– the DRIVA dowel is the fastest fastener in drywall, the plasterboard does not need to be drilled first and the back side of the drywall will be intact,
– the MOLLY dowel for plasterboard is the most powerful, more details here, but requires pre-drilling and special pliers or training to open it from the back of the plasterboard sheet,
– the TNF/-W butterfly dowel (more details here) also requires preliminary drilling in the drywall and the result is not fast or powerful, but average and maybe just what you need?
What drill to use to drill a hole in the wall
You can easily drill a wall or prepare a through hole by choosing the right drill for the equipment you are using, be it a drill or a hammer drill. For any purpose, the hole must have smooth edges and the right size. Accuracy is quite easy to achieve. Let's talk about the right choice of drills and features of drilling walls.
You need to select the type of shank (hexagon, cylinder or SDS mount) suitable for the selected tool, and the working part, based on the wall material.
In the store, the color of drill bits and drill bits will definitely catch your eye:
- Faded gray color - drills for metal or wood with additional hardening. Standard strength and durability.
- Black metallic color - the drill was treated with superheated steam at the last stage of production to form an oxide protective film. Increased durability, but strength depends on the choice of steel grade.
- The bright golden uniform color of the entire drill is the result of the internal stress release technique within the drill material.
- The yellowish tint (golden) mainly only of the working part of the drill is a protective coating based on titanium compounds, which increases the strength of the cutting edge and the entire working part.
Concrete, brick, stone
You will need a drill with a carbide insert. The plate is welded at the end of the working area of the drill, made of an alloy of cobalt, tungsten carbide and a number of other elements, which together give it strength and abrasion resistance. The name of the alloy is “win”, firmly entrenched in everyday life and the technical environment.
When choosing a Pobedit drill in a store, you should pay attention to how smoothly the nozzle is welded. Often there are drills from nameless manufacturers with poor-quality alignment, which is easy to determine even by eye.
The process of drilling holes in concrete or stone is based on the crushing process, so a hammer drill is used as the main tool. An impact drill is suitable for brick. Depending on the selected tool, the type of drill shank is determined.
- SDS, SDS-plus - mount with a diameter of 10 mm and a part inserted into the chuck 40 mm for quick change of drill used in rotary hammers. Drill diameter 4–26 mm, length from 110 to 1000 mm.
- SDS-max - mount for large drills used with powerful hammer drills. Shank diameter 18 mm, used for concrete drills with a diameter over 20 mm.
For an impact drill, the shank is cylindrical. Drill diameter - 4–11 mm, length - up to 110 mm.
For drilling holes with a diameter of 4–10 mm and a depth of up to 100 mm for a dowel or anchor, drills with SDS-plus mounts or drills with a cylindrical shank are suitable.
For holes with a diameter of up to 42 mm and a depth of up to a meter or through holes for laying communications, pipes or connecting an air conditioner, drills with an SDS-plus, SDS-max shank are used.
When drilling deep holes with a diameter of over 10 mm, it is advisable to perform the work in two or three passes, selecting drills from smaller to larger diameters, the same applies to the length of the drill. First, short 110 mm drills are used, and then half a meter or meter drills are used to reduce the risk of damaging a larger drill and ensure a smooth edge at the hole.
To drill holes in a wall with a diameter of over 42 mm, crowns are used, for example, to install a socket box. This is a cutting tool with a ring cutting edge, often mounted on a cylindrical base with an SDS-plus, SDS-max shank. The cutting edge is formed by a series of teeth made of Victory alloy or coated with diamond.
How to choose the right drill for a dowel for fastening various objects
Knowledge of how to select a drill for a dowel is relevant in situations where it is necessary to drill a hole to fix this fastener in it. Dowels are used in cases where it is necessary to fasten various objects to the wall surface - furniture elements, photographs, paintings, etc. The reliability of the fastening will largely depend on how correctly the drill is selected to create the hole in which the dowel will be placed.
First, we select a dowel depending on the wall material and the weight of the object, and then we select a drill based on the wall material and the size of the dowel
What to consider when choosing a drill for a dowel
Selecting a drill to create a hole in which the dowel will be fixed should take into account:
- the material from which the wall itself is made, as well as its finishing;
- expected loads of the fastener.
You should also choose a drill depending on the diameter of the fasteners used. On the outer surface of factory-produced dowels, as a rule, there are markings that allow you to correctly select drills of the appropriate diameter for them.
