Home |Reinforcement |Features of reinforcement of reinforced concrete beams
Date: November 20, 2018
Comments: 1
Enterprises producing reinforced concrete products produce a wide range of products. It is not always possible to use standard products when implementing a specific building project. Surely many people paid attention to the builders placing steel reinforcement in the formwork. Everyone understands that steel rods provide high strength characteristics of reinforced concrete beams.
However, only specialists who know the calculation methods can correctly determine the diameter of the rods and their number. For most ordinary people who have not encountered the methodology for calculating beams of rectangular cross-section, this process remains a mystery.
The reinforcing bar can withstand significant tensile loads, but is unstable to compression and bending.
A serious construction task is to perform reinforcement calculations. The need for this arises when carrying out construction activities in private buildings. You can, of course, turn to professionals or use special software. But, unfortunately, this opportunity is not always available, so we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the recommendations presented in the material. We are sure that they will help you make the right decision when reinforcing beams.
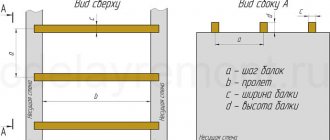
Types of beams
What is a reinforced concrete beam structure? What are the differences in installation method and section shape?
A beam is an element made of concrete and reinforced with steel rods that works as part of a building structure and absorbs force loads. Such building structures are also called crossbars or purlins. Depending on the installation method, they can be:
- Monolithic elements, which are single-span structures freely located or clamped on one or both sides.
- Combined (prefabricated-monolithic) structures, including cantilever ones.
- Prefabricated, consisting of individual parts that are part of an overall multi-span structure.
Solid reinforced beams are used in construction as elements of foundations and floors.
The cross-section of the elements is different and can be rectangular, trapezoid, T-beam, I-beam or other types. According to building codes, the section width is taken to be 5 centimeters and is a digital series, starting from 100 mm and ending with 250 mm. The height of the product changes accordingly.
The combination of reinforcing bars and concrete gives a combination of their properties
Which areas of the masonry need to be reinforced?
Fig. 3 Reinforcement diagram for the construction of a house from Twin Block
Construction from aerated block does not imply total reinforcement of the entire masonry. Reinforcement of the following zones is considered appropriate, necessary and sufficient:
- 1st row of masonry;
- Every 4th row of masonry when reinforced with steel rod reinforcement and every 2nd row when reinforced with composite mesh in areas longer than 6 meters;
- Areas around lintel supports;
- Rows above and below window openings;
- Zones in the floor level under the rafter system. A reinforced strapping belt is installed here;
- Rows at the level of the mauerlat (roofing element, timber or log, laid along the perimeter of the outer wall, which serves as a support for the rafters);
- Top edge of masonry;
| Recommendations from Gleb Grinfeld, one of the most authoritative experts in Russia in the field of construction |
For masonry thickness:
- blind areas from 4 meters should be reinforced up to 150 mm;
- up to 250 mm - from 6 meters;
- from 300 mm - from 8–9 meters.
For masonry lengths of 12 meters or more, expansion joints should be provided in the masonry. If we are not talking about a single heated volume (part of the house is unheated), in this case you will have to come to terms with the risk of cracks. When constructing a group of buildings (for example: a house + garage), it is better to provide expansion joints.
Main objectives of strengthening
Discussing the issue of strengthening reinforced concrete structures with a rectangular profile, we will dwell separately on terminology. In specialized construction sources, the process of increasing the strength of concrete structures associated with the installation of reinforcement is called reinforcement of reinforced concrete products. What do the letters of the abbreviation stand for? We will answer:
- Ж
– abbreviated designation for the presence in the structure of iron (steel) reinforcing bars or mesh frames, which help to increase the strength characteristics. - B
– characterizes the material concrete, the mass of which is reinforced with embedded elements.
The main objectives of strengthening reinforced concrete beam elements are:
- Ensuring high load-bearing capacity of products.
- Increased strength characteristics.
- Resistance to destruction.
- Increased resistance to the perception of increased loads.
Solving the assigned tasks to ensure strength is carried out through reinforcement and implementation of special methods aimed at:
- assessment of strength characteristics;
- testing the endurance of a concrete support under the influence of multiple loading cycles;
- control of the stability of a reinforced concrete beam, maintaining its integrity and location.
