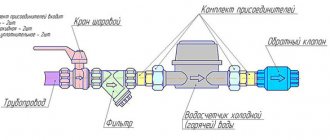
One of the main tasks of the indoor electrical network is to ensure the safety of people and the safety of electrical appliances. The presence of residual current devices (RCDs) in the network does not guarantee complete safety; they only protect against voltage surges and short circuits.
But if you choose the right protective devices and think through the circuit diagram for connecting the RCD, then the level of protection will be maximum. In this article you will learn how to correctly connect an RCD to an existing power supply circuit.
Purpose and operating principle of RCD
The operation of the residual current device is based on a constant comparison of the current values that flow through the phase and neutral conductors. If you touch a live wire, some of the current will pass through the human body. Almost instantly (0.2-0.4 seconds) the RCD trips and cuts off the current, because the values of the phase and zero currents are unequal.
Installation of heated electric floors: types, power calculations, pitch
An RCD will not only save you from electric shock, but also prevent fires. If the insulation is damaged, current leakage begins. At the point of current leakage, heating occurs and the wiring may catch fire. If there is a shutdown protection device in the circuit, this situation is impossible.
If your apartment currently does not have a security device, we recommend purchasing one. How to connect an RCD before or after the machine, what other types of protective devices exist, we will consider further.
Connection errors: how to avoid them
The question is often asked: how to connect an RCD correctly so that the circuit works without failures? As an answer, the following are the most typical miscalculations when connecting protective equipment without grounding.
- Interweaving of neutral conductors coming out of the device into a single unit. This provokes unreasonable alarms and makes it difficult to check the correct installation. To make sure that the assembly procedure without grounding is followed, plug the electrical appliance into the socket connected to the RCD. If it works, the circuit is assembled correctly.
- Connecting the grounding wires of sockets to the neutral wire of the RCD or to a homemade grounding circuit. This violates electrical safety standards: an amateur circuit often causes a short circuit. When connecting the grounding switches of the sockets to water supply or heating pipes, an electric shock can strike not only the people living in the apartment, but also their neighbors.
- Neutral and ground connection. In this case, the RCD simply will not operate, since it works due to the difference in current strength in the phase and neutral wires. The connection between zero and ground provokes stable power outages in the apartment. If the grounding circuit does not work, then the grounding wires from the devices coming to the electrical panel should be wrapped with insulating tape: otherwise, the conductive parts of the household appliances may be exposed to dangerous voltage.
How to properly connect an RCD. demonstrates a video clip that details the sequence of all operations - thanks to the visual lesson, even a non-professional can easily cope with installing single-level protection. If the circuit is more complex, requires the coordinated operation of several protective devices, and is associated with a grounding connection, it is better to order installation by a professional electrician - so as not to be constantly without power and to operate electrical appliances safely.
RCD selection
So what should you choose? Installation of RCD + automatic or difavtomatic? The first option is cheaper, and the second takes up less space in the electrical room. There is one more advantage in favor of the first option. If one of the devices fails, replacement will be cheaper. To properly protect your electrical network, you need to select the correct parameters of protective devices. Let's take a look at how they differ and what is right for you.
You may be interested in the article “Soldering polypropylene pipes: temperature table, installation instructions + top best pp systems” Go>>
Selection by parameters
Based on sensitivity, RCDs are divided into two types:
- protect against electric shock;
- fire protection
For the first type, the current value is set, taking into account that a current of 50 mA is dangerous for humans.
The choice also depends on the room in which the protection device is used.
Choose from two types:
- At 10 mA, if the room has high humidity (bathtub, kitchen, swimming pool, bathroom), for connecting washing machines and boilers.
- At 30 mA, if the room conditions are normal.
It is not recommended to install an RCD with a sensitivity of less than 10 mA; there is a high probability of false shutdown.
The fire-fighting type of RCD according to the current value is divided into:
- 100 mA;
- 200 mA;
- 300 mA.
Selection by type
Let's decide on the second parameter. According to the type of current leakage, they are divided into the following classes:
- AC - alternating current. Suitable for apartments, they can be connected to: warm electric floors, refrigerators and freezers, boilers, electric heating devices.
- A - for alternating and rectified (pulsating) current. Suitable for devices with switching power supplies or rectifiers. These are televisions, computers, microwaves, dishwashers and washing machines.
- B - suitable for any current, but are not used in the house.