Table 1. Selection of drill and screw for dowel
It is important to know not only how to choose a drill for a dowel, but also how to drill a hole correctly. If it is necessary to drill a hole in the wall for a dowel, the diameter of which is 10 mm, then first use a drill with a diameter of 8 mm and an impact drilling mode. After the hole is drilled, the tool is replaced with a drill with a diameter of 10 mm and is used without using the impact drilling mode. This approach will allow you to get a hole in the wall of the required diameter with smooth and neat edges.
If you need to drill a concrete wall, it is better to use a Pobedit drill, which can handle such a durable material without any problems. The selected cutting tool must be at least 3 mm longer than the dowel itself. If you neglect this requirement, the dowel will not completely fit into the resulting hole, in the final part of which dust and pieces of crumbled material, as a rule, accumulate. In addition, the shape of the bottom of the hole may not match the shape of the tip of the fastener.
Calculate the drilling depth with a margin relative to the dowel length
How to fasten light weight objects
In order to fasten objects that are light in weight, use a quick mounting dowel. It is usually used for fastening lightweight objects to building structures made of brick and reinforced concrete.
As a rule, to solve this problem, a dowel is selected, the diameter of which, like the transverse size of the drill, is 6 mm. In this case, the length of the fastening element depends on the thickness of the wall of the object being fixed with it. If you need to select a dowel for mounting on the wall, then its length should be at least 4 cm, but if the mounting is on the ceiling, you need fasteners at least 6 cm long.
Securing medium weight items
Fixing objects of average weight is performed using impact-type dowels. In this case, the transverse dimensions of the dowels, as well as the corresponding drills, must be at least 8 mm. The dowel chosen for these purposes must go into the wall to a depth of at least 6 cm, and when attached to the ceiling surface - to a depth of 8 cm. To securely fasten an object of average weight (up to 10 kg) to the wall or ceiling, you must use 4 dowels at the same time.
It is convenient to hang medium-weight objects on quick-installation dowels if the design allows the use of through fastening
Installation of objects with significant weight
To fasten heavy objects (furniture cabinets, shelves, TV stands, etc.), you must choose a dowel, also of the impact type. In this case, the diameter of such a dowel, as well as the transverse size of the drill, must be at least 10 mm. Such dowels are buried 6 cm into the walls, and 8 cm into the ceiling. For reliable fastening of heavy objects, as a rule, at least 6 dowels are used.
To fasten the horizontal bar and ladder, anchor bolts are used, the diameter of which must be at least 8 mm. Such bolts are buried 6 cm into the surface of the walls, and 8 cm into the ceiling.
The procedure for installing an anchor in a concrete wall
Types of anchor bolts
Anchor bolts used to secure various objects are divided into three main types:
- anchor bolts with a nut, which, after installing the fastener, is tightened with a spanner or open-end wrench (with the help of such bolts, hidden fasteners are performed);
- anchor bolts with a self-locking nut, which is tightened using a Phillips-type screwdriver (such bolts can be used for fastening in places that are visible);
- double-expansion anchor bolts are the most reliable fasteners that are used to fix even very heavy objects.
Tile, glass
To drill small holes of 4–25 mm, special cone-shaped drills with diamond coating are used. The main task is to go through the surface of the tile and its base. After this, you need to switch to a drill suitable for the wall material and continue drilling with it (a drill for metal or wood will win).
It is especially difficult to start drilling in a strictly defined position. You need to stick tape over the mark or mark a point along the mark, carefully knocking off part of the glaze or polished surface so that the drill does not “walk” along the surface.
Large diameter holes for the socket are drilled with a ballerina drill. It contains a sprayed support cone on the main axis. An adjustable arm with a fixed cutting tip is moved away from it. It is better to start at low speeds until the surface of the tile is passed. When the surface has been covered by 2–3 mm, you need to move on to a crown for the corresponding wall material.
Spring anchor
This fastener element is also called a dowel, although this is not entirely true. It is often used for attaching suspended structures, such as lamps, to the ceiling. It is a screw equipped with two stops that are released by a spring.
They attach it like this:
- A hole of the required diameter is drilled in the ceiling.
- An anchor is inserted into it, having previously folded the blades and holding them from opening. Once behind the plasterboard surface, they will automatically open, ensuring reliable fastening.
Please note that it is impossible to dismantle the spring suspension.
A competent choice of fastening elements will not only ensure reliable fixation of suspended structures on the surface of the drywall, but will also protect the plasterboard from unnecessary damage.
