Sketch of a bored foundation with dimensions. Bored piles in terms of reliability are practically in no way inferior to other supports in the construction of low-rise buildings. This is one of the most reliable methods for constructing foundations on soils subject to seasonal heaving. The resulting structures guarantee the integrity and strength of the foundation and, accordingly, the walls of the house being built.
It is advisable to build such a foundation with your own hands in cases where it is impossible to build other types of foundations. It is logical to use it if the incompressible layer is located very deep, for example, when performing construction work in wetlands or other weakened soils.
The costs of a bored foundation with a grillage for a brick house can be considered justified when construction is carried out on an area with a significant slope. Experts also recommend the use of this type of foundation for the construction of lightweight wooden or frame buildings.
Pile installation technology
Carrying out the process of drilling wells with a hole drill
The construction of this type of foundation includes drilling wells and their further filling with concrete mixture. Hand and electric/gasoline drills are used for drilling. A less labor-intensive stage of well preparation is the use of special drilling equipment.
The process of drilling holes for piles can be done with your own hands using a hand-held motor drill, setting the appropriate tip diameter.
The strength of each pile is increased by a frame made of reinforcement: 3-4 reinforcing elements with a cross-section of 10-12 mm are lowered into the drilled holes.
Experts advise performing horizontal ligation of frame elements in case of eccentric loads or shear forces. For dressing, it is recommended to use smooth reinforcement with a cross-section of 6-8 mm, and a pitch of approximately 1 meter.
In this case, the reinforcing rods will serve as a connection between the pile and the reinforced concrete grillage. That is, the above-ground and buried parts of the foundation will be combined into a single whole. When installing a grillage, the rods must protrude from the pile head.
In addition to the above, the frame made of reinforcement will not allow possible ruptures and deformations due to the influence of frost heaving.
Insulation of a bored foundation with a grillage
When insulating a foundation made of bored piles, two options can be considered. The first option is when a shallow grillage is poured. With this device, an insulation scheme is used as for a strip foundation. That is, sheets of extruded polystyrene foam are attached directly to the grillage and the finishing is done. After this, if necessary, an insulated blind area is installed.
The second case is when a monolithic grillage is poured above the ground or a frame is made of timber or channel. In this case, install a sheathing made of wooden beams or a metal profile from the surface of the base to the ground, lay a layer of insulation and cover the base with decorative panels or siding. On the back side of the foundation, as a rule, the empty space is filled with sand. Another common option is when the base of a bored foundation is laid out with decorative bricks.
The construction of bored piles with a monolithic grillage is not difficult for a novice builder - anyone can master this popular technology. With correct calculations and compliance with the device technology, such a foundation can be laid by a team of 2-3 people.
At the end, we offer you to watch an interesting video about errors when constructing a foundation on bored piles:
Did the article help? Rate her
Partial and complete formwork construction
Arrangement of formwork for the bored base of the building
Next, the formwork is installed in the drilled well. But its function can be performed by the soil itself, if it is dense enough and does not crumble. Then only the upper part of the formwork structure is exposed to make pile caps.
So, the formwork can be the soil itself, drilled with a tip of 200-250 mm to 90 and up to 150 mm in depth, taking into account the condition of the soil. If, due to the characteristics of the soil, it has to be dug up, then metal or asbestos-cement pipes of the appropriate cross-section can be used as formwork. When constructing a bored foundation with your own hands, you can roll up the roofing material, turning it into something like a pipe.
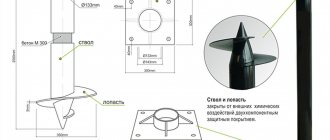
In order to prevent the bored foundation from being squeezed out during seasonal swelling, its head, which is located half a meter (or more) below ground level, must be insulated with a galvanized steel roofing cover, several layers of film or roofing felt.
Experts call this cover a “shirt,” which is recommended to be made to cover the entire depth of the pile. The reasoning for performing this action is as follows. The rising soil “slides over or lifts the installed protection, leaving the base itself motionless.” In addition, the “jacket” prevents cement lait from flowing into the ground, and accordingly, the strength characteristics of concrete do not decrease.
