Slab foundations are successfully laid under private houses of any type, with maximum effect when constructing on weak and heaving soils.
The technology of constructing and pouring a monolithic slab foundation is considered labor-intensive and costly, but with proper calculation and implementation of all or individual stages on your own, the estimate is reduced by 20-30%.
In this article we will tell you in detail how to correctly pour a monolithic slab under a house yourself, what the process consists of and how to avoid possible mistakes.
Types of reinforced concrete foundation slabs, arrangement of flat and ribbed
The main criterion for distinguishing reinforced concrete slab foundations is their internal structure. On this basis, power structures are divided into two types:
- Monolithic.
- Prefabricated monolithic.
The first technique is a classic sequence of technological operations for pouring concrete into formwork onto a prepared base of non-metallic materials. In this case, the slab is poured with reinforcement to increase the rigidity and resistance of the foundation to tensile and other moments.
The technology for constructing a prefabricated monolithic base involves the use of ready-made reinforced concrete slabs, which are laid on a sand and crushed stone substrate and then filled with concrete mortar. The strength and load-bearing capacity of the foundation in this case is ensured by factory blocks.
The surface shape of the slabs can be flat or ribbed.
The construction of a slab ribbed base with your own hands involves additional digging of trenches. The space that is formed between the relief bends is filled with a mixture of non-metallic materials.
Thermal insulation of joints
After laying the slab, the perimeter of the foundation is leveled with brickwork. This material is a cold bridge by default, so it is necessary to lay bars of extruded polystyrene foam or mineral wool between it and the floor slab. Only in this case will heat loss through the floor be minimal.
Scheme of insulation of the ends of floor slabs.
It is allowed to use solid strips along the entire length of the wall, assembled from pieces of insulation. If there are cracks, it is necessary to fill them with polyurethane foam, the characteristics of which are almost similar to the specified heat insulator.
Types of slab foundation
There are two types of slab foundations based on execution technology: prefabricated and monolithic.
- for heavy structures on bulk soils with deepening to continental soil;
- construction on mixed soils with different load-bearing properties;
- for arranging a basement in conditions of high groundwater levels.
According to the profile, there are three foundation options:
- Solid slab. A house without a base, when the surface of the slab serves as the subfloor of the first floor (for example, a Swedish stove). It can be either monolithic or prefabricated.
- Ribbed plate. There are stiffening ribs in the lower part. If this is a monolithic technology, then additional trenches are dug for them, and the formwork and reinforcement are combined with the common part. If this is a prefabricated technology, then ribbed ready-made slabs are used for the foundation.
Additional stiffening ribs will make the structure more reliable even with a small thickness of the main part of the foundation. Source vamnapolzu.ru
Box foundation. A house with a base on a slab and a concrete floor on the first floor. The slab and plinth can have monolithic, prefabricated or combined technology.
Structure by layers
This is what the most complete structure of a monolithic slab as the foundation of a house looks like. Source pinterest.ru
The standard full-profile “pie” looks like this:
- leveled and compacted “mainland” soil;
- separating geomembrane (desirable, but not required);
- a cushion made of sand (or two layers - sand and crushed stone)
- footing;
- waterproofing;
- sheet insulation;
- base plate.
In Europe and here, a modification of the foundation called the “Swedish slab” has recently become increasingly popular. The peculiarity is that the warm water floor is not laid in the screed, but in the slab itself.
Swedish foundation slab for a private house with heated floorsSource pinterest.com
Mixing the solution yourself
As already mentioned, to pour a monolithic foundation slab for small structures, the owners of suburban areas often prepare the concrete mixture themselves. When carrying out this procedure, it is important to follow a certain procedure.
Experienced builders recommend mixing the concrete mixture for the floating foundation of a building only in a concrete mixer. Unfortunately, it will not be possible to prepare a very high-quality solution in a trough using a shovel. Concrete mixed in a concrete mixer is as homogeneous as possible. And therefore, the supporting structure for the house itself will subsequently become very durable.
When using M400 cement to prepare a mortar, owners of suburban areas usually maintain a cement/sand/crushed stone ratio of 1/3/4. The sand is thoroughly sifted before being used to prepare concrete.