We also pay attention to the delay time before shutdown. Suitable for home and apartment without delay. Response time from 2 ms to 3 ms.
If you have decided on the choice of protective devices, then move on to connecting them to the network.
Operating principle of RCD, differences from difavtomat
The requirements of the PUE indicate the need to install protective equipment. It provides protection against electric shock and breakdowns of the cable insulation coating. The RCD can be connected to 2 wires in a network with a voltage of 220 V and to 4 wires in a network of 380 V.
The disadvantage of the device is the inability to detect overload or short circuit. An automatic switch will further protect it. The difference between the devices is the response of the RCD to the current imbalance of phase and zero with a nominal value of 10-30 mA. The device does not recognize overcurrents and may even catch fire under their influence.
The difavtomat operates normally at a current of up to 16 A, and turns off the line in case of leaks. Unlike an RCD, it has a time-current characteristic, which determines the speed of shutdown.
A switch with an electromagnetic release trips when the current value exceeds 5-10 times.
RCD diagram in a single-phase voltage network
Today, many manufacturers of household appliances recommend using protective devices when installing electrical wiring. It is advisable to additionally secure such household appliances as: washing machine, boiler, dishwasher. If we take into account that a modern electrical network in an apartment consists of several circuits designed for different loads, then there will also be several options for placing an RCD in the circuit.
Installation of electrical wiring in a wooden house
For apartments and private houses, a single-phase network is most often used. There are two possible wire options:
- With two wires. One wire is phase, the other is neutral. Which wire is which can be determined using a simple tester in the form of a screwdriver. The light on the phase wire will light up. This is an old Soviet design.
- Three wires: phase, neutral and ground. This is a modern design that came to us from abroad.
Let's consider popular circuits for connecting RCDs in a single-phase network.
Scheme without grounding
In the case when the house has single-phase electrical wiring without grounding and a simple connection diagram for all devices, i.e. there are no separate circuits for lighting, sockets, and household appliances. Then, for protection, one common RCD is used for all devices.
Connecting an RCD to an electrical circuit is not difficult. It is necessary to connect the protection device to the wires that enter the apartment or house. When connecting, observe polarity.
The phase wire is to terminal L, and the neutral wire is to terminal N. In this case, it is recommended to use an RCD with a sensitivity of 30 mA and a load of 25 A.
The disadvantage of this scheme is the difficulty of determining a leak in the network when an RCD is triggered. But this is a very simple and inexpensive way to protect electrical appliances.
Circuit with ground wire
If the apartment or house uses single-phase electrical wiring with grounding, then connecting the RCD to the network is similar to the previous option. The same type of RCD is used and the connection is made in the same way. The phase wire is to terminal L, and the neutral wire is to terminal N. The ground wire (yellow-green) is not used.
The diagram shows the connection of an RCD in a single-phase network with grounding.
In modern apartments and private houses, specialists today use electrical wiring with grounding. Together with RCDs, other protection devices are used: circuit breakers, voltage relays.
Depending on the number of household appliances, lighting fixtures, the presence of a swimming pool, saunas, the electrical network circuit has many circuits. Therefore, the installation of an RCD and its position in the circuit depends on many factors.
Let's consider several options for such connections.
General RCD at input
If the house or apartment is small and the wiring is in good condition, then you can use the simplest RCD connection diagram. Installation of the RCD in the circuit is mounted at the input.
This connection has a number of advantages:
- not expensive;
- easy to install;
- does not require changes in the electrical network;
- takes up little space.
You may be interested in the article “How to connect a washing machine yourself: step-by-step installation instructions” Go>>
But there are also disadvantages:
- if a leak occurs, the entire house will lose power;
- it is not possible to separate electrical appliances by leakage current;
- false shutdowns may occur;
- Finding the problem area becomes difficult.
General input RCD and single-phase meter
Connection diagram for RCD with single-phase meter:
The following connection diagram is more often found in a private home. If everything is done correctly, then there is a common machine in front of the electricity meter.
In this case, the RCD is connected after the meter. If the meter is in a special sealed box, then we connect the RCD to the wires that come out of it. The phase wire is to terminal L, and the neutral wire is to terminal N.
When you connect directly to the terminals of the electric meter, be careful. You may be fined for incorrect connection.
Connection to the meter:
- connect the second terminal to terminal L;
- the fourth with terminal N.
