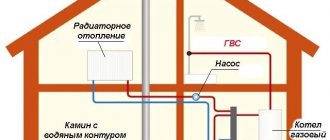
To keep your home warm, it is important to properly develop a heating scheme. One of the components of its effectiveness is the connection of heating radiators. It doesn’t matter whether you are going to install cast iron, aluminum, bimetallic or steel radiators, it is important to choose the right way to connect them.
The way the radiator is connected affects its heat transfer
Types of heating systems
The amount of heat that the heating radiator will emit depends not least on the type of heating system and the selected type of connection. To choose the best option, you must first understand what kind of heating systems there are and how they differ.
Monotube
A single-pipe heating system is the most economical option in terms of installation costs. Therefore, this type of wiring is preferred in multi-storey buildings, although in private buildings such a system is far from uncommon. With this scheme, the radiators are connected to the main line in series and the coolant first passes through one heating outlet, then enters the input of the second, and so on. The output of the last radiator is connected to the input of the heating boiler or to the riser in high-rise buildings.
Example of a one-pipe system
The disadvantage of this wiring method is the impossibility of adjusting the heat transfer of radiators. By installing a regulator on any of the radiators, you will regulate the rest of the system. The second significant drawback is the different coolant temperatures on different radiators. Those that are closer to the boiler heat up very well, those that are further away become increasingly colder. This is a consequence of the serial connection of heating radiators.
Two-pipe wiring
A two-pipe heating system is distinguished by the fact that it has two pipelines - supply and return. Each radiator is connected to both, that is, it turns out that all radiators are connected to the system in parallel. This is good because the coolant of the same temperature enters the input of each of them. The second positive point is that you can install a thermostat on each of the radiators and use it to change the amount of heat it emits.
The disadvantage of such a system is that the number of pipes when laying out the system is almost twice as large. But the system can be easily balanced.
How to correct the situation when there is a drop
Everything here is extremely simple. First, you need to look at the pressure gauge, which has several characteristic zones. If the arrow is in the green, then everything is fine, but if it is noticed that the pressure in the heating system is dropping, then the indicator will be in the white zone. There is also a red one, it signals an increase. In most cases, you can handle it on your own. First you need to find two valves. One of them is used for injection, the second is used for bleeding media from the system. Then everything is simple and clear. If there is a shortage of media in the system, it is necessary to open the discharge valve and monitor the pressure gauge installed on the boiler. When the arrow reaches the required value, close the valve. If bleeding is needed, everything is done in the same way with the only difference being that you need to take with you a vessel into which the water from the system will be drained. When the pressure gauge needle shows normal, tighten the valve. Often this is how the pressure drop in the heating system is “treated”. Now let's move on.
They are widely used in constant flow systems. The main advantage of manual balance valves is their low cost. The main disadvantage is that every change in the installation must rebuild the system, which is labor-intensive and expensive.
Automatic balance valves Automatic balance valves allow you to flexibly change the parameters of the pipeline system depending on fluctuations in pressure and flow of the working medium. They are proportional regulators that maintain a constant differential pressure in the system and minimize disturbances caused by control valves. They are characterized by high performance, which allows them to maintain the established hydraulic conditions in systems, compensating for interference caused by the control valve.
Where to put radiators
Traditionally, heating radiators are placed under windows, and this is no accident. The rising flow of warm air cuts off the cold air that comes from the windows. In addition, warm air heats the glass, preventing condensation from forming on it. Only for this it is necessary that the radiator occupies at least 70% of the width of the window opening. This is the only way the window will not fog up. Therefore, when choosing the power of radiators, select it so that the width of the entire heating battery is not less than the specified value.
How to place a radiator under a window
In addition, it is necessary to correctly select the height of the radiator and the location for its placement under the window. It must be placed so that the distance to the floor is around 8-12 cm. If you lower it lower, it will be inconvenient to clean, if you raise it higher, your feet will be cold. The distance to the window sill is also regulated - it should be 10-12 cm. In this case, warm air will freely go around the obstacle - the window sill - and rise along the window glass.