First, load the dry ingredients into the concrete mixer and swirl them thoroughly. Next, add water in 1-2 steps. The amount of the latter is calculated in such a way that the finished concrete does not flow off the shovel and does not crumble into pieces after being compressed in the hand.
Drainage and waterproofing
The main reason for the soil getting wet and losing its load-bearing properties is not groundwater, which lies much deeper than the base of a shallow foundation, but in the perched water. This includes precipitation, seasonal snow melting, as well as water infiltration from nearby bodies of water if their “mirror” is at the same level as the slab. To a lesser extent, but the capillary rise of water in some types of soil also has an effect.
The nature of drainage measures depends on the characteristics of the region and site. If the house is located on a slope, then it is possible to install a cut-off drainage. On flat areas, it is possible to install a comprehensive storm drainage system, including drainage of water from platforms and paths outside the site. But in any case, below the level of the concrete foundation slab, along the perimeter of the blind area, drainage pipes are laid, which are led with a slight slope into a drainage well.
Laying a drainage pipeSource katlavan.ru
Waterproofing is complex. To briefly formulate the essence of the technology, it lies in the fact that the slab is literally wrapped in two layers of rolled insulation. The full list of works looks like this:
- After carrying out the zero cycle and backfilling the sand and gravel cushion, two layers of rolled bitumen insulation sheets are laid on the leveled area.
- All sheets are laid overlapping, and the top layer relative to the bottom is shifted by a width of half a sheet.
- Along the entire perimeter, roll waterproofing should be laid with a margin sufficient to bend the edges towards the end of the slab.
- After pouring and curing the concrete, the protruding edges of the waterproofing are glued with bitumen to the end of the base.
- Carry out waterproofing work to protect the top and side surfaces of the foundation
The final stage of pouring
Immediately after pouring, experienced builders recommend covering the entire area with polyethylene over the monolithic foundation slab. Subsequently, the concrete structure should be watered with water from a hose twice a day for 2 weeks. Such measures will prevent the appearance of surface cracks on the finished slab. And this in turn will improve the performance of the foundation.
The formwork from the finished structure can be removed within 2-3 days after the pouring procedure. In the future, the foundation must stand for at least a month. It is allowed to begin building the walls of a house on it at least a month after pouring. During this time, the hardened concrete will gain sufficient strength to support the weight of the building frame and its roof.
Video description
All stages of work are clearly shown in the video:
In conclusion. Whatever they write about the possibility of constructing a monolithic slab foundation with your own hands, its construction technology requires, even for a small house, a significant amount of concreting with a continuous pouring cycle. And with a foundation thickness of 25 cm and a modest house size of 10x10 m, this is 25 m3 of concrete. And this does not take into account the concrete layer. Plus you need:
- carry out a zero cycle;
- make drainage;
- bring, level and compact at least 30 m3 of sand and crushed stone for the cushion;
- properly waterproof the slab;
- install formwork;
- connect two meshes of the reinforcing frame.
Only a team of professionals can carry out such a house foundation project with high quality. Source loghouse.msk.ru
List of required materials and tools
Before pouring concrete, you need to prepare a flat area and compact it properly with a special machine (vibrating plate). Do-it-yourself vibrating plate: (read more)
List of materials required for constructing the foundation:
- medium sand;
- medium-sized crushed stone;
- geotextiles;
- extruded polystyrene foam 100 mm thick;
- drainage pipes;
- wooden boards;
- reinforcement bars;
- knitting wire;
- pipes of different diameters for utilities and water heated floors;
- nylon clamps;
To work you will need the following tools:
- scoop and bayonet blades;
- wheelbarrow;
- level;
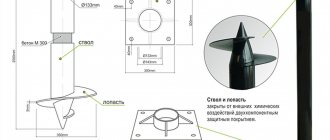
L-blocks are lined with flat slate for laying the foundation.
- building level;
- screwdriver;
- knife;
- Bulgarian;
- vibrating plate;
- deep vibrator;
- hacksaw;
- concrete mixer;
- trowel;
- protective clothing.
Pouring concrete. Nuances
So, how to properly pour a slab under the foundation? What are the features of the actual procedure for laying mortar into the formwork? Concrete is poured into the foundation pit when constructing a floating foundation using special equipment. It is believed that when performing such an operation, the height of the mortar dumping into the formwork from the machine hose should be approximately 0.5-1 meter. Also, when pouring, the following rules should be observed:
- concrete inside the formwork cannot be moved more than 2 meters;
- when pouring, use a compactor vibrator to remove air bubbles;
- the solution should be poured in layers to the length of the working nozzle of the deep-well vibrator-compactor.
