A cozy bathroom needs heating. It is ensured by water circulation through risers and heated towel rails
Circulating water supply began to appear in apartment buildings from the late 70s of the last century. Today we will figure out what its benefits are, how it is implemented in old and modern engineering systems, and how to ensure circulation in a private home.
Coarse filter
As mentioned above, one of the reasons that there is no coolant circulation may be the accumulation of debris in the pipeline.
To completely avoid this, again, we don’t save a penny, but install a coarse filter in front of each device: Using a filter, catching dirt is easier than correcting the consequences of a clogged pipeline or boiler heat exchangers.
Conclusion! We place coarse filters in front of each heating system device (pump, boiler, etc.) and in front of each plumbing fixture. We do NOT save pennies to “buy” problems. There are arrows stamped on the filter housing indicating the direction of movement of the coolant or water in the water supply...
The filter needs to be cleaned regularly. And this is very simple to do: close the valves before and after the filter - unscrew the plug (1) on the filter - remove and rinse the mesh under the tap - put it in place and tighten the plug. All. Not like changing pipes
These are the simple “body movements” you need to perform in order to never complain that there is no circulation in the heating system. Good luck.
The heating system must ensure uniform heating of all rooms. If the temperature in radiators or risers drops, this is often caused by a circulation problem. For efficient operation of the heating network and comfortable climatic conditions in housing, there must be free circulation of coolant through the main line. This should be taken into account at the design stage. Why there is no coolant circulation in the riser and main and what needs to be done, you should know thoroughly in order to promptly eliminate this problem in the future.
Reducing clearance in old heating pipes
In old “Khrushchev” buildings, problems in the heating system are obvious and predictable. There, the service life of the pipelines has long expired, and therefore they cause not only a decrease in heat, but also accidents. Over many decades, the pipes become so clogged with sediment that they are unable to provide normal circulation. The decision must be drastic - replace all the pipes.
In addition, a decrease in pressure in the system is caused by the formation of scale on the heat exchanger of the heating boiler. Using too hard water leads to such consequences. To prevent a similar problem with heating devices, special water softening agents are added to the system.
Rules of operation and maintenance
In order not to encounter situations in which the circulation pump installed in the heating system will require repair, it is necessary to strictly follow the operating rules for such equipment, which are as follows.
If there is no water in the pipeline, the circulation pump cannot be started. The amount of water pressure generated must be within the characteristics specified in the technical data sheet of the circulation pump
If the device produces a reduced or, conversely, increased water pressure, this can lead to its rapid wear and, accordingly, failure. During the period when the heating system is not in use, the pump must be turned on for circulation at least once a month for a quarter of an hour, which will prevent oxidation and blocking of its moving parts. It is very important to ensure that the water temperature in the heating system does not exceed 65°. In water heated to a higher temperature, sediment begins to actively fall out, which, interacting with the moving parts of the hydraulic machine, contributes to their active wear and, accordingly, failure of the entire device.
Periodic checking of the circulation pump will significantly reduce the likelihood of its failure during the heating season
Checking the circulation pump for correct operation includes actions such as:
- turning on the hydraulic machine to operating mode and checking the level of noise and vibration it creates;
- checking the pressure (pressure level) of the coolant created in the discharge pipe (as mentioned above, the liquid pressure must be within the values given in the technical data sheet);
- control of the degree of engine heating, which should not be too high;
- checking the presence of lubricant on the threaded connecting elements of the pump and applying it if it is missing;
- checking the presence and correct grounding of the hydraulic machine body;
- checking for leaks both on the pump body and in the places where it is connected to the pipeline (if there are leaks in such places, it is necessary to tighten the threaded connections and check the integrity of the installed gaskets);
- inspecting the terminal box and checking that the wire is fixed in it (in addition, it is necessary to check whether moisture is getting into the terminal box, which is unacceptable).
The main reason for the rapid wear of friction bearings in pumps is considered to be increased contamination of the coolant.
Temperature standards
It is quite difficult to regulate heating in a residential apartment building. Even if residents have access to the system and the ability to increase/decrease the heat supply, it is not always possible to find a common language with their neighbors. In this case, it is worth focusing on the current regulations.
Temperature standards are regulated in accordance with GOST R 51617-2000, approved. . According to this document, the minimum temperature in apartments during the heating season should be:
- in living rooms, toilets, and kitchens - at least 18˚С;
- in the bathroom - not lower than 25˚С;
- in corner rooms, regardless of purpose, as well as for families where disabled people live - 2˚C above the established norm.
If the readings in your apartment are lower, you can safely demand an increase in temperature.
Read more about what temperature standards are set in the apartment.