And the last distance that must be maintained when connecting heating radiators is the distance to the wall. It should be 3-5 cm. In this case, rising currents of warm air will rise along the back wall of the radiator, and the rate of heating the room will improve.
Pipe diameter and degree of wear
It is necessary to remember that the size of the pipe must also be taken into account. Often, residents set the diameter they need, which is almost always slightly larger than the standard sizes. This leads to the fact that the pressure in the system decreases slightly, which is due to the large amount of coolant that will fit into the system. Do not forget that in corner rooms the pressure in the pipes is always less, since this is the most remote point of the pipeline. The degree of wear of pipes and radiators also influences the pressure in the heating system of the house. As practice shows, the older the batteries, the worse. Of course, not everyone can change them every 5-10 years, and it is not advisable to do this, but it doesn’t hurt to carry out preventive maintenance from time to time. If you are moving to a new place of residence and you know that the heating system there is old, then it is better to change it immediately, so you will avoid many troubles.
Hydraulic balance of hot water supply systems. The hot water temperature in hot water systems drops significantly when demand is low or absent. This leads to several problems: long waits for hot water, water overflow, and the possibility of unwanted bacteria developing. To maintain the water temperature at the required level, this is usually a constant circulation of water in the systems, through a circulation pump and a circulation pipe. Hydraulic balance in these systems is usually maintained using direct acting temperature controllers.
Radiator connection diagrams
How well the radiators will heat depends on how the coolant is supplied to them. There are more and less effective options.
Radiators with bottom connection
All heating radiators have two types of connection - side and bottom. There can be no discrepancies with the bottom connection. There are only two pipes - inlet and outlet. Accordingly, coolant is supplied to the radiator on one side and removed from the other.
Bottom connection of heating radiators for single-pipe and two-pipe heating systems
Specifically, where to connect the supply and where the return is connected is written in the installation instructions, which must be available.
Heating radiators with side connection
With a lateral connection, there are many more options: here the supply and return pipelines can be connected into two pipes, respectively, there are four options.
Option #1. Diagonal connection
This connection of heating radiators is considered the most effective, it is taken as a standard and this is how manufacturers test their heating devices and the data in the thermal power passport for such a connection. All other connection types transfer heat less efficiently.
Pressure norm
Effective transfer and uniform distribution of coolant for the performance of the entire system with minimal heat loss is possible at normal operating pressure in the pipe lines.
The coolant pressure in the system is divided according to the method of action into types:
- Static. The force of influence of a stationary coolant per unit area.
- Dynamic. Force of action during movement.
- Maximum pressure. Corresponds to the optimal value of liquid pressure in the pipes and is capable of maintaining the operation of all heating devices at a normal level.
According to SNiP, the optimal indicator is 8-9.5 atm, reducing the pressure to 5-5.5 atm. often leads to heating interruptions.
For each specific home, the normal pressure indicator is individual. Its value is influenced by factors:
- power of the pumping system supplying coolant;
- pipeline diameter;
- remoteness of the room from the boiler equipment;
- wear of parts;
- pressure
Pressure control is possible using pressure gauges mounted directly into the pipeline.
Where is the return route?
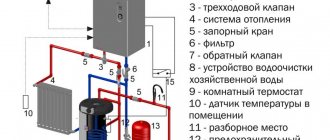
In short, the heating circuit consists of several important elements : a heating boiler, batteries and an expansion tank. In order for heat to flow through radiators, a coolant is needed: water or antifreeze . If the circuit is constructed correctly, the coolant heats up in the boiler, rises through the pipes, increasing its volume, and all excess ends up in the expansion tank.
Based on the fact that the batteries are filled with liquid, hot water displaces cold water , which, in turn, enters the boiler again for subsequent heating. Gradually the water temperature increases and reaches the desired temperature. circulation can be natural or gravitational , carried out using pumps.
Based on this, the return can be considered a coolant that has passed through the entire circuit, giving off heat, and, already cooled, returned to the boiler for subsequent heating.
