The predominant type of foundation construction for most buildings is strip.
Alternative options are mostly specialized types of support structures used only in certain conditions.
Only the tape is capable of working in almost any conditions, has all the necessary qualities and allows the design to be combined with elements of other support systems.
The capabilities and properties of the foundation have been studied in detail over the centuries-old history of use, and impressive statistics have been collected confirming existing construction and operation methods.
Let's take a closer look at the process of creating a strip foundation.
What is a strip foundation
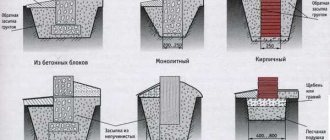
A strip foundation is a closed support system for buildings of various types, which is a strip of concrete or prefabricated elements located under all external and internal load-bearing walls.
Initially, only prefabricated types of tape were built from natural stone or brick, but with the advent of concrete, monolithic reinforced concrete casting . It demonstrates excellent performance, high strength and rigidity.
The durability of a monolithic strip foundation reaches 150 years, which is 2-5 times superior to prefabricated types.
A strip foundation is the only type of foundation that allows you to build a full basement or ground floor. The underground part of the tape requires a special approach in terms of waterproofing and drainage, which is due to the hydrogeological features of the site.
In addition, strip bases allow you to carry out repair work, strengthen or supplement the structure with new elements.
NOTE!
Its versatility and great design capabilities have made the tape the undisputed leader among all types of foundations.
Useful tips
Recommendations from experienced builders will help you avoid mistakes when laying a strip foundation:
- concrete will set faster in cold weather if the solution is mixed with warm water;
- the strength of concrete decreases when using sand and gravel mixed with earth or clay;
- when using wet sand, the amount of water must be reduced, otherwise the solution will turn out liquid;
- there should be no shoe marks on a well-compacted cushion, otherwise the building will sag due to poor-quality compaction;
- You should not neglect insulation, since thermal insulation of a strip foundation, even for a light frame house only from the outside, reduces heating costs by 15 - 20%.
To drain rain and melt water from the strip foundation and reduce the amount of heaving, it is recommended to install a blind area. To enhance protection and give a presentable appearance, the base part of the tape is trimmed with stone, clinker tiles, and siding.
What is its structure
A strip foundation is a continuation of load-bearing walls, immersed in the ground. During construction , a trench or pit is first dug, at the bottom of which a layer of sand cushion . Then the formwork is installed, the reinforcement frame is assembled and concrete is poured.
This is a schematic and abbreviated description of the technology for creating a monolithic tape; in practice, the number of steps can be increased.
To create prefabricated types of foundation, the sequence changes - after a layer of sand cushion, a concrete base is installed (or poured), on the surface of which a strip of brick or block elements is built.
There are combined base options, such as pile-tape . They consist of a regular tape, to which piles are attached as additional supports, reaching dense layers of soil.
Redistribution of loads allows you to build houses on problematic soils, loose or weak-bearing.
Cutaway photo of him:
Video description
What are the features of concrete driven piles?
We will talk about pile foundations in our video: Since this technology is relatively new and not all construction companies can boast that they master it perfectly, there are still cases when, some time after construction, a house sags somewhat under some piles. But foreign experience shows that such incidents occur only when the technology is not followed, and if the installation of a pile foundation is carried out according to all the rules, then it will become a reliable support for the house. In addition, piles allow the construction of buildings even on soils with a high degree of mobility.
Pile foundation in section Source rust-mint.ru
Kinds
There are different types of tape.
By design there are:
- Prefabricated views . They are built from brick, cinder blocks, stone or (most often) from specialized FBS reinforced concrete blocks. The performance characteristics of prefabricated belts are weaker than those of monolithic ones, but construction time is significantly reduced and there is no connection to temperature conditions.
- Monolithic tape . It has maximum rigidity and strength, and is resistant to all external manifestations - the weight of the house, the effects of frost heaving forces, etc. The disadvantage is the long hardening time of concrete - the full cycle from the moment of pouring lasts 28 days. In addition, the material can only be poured under appropriate temperature conditions, which limits the possibilities of construction to the spring-summer period.
The tapes are also distinguished by the depth of immersion in the ground:
- Not buried . The tape is built entirely on the daytime soil surface. An option possible only on rocky or very dense soil types, with deep groundwater. It is relatively rare, since the conditions of most regions of Russia are sharply different.
