One of the most interesting ways to reduce heat loss in a room involves insulating the floor with polystyrene foam. Despite the existing prejudice against the use of foamed polystyrene, the method turns out to be incredibly effective and efficient, which to a certain extent compensates for all the shortcomings of polymer insulation.
The strength of extruded polystyrene foam is enough to carry out insulation directly over sandy fill, without screeding with concrete
Is it possible to insulate the floor with polystyrene foam?
The first and most important question that will need to be answered is related to the use of the material, how justified will it be to lay polystyrene foam on the floor, from the point of view of sanitation, hygiene and safety of people in the room.
Typically, opponents of floor insulation with polystyrene slabs refer to the following arguments:
- The material contains a large amount of foaming gas agent, which poses a certain danger to the respiratory system, mucous membranes and skin of people;
- Insulation with expanded polystyrene is unsafe due to flammability and the release of large amounts of toxic gases when heated above the decomposition temperature.
On the one hand, everything is correct. An outdated production technology, widely used in China and Southeast Asian countries, involves the use of freons for foaming polystyrene. In modern methods, freon has long been replaced by inert gases butane and argon. Therefore, the issue of safety of insulation based on polystyrene foam is directly related to the origin of the material.
A safe option for insulation with polystyrene foam with an intermediate layer of DSP
You can long ago forget about the risk of fire in insulation under the floor. Modern brands of polystyrene foam and extruded polystyrene foam contain special flame retardant additives, so the insulation practically does not burn and even self-extinguishes upon prolonged contact with an open flame. In addition, when planning to insulate the floor in your dacha from below with expanded polystyrene, you can always provide additional fire safety measures. For example, make insulation in several layers with gaskets made of mineral fiber or expanded clay.
The feasibility of using polystyrene foam for floor insulation can be explained by two points:
- Foamed polystyrene has the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient of all available types of insulation;
- The cost of installing floor thermal insulation compared to mineral wool or expanded clay will be much less, and the material itself, when installed correctly, can last much longer than its competitors.
The only significant disadvantage is the large number of brands of insulation. The industry produces foamed polystyrene in slabs and blocks for a variety of purposes, from insulating the walls of frame buildings, bathhouses, refrigerators to laying out the insulating base of foundations and the sole of highways. And everywhere different brands of polystyrene foam insulation are used.
Adding polystyrene chips to concrete
To give the concrete layer additional protective characteristics, granules of extruded polystyrene foam can be added to the solution (the latter can be purchased for approximately 1000-1800 rubles per cubic meter). This is done as follows.
Foam balls for concrete can be purchased pre-packaged
Step 1. A little water is poured into the prepared container, then dry cement is poured into it. All this is mixed with a mixer attachment until the consistency of thick sour cream.
Mixing the solution with polystyrene balls
Step 2. During the mixing process, polystyrene foam granules are added. The proportions of concrete can be very different - both 1:3 and 1:6.
Types of polystyrene foam for floor insulation
Thermal insulation based on foamed polystyrene is divided into two large groups:
- Foam plastics are produced in the form of blocks or sheets of large thickness, from 30 to 300 mm. They are a hot-pressed mass of granules 3-5 mm in size. Density, depending on the brand, ranges from 20 to 55 kg/m3, has low vapor permeability, and can absorb moisture in small quantities;
- Extruded polystyrene foam is produced in the form of sheets with a thickness of 10 to 150 mm. The material is a homogeneous mass of polystyrene saturated with bubbles. The density is noticeably greater than that of foam plastics and is impenetrable to steam and water.
The main difference between polystyrene foam and extruded polystyrene foam is its low mechanical strength. For comparison, you can take thin sheets of foam insulation and extruded material. Place it on an uneven surface, for example, on a platform strewn with pebbles, and step on it. The foam will become cracked and split into several pieces, the extruded insulation will remain intact, and perhaps several dents will appear.
Therefore, polystyrene foam is recommended for thermal insulation of closed surfaces where there is no high contact load. For example, it can be used as floor insulation along joists, or under screed and tiling the surface.
General information
Extruded polystyrene foam is a thermal insulating synthetic material created in the fifties of the last century in the USA by specialists from The Dow Chemical Company. It was then that a more modern technique of foaming a special “cocktail” of polymers during extrusion (extrusion through a die) was first used.