It is imperative to compact the poured mixture when constructing a slab foundation. This will make the foundation of the house much stronger and more durable.
Reinforcement schemes used
The classic reinforcement scheme for a monolithic slab is two rows of mesh made of AIII rods with a diameter of 12 to 16 mm. The cell size of both meshes is in the range of 20–25 mm, so the thickness of the reinforcement is selected based on a minimum steel content of about 0.2% in both cross sections of the slab.
Installation of fittings begins with the installation of spacer plugs, ensuring a protective layer thickness of 50 mm. Longitudinal reinforcement bars are laid on the plugs, located in increments of 20–25 cm, and transverse reinforcement bars on them, thus forming a mesh. All intersections of the reinforcement are connected, a vertical rod is welded to every third one to distance the top row of reinforcement.
The longitudinal rods of the third row are welded to the rods, then those that do not have a rigid fixation to the vertical structural reinforcement are placed in the mold. The transverse ones are placed and tied onto the welded longitudinal rods, then the remaining ones are lifted from below and tied to them, while maintaining the nominal installation pitch. If it is necessary to increase the length of the reinforcing bars, they are connected with an overlap of at least 50 nominal diameters.
If, according to the design, the slab has lower stiffening ribs, they are formed by trenches in the preparation layer, reinforced with sheet permanent formwork. In this case, the space between the trenches - the so-called sandboxes - is tightly compacted and leveled along the upper edges of the rib formwork. Reinforcement of the protrusions is carried out with U-shaped mortgages, which are subsequently connected to both rows of the reinforcing mesh of the slab. As working reinforcement for the ribs, two rows of rods are used, located in the lower corners of the U-shaped anchorages. When installing rib reinforcement, we must also not forget about the minimum protective layer of 50 mm.
Types of monolithic foundation designs
Types of monolithic foundation designs
As already noted, a monolithic foundation is a slab laid in a previously prepared place. But, nevertheless, there are several ways to make such a base. They differ from each other in their hydro- and thermal insulation options. As you already understand, a strip monolithic foundation is a little different. There, the earth is dug up only for the foundation, if there is no basement, and the earth remains under the space of the rooms. Here the entire volume of earth is excavated, under the entire area of the house.
The simplest of these types of foundations is performed according to the following scheme:
A reinforcement structure is installed at the bottom of the pit, on a pre-compacted sand cushion, and then filled with concrete. More complex ones include structures that use sheets of waterproofing material, geotextiles, and, depending on the type of soil, it is possible to make an additional cushion from crushed stone.
The most complex monolithic foundation looks like a multi-layer sandwich in cross-section:
- sand cushion;
- layer of geotextile;
- layer of crushed stone;
- the so-called preparatory layer of concrete;
- waterproofing layer;
- monolithic slab.
Such complex structures are used on difficult soils, for example, with a high groundwater level. Builders with extensive experience say that a monolithic foundation can be used even in peat bogs.
Main stages of construction
In principle, the technological procedure for pouring a slab foundation is not particularly complicated. This work includes several basic steps:
- markings are made at the site chosen for the construction;
- excavation work is being carried out;
- a crushed stone-sand cushion is laid at the bottom of the dug pit;
- formwork is installed;
- the reinforcement frame is installed;
- The concrete mixture is poured.
At the final stage, the formwork is removed from the finished foundation, and then, after the concrete gains strength, the construction of the building itself begins.
Columnar foundation for a bathhouse
This foundation is suitable for one-story, lightweight buildings, for example, frame ones. Its use is allowed only on soils that are not prone to horizontal shifts. Columnar foundations are most often used on slightly heaving soils.
Point supports for the bathhouse, located along the perimeter of the building and under the internal walls, are brick or block pillars buried at least 1.5 meters into the ground. You will find complete, step-by-step instructions for arranging a columnar foundation here.
Installation of this type of foundation does not require special construction skills or a large amount of excavation work. The main disadvantage is restrictions on the weight of the structure.