Introductory and group RCD with electric meter
This connection is the safest and most practical. During major renovations or construction, such a scheme is often used today. Let's consider how to connect the RCD in this case.
The entire electrical network of the house is divided into separate circuits. Each of these circuits is controlled by a separate protection group - RCD + AB. A common RCD is also connected to the circuit. We get double protection against current leakage.
Another advantage of this connection scheme is that it is much easier to determine the current leakage when the protection is triggered. The search is narrowed down to devices in the same circuit.
To prevent simultaneous shutdown of the general RCD and in the circuit, it is necessary to correctly select the shutdown time and current values.
If a shutdown still occurs, it means that there are problems with the RCD in one of the circuits:
- out of order;
- with marriage;
- the load is not selected correctly.
The disadvantages of this scheme are the large workload of the electrical panel and its high cost.
Only group RCD networks
This connection option is also found. The only difference from the previous scheme is the absence of a common RCD. This scheme is also quite reliable.
Of course, in such a connection we rely on the reliable operation of one device. Therefore, you should not skimp on protection devices and purchase them from reliable manufacturers.
Fire protection RCD: before or after the meter.
Dear pros! An electrician from the management company came and contributed to the installation of the panel. Please clarify, should a 63A* 300 mA fire protection RCD be installed before or after the meter? Meter in the apartment panel. If it is before the meter and in the apartment panel, should there be a seal on the RCD? If a fire protection RCD is installed after the panel, does it not protect the meter and input? so where should I put it? Help me to understand. Thank you.
Masters online: 475 Orders per week: 2,860 Offers per day: 1,321
The RCD should be installed before the meter, so access to its terminals should be closed if the management company wants it.
The RCD does not protect the network from short circuits, but protects people from electrical damage. current, so it’s okay if it’s after the meter. And to protect the meter and input, you have a machine in the floor panel.
From the input machine, the phase and working zero are supplied directly to the metering device (electricity meter). Further, after the metering device, as a rule, a fire protection RCD (residual current device) is installed. The terminals of the input circuit breaker are closed and sealed (at the same time as the meter). A fire protection RCD only protects against significant leakage currents that can lead to a fire, and does not protect people from electrical damage. electric shock I support the statement of Sergei Evgenievich
placed only after the meter. Designed to protect against current leakage. , that is, it is not a reading of current consumers
ONLY. after the counter. The RCD should not protect the metering device.
There is no need for a fire protection RCD in an apartment. But if you want to install it, then in the floor panel, after the meter.
thanks for the answer, but the meter is in the apartment
If you are afraid that the meter will short out, then install a 2-pole circuit breaker. switch (1 phase) before the meter, but it will have to be placed in a separate box and sealed, but the RCD can be done after
The fire-fighting RCD should be installed in the Floor panel, and if it is installed in the apartment panel, then it automatically ceases to be fire-resistant.
The installation of fire protection is recommended in the PUE, but is not required. This is due to the fact that not every consumer has protective shutdown devices installed on group lines. So they propose installing an RCD with an operating current from 100 mA to 300 mA at the input in floor boards. Contractor organizations that service internal electrical networks are interested in increasing the volume of work, as this means additional money and an increase in the estimated cost. Personally, I never install a fire RCD at the input, as I consider it pointless and a waste of money. 7.1.84. To increase the level of fire protection during short circuits to grounded parts, when the current value is insufficient to trigger the maximum current protection, at the entrance to an apartment, individual house, etc. It is recommended to install an RCD with a trip current of up to 300 mA.
The RCD protects against damage to a person, not the meter. A machine is installed in front of the meter and sealed. Perhaps you are confusing RCD with Difavtomat?
PUE, clause 7.1.64 regulates the installation of a SWITCHING DEVICE in front of the meter. What kind of device it should be (fuse, automatic, RCD, switch, etc., etc.) is not regulated.
An electrician from the management company can be recommended to install an RCD in the main distribution board for protection, or move the meter there. In an apartment switchboard, all protective and other devices are installed after the metering device.
Hello! It must be installed after the meter; there should not be a seal on the RCD (and there is nowhere to put it there). The purpose of the RCD is not to protect the meter and the input circuit breaker; the purpose of the RCD is to measure how much current has come in and how much has gone out, and if the current more has come than has gone, de-energize the area for which the RCD is responsible. This type of RCD must be installed after the machine, which comes after the meter (and is usually located in the apartment). Please note that this RCD does not protect against electric shock to a person, it is necessary to put it in RCD panel with 30mA triggering.