Poor quality equipment
Due to the wide range of heating boilers and the variety of models and manufacturers, the buyer can easily make a mistake in choosing the right unit. Therefore, it is necessary to focus on the approved project. All parts and elements of equipment must meet its requirements.
It is according to the plan that a certain type of radiators with a suitable number of sections in them is purchased. Shut-off valves, adjusting elements and connecting units must be mutually compatible.
Most often, problems arise due to insufficient circulation of coolant through the pipes
. Special pumps can enhance the movement of water, but they must be chosen carefully, otherwise the devices will become a source of hum and noise. Additionally, old iron pipes are replaced with modern products made of metal-plastic or polypropylene. This will avoid some problems in certain heating systems.
Plastic pipelines are easy to install and connect to the boiler, but it is better to entrust this work to a specialist. After all, not all types of plastic are suitable for use in heating equipment; some models cannot withstand high temperatures and burst under their influence.
Installing a heating meter
Many are not satisfied with paying for heat at an average tariff based on consumption standards. In this regard, some people prefer to install a heat meter and pay only for the heat received.
The design features of heating systems, in particular, the widespread vertical distribution, do not allow apartment-by-apartment accounting of consumed heat, be it an open or a closed heating system of a high-rise building.
The only way out is door-to-door accounting. In this case, the procedure will be as follows:
- The management organization develops technical specifications for the installation.
- Housing departments or residents purchase a heat meter on their own.
- Based on the documents for the meter, a project for its installation is developed and agreed upon with the heat supply organization.
- The metering device is installed, the heat supply representative seals the meter and draws up the corresponding report.
Find out how a common house heat meter is installed in an apartment building.
Preventing heating problems
Preventative work should be performed in the summer. It is better to combine them with major or current repairs. For the heating system to work properly, you need to:
- analyze the heating operation in the previous winter, find weak points;
- check the operation of shut-off valves, repair or replace faulty ones;
- if Mayevsky taps or valves for supplying coolant to heating devices are missing, they should be installed;
- check the slopes of the supply pipes, eliminate violations, if this is not possible, install Mayevsky taps in problem areas;
- flush or replace radiators that did not heat up enough during the previous heating season.
Prepare your heating system for operation in the summer and the likelihood of failures will be greatly reduced.
Is assembly required
If the radiators are supplied assembled, it is enough to install plugs and a Mayevsky tap. Most models have four holes located at the four corners of the body. They are used to connect heating lines. In this case, any scheme can be implemented.
Before installation of the system begins, it is necessary to close excess holes using special plugs or air vent valves. The batteries are supplied with adapters that must be screwed into the collectors of the product. In the future, various communications should be connected to these adapters.
Prefabricated models
Assembling batteries should begin by laying the entire product or its sections on a flat surface. Best on the floor. Before this stage, it is worth deciding how many sections will be installed. There are standards that allow you to determine the optimal amount.
The sections are connected using nipples having two external threads: right and left, as well as a turnkey lug. The nipples should be screwed into two blocks: at the top and at the bottom.
When assembling the radiator, be sure to use the gaskets supplied with the product.
It is necessary to ensure that the upper edges of the sections are correctly located - in the same plane. The tolerance is 3 mm.
Design, types and principle of operation of circulation pumps
Without knowing the structure of the circulation pump, you will not only be able to repair such a hydraulic machine if the need arises, but also carry out its regular maintenance. The design of circulation pumps consists of:
- body made of stainless steel or non-ferrous alloys;
- an electric motor whose shaft is connected to the rotor;
- The rotor itself, on which the wheel with blades is installed, is the impeller (its blades, which are in constant contact with the pumped medium, can be made of metal or polymer materials).
Circulation pump design
The circulation pump operates, regardless of its design, according to the following principle.
- After applying electric current, the drive motor shaft begins to rotate the rotor on which the impeller is mounted.
- The coolant liquid entering the internal part of the pump through the suction pipe is thrown away by the impeller and centrifugal force to the walls of the working chamber.
- The liquid, which is affected by centrifugal force, is pushed into the discharge pipe.
As mentioned above, depending on the design features, the heating circulation pump can be of different types. Thus, devices with a rotor are distinguished:
- "wet";
- "dry".
In private homes, “wet” type circulation pumps are most often used.
For circulation pumps of the first type, which are used primarily to equip household heating systems, the rotor is constantly in a liquid medium. This contributes not only to the lubrication of moving elements, but also to their effective cooling. The main advantages of this type of equipment include:
- low noise level during operation, since the water in which all the moving elements of such a device are located perfectly absorbs vibrations;
- ease of installation (such pumps simply cut into the pipeline), maintenance and repair.