Pressure regulator
The operation of the batteries and the pump is disrupted due to high or low pressure levels. Correct control of the heating system will help to avoid this negative factor. The pressure in the system plays a significant role, it ensures that water gets into the pipes and radiators. Heat loss will be reduced if the pressure is standard and maintained. This is where water pressure regulators come to the rescue. Their mission is primarily to protect the system from too much pressure. The operating principle of this device is based on the fact that the heating system valve located in the regulator works as a force equalizer. Depending on the type of pressure, regulators are classified into: statistical, dynamic. It is necessary to select a pressure regulator based on throughput. This is the ability to pass the required volume of coolant, in the presence of the required constant pressure drop.
Differences between them
The difference between the described concepts is as follows:
- The supply is a coolant that flows through the radiators from the heat source.
- The return is a liquid that has passed through the entire circuit, and cooled down again to the heat source for subsequent heating. Therefore, occurs at the output .
- The difference is in temperature: the return is colder .
- The difference is in the installation. The water line that is attached to the top of the battery is the supply. What is attached to the bottom is the return line.
Important! Some tips need to be followed. The entire system must be completely filled with water or antifreeze . Maintaining fluid speed, circulation and pressure is equally important.
Temperature difference across radiators
The temperature difference should be 30 °C . In this case, the batteries will feel approximately the same to the touch . It is important to ensure that the difference in these values is not too large.
Photo 2. Heating diagram for 6 radiators: changes in flow and return temperatures on each of them are indicated.
Safety valves
Any boiler equipment is a source of danger. Boilers are considered explosive because they have a water jacket, i.e. pressure vessel. One of the most reliable and widespread safety devices that reduces the danger to a minimum is the safety valve of the heating system. The installation of this device is due to the protection of heating systems from excess pressure. Often this pressure occurs as a result of boiling water in the boiler. The safety valve is installed on the supply pipe, as close to the boiler as possible. The valve has a fairly simple design. The body is made of good quality brass. The main working element of the valve is the spring. The spring, in turn, acts on the membrane, which closes the passage to the outside. The membrane is made of polymer materials, the spring is made of steel. When choosing a safety valve, it should be taken into account that full opening occurs when the pressure in the heating system increases above the value by 10%, and full closure occurs when the pressure drops below the response value by 20%. Due to these characteristics, it is necessary to select a valve with a response pressure higher than 20-30% of the actual one.
What to do if the radiators in the apartment are cold and the riser is hot?
Regardless of whether the cold heating equipment is only in the riser or in the entire entrance, and possibly throughout the house, you must seek help from qualified specialists.
In the case of an apartment building, this is a plumber of the company that is responsible for the heating supply of the house. Cold batteries with a hot riser may be due to a clogged system or the formation of an air lock in it. An important factor is the pressure in the wiring. In some cases, the problem of low coolant flow is relevant. It is possible to independently find out the reason for the low efficiency of heating elements. But only a true professional in his field will clearly answer any questions that arise and competently fix the breakdown. This video will help you to make your radiators heat better:
Often, residents of both apartment buildings and private houses are faced with the problem of cold radiators. In this article we will explain why this problem occurs and what to do if the batteries are cold.
What does it depend on?
The temperature curve depends on two quantities:
outside air and coolant. Frosty weather leads to an increase in coolant temperature. When designing a central source, the size of the equipment, building and pipe size are taken into account.
The temperature leaving the boiler room is 90 degrees, so that at minus 23°C, the apartments are warm and have a value of 22°C. Then the return water returns to 70 degrees. Such standards correspond to normal and comfortable living in the house.
Analysis and adjustment of operating modes is carried out using a temperature diagram.
For example, the return of liquid with an elevated temperature will indicate high coolant costs. Underestimated data will be considered a consumption deficit.
Previously, for 10-story buildings, a scheme with calculated data of 95-70°C was introduced. The buildings above had their own chart of 105-70°C. Modern new buildings may have a different layout, at the discretion of the designer. More often, there are diagrams of 90-70°C, and maybe 80-60°C.
Temperature chart 95-70:
Temperature chart
What is needed for this
To calculate the diameter of the pipe, as a rule, the following factors are taken into account:
- Total heat loss of the home.