At first, the foaming reagents were carbon dioxide and freon. But since 1999, due to the fact that freon has a detrimental effect on the ozone layer of the planet, they began to use a freon-free method for manufacturing the material.
Extruded polystyrene foam
Technical characteristics and types of extruded polystyrene foam
| Index | Polyspen | Polyspen Standard | Polyspen 45 | Control method |
| Density, kg/m3 | 30-38 | 30-38 | 38,1-45 | 5.6 each |
| Bending strength, MPa, not less | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 5.8 each |
| Water absorption in 24 hours, % by volume, no more | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 5.9 each |
| Thermal conductivity at 25+-5 degrees Celsius, W/m * °C, no more | 0,028 | 0,028 | 0,030 | at 5.10 |
| Toxicity, Hcl 50, g/m3 | T2 moderately hazardous | T2 moderately hazardous | T2 moderately hazardous | at 5.11 |
| Flammability group | G-3 normal-flammable | G-4 highly flammable | G-4 highly flammable | at 5.12 |
| Flammability group | B-2 moderately flammable | B-3 flammable | B-3 flammable | at 5.13 |
| Smoke coefficient | High smoke generating ability | High smoke generating ability | High smoke generating ability | at 5.14 |
| Compressive strength at 10% linear deformation, MPa, not less | 0,2 | 0,2 | 0,3 | 5.7 each |
What thickness of extruded polystyrene foam is needed for floor insulation?
It remains to determine the power of thermal insulation, its design and the thickness of the polystyrene foam sheet placed in the base of the floor. The thickness of the floor insulation depends on several factors:
- Schemes for laying polystyrene foam in the floor, whether it will be a concrete screed or a standard insulation scheme using joists;
- The presence of a basement or additional insulation of the foundation;
- Is it planned to insulate directly on the ground, or will the insulation of the ground floor floor with polystyrene foam be done on an insulating basis?
Most capital buildings are placed on a strip, shallow or pile foundation. In this case, the logs or load-bearing floor beams are raised to the height of the base. An air gap remains between the floor insulation and the ground, which is actively warmed up due to heat leakage from the heated room on the first floor.
In general, the thickness of floor insulation with polystyrene foam in a frame house can be taken to be equal to the thermal insulation of the building walls. In this case, the thermal insulation power can be reduced:
- By 15% in the presence of additional filling of the ground with expanded clay, the use of insulating insulation of the foundation tape with sheets of extruded polystyrene foam or backfilling with foam glass;
- By 10%, provided there is a basement under the house without a garage.
Important! If a storage area for a car or any other similar room with a high ventilation rate is equipped under the building, the floor insulation must be no less than the thickness of the wall insulation.
In this case, it is necessary to lay insulation for the floor over concrete, and install the thermal insulation of the ceiling of the basement room separately.
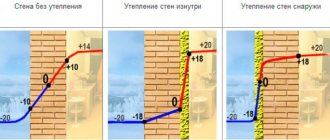
The plan is to insulate the floors in the bathhouse with polystyrene foam in a completely different way. Firstly, thermal insulation is formed from at least two layers with an air gap between them. The first layer, relatively thin, 25-30 mm, is laid from polystyrene foam, the second - from extruded polystyrene foam with a thickness of at least 50 mm. In general, the efficiency of floor insulation with extruded polystyrene foam is lower than for walls and ceilings. This is done deliberately in order to warm up the thermal insulation layer, the air gap, and even part of the soil underneath deeper and stronger. This is the only way to shift the condensation point, dry the subfloor using residual heat, and get rid of dampness on the floors in the bathhouse.
Where installation is allowed
Expanded polystyrene is recommended as insulation where an increase in the load on the load-bearing floors of the room is unacceptable, and in cases with low ceilings. During construction work, polystyrene foam is used to insulate:
- water pipeline;
- roofing;
- floor;
- door and window slopes;
- walls.
For example, thermal insulation of pipe materials with polystyrene foam for water-heated floors is considered financially justified due to its properties.
In addition, the use of block polystyrene foam makes it possible, in case of problems, to gain access to the pipeline by removing a separate section of the coating. For the same reason, the product is often installed when constructing warm electric floors.
Thickness of polystyrene foam for floor insulation on the ground
The power of thermal insulation and the insulation scheme directly depend on the characteristics of the soil, the saturation of the soil with water and the average air temperature in winter.