“There shouldn’t be a seal on the RCD (and there’s nowhere to put it there).” It's right. The seal is placed on a box in which the RCD is installed, and which in turn is installed in the metering panel. Although today both RCDs and circuit breakers are produced with protective covers for each contact and with the ability to install a seal on them in order to prevent unauthorized connection to the device contacts. For example, EKF makes such devices. KEAZ too. I think Schneider’s household line will also catch up.
Ouzo must be placed after the counter. Moreover, at 63a, it will be the introductory machine. And the meter is protected by an automatic switch at the control panel. Would you like to consult in more detail?
Connecting a 3-phase network
A three-phase network is not found in apartments. It can be found in a private home. Woodworking machines, lathes, and high-power engines are connected to it.
The connection diagram for a three-phase RCD differs only in the number of pins in the device. A three-pole RCD has 8 outputs: 4 incoming L1, L2, L3 and N and the same number of outgoing. To avoid getting tangled in wires when connecting, use the wire designations from the following table:
| Russian designations | European designations | ||
| Phase A | Yellow | L1 | Brown |
| Phase B | Green | L2 | Black |
| Phase C | Red | L3 | Grey |
| Neutral wire | Blue (cyan) | N | Blue (cyan) |
| Ground wire | P.E. | Green-yellow | |
Let's consider two connection options.
General RCD for 3-phase network and group RCDs
The 380V network uses 4 wires: 3 phase and one neutral. The RCD must be connected to the input three-pole circuit breaker, observing the markings.
The wires after the introductory RCD are connected to group circuit breakers. Each phase wire is connected to a single-pole RCD, and the neutral wire is taken from the common bus.
General RCD on a 3-phase network diagram:
General RCD for 3-phase network with meter
This connection diagram is practically no different from the previous one. The only difference is that the circuit has an electric meter. Group RCDs are also connected to separate power lines.
Connection diagram for an RCD in a three-phase network with a meter:
#3. Connecting an RCD to each group
This is the most convenient option for connecting differential protection devices for operation and repair. In this case, for each of the lines leaving the electrical panel, its own circuit breaker is installed along with a separate residual current device.
In this case, in the event of a malfunction, only those protective devices that are located on the emergency line will operate. This simplifies troubleshooting and allows you to use the remaining undamaged part of the electrical wiring.
If there are differential protection devices on each line, it is advisable to install a common RCD with a setting of 100 mA. It is installed after the introductory machine and is called “fire safety”. This device does not protect people from electric shock, but protects electrical wiring from fire.
The disadvantage of this scheme is the large number of protective devices and space for their installation. Therefore, a compromise option is possible - installing RCCBs not on each line, but on a group of consumers.
Basic mistakes
When installing protection devices on their own, people often make mistakes that can lead to trouble.
These include the following incorrect actions:
- Incorrect connection of wires to the terminals of the devices. To avoid problems, we use the rule: the input phase and zero are connected to the upper terminals of the device. To the lower terminals are the wires going into the house.
- Incorrect bus connection to group circuit breakers. It must be connected above the RCD and AB groups; the circuit it protects must be isolated.
- The zeros of different groups are confused.
- Error when choosing the rated current for the protection device; it must be selected with a margin. For example, for RCD 63, AB 50A is suitable.
- When installing the socket, do not connect the yellow wire (ground) to zero.
- The neutral and ground buses are confused; different buses are used for the two conductors. The number of such tires is equal to the number of RCDs.
Always follow the connection diagram and keep it in front of you.
Financial aspect
And the main thing that distinguishes RCDs and RCBOs in cases of private use at home is cost. It demonstrates well what most users will prefer, especially if we consider the device from the point of view of reliability, which is the same among famous manufacturers.
And here's why price will ultimately become the main aspect when choosing:
- the complexity of the connection will cease to bother you over time, as you gain experience and the installation will no longer be something difficult and unknown;
- finding the reasons for the shutdown will also not become a problem over time, when you have to go through about five unforeseen situations;
- reliability and workmanship will be the main aspect, because it will speak about long-term operation more than anything.
And now, when we come to the cost, taking into account all the connections and purchasing a panel with enough space for everything, the difference in price will not even exceed 4,000 rubles. This is not such a large amount that is worth saving in electrical matters, since you can lose much more due to improper power supply.