Most factory products are manufactured using prestressed reinforcement
Advantages and disadvantages of monolithic frame technology
Monolithic reinforced walls have the following advantages:
- the one-piece construction without seams is strong and reliable, it does not blow through, and temperature bridges do not form;
- a smooth, even surface allows you to begin finishing work without prior preparation;
- building construction in a short time;
- monolithic houses have an open layout;
- increased service life of reinforced concrete structures;
- complex architectural curved elements and arches are made quite easily.
Disadvantages of monolithic walls:
- low sound insulation;
- mandatory wall insulation;
- the ability of concrete to conduct vibrations.
Purpose of calculations
The calculation allows you to determine the area of the reinforcement elements, depending on the specified forces, or the load-bearing capacity, according to the actual dimensions of the rods used. In particular, performing preliminary calculations helps determine:
- Size of rods in diameter.
- Length of elements.
- The nature of the location in the product.
[testimonial_view id=”24"]
To determine the optimal reinforcement option for a specific concrete beam, consider the following parameters:
- geometric dimensions of the product (length, width, height);
- the thickness of the protective layer, which characterizes the distance from the reinforcement to the outer plane of the concrete surface;
- the magnitude of the distributed or point load.
Expenses
Reinforcement costs depend on:
- Depending on the accepted option for constructing a monolithic floor slab: with removable or permanent formwork.
- Support method: beam or beamless.
- Its dimensions: length-width-thickness.
In addition, the cost will increase when using a manual method of tying reinforcement versus a machine one .
Average prices for individual stages of creating a reinforced frame for a monolithic floor slab are summarized in the table:
| Name of works | Units | price, rub. |
| Reinforcement with continuous mesh, laying of reinforced structures | m2 | 100 |
| Knitting horizontal mesh 1 rod | tn | 17000 |
| Knitting a vertical mesh in 1 rod | tn | 15000 |
| Frame knitting | tn | 9600 |
| Reinforcement with mesh 100×100 mm | m2 | 450 |
| Reinforcement with 100×100 mm mesh fixed to the base | m2 | 570 |
| Reinforcement with mesh 200×200 mm | m2 | 550 |
| Double-layer mesh reinforcement 200×200 mm | m2 | 930 |
Principles of reinforcement
Strengthening of concrete structures is carried out using the following elements:
- Individual steel reinforcing bars.
- Metal frames.
- Steel mesh.
In high-rise buildings, the reinforcement frame serves as the basis for the entire structure
During the reinforcement process, rods can be installed both in stretched areas of a concrete beam and in compressed areas. The specificity of the use of supports during construction work makes it possible to classify them as bendable elements, in which, under the influence of applied forces, a stretched zone or a compressed section appears, as a bending moment and transverse forces act.
Reinforcement of beams is carried out by rods located longitudinally and transversely. Depending on the direction of application of forces, the upper and lower reinforcing bars of the frame can be either stretched or compressed.
Let us consider the main parts of the horizontal reinforcement frame, which is under the influence of applied vertical forces. It consists of the following elements:
- rods located in the upper part of the frame, which are in a compressed state;
- rods located below, stretching under the influence of loads and strengthening the concrete beam;
- transverse elements providing the strength of the rectangular section;
- distribution fittings connecting the elements with a single circuit.
Pros and cons of the design type
The main advantages of the beam structure:
- ensuring the overlap of spans with increased dimensions;
- large margin of safety, which allows you to distribute high loads;
- good sound insulation and noise protection characteristics.
The disadvantages include the need to use lifting equipment for installation, as well as additional costs associated with delivering crossbars to the site.
Requirements for fittings
A set of special requirements are imposed on the surface of reinforcement elements.
When reinforcing ribs with flat welded frames, the rods are welded between
- Degrease the rods.
- Clean the rods from dirt, paint and non-metallic coatings.
- Remove loose rust from the surface using a wire brush.
There is an opinion about the advisability of moistening reinforcing bars with water a week before laying and concreting. As a result, it will become covered with rust, and the concrete solution will stick to it more strongly. Experts confirm that the rust present on the surface of the rods, which does not have peeling, increases the coefficient of adhesion of the reinforcement to the mortar. Rods with a rusty surface are more effectively glued together with a concrete composition, but at the same time, rusty peeling is not allowed.
Steel rods with a variable profile have a 3-fold reserve of pull-out resistance compared to smooth reinforcement.
What should I put the first row on?
If the difference in the base is more than 5 mm, which is quite common, then ordinary adhesive for aerated blocks will not work. Here you will need to combine the laying of the initial row with leveling the surface for the subsequent laying of blocks.
