For quite some time now, modern homes have stopped using corks. They were replaced by more technological devices - automatic machines, also known as baggers, although some still call them traffic jams, but this is wrong, because the operating principle of a traffic jam and a machine is somewhat different. Since in this article we will consider the selection of a machine depending on the cable cross-section, there will be no talk about traffic jams.
So, the machine is a device that allows you to open the electrical circuit automatically in two cases:
- line current overload;
- occurrence of a short circuit (SC).
In the first case, overload occurs due to a malfunction of electrical appliances or their large number and power density. In the second case, due to a short circuit, electricity is consumed to heat the wires with the maximum possible current for this section. In addition to the above cases of circuit breakage, the machine provides the possibility of manual control. There is a switch on the body of the device that allows you to open the circuit.
The purpose of the circuit breaker is to protect the section of the electrical circuit for which it is installed, as well as timely opening of this section in the event of an overload or short circuit.
Possible correction of the core cross-section for line resistance
Any conductor has its own resistance - we talked about this at the very beginning of the article, when we cited the resistivity values of materials, copper and aluminum.
Both of these metals have very decent conductivity, and in short sections the line’s own resistance does not have any significant effect on the overall parameters of the circuit. But if you plan to lay a long line, or, for example, a long-length carrying extension cord is being manufactured to work at a considerable distance from the house, then it is advisable to calculate your own resistance and compare the voltage drop it causes with the supply voltage. If the voltage drop is more than 5% of the nominal voltage in the circuit, the operating rules for electrical installations require the use of a cable with conductors of a larger cross-section.
For example, a carrying case for a welding inverter is made. If the resistance of the cable itself is excessive, the wires will overheat greatly under load, and the voltage may not be enough for the device to operate correctly.
The cable's own resistance can be calculated using the formula:
Rk = 2 × ρ × L/S
Rk—own resistance of the cable (line), Ohm;
2 - the cable length doubles, since the entire current path is taken into account, that is, “there and back”;
ρ is the resistivity of the cable core material;
L—cable length, m;
S is the cross-sectional area of the core, mm².
It is assumed that we already know what current we will have to deal with when connecting the load - this has already been discussed more than once in this article.
Knowing the current strength, it is easy to calculate the voltage drop using Ohm's law and then compare it with the nominal value.
Ur = Rk × I
ΔU (%) = (Ur / Unom) × 100
If the test result is more than 5%, then the cross-section of the cable cores should be increased by one step.
Another online calculator will help you quickly carry out such a check. It seems that he will not require additional explanations.
Long distance line voltage drop test calculator
As already mentioned, with a value of up to 5% you can not change anything. If it turns out more, the cross-section of the cable core is increased, also with subsequent checking.
* * * * * * *
So, the main issues regarding the required cable cross-section depending on the planned load on it were considered. The reader is free to choose any of the proposed calculation methods, whichever he likes best.
Let's end the article with a video on the same topic.
Application of measuring instruments
To determine the diameter of the cores of wires and cables, various measuring instruments are widely used, showing the most accurate results. Basically, the use of micrometers and calipers is practiced for these purposes. Despite their high efficiency, a significant drawback of these devices is their high cost, which is of great importance if the tool is planned to be used only 1-2 times.
As a rule, professional electricians who are constantly engaged in electrical installation work use special devices. With the right approach, it becomes possible to measure the diameter of wire cores even on working lines. After obtaining the necessary data, all that remains is to use a special formula:
The result of the calculation will be the area of the circle, which is the cross-section of the wire or cable core.
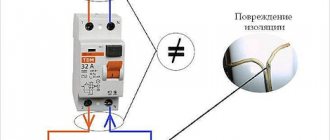
What is a machine gun for?
Automatic switches for an apartment, townhouse, or small industrial facility have a general operating principle.
They are equipped with a two-stage protection system:
- Thermal. The thermal release is made of a bimetallic plate. With prolonged exposure to high power current, the flexibility of the plate increases, which is why it touches the switch.