Step-by-step installation instructions
Setting up a slab foundation with your own hands is quite labor-intensive, but to make the process easier, step-by-step instructions are provided. By performing all work according to this algorithm, you can achieve positive results and obtain a high-quality slab foundation.
Site preparation
We prepare the site. We remove foreign objects, clear the grass and begin the breakdown according to the diagram of the future structure. Let's start digging a pit. This process can be carried out using an excavator. But try to remove the bottom layer 15-20 cm deep by hand. The depth of a pit for an ordinary private house can be about 0.5 m. If you plan to build a house with a basement, then the pit should be made deeper.
Arrangement of the drainage system
A properly organized drainage system will protect the base from erosion
Now, if desired, you can make a drainage system. To do this, you need to dig trenches perpendicular to the perimeter. Lay geotextiles at the bottom and pour crushed stone on top. Then pipes made of two-layer polyethylene with holes are installed.
Pipes must be laid with the holes up and with a certain slope, which should be in the ratio: 1 m of pipe – 1 cm of slope. It is also necessary to lay pipes in compliance with the given technology and along the perimeter of the slab foundation.
In this case, the dimensions of the pit must be expanded by 1-1.5 m. Laying pipes around the perimeter must also be done with a slope. You need to start from the middle of the foundation wall to its corners. Then the pipes are covered with crushed stone and covered with geotextiles.
Carrying out work before pouring
The next stage is the arrangement of the sand cushion. You can also make a sand and gravel pillow. It must be done to reduce the effect of moisture on the monolithic slab. The thickness of the pillow is usually 20-25 cm. The pillow is carefully compacted and spilled with water. Tamping must be done until there are no traces of shoes left on its surface. It is best to make a pillow in layers. Pour and spill every 10 cm.
Now you need to install the formwork. It is better to make the formwork removable. It is necessary to install only on the outside of the future slab. In this case, it is necessary to check the following points: the surface of the formwork boards adjacent to the slab must be flat, the boards must be carefully connected to each other, only in this case the formwork will help to obtain a perfectly flat surface.
Reinforcement and filling
The foundation frame is created using reinforcement
To prevent cement liquid from leaking into the sand when pouring concrete, we lay a waterproofing layer. This process must be done in two layers using roofing felt.
We proceed to the installation of the reinforcing frame. For this, special steel reinforcing rods with a diametrical cross-section of 10 mm or 15 mm are used. The rods are connected to each other with wire. Supports of the same size are laid on roofing felt under the bottom layer of the reinforcing belt.
This is necessary so that the reinforcing bars are hidden in the concrete. Then, using auxiliary rods, we connect the lower layer of the reinforcing belt with the upper one.
Let's start pouring concrete. To obtain a truly monolithic slab, concrete should be poured fairly quickly. It is better to use ready-made concrete. In the case of pouring concrete by yourself, it must be remembered that the interruption in the supply of concrete should not exceed one hour.
Watch the video to see how the base slab is reinforced and poured.
This is how we get a monolithic slab. The main thing to get a quality result is to follow the above step-by-step instructions. It is also necessary to properly dry the slab. To do this, it is covered with polyethylene or at first constantly spilled with water throughout the week.
Depth of the establishment on the walls
The minimum support of floor slabs is regulated by regulatory documents. It depends on:
- Type of building - industrial, administrative or residential.
- Thickness of a brick load-bearing wall.
- Types of load - dynamic or static.
- Load sizes - point and distributed.
- Lengths of reinforced concrete products.
- Dimensions of the overlapped span.
Accurate data on the size of the overlap is obtained using calculations by design engineers; they must fit within the standard of 9-12 cm.
Elements of interfloor ceilings are produced in 2 sizes:
- constructive, which is equal to the distance between the ends of the ceiling slab (net length);
- modular - planned span width.
So, when laying 6-meter hollow core slabs, the actual size of the product is 5.98 m. If you leave 2 cm for the plaster on each side, then to make a room 5.7 m wide, you should install the product with an overlap depth of 12 cm .
In the case when the amount of support is greater than that established by the rules, the reinforced concrete products are pinched. That is, part of the load falls on the end of the floor element. The brickwork of load-bearing walls will slowly crack due to improper operation of the entire structure.
In addition to this, the increased overlap leads to excessive heat loss, since the end is located outward.