Metal
Metal drills have the most familiar appearance. This is a spiral-shaped working part and a cylindrical shank. The sharpening is cone-shaped without a sharp tip with an inclination angle of the cutting edges from 90 to 140 degrees. The spiral is formed by two protruding parts and twisted at an angle of 27 degrees. The outer edge has a cutting edge along its entire length, due to which holes in soft metals and wood can be expanded by lateral movements of the drill, like a milling cutter.
Depending on the specific metal, the sharpening angle at the tip of the working part is selected:
- for most grades of steel used in construction - 140 degrees;
- duralumin, bronze and brass - 110–120 degrees;
- copper, aluminum, wood and plastic - 90–100 degrees.
Universal drill sets contain metal drills, mostly with an average sharpening angle of 110–120 degrees, which is quite enough for most tasks.
When drilling walls, metal drills are needed if there is reinforcement or profile frame elements inside the base material. It is impossible to go through these obstacles with a drill with a pobedit tip; both the tool and the already passed section of the hole will be damaged. You need to switch to a regular drill with a metal drill, go through an obstacle, and then continue working with a drill or drill on the selected material.
Wood, drywall
A distinctive feature of a drill for wood with a diameter from 2 to 16–24 mm from a similar one for metal is the presence of a sharp tip in the center of the main sharpening at the end of the working part. This is necessary for normal alignment of the drill in relation to the hole and for easy starting. The tip easily enters the wood fibers in a strictly marked place and no longer allows the drill to jump off.
Metal drills are suitable for drilling wood and drywall, but often the holes turn out uneven, especially if you do not select the correct drill speed depending on the type of wood. In soft rocks, the fibers along the edges of the hole will diverge, but in hard rocks, they may split if the drill moves.
For large diameter and/or deep holes use:
- Feather (feather) drill.
- Ballerina.
- Screw drill.
- Wood saw bits.
A point drill is a flat plate with two sharpened edges and a point for determining direction. Fixed point drill bits help drill holes with a diameter of 8–45 (60) mm. However, without rigid fixation of the tool and the base, the shape of the hole is unlikely to be even, and due to the absence of side cutting edges, the walls of the holes often end up with broken fibers.
Ballerinas for wood help to drill holes of large diameter, but only in a base with a thickness not exceeding a certain threshold, for example, up to 50–70 mm.
Screw drills are optimized for bringing wood chips out and are a direct analogue of large drills for concrete. Used for drilling holes with a diameter of up to 45 mm and a depth of up to a meter.
Saw bits drill out the material around the circumference. A fine file is formed along the edge of the crown. Afterwards, you need to use a chisel to select the material inside if you need to make a blind hole.
How and with what to drill | Construction portal
The answer to this question is of interest not only to beginners in carrying out repair work, but also to professional builders. After all, without using a drill, even the most ordinary shelf or hook cannot be secured. A hammer and nail are not the answer when it comes to metal, concrete, tile, glass or stone. To drill a beautiful, neat hole, you need not only certain skills, the choice of a suitable drill and its sharpening play an important role.
Content
What types of drills are there?
Drilling is the most common way to make a hole in any material. The main element of this process is a drill, the type of which is selected depending on the type of surface being processed and the purpose of the work.
There are several classifications of this cutting tool.
According to the design of the working part, drills are divided into spiral, flat, annular, centering, single-sided cutting drills, and for deep drilling.
Depending on the design of the tail part, drills are divided into cylindrical, conical, three-, four- and hexagonal, SDS drills.
By purpose (type of material being processed): drills for metal, wood, concrete, glass, stone, ceramics, universal.
How to choose the right drill?
The main rule when choosing a drill is that the structure of the cutting tool must be harder than the structure of the material being processed. To drill drywall, wood, and plastic, you can use a regular drill made of high-strength steel. And to drill into stone, brick or concrete, you need to use a carbide drill - the tips of such drills have plates made of alloys that are harder than concrete and stone. Most often, the role of such an alloy is victorious - an alloy of tungsten with cobalt in a ratio of 9:1.
It is necessary to select a drill of the correct size and appropriate for the type of work being performed. The diameter and length of the drill are selected depending on the mass of the surface being processed - the larger it is, the thicker and longer the drill is required. The most commonly used drill diameters in everyday life are from 6 to 12 mm. Small shelves or curtain rods can be secured using a 6 or 8mm drill bit. You can fix the toilet in holes drilled with a drill with a diameter of 10 mm. More specific types of work require different drill sizes.