- What power do heating radiators have separately in each room.
- The total length of the circuit pipes.
- How is the system wired?
To be able to calculate the diameter of the pipes, it is necessary to determine in advance the total heat loss, the power of the boiler equipment and batteries for each room. It is also important which method will be chosen for pipe routing. Having all these parameters in hand, a future calculation scheme is drawn up.
It is also important to remember some of the specific markings of different pipes. Thus, on polypropylene pipes for heating a private house, the outer diameter is indicated (the same applies to copper products). To calculate the internal parameter, the wall thickness is subtracted from this indicator. Steel and metal-plastic pipes are marked by their internal cross-section.
Pipeline layout in a multi-storey building
As a rule, multi-storey buildings use a single-pipe wiring diagram with top or bottom filling. The location of the forward and return pipes can vary depending on many factors, including even the region where the building is located. For example, the heating scheme in a five-story building will be structurally different from the heating in three-story buildings.
When designing a heating system, all these factors are taken into account, and the most successful scheme is created, allowing all parameters to be maximized. The project may involve various options for bottling the coolant: from bottom to top or vice versa. In individual houses, universal risers are installed, which ensure alternating movement of the coolant.
Consumer choice: cast iron or aluminum
The aesthetics of cast iron radiators is the talk of the town. They require periodic painting, since the rules require that the working surface have a smooth surface and allow dust and dirt to be easily removed.
A dirty coating forms on the rough inner surface of the sections, which reduces the heat transfer of the device. But the technical parameters of cast iron products are excellent:
- are slightly susceptible to water corrosion and can be used for more than 45 years;
- have high thermal power per section, therefore they are compact;
- are inert in heat transfer, so they smooth out temperature changes in the room well.
Another type of radiator is made of aluminum. Lightweight, factory-painted design, does not require painting, and is easy to maintain.
But there is a drawback that overshadows the advantages - corrosion in an aquatic environment. Of course, the inner surface of the heater is insulated with plastic to avoid contact of aluminum with water. But the film may be damaged, then a chemical reaction will begin with the release of hydrogen, and when excess gas pressure is created, the aluminum device may burst.
The temperature standards for heating radiators are subject to the same rules as batteries: it is not so much the heating of a metal object that is important, but the heating of the air in the room.
In order for the air to warm up well, there must be sufficient heat removal from the working surface of the heating structure. Therefore, it is strictly not recommended to increase the aesthetics of the room with shields in front of the heating device.
Reasons for uneven heating of batteries
When approaching various types of repair work, it is useful to use the rule - go from simple to complex. Often the cause of a problem can be eliminated through preventative maintenance.
The answer to the question why heating radiators are cold from below and hot from above lies in the following:
- The shut-off valves are not fully open or closed;
- air entered the system and a plug formed;
- a lot of salt deposits and impurities have accumulated in the radiator, interfering with circulation;
- shut-off valves broke and the conditions for uniform movement of the coolant were violated;
- The radiator is not connected correctly;
- there is low pressure or coolant speed in the system;
- the room is too cold.
The radiator is clogged
Water in central heating systems contains impurities of salts, which settle in any convenient place (turns, bends, recesses, shells on the inner surface).
The coolant may contain various foreign impurities:
- metal shavings and rust;
- sand;
- pieces of gaskets and plumbing sealant for threaded connections.
Over time, a jelly-like mass accumulates at the bottom of the heating battery, clogging the fluid flow paths. Over time, the dirt substance can turn into a solid state.
Shut-off valves are not working properly
The taps installed on the inlet and outlet pipes to the battery must be open and freely allow coolant flows to pass through. A malfunction can lead to changes in pressure and circulation of the working fluid.
A breakdown is considered to be the incorrect operation of the faucet locking mechanism, the inability to turn it to the closed or open position.
Low system pressure
The coolant is supplied to the system under the influence of a set pressure. If its value is below normal, the working fluid will not be able to completely fill the radiator, and as a result there will be no effective heat transfer.
A decrease in pressure can be caused by a number of reasons:
- Malfunction in the central boiler room or main line.