What is a bored foundation
A bored foundation is one of the types of pile foundations in which the piles are not driven or twisted, but are cast directly in the ground, in the place where they are to be installed. In this case, no equipment is required for driving piles and there is no need to overpay for ready-made reinforced concrete structures. In addition, you can drill wells for such structures with your own hands, using a hand drill or a gas drill.
In addition to the financial component, this type of foundation is good because the construction technology allows it to be used in areas with the weakest and most unstable soils, as well as on a slope, which will not lead to a significant increase in the cost of the structure, as, for example, when constructing a strip foundation or, even more so , USHP.
A foundation with bored piles is a combination of a strip foundation and a pile foundation, but the strip, which acts as a grillage, does not carry loads, since it does not come into direct contact with the ground.
A foundation with a monolithic grillage can easily withstand heavy loads, since the grillage, by transferring the load from the house to the piles, helps to evenly distribute the weight of the structure throughout the pile field. For multi-storey buildings, it is important to make a detailed design calculation, as well as think through all the nuances regarding the protection of concrete piles from precipitation and external influences.
When building light houses, or bathhouses and outbuildings, instead of a monolithic grillage, you can use a frame made of an iron profile or timber.
The disadvantages of this foundation, like all pile structures, include the impossibility of arranging a basement under the house. But owners of areas with high groundwater levels, as a rule, do not think about having a basement in the house, even with a strip foundation, as this can lead to additional problems.
Concrete laying
Schematic representation of the constituent elements of a bored base.
After the drilling process is completed, the formwork and frame are constructed, the concrete mixture can be poured. Concrete is laid in layers with gradual compaction - bayoneting. Only a “heavy” solution is suitable for this. This term implies the use of the following "heavy" aggregates:
- quartz sand;
- crushed stone/gravel (hard rocks).
Concreting of each bored pile is carried out continuously. This means that the time interval between laying each layer should not exceed 1 hour. The process of complete setting of concrete is completed after 28 days, after which the resulting foundation structure can be loaded.
A few final details
When assessing the weight of the house that will put pressure on a bored foundation with a buried grillage, also take into account the snow load. Asbestos-cement or steel pipes are mainly used two-meter pipes with a diameter of fifteen to twenty-five centimeters. No more than 1,600 kilograms of the house’s mass should put pressure on one pile, and based on this, it is possible to calculate the number of piles required and the distance between them. Houses of average size and weight require three to five dozen piles. The above example with roofing felt can be implemented in practice only in stable soil. If there is a possibility of progress, then the only option left is with steel pipes. From the outside, the same roofing material (in two layers) will help to insulate them from moisture. The fittings inside the pipes are protected from moisture by not reaching a few centimeters to the ground. A protrusion is made on top for connection with the grillage reinforcement.
Application of bored technology in private construction
Scheme for constructing a foundation using TISE technology
The technology for constructing bored structures is simple and suitable for constructing a foundation with your own hands. The construction industry has at its disposal various types of drills for wells with different sections. Their use helps to drill wells up to several meters deep.
The diameters of the piles can also be different: from 15 to 40 cm. The so-called TISE technology involves the use of a special drill, with which you can drill wells 20 cm in diameter with an expansion at the base (up to 40 or 60 cm). Thus, an increase in the support area is achieved, which does not allow heaving to push the pile out.
There are also special mechanisms (hole drills, motorized drills, etc.) that can significantly facilitate the installation of supports.
Methods for installing bored piles
The technology for installing bored piles is carried out using three methods, the choice of which depends on the characteristics of the soil:
- In the presence of unstable water-saturated soils, the method of circulating a clay mixture with a density of 1.2-1.3 g/cm3 is used. The bentonite clay solution is fed through a hose under pressure into the shaft. When the well is filled, the solution, mixing with the soil, rises outwards, falls into the settling tank, and is again transferred from it to the well using a pump. A clay crust forms on the walls of the drill shaft, preventing moisture from penetrating inside. After the formation of the clay cake, a frame of metal rods is installed, and the supply of concrete mixture begins, which pushes clay out of it as the well fills. Concrete must be supplied without interruption until the shaft is completely filled. If you stop supplying it for a while, a clay layer will form between the layers of concrete, which will reduce the strength of the pile. This method allows you to do without the use of casing pipe.
