In the vast majority of regions of our country, it is impossible to do without proper heating. Unfortunately, it is not always possible to connect the house to a centralized heating system, which leads to the need to find other heating methods.
In particular, air heating allows you to solve the problem of heating residential or industrial premises. This system is a massive fan with a built-in heater that takes air from the street, heats it, and supplies it to the room. The disadvantage of air heaters is their high energy consumption, since heating is carried out either through electric heating elements or using water heaters.
Modern air source heat pumps integrated into the ventilation unit can reduce energy consumption to a minimum without losing efficiency. The fact is that air-to-air heaters use the principle of heat recovery, heating the incoming air with the heat that has accumulated in the outgoing air flow. Thus, electricity consumption is reduced to almost zero, allowing you to heat the house at minimal cost. Next, we will talk in more detail about how supply and exhaust ventilation units with vapor compression and traditional recovery are designed.
Operating principle of air-to-air pumps
Air-to-air pumps work on a similar principle to air conditioners, with the difference that air conditioners work to cool the air, and heaters work to heat the air. At the same time, low-potential energy of the air in the room is used to heat the incoming flow, which makes it possible to reduce energy consumption several times when compared with heaters using electricity or water.
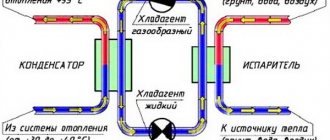
Let's look at the principle of operation using the example of an installation with freon elements:
- Even at subzero temperatures, air contains some heat that can be extracted under certain conditions. Most pump models are capable of converting heat at temperatures down to -15°C. Some pumps are capable of operating at -25°C, but the conversion coefficient will be equal to unity.
- The refrigerant circulates through the internal circuit of the pump, which at the right moment, with the help of an evaporator, changes from liquid to gaseous state. When freon becomes a gas, it absorbs heat, which is contained in some quantities in the air even at low temperatures.
- Having gained heat, freon enters the compressor, where under pressure it again takes on a liquid state. Just at this moment the freon heats up, releasing heat, the amount of which depends on the air temperature. Heat accumulation occurs in the condenser. The compressor is usually made in the form of a spiral, which facilitates easier start-up during cold periods.
- The condenser is located in the indoor unit, installed directly in the room. It is in the condenser that heat accumulates due to the arrival of heated freon. The indoor unit functions as a heat exchanger in which the incoming flow is heated and then distributed throughout the building.
The energy efficiency of air-to-air heat pumps directly depends on the temperature of the low-grade heat source. That is, the warmer it is outside, the more heat the device will absorb. Most models completely lose their ability to absorb heat at a temperature of -20°C. Therefore, in some cases, the system is equipped with additional heaters - electric or water. In any case, the electricity consumption of HP is approximately 3 times less than that of devices operating exclusively on electricity or water.
According to the layout method, heat pumps resemble standard split systems. The TN consists of two blocks, one of which is mounted outdoors, and the second indoors (on the wall or ceiling). Control is carried out remotely.
Installation Features
First of all, it is worth noting that the installation of such systems requires certain qualifications of craftsmen and it is better that it is carried out by professionals. The heat pump diagram of an air-to-air system assumes the presence of two blocks, external and internal. The entire structure is quite lightweight, which allows the external block to be installed even on top of roofing material, such as tiles.
When placing the indoor unit, you must be guided by the principle of maximum efficiency of heated air circulation throughout the room. Its installation can be done both on the wall and on the ceiling.
The use of air heating as the main source of heating the room involves the creation of a complex branched system of air ducts
The length and location of air ducts must be carefully calculated by specialist installers. The optimal solution to disguise them would be to install suspended ceilings.
Difference between a heat pump and an air conditioner
Structurally, an air conditioner is similar to a heat pump. For example, both devices use freon to change temperature. In addition, both HP and air conditioner contain a compressor, evaporator and condenser in their design. However, this is where the similarities end. Let's take a closer look at the differences:
- The main difference is performance. The purpose of the heat pump is to heat the room. Just like an air conditioner, a heat pump can provide cooling, but with less efficiency. This statement is also true in the opposite direction - the air conditioner can heat the air at a temperature of at least -5°C, but the efficiency will be low.
- Energy saving. A heat pump uses less electricity in heating mode than an inverter air conditioner. This effect is achieved through the selection of refrigerant, the volume of its charge and the increased size of the evaporator. The average energy consumption of HP is 1 kW per 3-4 kW of heat.