Meanwhile, pumps with a “wet” rotor, if we talk about their disadvantages, are characterized by not very high efficiency, can only be installed in a horizontal position and are very critical of the lack of liquid in the heating system.
Pumps with a dry rotor are installed in separate boiler rooms and are used in systems that heat large areas
The drive motor of pumps with a dry rotor is placed in a separate unit. Rotation from the electric motor shaft is transmitted to the impeller through a special coupling. Unlike devices with a “wet” rotor, pumps of this type are characterized by a higher efficiency (up to 80%), but also a more complex design, which somewhat complicates their maintenance and repair procedures. Circulation pumps with a dry rotor are cut into the pipeline and their housing is attached to the wall, for which a special console is used.
Pump design elements
In order for the operation of the circulation pump to be problem-free, it is necessary to regularly check the condition of the equipment. A preventive inspection will help identify negative factors that can lead to serious breakdowns in the future. Their timely elimination will allow you to avoid force majeure situations and complex repair procedures.
A standard inspection includes a few simple steps:
- checking the tightness of connections. It is necessary to carefully inspect all fittings with which the pump is attached to the heating system. Some types of connecting elements may become loose over time and must be tightened. In addition, problems may arise with the destruction of the thread or seal - in this case, you need to unscrew the fitting, cut additional turns or wind a new layer of FUM tape, and then reassemble the element;
- adding lubricant. There are bearings inside the device that must be well lubricated. Otherwise, they will work worse, which will lead to overheating of the device;
- cleaning the filter. The mesh element gradually becomes clogged with dirt, even if you use a very high-quality coolant. Therefore, it is necessary to promptly remove rust and scale particles stuck in the filter.
Actually, this is a basic set of actions that need to be performed for prevention. In addition, you should follow some rules for operating the circulation pump:
- Avoid dry running. The pump should only be turned on if the required amount of coolant is present in the heating system. Equipment running “dry” will burn out very quickly, and may even drag down some other electrical appliances;
- Avoid prolonged idle time. In many regions, the heating system operates in seasonal mode - from September to May. It is clear that there is no point in launching it in thirty-degree heat. But if left idle for such a long time, some elements of the circulation pump may fail. Therefore, it must be turned on at least once a month for a quarter of an hour. Agree, it takes a little time, but it will help to avoid possible problems in the future;
- initially purchase a pump whose characteristics fully correspond to the needs of your heating system. It happens that owners, in an attempt to save money, buy a low-power device and try to use it in a system with a large volume of coolant. As a result, the device constantly works at the limit of its capabilities and, of course, fails very quickly. That is why it is important to make advance calculations of the parameters that you should focus on when purchasing. You can find information on how to do this on our portal;
- provide for overheating and “dry running” sensors. These regulators are not available on all models, but it is advisable to find and purchase a device with them. You may not immediately notice the problem on your own. For example, if there is a coolant leak in the system, then until you detect it, the pump will run idle and may simply burn out. And the sensor will react instantly, automatically turning off the equipment, and thereby preventing breakdown.
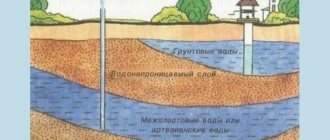
Basic physical parameters of a natural circulation heating system
Circulation pressure Рc is a physical quantity determined by the difference in the heights of the centers of the boiler and the lowest heating device (radiator).
The greater the height difference (h) and the difference in densities of heated (ρ g) and cooled (ρ o) liquids in the system, the better and more stable the coolant circulation will be.
R c =h(ρ o -ρ g)=m(kg/m 3 -kg/m 3)=kg/m 2 =mm.water column.
Let’s “look” for the reason for the appearance of circulation pressure in a heating system with natural circulation in the “wild” of the laws of physics.
If we assume that the temperature of the coolant in the heating system “jumps” between the centers of the devices (boiler and radiators), that is, the upper part of the system contains hotter water than the lower part of the system.
Density (ρ g)(ρ g).
We cut off (mentally) the upper part on the circuit diagram and... What do we see? A familiar picture from school - two communicating vessels located at different levels. And this will lead to the fact that liquid from a higher point, under the influence of gravitational force, will flow to a lower one.
Due to the fact that the heating system is a closed circuit, the water does not splash out, but simply strives to equalize its level, which leads to the heated water being pushed upward and to its further “independent gravitational” path through the heating system.
The conclusion is this! The fundamental indicator of the circulation pressure is the difference in the installation heights of the boiler and the last (lowest) radiator in the system. Therefore, in heating systems of private houses, boilers are located in basements whenever possible, observing a maximum height of 3 m.