If the minimum depth of the depth is less than required, the load transfers to the edge of the masonry and causes its collapse.
Excerpt from SNiP
The required depth of support for the floor slab is indicated in SNiP. In the section regarding large-panel structural systems, it is noted that on 2 sides hollow-core slabs must overlap the load-bearing panels:
- by 100 mm - with a height of more than 220 mm;
- by 80 mm - with a height of less than 220 mm.
In any case, the support distance should not exceed 15 cm. Concrete products with many voids are not laid on the 3rd and 4th sides.
Products made monolithically are laid on walls made of reinforced concrete or concrete with a support depth of:- 7 cm - with a span of more than 4.2 m and installation on 2 sides;
- 5 cm - if the value is less than 4.2 m and 2 sides or more than 4.2 m and 3 sides;
- 4 cm - on 4 sides (along the contour).
Slab foundation - what is it?
The basis of this type of foundation is a reinforced concrete monolith, made by pouring concrete under the base area of the structure being designed. During the concreting process, the slab is reinforced with a load-bearing frame, which consists of steel reinforcing bars connected into a single pattern.
Due to the fact that the foundation is a solid structure, it can rise and fall evenly as the soil masses located on it move. Due to this quality, the base is called a “floating slab”.
In order for the finished load-bearing structure to guarantee the integrity of the building, and during its operation there is no risk of cracking or damage, the construction and design of the foundation must be carried out strictly in accordance with the current standards for SNiP and SP, namely:
- SNiP 2.02.01-83 – foundations of buildings;
- SP 50-101-2004 – design and construction of foundations of various structures;
- SP 63.13330.2018 – construction of reinforced concrete structures.
Useful tips
You cannot install slabs with broken hinges.
The installation of slabs is constantly monitored. The quality of covering products, certificates and passports for them are checked. The correctness of storage and transportation is taken into account. During the work, compliance with the project, the quality of sealing joints and welding of embedded parts are examined. If the joints are filled with concrete in winter, the area is heated until the mixture completely hardens.
On large-scale construction, joints are checked after reaching the design strength, and the installation is checked using levels and laser levels. If there were changes to the project, detailed drawings are made, welding logs are kept, connections are sealed, and hidden work reports are drawn up.
You cannot install slabs that have broken hinges or are not cleaned of dirt or adhering layers. During the break, the raised structures are not left hanging, but are laid down after welding is completed. You cannot level the panels with a crowbar after removing the slings, nor can you move them through the air in winds exceeding 15 m/s or in fog.
Calculation and layout drawings are carried out before the construction of foundations in order to accurately determine the position of walls and columns in space and ensure the correct support depth.
Types of slab foundation
The monolithic cushion slab has an average thickness of up to 50 cm and is poured from concrete mortar along the entire perimeter of the pit.
In construction all over the world, there are three types of slab monolithic foundations:
- Monolithic pillow-slab. It has an average thickness of up to 50 cm and is poured with concrete mortar along the entire perimeter of the pit. Most often, such slabs are used in the construction of private houses with one or two floors. Moreover, the building can be built from any materials from wood to brick.
- The slab foundation is reinforced concrete with stiffening ribs. This more complex design solution is used in industrial or urban construction. Here, either a foundation is assembled from monolithic floor slabs using a rigid bond, or it is poured into a special formwork that has stiffening ribs. This design is thick (up to 1.2 meters) and is able to withstand soil heaving in seismically active zones.
- Box-shaped monolithic slab. The most complex of all types of slab foundations. Such a foundation is mounted from specially produced concrete boxes, which are fastened together according to the principle of increased rigidity. Such slab foundations are rarely used and only in industrial construction.
Rigging work
PCs are heavy and difficult to handle. Most heavy reinforced concrete products have embedded hinges
for hooking sling rope hooks.
However, a number of hollow-core reinforced concrete floors without hinges
.
Slabs made of cellular concrete, produced under licenses from German companies, are also not equipped with rigging loops. To lift such PCs, gripping devices, so-called conductors,
. PCs that are not equipped with hinges have a trapezoidal cross-section, tapering upward. On the side surfaces there are protrusions for which the conductor's hooks are fixed.
What is a monolithic slab
A monolithic foundation is a solid reinforced concrete slab on which a house is built. It does not create a significant load on the ground, since due to the large area the specific pressure is relatively low.