Under relatively mild frost conditions, at -5°C, the heat capacity and thermal conductivity of anhydrous sandy or peaty soil are only slightly higher than those of air. Wet soil, regardless of its composition, has a heat capacity and thermal conductivity approximately an order of magnitude higher than that of air.
Therefore, SNiPs regulating the process of insulating walls and foundations of residential buildings require that the thickness of floor insulation in a wooden house with extruded polystyrene foam be at least 100 mm in the presence of a sand-crushed stone cushion and at least 150 mm when laid out on a compacted and waterproofed soil base.
What is EPPS?
In everyday life, this material can be found under the name “foam plastic,” but this is fundamentally incorrect. These two materials are significantly different from each other. For example, extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) is one of the most deformation-resistant and durable varieties, and its heat-shielding properties are almost not affected by this.
High-strength EPS is produced on special production lines through chemical extrusion of the original raw material, which is pure polystyrene granules.
Using special equipment, raw materials are converted into foam, from which, in turn, small granules are produced. During the hardening process, these granules are pressed into layers of the required shapes and sizes, after which they can be used not only for insulating houses, but also for other purposes.
It is precisely due to its fine porosity that EPS is an order of magnitude stronger than ordinary polystyrene foam. These granules, pressed under high pressure and at high temperatures, give the material greater strength, hardness and reliability.
The main difference between extruded polystyrene foam and pressed polystyrene is in the characteristics of its granules. They are smaller, which makes this building material more resistant to physical stress. The size of granules of heat-insulating material produced by extrusion does not exceed 0.1 mm, while granules of non-pressed material can reach up to 10 mm.
In foreign interpretation, EPPS may be called XPS. It is produced in several varieties. After the abbreviation “XPS”, the markings of this material contain numbers from 25 to 45, which indicate its density.
The higher the value, the higher the density of the material. Particularly dense extruded material can even be used to insulate asphalt road surfaces, for example, the products ]Penoplex[/anchor].
Now that we have figured out what EPS is, we will discuss in detail all its pros and cons.
What tools and materials will be needed
First of all, you need to purchase a waterproofing film and the insulation itself. As waterproofing, you can use glass roofing felt, polyethylene with a thickness of at least 0.5-0.8 mm. The brand of thermal insulation is selected depending on the insulation scheme:
- When laying insulation directly on the ground under a concrete screed, extruded polystyrene foam is used;
- For insulation along joists, low-density foam is best suited.
It is advisable to purchase sheets of maximum thickness and not try to form floor insulation from several layers of insulation. A multi-layer floor insulation scheme has no advantages and often only causes moisture leaks and condensation.
When insulating, be sure to use film waterproofing
In addition, you will need to purchase polyurethane foam, an electric cutter for cutting polystyrene foam, or a special knife for cutting polystyrene foam. The same tools can be used for cutting hydro- and vapor barrier films. If you plan to insulate over a concrete screed, you will additionally have to purchase mounting mushrooms and rent an impact drill with a set of carbide drills.
Review of manufacturers
When choosing a model for insulating a garage floor with polystyrene foam, we pay attention to the manufacturer of this material. The main guarantee of a long service life is compliance with technology during manufacturing. Currently, there are a number of companies whose products meet quality standards. Among the foreign ones the following can be distinguished:
- Basf;
- Polimeri Europa;
- Nova Chemicals.
Products from Russian manufacturers are no less quality:
- TechnoNIKOL;
- Penoplex.
To create a heat-insulating layer, it is best to use materials of the same brand. Even a slight difference in manufacturing technology can affect their compatibility.
© 2022 prestigpol.ru
How to insulate a concrete floor with polystyrene foam
Initially, you will need to decide on the final flooring option. If you plan to make a protective screed on top of the installed insulation, lay plywood under laminate or parquet floors, then, in principle, you can use foam plastic with a density of at least 35 kg/m3. If a concrete screed is poured over the insulation without further finishing, then only extruded polystyrene foam should be used.
Important! In any case, low-density foam cannot be used, otherwise, even with screed reinforcement, cracks and breaks will appear. The surface of the foam sheet can be easily deformed even with your fingers.
Floor insulation scheme for concrete in an unheated room
Preparing the site for insulation
It is impossible to lay thermal insulation sheets directly on concrete without preparation. Firstly, the foamed polystyrene should fit as tightly as possible to the concrete surface, without any cracks or gaps. Otherwise, the thermal insulation will “play” under load and deform. As a result, the finishing screed, which will be laid on top of the polystyrene foam, will become covered with cracks.