In apartment versions, they try to “deepen” the boilers to the floor slab, accordingly “fireproofing” the “nest” where the boiler is placed in the floor.
According to the formula given above, the difference in the densities of cold and hot water in the system also has a significant influence on the circulation pressure.
A heating system with natural circulation is a self-regulating system, that is, for example, when the heating temperature of the coolant increases naturally (see formula), the circulation pressure and, accordingly, water flow increases.
At low temperatures in a heated room, the difference in water densities is large and the circulation pressure is quite large. When the room is heated, the coolant no longer cools down as much in the radiators, and the difference in the densities of the heated and cooled coolant decreases. Accordingly, the circulation pressure decreases, reducing the “consumption” of water.
Is the air in the room cool? For example, someone opened the doors to the street. The density difference increased again, increasing the water pressure.
Background
Dead-end cold and hot water supply systems are typical for buildings built by Stalin and Khrushchev. In a dead-end system, the bottling flows into risers, and each riser ends with a water supply on the top floor with a cistern and mixers connected to it. Water in such a system begins to move only at the moment when one of the residents opens the taps.
Black pipes - tie-ins of a dead-end hot water system into the supply and return of the heating network
For cold water this is quite acceptable, but in hot water it has a couple of unpleasant consequences:
- If in your part of the house (along a riser or in a group of risers) no one has used hot water for a long time, it cools down in the pipes. Yes, yes, despite the thermal insulation of the bottlings: insulation slows down cooling, but does not stop it completely.
As a result, in order for hot water to come out of the tap, you are forced to drain cold water for several minutes: its volume with a DHW filling diameter of 80-100 mm can amount to tens of liters;
Do you want to wash your face? Drain the cooled water in the pipes!
Please note: this situation is especially bad for the owners of water meters installed in the apartment. They drain cold water and pay for hot water: there are no temperature sensors on mechanical metering devices.
A mechanical device takes into account water flow without recording its temperature
- Heated towel rails were installed everywhere in Khrushchev-era bathrooms. They are connected to the gap in the hot water supply, between the riser and the taps, and heat up only when water is consumed in that particular apartment.
Khrushchev: the dismantled heated towel rail was installed between the water supply and the riser
Since hot water is rarely used for more than an hour a day, these appliances sit cold most of the day and night. Hence the musty smell of towels, cold and dampness in the bathroom, and often fungus on the walls.
Mold is one of the consequences of cold in the bathroom
A revolution in the design of domestic hot water systems took place on January 1, 1977, when SNiP II-34-76 was released. Paragraph 2.8 directly stated that hot water supply must now be designed with continuous circulation of water through ring jumpers and risers.
The document has now been canceled, but there are current reissues of it.
What the circulation of water in the water supply system does is quite obvious: from now on, the water in the hot water supply and in the risers has become hot around the clock. To heat the water flowing from the tap, it is enough to drain the few liters of water that are in the water supply.
Heated towel rails migrated from the supply to the riser and began to heat constantly - as long as circulation was maintained in the risers. As we will find out later, it is possible that this circulation may stop.
In new houses, dryers are connected not to the inlets, but to the risers
Pipelines: reasons for low heating
Determining air pockets in batteries using a thermal imager
Failures in the heating mode are typical for a two-pipe heating system. In this case, the supply line that distributes the coolant to the radiators does not heat. Identification of the “problem” area can be done by measuring the temperature on the surface of the pipes or a thermal imager.
Natural circulation
Pipe slope for heating with natural circulation
What could cause such problems? If the heating does not heat well, the slope of the line may not be observed. This only applies to natural circulation systems. According to the standards, the slope of the pipes should be 10 mm per 1 m.p. In addition, the direction is taken into account - from the accelerating riser to the radiators. For the return pipe, the slope must be towards the boiler.
At the first stage, it is necessary to measure this indicator using a building level. If it meets the standard, but the heating radiator does not heat, there is a possibility of air pockets forming. In this case, an integrated approach is recommended, which includes the following steps:
- Measuring the angle of inclination. If necessary, change it to the required value;
- Flushing pipes to remove limescale;
- Filling the system with coolant with open Mayevsky taps on the radiators.
This technique will eliminate the low heat transfer rate of the heating system.
Forced coolant circulation
Operating principle of the air vent
For a system with forced movement of water in pipes, the formation of air locks can be avoided by using an air vent installed at the top of the system. In part, it performs the functions of an open expansion tank, but it does not reduce the pressure in the pipes to a critical level. Its absence is an indirect cause of poor heating of the radiator.