- Shallow . The tape is immersed in the ground to a relatively small depth, on average 0.6-1.5 m (taking into account the thickness of the sand cushion layer). The base is subject to frost heaving loads, so it is necessary to carefully examine the hydrogeological conditions of the site, avoiding heaving soils (with a high content or frequent layers of clay).
- Recessed . This type of tape has the greatest load-bearing capabilities. The depth of immersion exceeds the level of winter soil freezing. This is the main condition for the construction of buried strip foundations. It ensures the absence of heaving loads directed from below, although lateral influences remain. Since the buried belt has a developed lateral surface, the total magnitude of these impacts is large and requires appropriate measures to be taken. Basically, the way out is to widen the trench and increase the thickness of the backfill layer in the sinuses.
IMPORTANT!
In addition to these types, there is a pile-strip foundation, which is a combination of a pile field tied with a concrete strip. The load from the weight of the building is distributed equally between them, allowing you to get all the advantages of the tape (economical consumption of building materials, the ability to create a basement) and the strong support on solid soil layers that piles provide.
Dependence on groundwater level
Underground springs, which are located in the upper layer of the earth, oversaturate the soil with moisture and gradually destroy the integrity of the reinforced concrete foundation. This factor must be taken into account when designing the foundation. The developer can hire a surveyor to perform a hydrogeological analysis or do the research themselves.
Deep occurrence of hot water
When groundwater passes below the frost line, the house is practically unaffected by it. The defining dimensions in this case are calculated only taking into account the geology of the site and the weight of the structure.
Above or at the level of the frost line
For the developer, such hydrogeological conditions are considered unfavorable and require compensatory measures. To avoid destructive effects, the tape is lowered below the frost line by 0.15 - 0.2 m.
Such a foundation should be classified as a buried type. Several layers of waterproofing are prudently laid between its layers.
Rocky, coarse-grained, gravel and similar rocks are dense enough that the engineer does not have to take into account the occurrence of sources in the calculations.
How to calculate depth and width
Tape parameters are determined by several factors:
- House weight.
- Composition and bearing capacity of the soil.
- Groundwater level.
Calculating the width and depth of the belt is a complex engineering task, the independent implementation of which is fraught with the appearance of a lot of errors. To create a project, the participation of professionals with appropriate education and experience is required.
In this case, some general rules should be taken into account. For example, the thickness of the tape should be 10 cm greater than the thickness of the walls. The load-bearing capacity of concrete is very high, and sometimes they make a compromise - they increase the thickness of the tape directly under the wall itself, forming something like a canopy.
The depth of installation is determined by the type of tape. For buried foundations, the determining factor is the depth of soil freezing in the region (tabular value available in SNiP annexes).
Shallow belts are usually immersed to a depth of 70 to 50 cm, depending on the amount of frost heaving in the soil.
In any case, the parameters of the tape should be determined by a project drawn up and calculated by competent specialists.
Regulatory regulation and features of project preparation
A design engineer is responsible for calculating the foundation for a specific structure and the conditions in the area being built .
The design objectives include eliminating the risks associated with deformation and destruction of the foundation and building. SP 50-101-2004 describes in detail the requirements for the design and construction of foundations, and provides references to related acts.
To analyze the bearing capacity of a site, it is necessary to collect information about its geology , seismic activity of the area, know the design features of the building and the conditions of its operation.
A comparison of technical and economic indicators of possible engineering solutions is carried out in order to select the most rational and reliable construction option. Measures must be taken that will ensure the durability and strength of the structure during construction and service.
The project is drawn up taking into account the design responsibilities described in GOST 27751:
- I degree of responsibility – petroleum product storage facilities, industrial facilities with large spans, unique houses.
- II degree – residential and public buildings, agricultural buildings.
- III degree – buildings of a temporary nature (summer sheds, gazebos, pavilions, storage buildings.
Before construction, a technical specification with initial data is drawn up, drawings of base options, their sections and layout diagrams on the plan are developed. This information is necessary to justify construction and installation work. Relevant regulatory documentation is attached to the project.
Correct height above ground
The section of the tape that rises above the ground level is called the plinth.
It is necessary to solve several problems:
- Raising the floor level of the first floor. The height of the plinth determines the installation plane of the ceiling, which most owners want to raise above the ground.
- Protection of wall material from contact with snow masses in winter. If the snowdrifts come into contact with the walls, the materials may become wet and saturated with water, which contributes to the destruction of the house’s structures.
- Giving the house solidity and respectability. A high base makes the house more attractive and increases its size.
Usually the height of the base is made at least (minimum value) 40 cm and above.