Secondly, moisture will accumulate in the gaps between the base and the insulation, which at low temperatures will turn into ice and tear the polystyrene foam away from the surface with all the ensuing consequences.
Therefore, a little preparation is required:
- We dilute a small amount of dry plaster to level concrete walls; on average, no more than a liter of mixture is required per 1 m2;
- We sweep the concrete floor, use a spatula to fill in small cavities and depressions;
- We check the condition of the surface using the usual rule or a steel bench ruler.
After cleaning and leveling, leave the surface for five to six hours to harden and set the repaired areas. For old floors, it is sometimes more convenient to fill one common screed. In any case, there should be no voids, otherwise polystyrene foam will be ineffective as insulation for concrete.
Laying polystyrene foam
If thermal insulation is laid in a non-residential area, then the process of laying out sheets is noticeably simplified:
- We lay a row of expanded polystyrene slabs from wall to wall;
- We cut with a knife or cutter - we adjust the dimensions and geometry so that the ends of the sheets are adjacent to each other with a minimum gap;
- We number the sheets, disassemble the row, apply a small amount of tile adhesive to the back side, carefully and evenly rub it over the surface of the polystyrene foam;
- We lay the thermal insulation, load it with a small load, about 2-3 kg for each square meter.
After a few hours, we seal the joints with tape and move on to laying the next row. If there is a slight difference or step left on the seams, it’s okay; subsequent filling with screed will hide the defects.
If the insulation of a concrete floor is carried out in a residential, constantly heated room, then the seams on the glued slabs are cut at an angle or cut and additionally blown with foam.
Floor insulation can also be made from extruded polystyrene foam. For this purpose, sheets with tongue-and-groove type end locks are used. It is enough to lay the panels on the floor, even without any glue, connect the locks and secure the insulation to the concrete using fungi. It is clear that the joints also need to be foamed.
It is better to reinforce a concrete screed with at least one layer of mesh
Final sealing of insulation
The insulation laid on the floor should be checked for any raised areas. If there are any, then we attach the polystyrene foam to the concrete using a dowel-fungus.
Attaching thermal insulation to concrete using fungi
The next step is to carefully trim the remaining foam and treat the insulation surface with a deep-penetrating acrylic primer. After a couple of hours, you can pour the concrete screed or glue the plywood. Of course, you will need to lay a waterproofing film under the screed. If reinforcement is used in the future concrete floor, then the mesh will need to be raised above the film, otherwise the metal will tear the waterproofing to shreds under load.
Methods for fixing coolant
There are several ways to fix the coolant.
Reinforcing mesh and ties
The pipes are fastened to a reinforcing mesh with cells 10 x 10 cm using plastic ties. As the pipe is laid to the mesh, it is fixed with plastic ties, cutting off the protruding tails. The pipe is secured with plastic ties every 1–1.5 meters. When bending a pipe 90 degrees, it is enough to use a pair of plastic ties; when bending 180 degrees, use three ties. The advantages of this method include simplicity and reliability, as well as the availability of plastic elements. The disadvantages include the labor intensity of the work, the likelihood of damage to the pipes on the mesh, especially if they are made of metal-plastic, when walking on the floor. Voids may form at the point of contact between the pipe and the mesh, which will lead to a decrease in the thermal efficiency of the floor.
Fixing pipes to the reinforcing mesh with ties
Reinforcing mesh and plastic fastenings
Manufacturers offer special devices for fixing pipes to reinforcing mesh. By fixing the mesh with a clip-mount, it and the coolant pipe are raised above the insulation. This ensures even distribution of the screed under the mesh and under the pipe. Thus, the mesh becomes an additional reinforcing layer, and maximum heat transfer is achieved from the surface of the pipe.
Special plastic fasteners
The advantages of this method of fixing the coolant include:
The disadvantages include the higher cost of fastenings compared to plastic ties.
Attaching the pipe to plastic guides
Pipes can be fixed using plastic guides laid on smooth polystyrene foam. Their length can vary, but more often they are 50 cm long and are inserted into each other, secured with clasps. In this way, they can acquire any required size depending on the parameters of the room. Before fixing the guides, you need to know the pipe layout pattern in advance. The planks can be laid in any pattern. They are attached to polystyrene with U-shaped plastic brackets. The pipe snaps tightly.