- Insufficiently open shut-off valves on heat supply risers and pipes.
- Increasing the volume of heat exchangers, for example, installing radiator sections or equipment for “warm floors” beyond the norm.
Incorrect radiator installation
The batteries are connected to the heating system according to the established scheme. Changing the order of supply and removal of working fluid leads to disruption of its circulation or complete cessation of movement. The radiator can be connected incorrectly by “specialists” with low qualifications or by property owners who have taken on the functions of plumbers.
Low coolant circulation rate
Reducing the time it takes for liquid to move in the heating radiator will result in the effect of a warm top and a cold bottom.
The pressure drop in the system was already mentioned above as the reason for the decrease in circulation rate. Another factor influencing the movement of fluid in the heating network is disruption of the natural (gravitational) type of heating, that is, the creation of traffic jams, obstacles to movement, and so on.
Cold room
In a room with a low temperature, the coolant cools faster, and the battery below, closer to the outlet pipe, will be colder than in the area where the hot liquid is supplied.
About Leak Testing
It is imperative to check the system for leaks. This is done to ensure that the heating operation is efficient and does not have failures. In multi-storey buildings with central heating, the cold water test is most often used. In this case, if the heating system drops by more than 0.06 MPa in 30 minutes or 0.02 MPa is lost in 120 minutes, it is necessary to look for places where there are gusts. If the indicators do not go beyond the norm, then you can start the system and begin the heating season. Hot water testing is carried out immediately before the heating season. In this case, the media is supplied under pressure, which is the maximum for the equipment.
Their purpose is to maintain temperature and minimize water consumption in hot water circulation systems
An important feature of these valves is the presence of periodic disinfection of the DHW pipeline network. Tags: balancing valves Manual balancing valves
Autonomous heating systems
Today you may not ask for cold, but your heating system will do it for you. If you did not pay enough attention during the summer season, an unpleasant surprise can be expected at the beginning or during the heating season. Do you have a cold house because your radiators are as bad as ever before? Errors in maintenance or poor adjustment of some parts of your heating system may be a malfunction. It's best to use the summer months to maintain your heating system, but many people will only start doing it when they need to flood for the first time.
Adjustment
How to adjust the pressure in the elevator unit?
Support washer
To be correct, when using a retaining washer, it is not necessary to adjust the pressure, but to periodically replace the washer with a similar one due to abrasive wear of the narrow metal sheet in process water. How to replace the washer with your own hands?
The instructions are generally quite simple:
- All valves or valves in the elevator are closed.
- One vent on the return and supply is opened to drain the unit.
- The bolts on the flange are loosened.
- Instead of the old washer, a new one is installed, equipped with a pair of gaskets - one on each side.
Tip: in the absence of paronitis, washers are cut from a dilapidated car inner tube. Don't forget to cut an eyelet that will allow the washer to fit into the flange groove.
- The bolts are tightened in pairs, crosswise. Once the gaskets are pressed, the nuts are tightened until they stop, no more than half a turn at a time. If you rush, uneven compression will certainly lead to the gasket being torn off by pressure from one side of the flange.
Heating system
The difference between the mixture and the return flow is normally regulated only by replacing, welding or drilling out the nozzle. But from time to time it becomes necessary to remove the difference without stopping the heating (in most cases, with important deviations from the temperature schedule during the peak of cold weather).
This is done by adjusting the inlet valve on the return pipeline; Thus, we remove the difference between the forward and reverse threads and between the mixture and the return.
- We measure the supply pressure at the end of the inlet valve.
- Switch the hot water supply to the supply thread.
- We screw the pressure gauge into the vent on the return line.
- We completely close the input check valve and then slowly open it until the difference decreases from the initial one by 0.2 kgf/cm2. Manipulation with subsequent opening and closing of the valve is necessary so that its cheeks descend as much as possible on the stem. If the valve is closed, the cheeks may sag in the future; the price of ridiculous time savings is at least defrosted access heating.
- The return temperature is monitored at daily intervals. If it is necessary to lower it further, the difference is removed 0.2 atmospheres at a time.