The specificity of closed heating systems is that it is not necessary to comply with the installation level of the pipes. However, when the critical heating level of the coolant is exceeded, steam is released, which is the main cause of air locks. Since air has a lower density than water, it will concentrate in the upper region of the pipeline sections. If heating radiators in a closed system do not heat well, the reason may be a decrease in the volume of coolant in the pipes due to air resistance.
What needs to be done in this case? First of all, check the functionality of the air vents. If the valve is idle for a long time, it may become covered with limescale, which makes it impossible to open it under air pressure.
In addition to this factor, it is necessary to take into account the excess of hydraulic resistance in the system. This is why the heating battery does not heat if the initial calculation is incorrect. Therefore, before you begin installing a new system or upgrading an old one, you should perform the calculation of the operational and technical parameters:
- Selection of pipes of the appropriate diameter - the larger it is, the lower the hydrodynamic resistance. However, this increases the volume of water;
- The likelihood that a two-pipe heating system will not heat is significantly less than that of a single-pipe one. Therefore, it is preferable to install radiators with parallel connections;
- Heating of the heating circulation pump occurs due to incorrectly selected power. It directly depends on the calculated hydrodynamic parameters.
The video shows the main reasons for poor radiator heating for a single-pipe heating system:
What are the consequences of inefficient operation of heating devices?
The problem of uneven heat distribution in a heating radiator cannot be solved by itself. If you do not pay attention to it, it is fraught with the following consequences:
- The efficiency of heating equipment decreases;
- The apartment becomes cold;
- The risk of a pipe burst increases;
- Economic losses. If in an apartment building the heat meter is common to the building, then the cost of services will be divided among all heat consumers, although the heat output will be low.
- There is a possibility of freezing the heating system. This possibility is unlikely, but such cases occur periodically.
If the air temperature in the room does not meet established standards, then residents will be forced to pay utility bills not for the supplied heat, but for the cold air.
In addition, people connect electric heating devices, which entails increased energy costs. Optimal room temperatures:
- living room and bedroom - from + 18 to + 22°C;
- toilet - + 18°C;
- bathroom - from + 20 to + 25°C;
- corner room - from + 20 to + 24°C.
According to GOST, at night (from 00:00 to 05:00) the temperature can drop by 3 degrees, which is not a deviation.
If the reason for the cold bottom of the radiators is a system failure due to the fault of the heat supplier, you need to write a statement to the management company with a clear description of the problem. The housing office is obliged to send a technician who will measure the temperature of the coolant, air and radiators.
As a result, the heating tariff may be recalculated.
If equipment failure is detected in the apartment, prepare for the following consequences:
- repairs are carried out at the expense of the owner of the house;
- If the equipment is outdated, then replacement is carried out by the owner of the apartment.
If the neighbors are proven guilty, they are obliged to fix the problem.
Recommendations for disassembling the circulation pump
Before disassembling the circulation pump, if the need arises (for example, during repairs), you must disconnect it from the power supply and remove it from the pipeline by unscrewing all fastening threaded elements.
After the pump has been removed from the heating system, you can begin to disassemble it:
- The cover is removed and secured to the pump body using special bolts.
- After removing the cover, the impeller is removed from the inside of the pump.
After this, access to all internal parts of the pump will be provided; they can be inspected, cleaned or replaced with new ones, if necessary.
Features of installation of various types
The material from which a particular heating element is made imposes certain requirements for its installation. While cast iron is not afraid of serious mechanical stress, others require special care.
Cast iron classic
Cast iron radiators are still relevant. The special characteristics of the material used in their manufacture make it possible to effectively heat a room of any size due to slow cooling.
To install such a heating element correctly, before connecting you should:
- disassemble the finished product into sections;
- Having pulled out all the nipples, assemble the product in the reverse order.
When performing installation work, it is worth taking into account the weight of the product and the composition of the material from which the house was built. The heating element can only be installed on brick and concrete walls. The battery is installed near a plasterboard wall on a floor stand.
Modern models
Such products are characterized by low weight and increased fragility. For them it is necessary to provide a Mayevsky crane.
During installation work, do not remove the packaging to prevent surface deformation.
Advantages and disadvantages
So, the pump installed in the system provides it with a large number of advantages:
- For such a system, it makes no difference which pipes and with what diameter will be installed in it.
- In this case, you can use inexpensive pipes with a smaller diameter, which will save money.
- The absence of temperature differences increases the service life of system components.
- It is possible to regulate the temperature in the system itself or in individual rooms of the house.
Of course, there are also disadvantages:
- Firstly, the pump operates from an electric current network, and this, although small, is an expense. In addition, when the power goes out, the pump also stops.
- Secondly, there is a slight noise from the operation of the pumping unit. It is practically inaudible, but it is still present.