- Electromagnetic. The role of the electromagnetic release is played by the solenoid. When an increased current power is detected, for which the machine and cable are not designed, the switch also trips. This is already short circuit protection.
AB (common abbreviation) protects the electrical network from heating the insulation and fire
It is precisely because of this operating scheme that it is important to know how many amperes to install the machine in the apartment: if you choose the wrong device, it will not be able to block a current that is inappropriate in power, and a fire will occur. An AV selected according to all recommendations will protect against fires, electric shocks, heating and combustion of microcircuits of household appliances
Importance of time-current characteristic
Some electrical appliances have a high inrush current when turned on. Its value may be higher than the rated current of the machine, but it operates for a short time. For an electric cable, such a current does not pose a danger (if its value is within reasonable limits related to the type of cable), but the machine can be triggered by the starting current, perceiving it as an overload.
In order to avoid constant shutdowns due to the startup of devices with high inrush currents, the machines are divided into types according to the time-current characteristic.
Structurally, the automatic circuit breaker consists of two releases: electromagnetic and thermal.
The electromagnetic release is designed to disconnect the device in the event of a short circuit. To operate this shutdown mechanism, the machine uses an electromagnetic coil and solenoid. When the electric current value is exceeded many times, a magnetic field appears in the coil, which activates the solenoid and it turns off the machine.
Automatic circuit breakers have a short-circuit current characteristic (maximum shutdown current), which is rated at 3, 4.5, 6 and 10 kA. For domestic purposes, when installing protection in an apartment or house, circuit breakers with a short-circuit current rating of 6 kA are most often used.
The thermal release is a plate consisting of two different metals. With a prolonged load exceeding the rated current, this plate heats up, bends, acts on the release lever and the device turns off. The main task of such a mechanism is to protect the line from long-term overloads above the rated current of the machine.
In order not to think about what load to plug into the outlet , not to constantly calculate the total power of devices and not to think about starting currents, a time-current characteristic was invented.
This characteristic shows the time and current that affect the shutdown of the device. On slot machines it is indicated by the letter B, C or D.
Circuit breakers with the same ratings and different time-current characteristics will turn off at different times and with different excess currents.
This separation of machines is very convenient and allows you to reduce the number of false shutdowns.
In accordance with GOST R 50345-2010, there are three standards for time-current characteristics:
- B – 3-5 times the rated current, the most sensitive machines have this characteristic and are used in networks with devices that do not have high starting currents.
- C - 5 - 10 times the rated current, the most popular machines with this characteristic, they are used in apartments and private houses.
- D – 10-20 times the rated current, used to protect networks with equipment with high inrush currents and short-term overloads.
Deciding on the denomination
Actually, from the functions of the circuit breaker, the rule for determining the rating of the circuit breaker follows: it must operate until the current exceeds the capabilities of the wiring. This means that the current rating of the machine must be less than the maximum current that the wiring can withstand.
For each line you need to choose the right circuit breaker
Based on this, the algorithm for selecting a circuit breaker is simple:
- Calculate the wiring cross-section for a specific area.
- See what maximum current this cable can withstand (see the table).
- Next, from all the ratings of the circuit breakers, we select the nearest smaller one. The ratings of the machines are tied to the permissible long-term load currents for a particular cable - they have a slightly lower rating (see the table). The list of denominations looks like this: 16 A, 25 A, 32 A, 40 A, 63 A. From this list you choose the appropriate one. There are smaller values, but they are practically not used anymore - we have too many electrical appliances and they have considerable power.