Load calculation
To form a reliable strip foundation, it is necessary to perform a calculation based on the actual parameters of the foundation. Let's calculate the foundation for heaving soil using the following approximate data :
- size - 6x3 m;
- upper segment – 0.2m;
- sole – 0.25m.
Building characteristics must be taken into account :
- wall thickness - 400mm - gas blocks;
- the floor covering of the first floor is an embankment of soil and granite crushed stone;
- the height of the house is 2 floors;
- ceilings between floors - reinforced concrete slabs;
- roof – pitched: 45° (wooden logs, tiles);
- the soil base is plastic clay.
Taking these indicators into account, it is necessary to calculate the following types of loads :
- roof - 1.5 x 80 = 1200 N (SNiP coefficient = = 800 N/m2);
- overlap - 1.5 x (300 + 500) = 12000 N;
- external walls (on 1 m of base) - 3 x 0.4 x 600 = 7200 N;
- gas block foundation - 0.450 x 2300.0 = 10350 N;
- sole (per 1 m length) -150.15+120+1200+720+1035 = 42250 N.
The area of the base is 50 x 100 cm = 5000.0 cm2 4225, 15/5000 = 9 N/cm2. Taking this data into account, you can proceed to calculating the volume of concrete that will be needed for construction. This can be done using this formula V=PI x r2 x h.
What soils is it suitable for?
The strip foundation has proven itself well on most types of soil. Only peat bogs are definitely not suitable for the construction of the belt; other options should be especially considered .
Rocky or gravelly soils with low groundwater levels are most successful. Loose sands are somewhat worse. The greatest danger is represented by clays and loams, which tend to not allow water to pass through, while at the same time actively absorbing it.
Such soils have significant heaving effects and require large amounts of additional work - the creation of an increased layer of bedding, drainage and insulation of the tape.
Tape: calculation algorithm
This issue is given great importance at FORUMHOUSE.
al185MODERATOR FORUMHOUSE
I beg you not to prescribe a foundation design based on “people’s experience” and the advice of various advisors who “have always built this way.”
A member of our portal with the nickname MaximGvozdev created the LentaOnline v calculator. 1.0, which will help with the construction of this type of foundation. The tool can calculate the resistance of the foundation soil, the width and length of the designed tape, reinforcement and concrete, concrete composition, and the number of concrete batches in a concrete mixer.
For beginners, the FORUMHOUSE moderator with the nickname al185 recommends first deciding on the soil conditions (soil composition, groundwater level, topography) to design a strip foundation and resort to the following methods:
- Ideally, order a project from an adequate designer who can get good recommendations on FORUMHOUSE.
- You can borrow an already calculated analogue foundation design for similar soil conditions and a similar building.
- Master design for amateurs: an algorithm for designing a strip foundation for dummies.
Next, you need to compare the cost of the options received and choose the appropriate one.
Step-by-step instructions for installing MZLF
One of the most popular types of tape for private houses is a shallow foundation. This is a good foundation option that allows you to save on the amount of building materials, reduce the amount of excavation work and general labor investment.
Given the relatively shallow immersion depth, a high-quality survey of the site is required, including test drilling and determination of the groundwater level. This will make it possible to determine the composition of the layers and give grounds to predict the presence of problematic factors, heaving loads, etc.
These actions, as well as the creation of the project, must be performed by a trained specialist.
Further actions are carried out in stages:
Surface marking
The top layer of soil is removed from the site and, if necessary, leveled. Then, using stakes, the corner points of the future tape are marked . Cords are pulled between the stakes, compliance with the design data, orientation to the cardinal points and other parameters is checked.
Be sure to check the correspondence of the lengths of the diagonals . If they are not equal, you need to find the error and correct it in order to obtain high-quality and accurate markings.
Preparing the trench
After the marking has been made, trench digging begins. Excavation is carried out to a predetermined depth . Typically an excavator is used for this purpose, so the corners have to be adjusted and cleaned manually.
The excavated soil is stored on the sides of the trench, but most often it is removed or stored in a separate place.
The width of the trench must provide enough space for the installation of formwork, for which it is usually taken 30 cm larger than the design width of the tape.
Pillow for strip foundation
The sand cushion performs several functions:
- Leveling the bottom of the trench, forming an even horizontal reference line.
- Performing drainage functions.
- Receiving heaving loads and redistributing them along the entire length of the tape.