In this case, the installation of the starting row should be carried out exclusively using properly prepared, high-quality cement-sand masonry mortars. Since the base of the plinth is not perfectly flat, with minor differences and roughness allowed, the use of expensive glue will be an unacceptable luxury for laying on the foundation. In addition, the glue is more flexible and is intended for thin-seam masonry.
Help: It is recommended to use a standard proportion of cement and sand passed through a sieve in a ratio of 1:3 for laying the initial row of blocks, with the addition of water until the mixture has a relatively thick consistency.
A properly prepared solution will not only allow you to obtain the most reliable connection between aerated concrete and the base, but will also help correct all existing irregularities. It is also allowed to use ready-made, factory-made mixtures made on the basis of cement and sand, supplemented with hydrophobic, water-retaining additives and plasticizers.
Gain Features
Reinforcement with reinforcing bars is carried out using longitudinal and transverse reinforcement bars, followed by welding or knitting. When knitting frames, use reinforcement with L-shaped bends.
When reinforcing beams, observe the following requirements:
- use rods with a diameter of more than 10 millimeters for longitudinal reinforcement;
- use steel rods with a diameter of at least 12 mm as non-tensioning reinforcing bars for knitted frames intended for supports with a height of more than 40 centimeters;
- provide an interval between the longitudinal load-bearing elements of the frame of at least 25 millimeters for the rods of the lower level, and 30 mm for the rods of the upper layer.
As a rule, two types of elements are made of reinforced concrete - beams and slabs
Depending on the change in the class of concrete from which the products are made, the diameter of the longitudinal rods changes. For reinforcement with a strength of 500 MPa, its diameter size should be:
- 16 mm
– for lightweight concrete class B12.5 and below. - 25 mm
– when reinforcing solid mass of class B15-B25. - 32 mm
– with reinforced composition of category B30 and higher.
If beams made of cellular compounds of class below B10 are reinforced, it is allowed to reduce the diameter of longitudinally located rods - less than 16 millimeters.
Construction of formwork
One of the most important points when creating a reinforced slab is the correct construction and installation of formwork. Thus, it is advisable to install it over the entire size of the slab, although partial installation is also allowed. Wood beams and boards can be used as formwork, which can later be used to strengthen the roof. A mandatory measure is to carefully secure the formwork due to the large weight of concrete.
To increase the strength and reliability of the foundation, it is recommended to reinforce the formwork.
It is necessary to lay fiberboard on top of the formwork, and it is allowed to use one sheet twice. The protective layer of the reinforcement must be at least twenty millimeters 20 mm with additional supports under the reinforcing mesh.
The entire structure must be filled with high quality concrete. In almost four weeks, the monolithic slab will be ready for use - this is exactly the time that is enough for the concrete to reach a 100% strength level. Only after this period is it possible to dismantle the formwork.
It is necessary to make sure that there are no holes in the formwork, since cement laitance can seep through the cracks, which will negatively affect the strength of the concrete itself.
Since the protective reinforcement layer cannot be less than 2 cm, it is advisable to supplement the formwork with dies. The consistency of the concrete should be neither too liquid nor too thick. The mass must be plastic and well-movable for maximum compaction and filling of possible voids.
Poured formwork requires regular maintenance. So, in order to avoid concrete drying out in the summer, the structure must be moistened with water from time to time and covered with polyethylene. If it becomes necessary to use the slab before the four-week period has expired, temporary supports must be erected.
In order to create additional sound insulation, it is recommended to pour crushed stone under the screed.
When creating a reinforcement slab for the floor, it is necessary to take care of additional sound insulation, since concrete has proven itself to be a good sound conductor. Sound insulation can be achieved by pouring gravel (expanded clay crushed stone) directly under the screed. Also in this situation, a cerosite sound-absorbing mixture is useful.
Making bends
Special requirements are imposed on the joints and locations of the bends of the rods, since they determine the strength characteristics. When determining the bend location of the rod, follow the recommendations:
- maintain the interval from the bend to the outer surface (no more than 50 millimeters);
- do not use short rods that have one inclined section and are freely located in the frame (“floating” rods);
- ensure the bending angle to the axis of the product is 45 degrees. It is allowed to increase the angle value for tall structures (more than 80 cm in height) up to 60 degrees, and for low structures working with point forces, decrease it to 30 degrees;
When placing bends, you must ensure that in the area where they are placed according to calculation, in any section normal to the axis of the beam, there is at least one bend
- make a bend on one longitudinal rod in each of the planes of the frame of the product, which has a width of less than 20 centimeters. When increasing the width of the product, bend at least 2 rods in each plane;
- position the bent parts of the rods symmetrically relative to the axis;
- Determine by calculation the interval between inclined sections of rods located in different planes of the frame.