- Scope of application. Air conditioners are used for cooling or heating, provided that the outside temperature does not fall below -5°C. Heat pumps, in turn, are used at outdoor temperatures down to -25 °C.
Air-to-air heat pumps are conventionally classified as sources of renewable energy, since they allow you to extract heat directly from the earth’s atmosphere, using a minimum of energy. Many years of experience in using such systems have shown their high energy efficiency and rapid self-sufficiency.
What happens if the electricity goes out?
In the event of a power outage, your home heat pump will eventually stop working... like any other modern heating gas, diesel or pellet boiler, which cannot operate without power from the control automation. The solution here is quite simple - an autonomous gasoline or diesel generator. At a cost of 200-300 dollars, this solution is the most optimal. h2 Emergency situations and breakdowns.
Any, even the most reliable equipment, can fail; no one is immune from this. What is really important is the time it takes for the service department to respond and fix the breakdown. Specialists of Nova Gros LLC travel to any point in Belarus within 24 hours, all main components and spare parts are stored in our warehouse.
Also, all HP produced by Stiebel Eltron have a built-in backup electric heater installed. It allows you to maintain an acceptable temperature in the building in case of compressor failure, freon leakage, damage to the external collector and other breakdowns.
Nova Gros LLC - Official service and warranty center of Stiebel Eltron
Connect with us
Connect with us
How to choose an air-to-air heat pump
The market offers several types of TN. Moreover, each of the models has a certain set of characteristics that affect the possibilities of application. When selecting equipment, you need to pay attention to the following parameters:
- Heat pump performance.
- Manufacturer company.
- The price of both the equipment itself and its installation.
The presence of additional functions matters. For example, some models can not only heat, but also cool the air. In cold regions, it is preferable to use devices with built-in electric or water heaters.
Simply put, the characteristics of the equipment must match the operational parameters of the building in which the installation will be performed. Therefore, when choosing a pump, it is necessary to consult with professionals.
Advantages and disadvantages of air-to-air pumps
To get an objective picture of the advantages and disadvantages of any equipment, experts study reviews from real owners. This makes it possible to learn not only about the strengths, but also about the disadvantages, which is impossible to do based solely on the advertising statements of manufacturers. Here's what people who use air-to-air pumps say:
- Installing a VT allows you to save significant money. The equipment pays for itself in approximately 2 years. Considering that the service life of a heat pump is 30-50 years, the benefits are obvious. In addition, the cost of operating HP is 3-4 times less than electric or LNG boilers.
- The device does not require traditional types of fuel - coal and gas - to operate, and it consumes much less electricity. If you install solar panels, you will not need external sources of electricity at all.
- Environmental friendliness of the equipment. When the heat pump operates, no harmful substances are released, which can be an important factor for those who care about the environment.
When studying reviews from real people, you inevitably come across negative reviews that need to be mentioned so as not to be biased. Experts have selected the most common references to the disadvantages of TN:
- Performance largely depends on the temperature of the heat source. For example, freon pumps can operate at external temperatures down to -25°C. Moreover, the colder it is, the less efficient it is.
- High cost, both of the equipment itself and of installation. This fact is decisive in the fact that heat pumps have not yet become widespread.
It must be said that the disadvantages mentioned above are not so critical as to abandon the use of air-to-air HP. The fact is that manufacturers are continuously improving their products, increasing efficiency, and adjusting pricing policies. For example, modern HP models can operate at lower temperatures than their predecessors, despite the fact that they cost less. Therefore, many experts in the field of heating systems recommend heat pumps.
Conclusions.
Geothermal heating has long been transformed from “exotic” into an independent, actively developing direction. It makes sense for you to use it in the following cases:
Full automation – ease of use.
In the absence of a central gas supply, HP is the only completely autonomous method of heating a building that does not require regular maintenance and fuel supply (like gas holders, pellet or diesel boilers). Therefore, if you adhere to the “set it and forget it” principle, a heat pump is the ideal option for you.
All individual constants are programmed during commissioning; subsequently, the operation of the equipment is controlled automatically based on sensor readings of external and internal air temperatures, coolant temperature in the house, external circuit antifreeze temperature, pressure, etc.
In the user settings, you can set the desired temperature in the building yourself, as well as program it for certain modes: reducing the temperature during your absence (vacation, business trips), lowering the temperature by 2-3 degrees at night, etc. Full-function control via a smartphone is possible via the Internet.
Security and lack of approvals from the Ministry of Emergency Situations.