The concrete pad, together with the house, moves freely on the surface of the soil as it moves; the rigidity of the slab is quite enough to ensure a level and reliable foundation for the building.
During construction, a small pit is dug - in most cases, the top layer of soil is simply removed. Then a layer of sand backfill is created, it is leveled and compacted, and a layer of geotextile is laid.
Insulation (mainly specialized polystyrene foam) is placed on top, formwork and reinforcement frame are installed. After this, concrete is poured and the slab is kept until it reaches technological strength.
As a result, a strong, insulated base is formed, ready to accept the loads from the building and resistant to soil influences.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of a monolithic base include:
- Possibility to build houses on weak-bearing, heaving or water-logged soils.
- The high load-bearing capacity of the slab allows the construction of fairly large and heavy buildings.
- With proper reinforcement, the slab is able to withstand all impacts that can arise and disappear suddenly. All ground movements are perceived quite easily; the slab “floats” on the soil surface like a raft.
- The design of the slab is simple, which allows you to avoid serious mistakes during construction.
- The creation of a slab immediately forms the floor of the 1st floor, which greatly simplifies further work.
Proponents of this technology claim that a monolithic foundation has no disadvantages.
This is not entirely true:
- The slab does not allow for a basement.
- There is practically no possibility of repairing the base.
- The consumption of building materials and the volume of excavation work are very high.
- The cost of such a foundation is very high, which is one of the main limiting factors.
The disadvantages are not too fundamental, since the conditions in which a monolithic slab is used are most often not suitable for alternative options.
Varieties
There are several types of slab base:
- Prefabricated slab. It consists of ready-made reinforced concrete slabs laid on a prepared site.
- Monolithic slab, which is poured directly on the site.
According to the type of construction, they are distinguished:
- Solid slab. Used for relatively light and small buildings.
- Ribbed plate. The sole of such a base has stiffening ribs that firmly anchor the supporting structure in the ground, preventing it from moving horizontally. In addition, the presence of ribs contributes to a more even distribution of loads from the weight of the building.
- Box. A type of slab in which the ground floor floor is a separate floor and the surface of the slab forms the basement.
NOTE! Slab foundations are not popular in our country due to high construction costs, so structural issues have so far been poorly developed.
Suitable conditions
The slab foundation is intended for use in regions with unstable, heaving or water-logged soils.
Usually it is an alternative to a pile foundation when it is not possible to deliver or use special equipment.
As an option, slab foundations are used when dense layers of soil are too deep and the piles are not long enough.
Laying rules
In order for the building to last as long as possible, you need to know how to correctly lay PNO floor slabs. To achieve the best result, the following rules are observed:
- Laying is carried out on a prepared base. If there are deviations in height, a suitable alignment method is selected.
- The support area when laying on a reinforced concrete base must be at least 6 cm. When laying on brickwork, the size of the supporting surface increases to a minimum of 12.5 cm.
- Before installation work begins, the end parts of the slabs are sealed with insulation, which can be the remains of mineral wool slabs or polystyrene foam placed in polyethylene. Let's say laying penoplex (extruded polystyrene foam). The surface is covered with cement mortar. This helps to increase the strength characteristics of floor slabs.
- Installation is carried out in such a way that the extreme sides rest on the opposite ones. The side part is sealed using different methods.
The installation procedure is strictly regulated Source zonaremonta-ufa.ru
- A metal scrap is used to adjust the position of the plate. To achieve the best result, the work should be performed by several people at once.
- The foundation is coated with a 2 cm thick concrete solution. To prevent it from being squeezed out, reinforcement rods are laid along the tape.
- The location of the upper and lower surfaces is precisely determined in order to understand how to lay the floor slabs. Under the influence of operational load, the lower surface is actively stretched. To avoid its premature destruction, during the production process the lower layer is subjected to more active reinforcement. The top layer compresses during operation, and therefore manufacturers may refuse reinforcement.
- The slabs are adjusted to size along the bottom side.
- The solution that will be used during installation work is prepared in advance by mixing the components in a given ratio and achieving a uniform consistency.
The ratio of components of the concrete solution must be maintained Source gbs-78.ru
The concrete solution poured into the space between the slabs includes a certain amount of limestone, expanded clay, and crushed stone. The presence of voids is unacceptable, since a large percentage of the solution used to form the concrete screed can escape through them, which will significantly increase the cost of installation work.