When choosing a drill, it is important to consider the functionality of the working tool, which is selected based on the type of material being processed. You can drill holes in wood or plastic with a regular mechanical drill. Using an electric drill or screwdriver will make the job easier. These tools are indispensable when drilling stone and metal surfaces. If you need to drill holes in concrete, it is best to use a hammer drill.
When choosing drills, it is important to pay attention to their appearance. A high-quality tool should not have chips, scratches or other defects.
It is best to choose drills from well-known manufacturers that have proven themselves in the market - this will protect you from purchasing low-quality tools and wasting money.
Selecting a drill for metal
A metal drill will help you easily make holes in cermets, alloyed and non-alloyed steel, non-ferrous metals and cast iron.
The most commonly used twist drill for metal is a cylindrical rod with two helical flutes that form the cutting edges.
Most often, such drills are made of high-speed or alloy steel. These materials make strong, durable drills that can help you get the job done as efficiently as possible.
Cylindrical and conical drills for metal are common. HSS conical drills are excellent for processing metal sheets. Hss Sprint metal drills are suitable for use with hand drills. Other brands of professional metal drills include DeWalt, Bosch and Ruco drills.
You can get a neat hole in sheet metal without deforming it using a step drill.
Choosing a drill for concrete
Processing concrete is not an easy task due to the strength and power of this material. Carbide and diamond drills are used to drill holes in concrete. The easiest way to drill concrete is with a drill with an asymmetric sharpening. It’s better to mark the hole and start drilling with a drill with a regular sharpening.
SDS drills for concrete are very popular. They are designed specifically for use with hard concrete structures and high impact loads.
For professional drilling in concrete, drill bits for bosch hammer drills are used. Bosch drills have a four-spiral shape, which allows you to quickly remove residual material from the hole.
Choosing a wood drill
You can drill several holes in a wooden surface with a metal drill, but for constant work with wood, where accuracy and precision are important, you cannot do without a special wood drill.
Twist, feather and cylindrical drills are most often used for processing wooden structures.
The advantage of twist drills is that they are easy to remove from the work area after finishing the job. To create blind holes in wood with a diameter of 10 mm or more, feather drills are used. Such drills are used specifically to create holes, since it is impossible to drill an existing hole with their help, due to the absence of cutting edges on the side surface. A cylindrical or core drill is used to create large diameter holes. Using such a drill allows you to get a neat hole without defects, with high processing efficiency.
What you need to know about drilling?
During the drilling process, the cutting tool heats up, which leads to a change in the structure of the steel and a reduction in the service life of the drill. Therefore, if you need to drill a large number of holes in a durable material, the drill must be cooled by lowering it into a vessel with water.
When working with various materials, it is worth knowing some drilling features. If you need to drill a hole in a tile, you need to make a notch in the place where the hole is planned. This is done because the glaze of the tile is much stronger than the tile itself, and at high speeds the drill can move, leaving marks on the tile. The notch is made using a pobedit drill, a steel dowel or a special punch. The same operation will help to drill high-quality holes in metal surfaces.
It is important to maintain the drilling depth of the holes. If the wall is thin, there is a risk of drilling through it. Conversely, when drilling thick brick or concrete walls, it is necessary to take into account the length of the fastener. You can make a hole of the desired depth using the special factory stops indicated on the drills. If there are no such marks, you can screw a little electrical tape onto the drill, thus marking the required drilling depth.
To avoid splitting the tiles when drilling, you should use a drill and turn off the impact mode.
Below is a demonstration video on drilling tiles.
Using a diamond drill will help you drill a hole in durable materials quickly and efficiently. This option is the best choice if you need to make a large number of holes in a short period of time.
To drill a center hole in a part and carry out its further processing, use a center drill.
This drill is also suitable when you need to drill out a “stubborn” screw or screw.
A Forstner drill is used to drill large-diameter blind holes, such as through holes or loop holes, to install hinges in furniture.
strport.ru
What is a crown
How to cut an even round hole in drywall of the required diameter? To do this, use a cylinder-shaped cutter with a serrated cutting edge on one side and a “tail” for attaching the cutter to the drill on the other. A drill is located in the center of this cylinder. This whole structure is called a plasterboard crown, or a core drill. How it works: the drill is the first to enter the drywall and sets the center of the future hole, while the nozzle is fixed in the desired position, the edge of the cutter enters the surface and makes a cut of the circle.
Types of crowns
Core drills can be divided into two types: solid and split.