The choice between an RCD and an RCD is really worth paying attention to, because the life of not only household appliances, but also people depends on electricity.
Negligence and economy can lead to death or fire, which is not worth either one or the other. No tags for this post.
Safety rules for installing RCD meters and automatic machines
When connecting protection devices, a number of safety regulations must be observed. Not only does this help ensure proper connections, but it will also save your life.
How to properly connect RCDs and circuit breakers, basic rules for safe installation:
- Start work only after completely turning off the power. The presence of current in the network can be checked using a tester or a regular test light.
- Label the connected wires. Use colored electrical tape or special heat-shrinkable tubes of different colors for this.
- Connect and extend wires using special terminal blocks, clamps, and sleeves.
- After connecting the wire to the machine or other device, check the reliability of the connection. Try pulling out the wire. The next day after installing the panel, tighten all the screws again.
- Be careful when connecting power for the first time. Short circuits and sparks are possible. Stay away from the control room.
- Test the protection device by pressing the “test” button.
- Do not use heating or water supply pipes in the apartment for grounding.
Machine denomination
On the body of any device the nominal value is indicated - the value of the maximum continuous current that passes through the device without harm. This parameter is safe for current switching.
To ensure protection of the RCD itself, it is necessary to install a circuit breaker with a rating similar to or 1 more than the rating of the device. If you have a machine with a rating of 16 A, the RCD should be about 25 A. This current reserve will be enough to prevent the flow of energy when the load increases.
The machine is triggered when a current appears 13% higher than the nominal value: a 16 A modification will operate at a current of 18 A. If the RCD rating is equal, the contacts may heat up. To select the rating of a system with several circuit breakers, you need to sum them up and select an RCD with a larger rating.
Installation instructions
Before installation, you first need to select a location for installation. For installation work, use a metal or plastic cabinet. They come in different sizes; you need to count the number of devices in advance to choose the right size.
Some models are equipped with viewing windows for taking meter readings.
How to correctly connect RCDs and machines yourself, basic rules:
- We begin any work after turning off the power supply.
- When installing wiring and protective devices, strictly follow the selected diagram; it is better to keep it in front of you.
- Connect wires strictly by color marking. Strip the ends of the wires by 0.5 cm and secure with screws.
- All protective devices, circuit breakers, voltage relays are mounted on a DIN rail. To fix them, engage the upper clamp, use a screwdriver to bend the lower clamp and press on the device, when it is in place, release the lower clamp.
- Label all protective devices on the panel so that you know which devices are connected through them.
- The machine is connected to the input wires first, only after it are all other devices installed.
- When choosing an input RCD, we calculate its parameters depending on the current flowing in the network. For example, for a current of 20-25 amperes, you should take a 32A protective disconnect device.
You might be interested in the article “Installing a toilet with your own hands: step-by-step connection instructions” Go>>
If a false shutdown occurs or the device does not work on the contrary, the reason may be the following:
- phase and neutral wires are connected after the RCD;
- check whether the neutral wire is secured;
- the neutral wire and ground are connected in the socket;
In the apartment
Let's look at the case when the installation of protection equipment takes place in an apartment panel. Some builders, when delivering houses with an open plan, rent out housing without wiring the internal electrical network. This is understandable; it is not known where the partitions and, accordingly, sockets and lighting will be located. Therefore, they only introduce cable into the apartment.
On the floor electrical panel there is an introductory circuit breaker and an electric meter. The future owner enters into a contract with another contractor for internal electrical work. The wiring diagram will vary depending on customer requirements. It will depend on the circuit and the loads which RCD to install. If desired, any man can do this work on his own.
We will assume that the wiring in the apartment corresponds to the protection installation diagram presented in the previous figure. The input machine and counter are located in the floor panel, and all other elements will be located in the apartment box. To do this, you need to install an electrical panel in the corridor, next to the cable entry point. The sequence of work during installation is as follows:
- the input machine is turned off. A sign “Do not turn on, people are working” is posted;
- An outlet is connected to the cable that was brought into the apartment. It will be needed to connect working tools and lighting;
- the plate is removed, the machine is turned on;
- holes are drilled in the wall using a hammer drill for fastening the box. Dowels are inserted and the shield is attached to the wall with screws;
- after this, a metal strip is inserted and secured to the inner wall of the box with screws.
There shouldn’t be any difficulties if you perform all the steps consistently and carefully.