The usual thickness of the pillow layer is 10-20 cm. Some builders indicate larger sizes - 30-40 cm, but it is not recommended to follow such advice . The main task of the bedding layer is to level the bottom of the trench.
The thicker the layer, the greater the amount of subsidence. The sand must be compacted carefully, but some settling will occur anyway, so the thickness of the cushion should be limited.
Installation of formwork
Formwork is usually assembled from edged boards 25-40 mm thick. The higher the tape, the thicker the boards .
Assembly begins with the manufacture of shields. They have a width slightly larger than the estimated height of the tape. When assembling, the maximum density of connections must be observed; all cracks are sealed with tow and wooden slats. The assembled panels are carefully lowered into the trench and installed in the desired position.
From the outside, the formwork is fixed with vertical and inclined stops; from the inside, cross members are installed that determine the width of the tape..
Installation must be done as firmly and accurately as possible, all fasteners must be placed outside to make it easier to dismantle the formwork later.
Reinforcement
The thickness of the reinforcement for shallow tape ranges from 10-12 mm for workers, and 6-8 mm for smooth rods.
You can make complex calculations, or use online calculators, but in the vast majority of cases the result will be exactly the same.
Traditional metal or modern composite reinforcement is used, which is non-corrosive and lightweight.
Knitting reinforcement
The reinforcement frame is assembled using the knitting method. To do this, you need soft annealed wire about 1 mm thick . The knitting process is simple - a piece of wire 25-30 cm long is bent in half, resulting in a kind of loop.
Then it is brought from below under the connection of the rods, the ends are raised up, grasping the connection. Then, use the end of a special hook to pick up a loop and twist it several times (4-6) around the other end.
Produces a strong and tight connection.
Selecting concrete for pouring
The most preferred option is to use concrete grade M200. It has sufficient strength, resistance to loads and external influences.
It is not recommended to use less durable grades, since concrete has large quality tolerances and may turn out to be very weak, although the grade of the material will be maintained.
The use of M200 concrete is guaranteed to provide the required quality of the material.
Fill
Pouring is the main stage of work. It is made from several points evenly spaced around the entire perimeter of the tape .
This allows you to get the same quality of concrete at any point in the foundation. The work must be completed at once, stopping is not allowed. The poured material is bayoneted or treated with a vibrating plate to remove air bubbles. Then the tape is covered with polyethylene to protect it from contact with sunlight. The formwork cannot be removed within 10 days.
At this time, periodic watering is necessary - for the first 3 days this is done every 4 hours, then for a week watering is done three times a day. Structural hardening is considered complete after 28 days of exposure.
Frame reinforcement technology
The strength of the foundation is ensured by the reinforcement structure, without which it is impossible to form a complete foundation. Reinforcement work includes several stages:
- installation of formwork - a plank frame is installed along the perimeter of the future building, the walls of which are lined with parchment on the inside, thanks to which it will be easy to remove later;
- driving vertically located reinforcing bars into the soil - the length of the reinforcement is comparable to the depth of the foundation. It is necessary to bury the rods at a distance of 50 mm from the walls of the formwork, while they are embedded in the ground in increments of up to 600 mm;
- installation of stands on the bottom (height up to 100 mm), on top of which horizontally located reinforcing bars are laid: the function of stands can be performed by halves of bricks installed on the edge;
- horizontal rows connected to vertical rods;
- fixing structural elements at intersections by welding or wire.
Useful
Basic installation mistakes
The main mistakes should be considered:
- Poor compaction of the sand bed, causing significant settlement.
- Use of low-quality or unsuitable materials.
- Lack of accuracy and thoroughness in work.
- Neglect of some stages of work.
CAREFULLY!
All these shortcomings can result in deformation or destruction of the tape during the first few years of service.
Work to eliminate errors is extremely expensive, time-consuming and does not guarantee a successful result, therefore construction should be approached with the utmost responsibility and care..
We make the plan correctly.
When creating supports for a strip foundation, the drawing must meet the following requirements.
- When determining the most appropriate scale, it is highly recommended to choose either 1 in 100 or 1 in 400.
- Before starting construction work, the site should be marked.
- If you plan to create a house or public structure with columns, be sure to indicate this designation and section on the drawing.
- All lines on the paper must be clear and precise, the thickness of each of them is 0.5-0.8 millimeters.
In the general diagram there must certainly be a designation of the sole, as well as the places in which various bulges or depressions will be located. This is important in order to calculate the location of communications from central highways.
Plan of a strip foundation made of FBS blocks drawing.