- Solid crowns are basically a drill bit with a single metal toothed cylinder on it;
- The collapsible crown device contains a universal disk into which cylinders of different diameters can be inserted. The cylinders themselves have an open shape and come complete with a disk. Like solid crowns, the collapsible edge is serrated.
The diameter of the cylinders can vary from 33 to 150 mm.
Both wood and metal drill bits are suitable for making holes in drywall. There are universal - bimetallic crowns that can be used to drill metal, wood, gypsum plasterboard, of course they are more expensive, but if you use them only for drywall, then we can say that they are eternal. When purchasing a bimetallic crown, you should pay attention to the fact that they are usually sold without a holder and a centering drill. In the assembly this is called an adapter, which will have to be purchased separately.
Preparatory work
If there are several spotlights and they are located at a small distance from each other (up to 500 mm), then it will be enough to stretch the wire to the nearest one. This process is carried out before the installation of the ceiling structure begins. Then, after the ceiling is completely installed, the cable is routed from device to device. Which wire should I use? Of course, from the point of view of ease of connection to the marks, it is flexible multi-core, but from the point of view of quality and reliability of installation, it is necessary to choose the same one as for all wiring. More often it is a hard copper wire, for example VVG-2x1.5.
We fix the wires in the terminal block
If a step-down transformer is used, then there is one important nuance. When using low supply voltage for halogen lamps (12 Volts), the voltage drop in the wires will be of great importance. In short, the wire must have a cross-section of more than 1.5 sq. mm, preferably 2.5. And the length of the cable to each lamp must be the same, so that the voltage drop is the same.
Selection of cutter
When you come to the store, it’s easy to get confused by the abundance of crowns on offer. How not to make a mistake with the choice so that it does not break when making the first hole?
- Take the crown in your hands and take a good look at it. If the product is of low quality, you will be able to visually immediately see, for example, elements of careless processing or defective coating. It is worth paying attention to the tail of the crown; if it is too light, it is made of low-quality metal and can quickly break;
- The centering drill and shank must be firmly secured, gaps are unacceptable. Also, if this is a dismountable bit, you need to check each cylinder included in the kit, how easily and evenly each of them fits into the groove of the disc. Make sure that none of the cylinders is loose in the groove, because the quality of the cut will depend on this;
- The element of the crown that bears the maximum load when drilling is the cylinders (glasses) with a serrated edge. The service life of the entire device depends on the quality of the material of this element. The saws should not be too thin and bend easily, the material should be elastic, otherwise you may not get a hole. Saws with hardened teeth are higher quality and more durable. Do not forget - the cutting teeth must ensure a clear and even cut of the material;
- Core drills come in different sizes (cylinder diameter, drilling depth), if you buy a set, make sure it has the one you need.
Crown for installing mounting boxes
The most common need to drill round holes in drywall is to install electrical outlets. The invisible part of the socket, the plastic round mounting box that is mounted in the wall, is called the socket box. There are socket boxes for concrete, wood and plasterboard.
The socket box for drywall is a plastic cup with adjustable plates made of plastic or metal. Thanks to these “claws,” the socket box is fixed to the back of the plasterboard sheet. The depth of the installation box can be 40, 50, 60 or 73 mm. As for the diameter, for a standard socket box it is usually 68-70 mm.
If you only need to drill holes to mount sockets, you will only need one hole saw. In this case, you should not purchase a set of dismountable crowns. It is enough to buy one special core drill, with a diameter of 68 or 70 mm (depending on the size of your socket boxes).
Today, the diameter of a core drill for drywall 68 mm is the most popular standard size.
Knauf-Hartmut
Withstands the heaviest loads on drywall dowels. Allows you to attach massive structures up to 55 kg on two-layer walls, about 35 kg from one layer and up to 6 kg/linear meter when placed on the ceiling.
Installation:
- Prepare a hole with a diameter of 1.3 cm in the gypsum board;
- One of the guide elements must be shifted so that the anchor strip made of galvanized steel profile fits into the hole;
- Align the guide elements so that their ends are at the same level. The anchor bar is in working position;
- Insert the plastic locking sleeve all the way;
- Place the plastic strips to the sides and break off the excess. The anchor strip securely fixes the fastener in the hole;
- Screw the screw into the dowel.
A dowel nail is used when there is no void between the dry plaster and the main wall. Nails are used for through fastening of skirting boards, cornices, and door frames.
Most often it is made of plastic.