- The dry method is used when the walls of the well do not require strengthening if there are semi-solid, non-plastic, hard clay soils at the construction site. A well of designed depth (up to 30 m) and diameter (400-1200 mm) is drilled using a bucket drill or auger column. The base of the shaft can be expanded using a special device with a mechanism at the end like a drop-down knife (diameter up to 3 m), an explosive method, or technology for enhanced compaction of the bottom of the shaft. The pile is concreted using formwork, which is raised as it is filled with mortar and removed after completion of the work. The head of the support is formed in the inventory jig; in winter it is necessary to insulate it. This method is not applicable if there are aggressive or industrial waters on the site.
- The use of a casing pipe for arranging piles installed by the bored method is acceptable in any type of soil. The shaft is drilled by impact or rotary methods; if necessary, its lower part is expanded by explosive methods or using equipment with an expander at the end. Casing pipes connected to each other are lowered into the well by driving, vibrating immersion or using hydraulic jacks. The casing pipe frame immersed in the shaft is filled with concrete. To compact the concrete mixture and release air from it, the pipe is given a semi-rotational and reciprocating movement, due to this the concrete is further compacted.
- In construction conditions on seismically unstable soil, piles are installed without dynamic impact using the fundex method. The well is drilled using the indentation method without excavation. Rollers or conical rollers are installed on a shaft, and a cast iron tip is lowered into the shaft, which presses the soil. At the end of the work, it remains inside the well; the lower end of the pipe is attached to it using a lock. If there is no water inside the pipe, then a metal frame is mounted and a plastic concrete mixture is supplied. As the pipe is filled with solution, it rises to the surface.
Disadvantages and argument in favor of drilling technology
Pouring a bored foundation with concrete
It is an accepted fact that the main disadvantage of this technology is the inability to make an accurate calculation of when exactly the required incompressible layer is reached that can withstand the pressure of the pile.
In order to avoid annoying mistakes, wells are drilled to 1.5-2 meters, that is, reaching a point below the freezing level, where the soil has a denser structure. With a low groundwater level, the calculation of the bearing capacity of the soil corresponds to 6 kg per 1 cm².
For individual developers, this technology looks quite attractive. Unlike the tape or monolithic type, where the entire required volume of concrete solution is laid at once, piles can be laid in stages. When pouring one support, the volume of concrete laid is disproportionately less than with monolithic concrete, which simplifies the process of preparation and pouring. Therefore, you can do this work yourself.
How to make a bored foundation with a grillage
The construction of any foundation must begin with a project. Bored foundation is no exception. After the calculations, you should have documents in your hands indicating the number of piles, their diameter, depth, as well as a diagram of the pile field, which shows the location of the piles in relation to the site.
Marking the foundation and drilling wells
Installation begins with marking and drilling wells (holes) for piles. The location of the piles and their diameter, as mentioned above, depends on the design of the house and on the transmitted loads on the foundation. The arrangement of the pile field is transferred from the drawings to the site using a rope, thus marking the rows and intersections of the future walls of the house. After marking, they begin to drill wells in the marked places. For drilling, as a rule, motorized drills are used, which allow you to make wells quickly and without much effort.
The diameter of the well is made slightly larger than the final diameter of the pile, since a so-called casing pipe will be inserted into the well, which will protect the walls of the well from collapse and into which concrete will subsequently be poured.
The depth of the wells is calculated for each area separately. It is necessary that the bottom sole of the pile must be below the freezing level of the soil. Otherwise, due to the small support area, the piles will be subject to soil heaving. When drilling wells for bored piles, the base of the well is made 2-3 times wider than the diameter of the well, thereby creating a stable base. This expansion is covered with sand, crushed stone and carefully compacted, forming a cushion.