How to check an RCD in 30 seconds
After the installation of the RCD and circuit breaker connection diagram has been completed, it is necessary to check the operation of the protective devices. To check the operation of the RCD, press the button. If the power turns off when pressed, then everything is in order and the device is working. It is recommended to perform such a check periodically to ensure the operation of the device.
The second method is not recommended to be used independently. It is used by professionals. The phase, through a resistor, is connected to the ground wire. In this way, a controlled leakage of current is carried out.
It is not always possible to use the services of a professional electrician, and you have to do the work yourself. In this case, remember and strictly follow the safety rules.
We have looked at several basic schemes for connecting protective devices; in practice there can be much more.
If you are professionally involved in electrical installation work and can give useful advice or suggest other connection diagrams, write to us in the comments.
By what parameters is the RCD selected?
To ensure the safety and long service life of a residual current device, several factors must be taken into account when choosing this device:
- Rated current . It is determined by the contacts located inside the device. For trouble-free operation, the rated current of the RCD must be equal to or, preferably, greater than the upstream circuit breaker.
- Number of poles . For a three-phase network, a four-pole RCD is selected; for single-phase voltage, a two-pole device is required.
- Leakage current . When connecting the RCD directly to the line or to an electrical appliance, the differential protection setting should be no more than 30 mA for rooms and 10 mA for the bathroom. In the event that there are downstream RCDs or RCBOs after the RCCB, then it is 100-500mA, depending on the installation location.
Briefly about the main thing
For most ordinary people, it is a mystery what an RCD is in electrical engineering and how to connect it correctly. But the safety of their home and everyone living in it actually depends on this device. It protects against possible current leakage in the network, and its use is especially important in rooms where there is no grounding.
There are quite a few types of RCDs, because... they are available for circuits with alternating or direct current, for single-phase or three-phase networks. In addition, they all differ in operating current parameters, of which there are quite a few. And you should not confuse an RCD with an automatic shutdown device; they have different tasks.
Professionals recommend installing, in addition to the general protection device, a separate device for each operating circuit.
Safety regulations
If you decide to connect the RCD yourself, the success and safety of the work performed will depend on your compliance with the safety rules:
- Before starting installation operations, be sure to remove the voltage from the area (after disconnecting it would be a good idea to check the presence of potential with an indicator);
- Take care of the marking of the wires - this will make it much more convenient to connect the device so as not to confuse the leads;
- Be sure to use factory terminals and clamps, and never allow twisting, soldering or other connections with poor contact;
- After installation, check the reliability of the connections and the presence of sufficient insulation on all current-carrying elements;
- When commissioning, be sure to check the functionality by pressing the test button;
- When you first apply voltage to a newly installed device, it may fly apart due to manufacturing defects or installation defects, so it is better not to stand nearby or take measures to protect your eyes.
Before applying voltage after completing installation, be sure to ensure that no one in your household or colleagues touches live elements.
Design
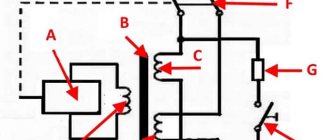
The design of the RCD will help us understand how it reacts to current leakage. The main working units of the RCD are:
- Differential current transformer.
- The mechanism by which an electrical circuit breaks.
- Electromagnetic relay.
- Test node.
The transformer is connected to opposite windings - phase and zero. When the network is operating in normal mode, these conductors in the transformer core help induce magnetic fluxes that are in the opposite direction relative to each other. Due to the opposite direction, the magnetic flux in total is zero.
The device and principle of operation of the RCD is clearly shown in the following video:
An electromagnetic relay is connected to the secondary winding of the transformer; under normal operating conditions it is at rest. A current leak occurs, and the picture immediately changes. Now various current quantities begin to pass through the phase and neutral conductors. Accordingly, there will no longer be equal magnetic fluxes on the transformer core (they will be different both in magnitude and direction).
A current will appear in the secondary winding and, when its value reaches the set value, the electromagnetic relay will operate. Its connection is made in conjunction with a release mechanism; it will instantly react and break the circuit.
An ordinary resistance (some kind of load, the connection of which is made without passing through the transformer) serves as a test unit. Using this mechanism, current leakage is simulated and the operating condition of the device is checked. How does this check work?