Floor slab drawing
A drawing is made to ensure proper assembly of the floor. Using it you can calculate the consumption of all materials, from tying wire to the amount of cement.
Algorithm of actions:
- Before drawing up a drawing, you should take measurements of all rooms and the outer perimeter of the house if there is no design. They are made from the axis of the wall.
- All holes that will not be filled are marked.
- The contours of all load-bearing walls and parts of intermediate ones are drawn. A detailed diagram of the strapping, mesh, and reinforcement is made, indicating the thickness of the rod, joints and connections.
- The drawing indicates the size of the cells and the location of the outermost longitudinal rod from the edge of the fill.
- The dimensions of the profiled sheet for the lower plane of the slab are calculated.
When creating a grid diagram, in most cases the number of cells is not an integer. The reinforcement should be shifted and the same reduced cell sizes near the walls obtained.
All that remains is to calculate the material. Multiply the length of the rod by their number. Add the cost of joints to the resulting number and increase the resulting figure by 2%. Round up when purchasing.
Based on the overlap area, the number of plastic fasteners is calculated and how much rolled stock will be used for inserts between the meshes.
The cement composition is calculated based on the thickness of the floor and its area.
The reinforcement above and below must be covered with mortar with a minimum thickness of 20 mm. When air enters, corrosion forms on the metal surface and destruction begins. When creating a floor thicker than 15 cm, with reinforcement in 2 layers, more mortar is distributed at the top.
The drawing also serves to calculate the amount of formwork, support columns and wooden beams to create a lower supporting plane - a platform for pouring the floor.
Any developer can install the rods on the clamps and tie all the intersections with wire. To guarantee safety, it is better to entrust the calculations of floors and the creation of a house project to professionals.
Specifics of transverse reinforcement
When performing transverse reinforcement of the frame, fulfill the following requirements:
- Use vertical reinforcement elements if the beam height is more than 15 centimeters.
- Do not install transverse reinforcement if the height is less than 15 centimeters.
- If there is one longitudinal reinforcement bar or welded mesh, building codes allow for the absence of transverse bars.
- Calculate using a calculation method that takes into account the peculiarities of welding the frame, the value of the diameter of the rods located in the transverse plane.
Compliance with the size of the protective layer
Maintaining the required value of the protective layer, which is the interval from the reinforcement to the outer surface of the product, allows you to protect the frame from moisture penetration and ensure optimal operation in the concrete mass. In addition, the protective layer determines the fire resistance of the structure.
For beams intended for installation in foundations and prefabricated structures, the value should not be less than the diameter of the reinforcement and is 30 millimeters.
The fixed size of the layer is ensured by the use of special pads and plastic clamps, ensuring the immobility of the frame and the required position when pouring concrete. If concrete products have a cross-section of less than 250 mm, then the size of the protective layer for transverse reinforcement is one centimeter. With a larger cross-sectional size, one and a half centimeters is enough to provide a protective interval.
Gain Errors
In the process of reinforcing concrete structures, violations of the reinforcement technology occur, causing a decrease in the strength of concrete products. When performing work, pay attention to the following points:
- It is not allowed to use aluminum products, industrial waste, wire and substandard metal of any configuration instead of working pipe fittings. The use of these materials that do not have the necessary performance characteristics will cause concrete deformation and cracking.
- It is forbidden to heat the bend areas with an autogen, or use a grinder to file deformed areas. This causes weakening of the rods and will lead to irreparable consequences under the influence of forces. All operations for bending rods are carried out without artificial heating.
- Class A-III reinforcement rods are bent at an angle of no more than 90 degrees using a special mandrel, the radius of which is equal to 5 times the cross-sectional size of the reinforcement. Performing a bend at a full angle (180 degrees) reduces the strength of the structure by 10 percent.
Briefly about the main thing
When building a two-story house to cover between levels, it is most practical to focus on the technology of creating a monolithic reinforced concrete slab. The resulting design is in no way inferior to the factory elements. And in some respects it will even surpass them.
Before work, you need consultation with a specialist and competently performed calculations. And it’s not difficult to reinforce the slab. The main thing is to choose a rod of the required cross-section. And, guided by the technical documentation, tie it into the grid. Most likely you will need to prepare two such elements and connect them into a frame.