. Behind it are group single-pole circuit breakers and residual current devices.
Does a washing machine need a separate RCD?
The machine is designed to protect the wiring and electrical components of a household appliance. An automatic washing machine is a large consumer of electricity, which puts a high load on the wiring. In addition, this electrical device operates in a damp environment, and therefore is at increased risk and requires additional protection. Therefore, experienced craftsmen recommend installing a separate RCD for the washing machine; it will not only preserve the functionality of the device, but also protect people from electrical injuries and property from fire. (See also: Which stabilizer to choose for an automatic washing machine?)
Connection rules
To install a residual current device yourself, you must adhere to a number of rules. The most important of them are the following:
- When installing wiring, you must strictly follow the diagram. The wires are connected according to their letter or color marking. Ideally, the installer should have a diagram on hand.
- The residual current device is connected only after the input circuit breaker. Connecting to the network without a machine is unacceptable.
- You should pay attention to the technical characteristics of the connected RCD. If currents of 20-25 A flow in the network, then the protective device is selected for at least 32 A.
- It is prohibited to use heating radiators or water pipes as a grounding conductor. Such a negligent approach can lead to death for one of the neighbors.
- The general rule is that all electrical installation work is carried out with the voltage removed, except in cases in which disconnection is impossible.
Installation diagram
Connecting an RCD in a single-phase and three-phase electrical network, where a phase L-conductor and an N-conductor are used, often uses the option of switching on protection without a grounding system. A similar procedure exists, as a rule, in old housing stock.
RCD diagram in network 220 with grounding
Modifications for connecting the device to a single-phase network:
- General protection 220 V network in a house without a ground loop. The device is mounted in an electrical panel. It is located between the introductory machines and other single-lane AVs. The device guarantees the protection of absolutely all outgoing power lines in the event of a leakage current. This option of connecting protection without grounding has the only drawback - since the protective device is common, in the event of an accident it will be impossible to correctly determine which power line the accident occurred on.
- General RCD for 220V, electric meter and grounding system.
It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that in the newest protective systems, in order to correctly connect the protection, it is not necessary to install supply lines only on the top or bottom of the device. They allow both options, therefore, in order to avoid mistakes, you will first need to carefully study the technical documentation when connecting the RCD.
Connecting a residual current device to a two-phase network
The case is exotic. Two-phase power supply networks were abandoned at the beginning of the twentieth century. The chance of a modern electrician encountering them is close to zero. It is worth thinking about connecting an RCD to a two-phase network as an elective.
Each pole of the socket is phase. It has a potential to ground of approximately 127 volts. The connection diagrams for residual current devices are similar to single-phase ones. But the circuit breaker must be mounted on each of the two incoming phases. Of course, it is impossible to connect one of the supply wires to grounding or the electrical panel housing.
Additional Information. Two-phase power supply to residential buildings is a thing of the past. However, many modern low-power transformers have windings designed from 380 V. It operates from 2 phases. Typically these are transformers for auxiliary needs in industrial equipment. It is not practical to install a separate RCD for them.
Trademark
Speaking about the brand, we will essentially analyze the price-quality ratio. The fact is that there is an unspoken classification of all RCD manufacturers according to their territorial location - European models, Asian and Russian.
One way to spot a fake video:
Each of their products has its own characteristic features:
- Both a fire-fighting RCD and a device that protects people from electric shock produced in Europe will cost an order of magnitude more than models from Russia and China. But this price guarantees quality and reliability. It will not be amiss to know that some European companies, in addition to the main high-quality assortment, produce RCDs for the markets of other countries with the same reliability, but with reduced technical characteristics.
- Domestic manufacturers offer RCDs at a lower price than their counterparts from Europe, however, they meet all regulatory requirements of Russian standards. So far, Russian manufacturers' sales network is not so strong, and the devices themselves are not able to compete with Asians in price or with Europe in terms of quality.
- RCDs from Asian manufacturers are in greatest demand in the world. Some manufacturers from Asia enter into contracts with suppliers of products to the Russian market and in this case produce devices under the Russian brand.
Before choosing an RCD brand, decide what means you have for installing automatic protective equipment in an apartment or private house. Most preferred companies:
- Swiss "ABB";
- French Legrand and Schneider Electric;
- German "Siemens" and "Moeller".
Among domestic manufacturers, the most widely used products are:
- Kursky, average price and quality, the company gives a two-year guarantee for the RCDs produced, which indicates the reliability of the products;
- Moscow (“IEC”), products do not always receive positive reviews, however, the demand for it is high due to its low cost;
- Ulyanovsk, it is part of the group, which affects the quality of the products and, accordingly, the price;
- relatively young St. Petersburg, on the Russian market it represents the world-famous company “Schneider Electric”.
As for Chinese manufacturers, the RCDs they produce are a direct competitor to Russian devices. Price and quality are approximately at the same level, while the warranty period for Chinese goods is five years.