One of the advantages is the quick and convenient layout of pipes and their reliable fixation. The disadvantages include the complexity of preliminary marking and the lack of additional screed reinforcement.
Fixing pipes using plastic guides
Laying on polystyrene foam boards with fixation
Slabs with bosses require additional fixation. The bosses play the role of guides, helping to lay the pipe in any pattern, and anchor brackets are used to secure them. They are also used when attaching to foil-coated flat polystyrene.
The advantages include the prevalence of such fasteners and mats in hardware stores; the bosses protect the pipe from damage and make the installation process easier. The disadvantages include the high cost of the slabs and the need to use additional means of fixing the pipes.
Fastening with plastic brackets
Mat with lugs with fixation
Modern manufacturers have improved polystyrene foam mats with bosses, correcting their shape so that they firmly hold the coolant pipes. The laying step should be a multiple of 50 cm. The advantages include reliable, durable and convenient fixation of the pipe. Such a mat is both insulation and a means of fixing the pipe. The ceiling is rigid and does not bend under loads, the pipe is reliably protected from damage. In addition, this mat is an excellent combination of price, convenience and reliability. The disadvantages include the high cost of the plates.
Improved bosses securely fix the pipe
Video - Advantages of mats
Velcro fastening
New – fastening pipes with Velcro. Fixation occurs due to reliable adhesion of the tape wrapping the pipe and the fleecy base. When laying, the pipe adheres tightly to the insulation. The advantages include speed of installation, ease of installation and fixation, and no need to use additional fastening devices. One of the disadvantages is the lack of markings, which complicates installation. There is an assumption that the pipes may shift when walking on the floor.
Prices for polystyrene foam for heated floors
Floor insulation on joists with polystyrene foam
There are two ways to install polystyrene foam boards in a wooden floor box. The first is using polyurethane foam, the second method is to lay foam slabs between the joists “dry”, only by wedging the material.
There are many prejudices against the use of polystyrene foam in wooden
In fact, foamed polystyrene is no worse or better than other types of insulation; an exception can be made only in the case of insulating the floor in a steam room of a bathhouse.
In a residential, constantly heated room, polystyrene foam can simply be glued onto the foam into the space between the joists:
We first lay the waterproofing film on the bottom plank flooring. Be sure to turn the edges of the canvas down towards the ground. In this case, there should be a free space or air gap of at least 2-3 cm high between the foam plastic and the film insulation. Thanks to it, some of the water vapor will go lower, into the ventilated space under the floors.
After laying the foam, we lay a vapor barrier. Again, there should be an air gap of 35-40 mm between the finished floors and the film vapor barrier. If polystyrene foam is laid flush with the joists, then before laying the floorboards you will have to fill the counter-batten.
For cold rooms, waterproofing is laid in an “accordion” or “wave” manner, covering the joists and all parts of the supporting wooden structure. In this case, the insulation is laid with a slight tension, without glue, on top of the waterproofing. All that remains is to lay a vapor barrier, sew a counter-batten onto the joists and lay the finished floor.
If there is no basement
*
Here all processes are carried out from the premises.
- The so-called cranial bars are packed along the joists along their lower edges.
- The logs are laid across them and boards, plywood, OSB, chipboard, etc. are attached.
- A waterproofing membrane is laid along the joists and formed niches so that it exactly follows the contours of the assembled joist structure. Pay attention to the photo below. This is how waterproofing should be installed.
Waterproofing a wooden floor
All other operations are carried out in exactly the same way as in the previous case.
Insulation of the basement floor with extruded polystyrene foam over the ground under the screed
For any types of insulation associated with direct contact with the soil or ground surface, foam plastic, regardless of its density, is not used. The use of extruded polystyrene foam is allowed. This is due to the defrosting process, that is, the foam can be destroyed by severe watering, in low temperature conditions.
Preparing the backfill for laying thermal insulation
The soil base will need to be prepared for laying insulation. To do this, we dig up the floor in the basement and remove the soil, about the size of a shovel. We clean and compact the base; the easiest way to do this is with a sledgehammer mounted on a shovel shaft.
The next stage is to lay strips of extruded polystyrene foam, 25 cm high, around the perimeter of the basement floor. To prevent the tape from moving away from the concrete walls, it can be secured with pegs.