Such holes and protrusions must be displayed on the diagram as contours and broken lines. Explanatory notes and footnotes may be provided if necessary.
Fundamental differences in support schemes.
Above, we tried to describe in as much detail as possible the process of creating a structure plan for which a strip foundation drawing is used. But at the same time, we should not forget that the drawings containing information about the prefabricated type of supports are fundamentally different from monolithic ones in that they contain a section, as well as a designation of straight and angular reinforced concrete structures.
Strip foundation plan drawing.
How to make a construction joint when pouring concrete correctly?
The surface of construction joints, which are made when laying concrete mortar intermittently, should be located perpendicular to the axis of columns and beams. It follows from this that the working seam must be made vertically, because an inclined seam under the influence of shear stresses can weaken the foundation under the house.
The cut-off is made from a shield, which consists of boards. You need to make holes in the places where the reinforcement will be located.
Concreting can be done after the solution reaches a strength of 1.5 MPa or more. During hardening, concrete must be protected from atmospheric precipitation or moisture loss. In the future, it is necessary to maintain the temperature regime, creating conditions that allow the concrete to obtain the necessary strength.
The formwork can be installed after the solution reaches a strength of more than 1.5 MPa.
Fastening the formwork
The formwork, covered with plastic film, is installed along the edge of the dug trench along the outer and inner perimeter, and its lower edge should be in close contact with the ground, without cracks or irregularities. This position of the boards will help prevent the solution from leaking out when pouring the foundation.
The shields are supported by prepared bars driven into the ground, along the outer perimeter - from the outside, from the inside - from the inside. The formwork panels should be positioned strictly vertically, this will avoid further deformation of the entire foundation as a whole.
Additions to the scheme.
If you are going to create a monolithic or prefabricated type of strip base, then, to clarify the drawings, you should accompany them with the following technical documents:
- Scheme of reinforcement of the site based on the future load of the structure on the foundation;
- An application that displays the design features of a structure;
- Advisory explanations regarding preparatory work on the site;
- Tables and diagrams that are necessary for waterproofing and thermal insulation of foundations.
- Data on load standards on foundation supports.
Strip foundation plan drawing.
Making a sand pillow
In order to reduce the load on the foundation, the bottom of the dug trench is covered with a layer of sand, the so-called sand cushion. This, in turn, will allow you to save on building materials and significantly reduce construction costs.
As the name implies, coarse sand is usually used for such a cushion; in industrial construction, the use of medium-sized crushed stone or boiler slag is also acceptable.
The thickness of the sand layer should be about twenty centimeters. After this, the surface of the pillow should be tightly compacted, and the horizontalness should be verified with a level gauge. When all the necessary actions have been carried out, the sand cushion is filled with the required amount of water, which will allow it to shrink and be well compacted.
The top layer is covered with gravel or coarse crushed stone.
Tape-pile
Strip-pile foundations are used on soft soils and in areas with water-saturated soil. The tape promotes uniform load distribution. With the help of piles, the base is stabilized in case of excess moisture. Suitable for areas with differences in height, for the construction of low-rise buildings and buildings made of foam blocks.
Advantages:
- speed of construction;
- work can be carried out at any time of the year;
- low cost due to low consumption of materials.
The disadvantages include the difficulty of calculating the load; the house must have no basement. In addition, the building for such a foundation should be small and light.
Columnar
A columnar foundation is a structure made of pillars that serve as support for the most difficult points: the meeting points of the walls and corners of the house . The column is immersed into a drilled well or into the ground itself. At the top, the pillars are connected by reinforced concrete beams. When laying this type of foundation, a reinforced belt is required - a grillage; it prevents horizontal displacement of the foundation and distributes the load of the building onto the system of pillars.
It will be an excellent solution for a house made of wood or other lightweight materials. Suitable for frame structures, country houses. Used on stable soils without deformation and temperature changes. Does not include a basement. Particularly suitable for bathhouses, sheds and similar buildings, as well as for light private houses (panel or frame type, made of sawn/laminated timber).
They are made of brick, stone, wood, reinforced concrete.
Advantages:
- high stability;
- less shrinkage than a strip base;
- allows you to increase the load on the base by 25%;
- low cost.
The disadvantages include the impossibility of installation on weak and moving soil: peat, clay soil, subsidence rocks. This will cause the structure to sag. If there is no other way, it is necessary to install very powerful grillages, which will inevitably increase the cost of construction.
Similar to the strip base, it can be prefabricated or monolithic.