There is a special “TEST” button on the RCD. Its main purpose is to supply current from the phase wire to the test resistance and then to the neutral conductor, bypassing the transformer. Due to the resistance, the current at the input and output will be different, and the created imbalance will trigger the shutdown mechanism. If the RCD does not turn off during the test, then you will have to abandon its installation.
Note! The RCD must be checked regularly, ideally once a month. This is a fire safety requirement and should not be neglected. The internal design of different RCD manufacturers may differ, but the general principle of operation remains unchanged.
The internal design of different RCD manufacturers may differ, but the general operating principle remains unchanged.
All devices differ in the operating principle. They come in electronic and electromechanical types. Electronic RCDs have a complex circuitry and require additional power to operate. Electromechanical devices do not require external voltage.
Residual current device (RCD)
monitors the presence of leakage current (also called difference or differential). The latter most often appears due to a violation of the insulation of the phase wire. As a result, the external, non-current-carrying parts of the electrical device become energized - this is called current leakage to the housing. By touching them or carelessly picking up a bare phase wire, a person exposes his life and health to great danger. And here the RCD comes to the rescue, which instantly de-energizes the controlled section of the network.
1 of 3
On the picture:
Operating principle of RCD.
It is based on constant monitoring of the current strength in the supply (phase) and return (zero working) conductors, which go, respectively, to and from the electrical appliance. Under normal conditions, the current strength in them will be approximately the same - of course, its value is taken modulo, without taking into account the mathematical plus and minus signs. The short circuit of one of the wires to the body of the device or the human body causes a violation of this balance, that is, the current strength in the phase wire differs significantly from that in the neutral conductor. Having detected this difference, the RCD activates the release mechanism and stops the supply of voltage to the emergency section of the network. In this case, the device’s response threshold is the value of the differential current at which a power outage occurs. Simply put, this is the maximum permissible difference between the current strength in the phase and neutral working wires. So, for example, a device designed for 30 mA will operate precisely at this value of the resulting leakage current.
RCD + “automatic” It should be noted that the RCD, like other electrical appliances in the house, must be protected by the automatic device. The latter will not allow the influence of high currents (short circuit currents) on the power contacts of the RCD, thereby maintaining its functionality. Therefore, the RCD is always installed strictly after the circuit breaker.
Let's buy right!
First, pay attention to the direct name of the device itself. Today, almost all manufacturers have finally met consumers halfway, deigning to indicate on the body of the device itself information about whether it is a difavtomat or an RCD.
Therefore, we would not recommend buying such Chinese-made equipment. Nosy Asians either do not indicate anything at all, or they do it using only symbols that are understandable to them.
Approximately in the same category is the advice to carefully read the markings, which should always be indicated on the same body of the device or on its packaging (a less reliable option).
So, if you see on the body only the value of the rated current (16, for example), but there is no letter in front of this designation, then you are holding an RCD in your hands. Note that “16” in this case means “ampere”. If there are letters B, C or D in front of the numbers, then you have a difavtomatic machine in your hands
The letters indicate the typical characteristics of thermal and electromagnetic releases, but at the household level it is not necessary to pay special attention to them
In addition, it doesn’t hurt to look at the connection diagram. This method is somewhat more complicated, but it provides a 100% guarantee of differentiation. This information must also be displayed on the housing. So, if the diagram only indicates the presence of a difavtomat with the designation “Test”, then there is an RCD in front of you (do not confuse it!). Accordingly, if there is “Test” and the windings of the releases are indicated, then you are holding a differential machine in your hands.
Finally, it makes some sense to also pay attention to the overall dimensions. If we talk about old models of difavtomats, they are an order of magnitude wider than RCDs
In those days, they simply did not know how to produce sufficiently compact releases, and therefore housings with a larger internal volume were required. Attention! All modern differential automatic machines take up less space!
However, it is important to warn you that the last point is not worth paying any serious attention to, since currently there are a huge number of devices exactly the same in size
Correct electrical installation
Most RCDs fall into the category of modular equipment for installation on a 35 mm DIN rail. The height of the module and the size of the neck correspond to standard dimensions, so there are no problems with placing the diff protection in ordinary row boxes.
In terms of assembling panel wiring, there are some subtleties. The connection of the input working zero to the common bus or cross-module must be carried out immediately after the output from the RCD with one conductor without branches. In this case, only those lines whose protection is controlled by the device from which the working zero is taken should be connected to this bus. Thus, in a standard panel the following connection diagram applies:
vote
Article rating