How to place batteries
First of all, recommendations concern the installation location. Most often, heating devices are installed where heat loss is the most significant. And first of all these are windows. Even with modern energy-saving double-glazed windows, it is in these places that the most heat is lost. What can we say about old wooden frames?
It is important to place the radiator correctly and not make a mistake in choosing its size: not only power is important
If there is no radiator under the window, then the cold air descends along the wall and spreads along the floor. The situation is changed by installing a battery: warm air, rising upward, prevents cold air from “draining” onto the floor. It must be remembered that in order for such protection to be effective, the radiator must occupy at least 70% of the width of the window. This norm is prescribed in SNiP. Therefore, when choosing radiators, keep in mind that a small radiator under the window will not provide the required level of comfort. In this case, there will be zones on the sides where the cold air will go down, and there will be cold zones on the floor. In this case, the window may often “sweat”, condensation will form on the walls in the place where warm and cold air collide, and dampness will appear.
For this reason, do not try to find the model with the highest heat output. This is justified only for regions with a very harsh climate. But in the north, even the most powerful sections have large radiators. For central Russia, average heat transfer is required, for southern regions, low radiators are generally needed (with a small center distance). This is the only way you can fulfill the key rule for installing batteries: blocking most of the window opening.
A battery installed near the doors will work effectively
In cold climates, it makes sense to install a thermal curtain near the front door. This is the second problem area, but it is more typical for private houses. This problem may occur in ground floor apartments. The rules here are simple: you need to place the radiator as close to the door as possible. Choose a location depending on the layout, also taking into account the possibilities of piping.
How to protect the pump from malfunction
It is advisable to always maintain the required volume of coolant water in the pipes. Otherwise, the pump will wear out, both in case of excess water volume and in case of insufficient water volume.
To be on the safe side and avoid breakdowns of fairly expensive pumping equipment, it is recommended to adhere to some basic rules for operating equipment of this type:
- Do not allow the pump to turn on without coolant in the closed circuit. That is, if there is no water in the heating system pipes, then you should not “torture” the pump. This will cause your equipment to break down quickly.
- It is advisable to always maintain the required volume of coolant water in the pipes. Otherwise, the pump will wear out, both in case of excess water volume and in case of insufficient water volume. For example, if a pump can distill an amount of water from 5 to 105 liters, then the need to work with volumes from 3 to 103 liters will greatly wear out the working components of the unit, which will lead to its failure.
- In case of prolonged downtime of the pump (during the low heating season), it is necessary to run the unit in the operating position for at least 15 minutes once a month. This will avoid oxidation of all movable elements of the pump unit.
- Try not to exceed the coolant temperature above 65 degrees Celsius. A higher rate will negatively affect the working and movable parts of the structure.
- In this case, check the pump housing for leaks more often. If there is even the slightest leak somewhere, you should immediately identify the malfunction and carry out maintenance on the pump.
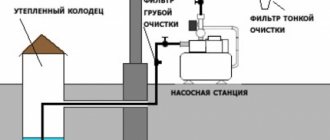
When is it necessary?
The need for circulation arises in long lines with a large number of subscribers, for example, in apartment buildings or public buildings. In a dead-end pipeline, the water will quickly cool down.
This phenomenon is pronounced at night, when water intake practically stops and the water loses thermal energy.
Starting circulation allows you to:
- constantly update the flow in the pipes,
- heat cooled water to ensure standard values.
In small water supply systems of one-story private houses, circulation is rarely used. The distance from the water heater to the water collection points is relatively small, so it is not advisable to spend money on purchasing or installing a pump, assembling a loop, and starting the process.
It’s easier to let a little water through, which has had time to cool down, to get a normal hot stream.
In two-story houses or cottages, a circulation system becomes a necessity.
Possible breakdowns and ways to eliminate them
So, if something goes wrong with your circulation pump and it refuses to work, then we’ll try to repair the unit ourselves.
If the pump makes a hum, but the impeller does not rotate
The reasons may be the following:
- Presence of a foreign object in the impeller area;
- The rotor shaft has oxidized due to long-term downtime of the unit;
- Loss of power supply to the mechanism terminals.
In the first case, you need to carefully remove the pump from the heating system and unscrew the housing in the area of the impeller. If a foreign object is found, remove it and rotate the shaft by hand. When assembling the pump in the reverse order, it is necessary to install a reliable filter on the pipe.
If there is oxidation, then clean it well, lubricate all movable elements of the working unit and reassemble the pump in the reverse order.