Formwork
Next you need to make the formwork for the pile. As a rule, casing pipes of either asbestos cement or plastic are used for this, which are inserted into the drilled well before the bottom begins. Ordinary roofing felt rolled into a tube can also be used for these purposes.
The formwork is made slightly higher than ground level, thereby raising the base of the building. Due to the relative high cost of large-diameter plastic pipes, when constructing bored piles, as a rule, asbestos-cement pipes are used, which are quite strong and have good geometry. It is not recommended to make formwork from roofing felt. This is a thin and brittle material that may not withstand the pressure of crumbling well walls and deform, which will lead to a violation of the geometry of the final pile and, as a result, to a deterioration in its load-bearing capacity.
Pile reinforcement
The next stage is the reinforcement of bored piles. Reinforcement gives additional strength to the piles and allows them to withstand lateral loads from the soil. To reinforce such piles, steel rods with a diameter of 10-12 mm, connected into one reinforcement cage, are most often used. As a rule, this is a frame of 3-4 rods - using more rods for standard piles is impractical.
Next, the reinforcement is lowered into the well onto special spacers so that the metal does not come into contact with the ground after pouring, this will eliminate the effects of moisture and corrosion. For further pouring of the monolithic grillage and its strong connection with the bored piles, reinforcement outlets are made on top of the piles by 50-60 cm.
Pouring piles
At this stage, concrete is poured into the prepared wells, and then it is compacted using improvised means or a special construction vibrator. Concrete used for pouring bored supports must comply with SNiP 2.03.01-84 and be at least class B12.5. For large, heavy houses it is better to use B15 concrete. Pouring is done in portions for better compaction and expulsion of excess air from the concrete using a vibrator.
Due to the relatively low consumption of concrete, bored piles can be poured independently using a concrete mixer. But it’s much easier to order ready-made concrete, which will be delivered to your construction site in a mixer and poured into the wells with a pump. It will cost more, but you will save much more time and effort.
Pouring a monolithic grillage
After pouring the piles and drying them for at least 7 days, proceed to pouring the monolithic grillage. To do this, a formwork similar to the formwork for a strip foundation is constructed on the poured piles, a reinforcing frame is knitted, which is connected to the reinforcement previously released from the bored piles. After this, concrete is poured into the formwork.
If a monolithic grillage is located above the ground, then the formwork for it will look like a wooden trough, so it is important to consider the lower stops for such formwork so that it does not collapse under the weight of the concrete poured into it.
To calculate the amount of concrete for a monolithic strip foundation, you can use a strip foundation calculator, taking the height of the grillage as the full height of the foundation.
To build light frame houses or houses made of timber on a bored foundation, it is not necessary to make a monolithic grillage made of concrete; it is enough to make a frame from a wooden beam or a metal channel, having previously aligned the length of the piles to the same level.
Calculation and installation location of piles
Schematic representation of the location of piles depending on the design features of the structure.
At the project development stage, the exact number of supports and their location are calculated. Supporting elements are installed in rows along the markings of the walls of the house, in its corners, at the intersections of walls and between them.
The calculation of the distance between the supports is determined by the total weight of the structure being erected: the heavier it is, the greater the number of elements and with less distance between them they will be installed.
In this case, the minimum permissible distance is taken into account - at least three diameters of the pile. The reason for this is that if supports are placed more often, their load-bearing capacity is reduced.
Approximate calculation for a pile support diameter of 40 cm, the permissible distance will be 120 cm (40x3). When performing installation work with your own hands, you should check the level of the heads - they should all protrude to an equal amount. In the future, the house itself will be built on them.
Creating a pile-grillage foundation with your own hands
It is quite possible to do the construction of a pile-grillage foundation with your own hands. For the construction of small buildings (gazebos, country houses), a grillage on a columnar base is chosen; the pile version is suitable for buildings of permanent use. The work is best done in late spring, early summer or early autumn. First, they prepare the site, clearing it of vegetation and debris, then implement further stages of the work.