Example
The algorithm is very simple, but it works flawlessly. To make it clearer, let's look at an example. Below is a table that shows the maximum permissible current for conductors that are used when laying wiring in a house and apartment. Recommendations regarding the use of machines are also given there. They are given in the column “Nominal current of the circuit breaker”. This is where we look for the ratings - it is slightly less than the maximum permissible for the wiring to work normally.
| Cross section of copper wires | Permissible continuous load current | Maximum load power for single-phase network 220 V | Rated current of circuit breaker | Circuit breaker current limit | Approximate load for single-phase circuit |
| 1.5 sq. mm | 19 A | 4.1 kW | 10 A | 16 A | lighting and alarm |
| 2.5 sq. mm | 27 A | 5.9 kW | 16 A | 25 A | socket groups and electric heated floor |
| 4 sq.mm | 38 A | 8.3 kW | 25 A | 32 A | air conditioners and water heaters |
| 6 sq.mm | 46 A | 10.1 kW | 32 A | 40 A | electric stoves and ovens |
| 10 sq. mm | 70 A | 15.4 kW | 50 A | 63 A | opening lines |
In the table we find the selected wire cross-section for this line. Suppose we need to lay a cable with a cross-section of 2.5 mm2 (the most common when laying to medium-power devices). A conductor with this cross-section can withstand a current of 27 A, and the recommended rating of the machine is 16 A.
How will the circuit work then? As long as the current does not exceed 25 A, the machine does not turn off, everything works as normal - the conductor heats up, but not to critical values. When the load current begins to increase and exceeds 25 A, the machine does not turn off for some time - perhaps these are starting currents and they are short-lived. It turns off if the current exceeds 25 A by 13% for a sufficiently long time. In this case, if it reaches 28.25 A. Then the power supply will work and de-energize the branch, since this current already poses a threat to the conductor and its insulation.
Power calculation
Is it possible to choose a machine based on load power? If only one device is connected to the power line (usually large household appliances with high power consumption), then it is permissible to make a calculation based on the power of this equipment. You can also choose an introductory machine based on power, which is installed at the entrance to a house or apartment.
If we are looking for the rating of the input circuit breaker, we need to add up the power of all devices that will be connected to the home network. Then the found total power is substituted into the formula, and the operating current for this load is found.
Formula for calculating current from total power
After we have found the current, select the value. It may be either slightly more or slightly less than the found value. The main thing is that its shutdown current does not exceed the maximum permissible current for this wiring.
When can you use this method? If the wiring is laid with a large margin (this is not bad, by the way). Then, in order to save money, you can automatically install switches corresponding to the load, and not the cross-section of the conductors
But once again we draw your attention to the fact that the long-term permissible current for the load must be greater than the maximum current of the circuit breaker. Only then will the choice of circuit breaker be correct
What is important to know when connecting electrical appliances
So, having calculated the approximate rating of the required machine, you need to give an explanation regarding the power. Many people wonder whether it is possible to plug in very powerful electrical appliances into a regular outlet, such as an electric boiler, for example.
According to the rules of the PUE, connecting an electric boiler with a power of more than 3 kW to a regular outlet is unacceptable. And each outlet has its own specific characteristics. Most often, home sockets are rated at 16 amperes, and, therefore, electrical appliances with a power of no more than 3.5 kW can be connected to them.
Therefore, any more or less powerful electrical appliance must be connected only through a separate circuit breaker. Moreover, it is the phase wire that is supplied to the circuit breaker, and not the working zero. Thus, knowing the approximate power of the equipment, you can easily calculate the rating of the circuit breaker.
Calculation of permissible current for heating cores
If a conductor of a suitable cross-section is selected, this will eliminate voltage drop and overheating of the line. Thus, the cross-section determines how optimal and economical the operating mode of the electrical network will be. It would seem that you can simply take and install a cable with a huge cross-section. But the cost of copper conductors is proportional to their cross-section, and the difference when installing electrical wiring in just one room can amount to several thousand rubles
Therefore, it is important to be able to correctly calculate the cable cross-section: on the one hand, you guarantee the safety of the network operation, on the other hand, you will not spend extra money on purchasing an overly “thick” conductor
To select the wire cross-section, two important criteria must be taken into account - permissible heating and voltage loss. Having received two values for the cross-sectional area of the conductor using different formulas, choose the larger value, rounding it to the standard. Overhead power lines are especially sensitive to voltage loss.