Next, we fill the floor with a layer of fine gravel; it’s even better to use screenings for insulation. The thickness of the fill is 10 cm. We lay an agrotextile fabric on top of the dry gravel and pour a layer of sand 5-7 cm thick.
Laying EPS boards
We lay a polyethylene waterproofing film on top of the sand cushion, seal the joints with tape, wrap the edges onto the concrete walls and glue them to the upper edge of the previously laid extruded polystyrene foam insulation.
To insulate the floor in the basement, we use 50 mm thick slabs, join the sheets together in locks and lay the insulation on top of the film.
We glue the joints with tape, including the gap with the previously laid insulation of the lower part of the walls.
Final finishing
The face screed in a basement is always subject to soil pressure, so the concrete must be reinforced. We apply a deep penetration primer to the lower part of the walls and to the polystyrene foam and lay a mesh of reinforcement.
Next, we install leveling beacons or simply place chips of the same height on the EPS. We fill the screed with liquid concrete, after 6 hours we take out the beacons and seal the remaining holes in the concrete. The level of the screed should be at least 40 mm higher than the previously installed wall insulation.
Technology for installing polystyrene foam in the Warm Floor system
Polystyrene foam or EPS can be used in underfloor heating schemes using central heating hot water. It is believed that foamed polystyrene maintains structural stability during prolonged heating to 100°C. Therefore, it is best to use it for film and water heating systems.
Floor insulation scheme with pipe laying in polystyrene foam
Thermal insulation for the water circuit
The easiest way to insulate a system is to lay heating pipes in grooves pre-cut in a sheet of polystyrene foam. The heating scheme with complete immersion of the circuit in foam is more economical and safe.
We install insulation in the following sequence:
- We protect the concrete, cover it with a primer and glue high-density foam sheets with a thickness of at least 50 mm;
- We mark the lines for laying the water circuit pipes;
- Using a metal ruler and a cutter, cut out an initial triangular groove in the insulation;
- We cut the grooves for the pipes again, but with an electric cutter with a heating edge in the form of a loop. We convert the triangular profile into an arcuate one. The depth must correspond to the diameter of the pipe;
- We lay heated floor heating pipes in polystyrene foam insulation;
- Glue aluminum foil on top with a thickness of at least 0.5-0.8 mm;
- All that remains is to fill the leveling screed or cover the floor with plywood. A floor covering in the form of linoleum or laminate is laid on top of the insulation.
How to insulate a floor with a film heating element
The general insulation device for a wooden floor on joists is shown in the diagram below.
In this case, extruded polystyrene foam is used, glued onto mounting foam along the lower level of the load-bearing beams. There should be an air gap of at least 3 cm high between the floor covering and the graphite film. This will help equalize the heating and avoid pressure on the heating element when the floorboards sag strongly.
Under the film, on top of the polystyrene insulation, we lay foil or a vapor barrier like Izospan FB.
A similar scheme can be used for a floor on a concrete screed. Instead of joists, wooden slats are glued onto the foam on the floor and immediately insulation is laid from expanded polystyrene with a thickness of at least 20 mm. The base for the floor covering is laid from plywood 10 mm thick. Thicker material increases heat leakage into the concrete, sheets less than 10 mm are too weak, the floor can sag to a depth of 5 mm, and this is too much for heating systems.
Parameters for choosing insulation, what we pay attention to
When purchasing floor heating from expanded polystyrene, you should take into account indicators such as: quality and variety.
Initially, the quality of polystyrene foam boards for heated floors is determined by their appearance. The following points should be taken into account:
For your information! Experts recommend especially inspecting the place of the cut or break. If the granules are intact in this area, we can talk about their poor adhesion to each other. In a high-quality slab, when broken, the granules should also be destroyed.
Recommendations and common mistakes
Often, owners try to save on auxiliary materials, such as polyurethane foam, tile adhesive or plastic film. Any attempts to lay polystyrene foam even on the smoothest concrete, without fixing it with glue, are doomed in advance to further destruction of the insulation at the joints and seams.
The second mistake is related to improper arrangement of vapor barrier. A membrane with one-way water vapor conductivity should always be used. Moreover, the insulation system must have vents that ensure normal ventilation and removal of steam from the warm side of the concrete towards the colder surface.