First you need to prepare materials and tools, order concrete of strength class B17.5-22.55, or purchase the ingredients from which it will be prepared in a concrete mixer. If necessary, you need to add gravel or small crushed stone under the future piping.
Formwork
The formwork is mounted 10 centimeters higher than the height of the strip grillage. Formwork is made from wooden panels or boards of sufficient strength so as not to crack or fall apart under the weight of concrete.
How is reinforcement performed?
A prefabricated monolithic grillage must be reinforced. For reinforcement, steel rods with a cross-section of 12-18 millimeters are chosen, the depth depends on the project, but the mesh is laid evenly, in increments of 15-30 centimeters. The strapping is installed around the entire perimeter of the base of the tape.
The wire is cut in advance, the frame is installed in the assembled formwork, and there it is connected to the pile reinforcement as rigidly as possible. Holes are drilled in the upper part of the piles that protrudes above the soil level, embeds are passed through them, and longitudinal bars of reinforcement are attached to them. Steel rods are inserted inside the piles, the rods are tied together with the top rods. Inside the piles, the reinforcement is laid in a layer of 2-3 rods.
Concrete
Concrete is poured in equal horizontal layers, the thickness of which should be 10-15 centimeters. After pouring, each layer is sequentially compacted with a vibrating tool, then the next one is poured.
The concrete grade M300 or M350 is suitable for pouring the grillage.
Grillage: weather and temperature-humidity conditions
The grillage is installed in hot weather, preferably calm and without precipitation. Direct sunlight should not hit the surface either. If the air temperature is negative, the concrete needs to ensure minimal heat loss at all stages - from preparation to installation. If work is carried out on heaving soils, the ground is first heated to above-zero temperatures and protected from freezing.
Dismantling the formwork
After pouring the concrete, the formwork is dismantled, first removing the fasteners and spacers, and only then the boards. The formwork panels should easily move away from the frozen monolith, but if this situation is not observed, this indicates that the solution has not yet hardened and has not gained the required strength.
Drying and care
When a concrete grillage is poured, you need to ensure proper care of the monolith. The design is reliably protected from sunlight, wind, and precipitation. The surface is covered with plastic film and periodically moistened with water if the air temperature exceeds +22C.
Waterproofing
The concrete grillage must be waterproofed, this is especially important when constructing buried pile-grillage foundations. It is also advisable to insulate raised grillages from moisture.
Waterproofing options:
- Penetrating - a special solution with excellent adhesive characteristics covers the foundation.
- Coating - the piping is covered with bitumen mastic.
- Sprayable - liquid compounds with high water-repellent properties are applied using a spray gun.
- Rolled - the tape is coated with mastic, and rolled material is placed on top.
The choice of method and material for waterproofing depends on the type of soil, groundwater level, type of grillage, financial capabilities and other factors.
Load capacity calculation
General view of the finished bored foundation of the structure.
To calculate the required number of supports, two indicators are needed - the weight of the structure and the load-bearing capacity of an individual element. Calculation of the strength of one pile support depends on the brand of concrete mortar used. So, when making a pile from M 100, it can withstand 100 kg per 1 cm². With a cross section of 20 x 20 cm, the area will be 400 cm², and the support can support up to 40 tons.
Thus, the bearing capacity of the soil is much less than that of the pile itself. According to this, calculating the exact number of elements and load-bearing capacity of the entire pile-grillage structure is impossible without taking into account the strength of the soil. Previously, a calculation was given for laying the support below the freezing level. But when the section changes, the area and load-bearing capacity of the pile-grillage foundation will be completely different.
Grillage is a unifying composition of a pile-grillage structure that increases the stability of the base. When choosing a pile foundation device without it, a calculation will be required that can ensure that all elements are installed to a sufficient depth. Then you can be sure that the structure will not sag and will not be “squeezed out” by the influence of frost heaving forces.
Description and Application
Figure 1. Bored foundation
The strip version of the pile-bored foundation is used in the following situations:
- Construction of a building in a populated area where the installation of a buried strip or monolithic foundation is impossible.