If there is a problem with the quality of the power supply, then you will have to check the voltage using a tester. First, completely replace the cable in all sections of the cable and if a break or fault is detected. Then, if the cable is OK, check the voltage at the terminals. If the tester shows infinity, a short circuit has occurred. If it shows less voltage, it means that the winding has broken. In both cases, the terminals are replaced.
If the unit shows no signs of life at all
This can happen if there is no voltage in the network. Using a tester, check the voltage and, if necessary, correct the problem.
By the way, it is recommended to protect the pump from surges in the network by installing a reliable stabilizer. This move will also protect the pump from the combustion of a fuse, which fails as a result of constant pressure drops in the network.
If the pump starts but then stops
The reasons may be:
- Presence of scale between the moving elements of the unit;
- Incorrect pump connection at the terminals.
In the first case, you will have to disassemble the pump and check it for scale. If detected, limescale deposits are removed and all joints between the rotor and stator are lubricated.
If there is no scale, then check the tightness of the fuse on the unit. You should remove it and thoroughly clean all the clamps. Here it is also worth checking that all wires in the terminal box are connected correctly in phases.
If the pump makes a loud noise when turned on
The reason for this is the presence of air in a closed circuit. It is necessary to release all air masses from the pipes, and install a special unit in the upper part of the pipeline to prevent the formation of air locks.
Another reason could be wear on the impeller bearing. In this case, you need to disassemble the unit housing, check the bearing and, if necessary, replace it.
If the pump is noisy and vibrates
Most likely, the issue is insufficient pressure in the system. It is necessary to add water to the pipes or increase the pressure in the area of the pump inlet.
If the pressure is still low
Here it is worth checking the direction of rotation of the working unit in the pump body. If the wheel does not spin correctly, then an error was probably made when connecting the device to the terminals in phases when using a three-phase network.
Another reason for a decrease in pressure may be too high a viscosity of the coolant. Here the impeller experiences a lot of resistance and does not cope with the assigned tasks. You will have to check the condition of the mesh filter and clean it if necessary. It would also be useful to check the cross-section of the inlet and outlet pipes and, if necessary, set the correct operating parameters of the pump.
Example of heating system calculation
As a rule, a simplified calculation is performed based on such parameters as the volume of the room, the level of its insulation, the flow rate of the coolant and the temperature difference in the inlet and outlet pipelines.
The diameter of the heating pipe with forced circulation is determined in the following sequence:
the total amount of heat that needs to be supplied to the room is determined (thermal power, kW), you can also rely on tabular data;
Thermal power value depending on the temperature difference and pump power
Having set the speed of water movement, the optimal D is determined.
Calculation of thermal power
As an example, a standard room with dimensions of 4.8x5.0x3.0m will be used. The heating circuit is with forced circulation; it is necessary to calculate the diameters of the heating pipes for distribution throughout the apartment. The basic calculation formula looks like this:
The following notations are used in the formula:
- V is the volume of the room. In the example, it is equal to 3.8∙4.0∙3.0 = 45.6m 3 ;
- Δt is the difference between the temperature outside and inside. In the example, 53ᵒС is taken;
Minimum temperatures by month for some cities
K is a special coefficient that determines the degree of insulation of the building. In general, its value ranges from 0.6-0.9 (effective thermal insulation is used, the floor and roof are insulated, at least double-glazed windows are installed) to 3-4 (buildings without thermal insulation, for example, change houses). In the example, an intermediate option is used - the apartment has standard thermal insulation (K = 1.0 - 1.9), K = 1.1 is accepted.
The total thermal power should be 45.6∙53∙1.1/860 = 3.09 kW.
You can use tabular data.
Table for calculating heat flow
Diameter determination
The diameter of the heating pipes is determined by the formula
Where notations are used:
- Δt – difference in coolant temperatures in the supply and discharge pipelines. Considering that water is supplied at a temperature of about 90-95ᵒС, and it has time to cool down to 65-70ᵒС, the temperature difference can be taken equal to 20ᵒС;
- v is the speed of water movement. It is undesirable for it to exceed 1.5 m/s, and the minimum acceptable threshold is 0.25 m/s. It is recommended to stay at an intermediate speed value of 0.8 - 1.3 m/s.
Note! An incorrect choice of pipe diameter for heating can lead to a drop in speed below the minimum threshold, which in turn will cause the formation of air locks. As a result, work efficiency will become zero.
The value of Din in the example will be √354∙(0.86∙3.09/20)/1.3 = 36.18 mm
If you pay attention to the standard sizes, for example, of a PP pipeline, you will see that there is simply no such Din. In this case, simply select the closest diameter of propylene pipes for heating
In this example, you can choose PN25 with a diameter of 33.2 mm, this will lead to a slight increase in the coolant flow rate, but it will still remain within acceptable limits.