At the same time, for underground lines and cables placed in corrugated pipes, it is important to take into account the permissible heating. Thus, the cross-section should be determined depending on the type of wiring
Permissible heating temperatures of current-carrying cable cores
Id - permissible load on the cable (heating current). This value corresponds to the current flowing through the conductor over a long period of time. In the process of this, a set, long-term permissible temperature (Td) appears. The calculated current strength (Ip) must correspond to the permissible current (Id), and to determine it you need to use the formula:
Iр=(1000*Pн*kз)/√(3*Un*hд*cos j),
Where:
- Pn — rated power, kW;
- Kz - load factor (0.85-0.9);
- Un — rated voltage of the equipment;
- hd - equipment efficiency;
- cos j - equipment power factor (0.85-0.92).
Even if we take into account the same current values, the thermal output will be different depending on the ambient temperature. The lower the temperature, the more efficient the heat transfer
Cable correction factors depending on ambient temperature
Temperatures differ depending on the region and time of year, so in the PUE you can find tables for specific values. If the temperature differs significantly from the calculated one, correction factors will have to be used. The base temperature indoors or outdoors is 25 degrees Celsius. If the cable is laid underground, the temperature changes by 15 degrees Celsius. However, it is underground that it remains constant.
What are the tariffs for rural areas and for the city?
To a large extent, electricity tariffs depend on the area in which the consumer lives (city or rural area). Thus, the tariff in rural areas will be 30% cheaper than in urban areas.
This point has its own nuances, namely: the reduced (preferential) tariff applies only in rural settlements. Whereas, in the case when a village, both dacha and cottage (for example: DNT, SNT, etc.) does not have the status of a rural municipality (is not located within the boundaries of a rural settlement), then residents will have to pay for electricity at the rates provided for the city. The same rule fully applies to urban settlements (urban-type settlements). Although the standard of living in them, as well as their amenities, does not differ significantly from villages and villages, residents of such urban settlements must pay for consumed electricity at the tariffs provided for the city.
In addition to the above information, we invite readers to watch a video that will tell you exactly how to calculate the cost of 1 kW of electricity and what this amount consists of.
In conclusion, it should be noted that electricity bills should be paid on time and at the tariffs that are provided in a particular region. Only in this case will subscribers not have any problems with regulatory authorities.
Voltage
230/400V - inscriptions of the rated voltage where this machine can be used.
If there is a 230V icon (without 400V), these devices should only be used in single-phase networks. You cannot put two or three single-phase switches in a row and thus supply 380V to a motor load or a three-phase pump or fan.
Also carefully study bipolar models. If they have the letter “N” written on one of the poles (not only automatic machines), then this is where the neutral conductor is connected, and not the phase conductor.
They are called slightly differently. For example VA63 1P+N.
The wave icon means - for operation in alternating voltage networks.
It is better not to install such devices for constant voltage and current. The characteristics of its shutdown and the result of operation during a short circuit will not be predictable.
Switches for direct current and voltage, in addition to the straight line icon, may have characteristic inscriptions “+” (plus) and “-” (minus) on their terminals.
Moreover, the correct connection of the poles is critical here. This is due to the fact that the conditions for extinguishing the arc at direct current are somewhat more difficult.
If during alternating periods the arc is naturally extinguished when the sinusoid passes through zero, then during constant periods there is no sinusoid as such. To sustainably extinguish the arc, they use a magnet installed near the arc extinguishing chamber.
Which will lead to inevitable destruction of the body.
Number of poles
Depending on the number of poles, the machines are:
- Single-pole (1p, 1p). This is the most common type. It stands in a circuit and protects one wire, one phase. This is shown at the beginning of the article.
- Bipolar (2p, 2p). In this case, these are two single-pole circuit breakers, with a combined switch (handle). As soon as the current through one of the machines exceeds the permissible value, both will turn off. These are mainly used to completely disconnect a single-phase load when both the zero and the phase break. It is the two-pole circuit breakers that are used at the entrance to our apartments.