- The sizes of these dowels for drywall are from 4 to 14 cm. Diameter is 4-7 mm.
- When it is hammered into a hole, it wedges and does not scroll.
- The hat is made in the form of a mushroom or hidden. Removing the nail is impossible without destroying the dry plaster.
Spotlights
Spotlights, so-called spots, which represent a point source of light, have become widespread these days. In most cases, spots are installed in plasterboard ceilings or boxes. For installation, it is necessary to cut a hole with a diameter corresponding to the diameter of the ceiling lamp. Usually, the required diameter for cutting is written on the packaging of the lamp or in the instructions for it, but it happens that there are no instructions, then you should measure the diameter yourself. This can also be done simply to check the specified information, so as not to accidentally make a hole of the wrong diameter, because nothing can be corrected later.
The most common diameters of holes for spots are 60 and 75 mm. To get a hole of the required diameter, you should use a special drill - a plasterboard crown. The main thing when you choose the size of the crown for drilling a hole for a spotlight is that the drilled diameter is smaller than the diameter of the spot, that is, the lamp must completely cover the lamp during installation.
General information about plasterboard ceilings
Let's start by understanding how the ceiling works, learning its features. All this will allow us to accurately install any lighting fixtures.
Structure
Half-assembled plasterboard ceiling
Plasterboard structures are frame structures, which, in turn, can be of two types:
- Suspended - those that are located at a certain distance from the main ceiling, and the entire structure is supported by various suspensions (straight, spring);
- Hemmed - profiles are nailed directly to the base to minimize the loss of room height. It can only be implemented in a room with flat ceilings, so this type is extremely rare.
Let's focus on the first option.
What features does it have:
- First, you will be able to lower the surface of the drywall low enough to integrate spotlights.
- Secondly, you can easily lay wires openly under any number of lighting fixtures - in this regard, the task is greatly simplified, since you do not need to perform dusty work on gating the ceiling, which can affect its strength.
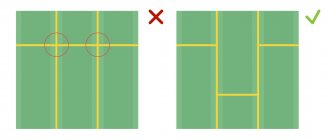
The frame of a plasterboard ceiling consists of metal profiles that form a lattice with cells of a certain size. The most commonly used options are 120x50 cm (such frames are assembled from a powerful Knauf profile), 60x60 cm, 40x40 cm.
- Some people manage to install without jumpers at all, as in the photo above, which is a direct violation of technology.
- The size of the cells directly determines how we will arrange the lamps in space. A simple example - spotlights can only be installed in free spaces so as not to run into the profile. In some situations it can be trimmed, but this may reduce the strength of the entire structure.
Room lighting project
Room with regular and decorative lighting
So, the first step is to develop a lighting scheme. Our website contains a lot of material with instructions on how to correctly calculate the number of lamps and their power for different rooms.
Also recently, material was published about decorative lighting. We advise you to read more if you are serious about installing lighting devices at home from scratch.
- Having decided on the number and type of lamps, draw up a project for your future ceiling. Here the dimensions of individual parts and levels of the structure, if any, are important to us. If you are planning a regular single-level flat ceiling, then write down the dimensions of the room and transfer them to scale on paper.
- Then mark on the drawing the desired locations of the lamps, strictly observing the proportions, that is, you should already know exactly what kind of lamps they will be: overhead, built-in, or you will limit yourself to just one chandelier. The size of these devices is also important, especially when it comes to installation.
- Next, on the drawing, indicate the location of the ceiling profile, according to the selected installation technology.
- Make sure there are no places where the profiles will interfere with the installation of the lamp. If conflicts occur, then change either the position of the electrical device or partially shift the interfering profiles.
In general, in order not to rack your brains later on how to correct mistakes, immediately develop an accurate plan for assembling the frame. Afterwards you can start working directly.
The process of assembling a frame from a metal profile
Install the guides and main profiles - this will allow you to better navigate when laying the wires, although if your calculations are correct, it will be much easier to pre-separate the wires, leaving some margin on the lamps.
Electrical PVC corrugation
Next, we lay the wiring, which should be hidden in a plastic or metal corrugation (the latter is used when laying on combustible bases). If you are attached to a reinforced concrete floor, then the cable can be installed without additional insulation.
Metal corrugation prevents fire of wooden structures during a short circuit
Attention! Under no circumstances connect electrical lines to a metal frame - this is prohibited at VSN level 28-95, as it can lead to electric shock.
Further actions will be outlined when discussing installation instructions for different lamps.