Flaws
The disadvantages of the technology include the following:
- High cost of construction due to the need for large quantities of concrete, reinforcement, crushed stone, sand, etc. The consumption of building materials is directly related to the bearing capacity of the soil and design loads. The height of the slab can be reduced by installing stiffeners, but to design a more complex foundation, the owner will have to involve a highly qualified specialist.
- Inappropriate for use in areas with steep slopes. As a rule, they compensate for the lack of space by increasing the height of the basement floor, which leads to overexpenditure of resources and increased construction costs.
- Significant labor and material costs when arranging an underground space, therefore most owners refuse the decision to build basements or storage facilities in or under the foundation slab.
- The construction of a power structure at sub-zero temperatures leads to an increase in the cost of adding additional substances to the concrete solution that help warm up the mixture. Otherwise, the hardened slab will have defects - microcracks and uneven composition throughout the entire volume, which will significantly reduce the load-carrying capacity and service life of the foundation itself.
Ribbon
A strip foundation is a buried reinforced concrete structure that is laid under the external and load-bearing walls of a building. The width, height and depth of depth may vary. The strength, stability and reliability of the foundation depend on these indicators.
Advantages and disadvantages
The strip foundation is considered universal. It is suitable for construction on different soils and for various architectural structures.
It has the following advantages:
- high construction speed;
- the ability to build the foundation of a house without the use of special construction equipment;
- efficiency (due to the fact that the foundation is laid only under the walls, and not under the entire building);
- possibility to build a ground floor or basement;
- high strength (a massive tape can become a reliable support for a three-story brick house).
This foundation option also has its disadvantages:
- This option is not suitable for construction on peat and subsidence soils;
- accurate preliminary calculations are required.
Area and conditions of application
This base option is suitable for the construction of buildings made of any materials up to 3 floors high. Moreover, it is possible to build using it under almost any site conditions. Tapes are used on sites with pronounced relief, with a predominance of rocks, with high occurrence of underground flows and increased heaving of the soil.
According to the standards laid down in SNIP, classic strip foundations can be used without restrictions on coarse clastic and rocky soils. When erecting buildings on other, less stable soils, careful calculations are required, and sometimes reinforcement of the structure is required.
On biogenic soils, the construction of a strip foundation is considered irrational. However, even in these cases it applies. But certain preparatory work is needed - strengthening the soil using bulk methods, replacing weak soils with dense bulk materials, installing piles under the belt.
General method for calculating thickness
Before starting the calculation, a geological analysis of the soil is carried out and the value of the specific pressure on the ground for the selected type of foundation is selected from the reference information. Taking into account the degree of soil heaving, the depth of the sole is calculated.
At the stage of determining the weight loads, all structural features of the building are taken into account (wall material, size of openings, weight of the roof, etc.). To the resulting value add the operating load for all floors and the average snow load for its roof type.
Knowing the area of the base of the monolithic slab and the magnitude of the specific load per square meter of the area, the calculated volume of the foundation and the preliminary thickness of the base are found.
After this, the calculation must be repeated, but taking into account the weight of the foundation pit, adding it to the building loads. The resulting number is compared with the permissible pressure for the selected area. The calculated parameters will be useful when choosing the grade of concrete for the solution and the reinforcement scheme.
Is it necessary to insulate?
So, we figured out how to pour a slab under the foundation. The order of work when performing this procedure must be followed exactly. But sometimes owners of suburban areas are also interested in whether such foundations need to be insulated.
In most cases, when pouring a floating cushion, owners of suburban areas do not perform this procedure. However, if desired, the slab foundation can, of course, be insulated at the construction stage. To do this, a crushed stone-sand cushion is first poured into the pit. Then the formwork is installed. Next, a layer of moisture-proof geotextile is laid on top of the sand.
At the next stage, concrete preparation is arranged. That is, cement mortar is poured into the pit in a layer of approximately 3 cm. After the latter hardens, roofing material (with sizing on mastic) is laid on top of it in one layer. Next, a dense, moisture-resistant insulation is placed over the waterproofing. At the final stage, a monolithic reinforced concrete foundation slab is poured in the usual way.