- Three-pole (3p, 3p). Used to break and protect three-phase circuits. Just as in the case of two-pole ones, these are actually three single-pole circuit breakers, with a common on/off handle.
- Four-pole (4p, 4p). They are rare, they are installed mainly at the input of three-phase switchgears (switchgears) to break not only the phases (L1, L2, L3), but also the working zero (N). Attention! Under no circumstances should the protective grounding (PE) wire be broken!
Weak link protection
In addition to the cross-section, when choosing suitable cable products, pay attention to the actual operating conditions. Standardized values are given for heating to a temperature not exceeding +60°C
When installing the line on a site near a country house, it is necessary to provide protection from humidity and other adverse external influences.
Carefully check all parts of the electrical network. The basic rule is reliable protection, taking into account the performance of the area with the worst parameters. It should be taken into account that copper is designed with the same cross-section for greater loads compared to aluminum. The purity of the metal is of certain importance. As impurities increase, conductivity deteriorates and losses due to useless and dangerous heating increase.
Indoor wiring device
- the introductory machine must be placed before the counter;
- a general residual current device (RCD) is installed behind the control device;
- Next, separate lines are equipped with automatic switches (AB).
The RCD prevents accidents that provoke leakage currents. In some situations, it prevents electric shock. However, complex protective measures are carried out using circuit breakers. Effective grounding must be used.
As a rule, it is convenient to install several groups in the kitchen to evenly distribute the loads. It is recommended to carefully select the distribution of powerful consumers:
- hobs;
- ovens;
- heating boilers, boilers, flow heaters;
- electric convectors, heat guns;
- air conditioners.
The wiring diagram has a tree structure. They make the necessary “branches” for connecting sockets and switches.
Current ratings of automatic machines table
In order to protect the line from overload and short circuit, you need to carefully and correctly select the current rating of the circuit breaker. For example, if you protect a line with a 2.5 sq. mm cable. with a 25A machine and several powerful household appliances are turned on at the same time, then the current may exceed the rating of the machine, but if the value is less than 1.45, the machine can operate for about an hour.
If the current is 28 A, the cable insulation will begin to melt (since the permissible current is only 25 A), this will lead to failure, fire and other sad consequences.
Therefore, the table of machines by power and current looks like this:
Nuances to consider
No one can know exactly what household appliances will be in a house or apartment. For this reason you should:
- increase the total calculated power of a three-phase automatic circuit breaker by 50%, or apply an increase factor of 1.5;
- a reduction factor is taken into account when there are not enough sockets in the room to simultaneously connect equipment;
- to simplify calculations, the load should be divided into groups;
- powerful devices should be connected separately, taking into account the low-power load;
- to calculate a low-power load, you will need to divide the power by the voltage;
- wiring is the main factor that is taken into account when choosing a 3-phase automatic switch; old aluminum wires can withstand 10 A, but if taken for 16 A sockets, they can melt;
- in domestic conditions, models with current ratings of 6, 16, 25, 32 and 40 A are most often used.
Source
Current ratings of circuit breakers
- clarify the consumer connection diagram;
- collect passport data of equipment, measure voltage;
- according to the presented diagram, they are calculated separately, the currents in individual circuits are summed up;
- for each group it is necessary to select a machine that will withstand the appropriate load;
- determine cable products with a suitable conductor cross-section.
Rules for choosing denomination
For correct conclusions, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the connected equipment. If the total current is calculated to be 19 amperes, users prefer to buy a 25A device. This solution assumes the possibility of applying additional loads without significant restrictions.
However, in some situations it is better to choose a 20A circuit breaker. This ensures a relatively shorter time for power outages when the current increases (temperature increases) with a bimetallic disconnector
This precaution will help maintain the integrity of the electric motor windings when the rotor rotation is blocked by a jammed drive.
Different response times are useful to ensure selective operation of protective equipment. Devices with lower latency are installed on the lines. In an emergency, only the damaged part is disconnected from electricity. The input machine will not have time to turn off. Power supply through other circuits is useful for maintaining lighting, alarms, and other engineering systems in working order.