- When the surface of the site is weak-bearing soil. In this case, piles are driven until solid soils are reached.
- A geological study of the territory has not been completed. Then it’s better to play it safe and organize a reliable foundation.
- A site with changes and difficult terrain. The base of the structure is leveled with different heights of piles and the installation of a suspended strip foundation.
- When the soil is too alkaline, it is not possible to build a pile-screw foundation with a monolithic slab or strip.
Bored-type strip foundations are convenient for constructing cottages. If heavy building materials are used, the number and diameter of supports are increased. When lightweight blocks are used, such a bored strip base is inexpensive.
Types of grillage and its structure
The grillage foundation, as a rule, can be made either in the form of a strip or in the form of a slab. If a slab grillage will combine the heads of each pile, then a strip grillage will combine the heads of only adjacent piles located under the walls of the structure.
Drilling rig specialists can use various materials to construct a grillage: steel, wood, precast or monolithic reinforced concrete. We do not recommend using metal, since its consumption in this case is quite high.
To install a metal grillage, you cannot do without a tap and subsequent anti-corrosion treatment. We consider a monolithic grillage made of reinforced concrete to be the most practical, technologically advantageous and inexpensive option.
Bored piles with a grillage are the most popular option for construction
Since piles in general are a very inexpensive material for strengthening the foundation (they are much cheaper than solid monolithic and strip foundations), it is also worth noting that such piles have a high load-bearing capacity.
One pile can withstand about 1600 kilograms, and in order to strengthen the foundation of a house, about 30-50 piles measuring 1600 kilograms are enough.
Bored piles with any type of grillage are located below the level at which the soil freezes and after that they are necessarily enclosed in a “jacket”, that is, in two layers of roofing felt. Such a jacket significantly reduces the pressure on the piles on frosty days, when it pushes the piles outward, and also reliably waterproofs them.
Stages of construction of a foundation based on bored piles with a grillage
We guarantee consistently high-quality work regardless of the time of year, and when it comes to the construction of a pile-grillage type foundation, its construction will proceed as follows:
- We will install the formwork on top of the piles.
- Then we will install the reinforcement cage inside the formwork.
- After this, you can fill the grillage with concrete (it is worth noting here that the pouring technology is similar to that used in the case of a strip foundation).
- The height of the grillage should ideally be at least 30 centimeters, and the width of the structure should be slightly larger than the thickness of the walls of the building, that is, about 40 centimeters.
It is important to note that a foundation on bored piles will not require a large amount of excavation work, as well as time and expense. If you choose this method of construction, you will receive a high-quality and reliable foundation that meets all modern requirements
Types of pile-grillage foundation
There are two varieties of such a foundation: with a recessed grillage and with a hanging grillage. Call us or leave a message in the feedback form if you would like to receive comprehensive advice regarding your specific case.
As a rule, with a hanging grillage, a foundation is obtained that is ideal not only for light frame houses made of wood, but also for heavy, more powerful structures.
A foundation on piles with a recessed grillage is recommended for wooden houses, the walls of which will be made of beams up to three hundred millimeters thick. But this option is also perfect if you plan to build a house made of brick or monolithic houses.
Advantages and disadvantages
Concrete mortar is not susceptible to the negative influence of the environment
. The structures are very popular in private construction if the owners do not have professional skills and do not have sufficient funds to attract hired labor and equipment.
Bored technology has the following advantages:
- versatility in terms of density, humidity and acidity of the soil on the site;
- ease of manufacturing supports, even novice developers can easily handle it;
- affordable cost of materials and necessary equipment;
- short production time for a pile field even for a large building;
- the ability to carry out work in stages, mixing the solution and installing supports at intervals necessary for rest or restoration of the weather.
Disadvantages of designs:
- limited strength, which is significantly inferior to screw and reinforced concrete factory analogues;
- inability to arrange a basement;
- the need for high-quality and expensive floor insulation;
- a piping or grillage is required.
Bored foundations are a reliable and cost-effective option for low-rise construction.