Since combustion processes in HP do not occur in principle, all associated risks disappear: fire, natural gas leaks, carbon monoxide formation, etc. Accordingly, there is no need to make and approve a project with the Ministry of Emergency Situations, install special forced ventilation and chimneys, or undergo annual inspections. control of inspectors of the Ministry of Emergency Situations. The equipment can be placed in any room for you - the noise from a running pump is no more than from a refrigerator.
Price.
As strange as it may sound, sometimes the costs of geothermal heating can end up being much lower than for classical systems. Of course, if you have a gas pipe laid down your street, and the financial factor is the main one for you, then you can give preference to a gas boiler. But if gas needs to be “pulled” 200-300 meters, a step-down station must be built, and design documentation must be prepared and approved for all this, then even the initial capital investment “gas” loses.
The cost of installing gas tanks, diesel and pellet boilers can be 15-20% lower, but this difference pays off in the first 2-3 years of use due to savings on fuel.
You can view the equipment “live” and ask any questions you may have in our office in Minsk. Call! (044) 765-29-58;.
SDAR-XXX
Air handling unit designed for heating and air conditioning. It works on the principle of recovery - air pumped in from the street is heated by the heat of the outgoing flow.
The presence of a heat pump reduces the load on the built-in heating elements. The productivity of household devices is from 300 m3/hour, industrial - up to 25,000 m3/hour.
External part
The outdoor heat pump unit sits behind air-transparent blinds. It is quite large and looks like an industrial air conditioner. In winter, the pump housing freezes and becomes covered with a thick coat of snow. This is a process provided for in its operation - according to its internal algorithms, the equipment regularly goes to defrost and completely thaws. After this everything repeats itself.
SDAR-INV-PL
Plate supply and exhaust recuperator with built-in heat pump. The fan forces air into a counterflow plate heat exchanger, where the air is heated by the heat that has accumulated in the flow emanating from the room. But the fact is that air of +20 °C will not be able to heat a flow with a temperature of -20 °C to room values. For example, let’s take a recuperator with an efficiency of 100%, 20-20 equals 0, this is the value that will be obtained under the ideal conditions we have come up with. As we know, a modern HP is capable of working with negative temperatures. 0 °C of the removed air is the low-potential source of heat due to which the vapor-compression heat pump reheats the inflow. At the same time, air is released into the street significantly below 0 ° C
Thus, the air-to-air pump described above, integrated into the PSU with a recuperator, almost doubles the overall efficiency of the installation.
Installed in residential, industrial and office buildings. Allows heating and cooling of incoming air. It works as a heater, without additional energy sources, up to an ambient temperature of -10 C. If the temperature drops below, the built-in heaters are connected. In summer it can serve as an air conditioner. Capacity from 300 m3/hour to 25,000 m3/hour.
Types of natural heat accumulators
Earth Energy
Earth masses in the depths of the planet serve to obtain free low-temperature energy. There are areas below the frost line that maintain stable above-zero temperatures throughout the year. to collect heat :
- laying long-distance horizontal pipelines in shallow depths (more than 1 m) and a distance between branches of about a meter;
- drilling vertical and inclined wells with a depth of 40 to 250 m to raise warm water, treat it and then discharge it into a reservoir.
Water heat
Warm lakes and rivers with a current and a non-freezing layer of water are suitable for this method. Sometimes a high rise in groundwater is also used to extract heat by pump. Pipes are laid at the bottom of the reservoir, pressed down with a weight, and an open method of collecting energy is used. It implies that liquid rises into one well along the flow of water, and after treatment it is discharged through the second well. For the option of using groundwater, there is a high risk that the height of the rise may change depending on the season or shifts in the earth's crust.
Use of air masses
This principle of heat intake is the most accessible and cheapest .
A heat exchanger is installed, which is a cluster of fins, thus increasing the contact area. To enhance energy collection, blowing fans are installed. It is very effective to use such a source for heating water in a swimming pool or increasing the temperature of water for household and household needs. This requires little electricity, and such a system is economically feasible. Lightweight, low-power systems are placed on the roof or wall of the house; more powerful systems require an independent foundation . In installations, work occurs due to inverter conversion of alternating current. If the desired fluid temperature is reached, the power is reduced, which saves money and extends the life of the pump.
SDAR-INV-W
An installation that works on the same principle as described above, but instead of a plate heat exchanger, a rotary one is used. This makes the design somewhat more expensive, but adds 5% recovery efficiency.
It is used for ventilation and heating in premises of any type - residential and industrial. It can also serve as an air conditioner. The volume of supplied air is from 500 m3/hour to 25,000 m3/hour.