Features of heating systems with natural circulation
Their main difference is that they do not use a circulation pump to create pressure. The liquid moves by gravity, after heating it is forced upward, then passes through the radiators, cools and returns to the boiler.
The diagram shows the principle of circulation pressure
Compared to systems with forced circulation, the diameter of pipes for heating with natural circulation must be larger. The basis of the calculation in this case is that the circulation pressure exceeds friction losses and local resistance.
Example of wiring with natural circulation
In order not to calculate the value of the circulation pressure each time, there are special tables compiled for different temperature differences. For example, if the length of the pipeline from the boiler to the radiator is 4.0 m, and the temperature difference is 20°C (70°C in the outlet and 90°C in the supply), then the circulation pressure will be 488 Pa. Based on this, the coolant speed is selected by changing D.
When performing calculations yourself, a verification calculation is also required. That is, the calculations are carried out in the reverse order, the purpose of the check is to determine whether friction losses and local resistance do not exceed the circulation pressure.
Pressure in the central heating system: GOST
Let's consider what pressure in the heating system of a multi-story building is set according to GOST.
Pressure is divided into:
- Working.
- Crimping.
Operating is the stable most comfortable indicator at which the system operates most of the time.
Pressure testing is an increased load that is created for a short time at the beginning of the heating season, when the heating is just started and its performance is checked.
- Static.
- Dynamic.
Static is created by a column of water under the influence of gravity.
And the higher the liquid was raised, the greater this indicator.
Dynamic is the excess pressure created by pumps.
In multi-storey buildings, water for radiators is first supplied to the upper floors using powerful pumping equipment. Of course, the flow of water acquires a certain speed and rises under pressure. And the higher the building, the greater the pressure needed to supply coolant to the top.
Standard for a 9-story building: 0.5 – 0.7 Pa (5 – 7 Atm).
Taller buildings: 0.7 – 1 Pa (7 – 10 Atm).
The difference in indicators between the first and last floors should not exceed 10%.
The crimping pressure should not exceed the working pressure by more than 20%.
Practice shows that the supply is usually 6 Atm., and the return is about 4 Atm. But many factors can influence this indicator.
Natural and forced circulation - what's the difference?
Natural is built on the physical process of heated water rising upward. The density of hot water is less than that of cold water, so warm layers are displaced by less heated layers. This phenomenon occurs without human participation, you just need to create the conditions to start the process.
However, natural circulation is unstable, without the necessary pressure. The speed of movement of layers of water is low; it cannot push the flow through the pipeline. In addition, it is almost impossible to regulate the natural process, just start or stop it.
Forced is the movement of water using special pumping equipment. The process occurs evenly, it can be adjusted, flow parameters changed or stopped as needed. The pump creates pressure that allows water to move through a branched, extended system.
The natural process is used where slow, ineffective mixing of layers of water at different temperatures is sufficient. As a rule, it is used in small water supply systems of a private home, when only a small exchange of layers is needed.
For apartment buildings, only forced circulation is suitable, allowing the water flow to be raised to the upper floors and effectively replacing cooled water.
How does the water heating system of a private house work?
The main equipment for heating installation is the boiler. It is necessary to transfer thermal energy, which is released during the combustion of fuel, to the coolant moving through the pipes.
Depending on the type of boiler, the following can be used as fuel:
- natural gas;
- firewood;
- coal;
- peat.
Heating schemes using electricity as a heat source have been developed and are successfully used. But this method is expensive, although it is the safest.
Expansion tank operation
The pressure stabilization device has a membrane that separates the working space from the air. The function of an expansion tank in a heating system is to receive excess coolant, which is formed due to expansion during heating, and release it back into the system during cooling.
When heated, water expands, and the pressure in all pipes and heating devices increases, and the excess volume flows into the tank. In this case, the membrane stretches and the volume of air decreases, that is, it compresses. At the same time, the pressure in the system increases.
As the temperature of the coolant decreases, its volume in the system drops, the pressure decreases, and thus the water that was previously taken into the tank is pushed out of it by compressed air.
Heating indoor air
Pipes are routed to radiators in various ways
The room is heated thanks to radiators installed in each room. Depending on the material used, they can be steel, aluminum, cast iron and bimetallic. Bimetal batteries have excellent heat dissipation and excellent appearance.
Water flows into heating devices through a branched pipe system. To ensure uniform and rapid movement of the coolant, as well as operating pressure in the heating system, a circulation pump is used. There are also systems with gravity flow of water.
Important elements are drain taps, release valves, shut-off valves and pressure gauges.
What it is?
It is impossible to organize continuous heating of water using conventional methods, so a simple and effective method is used - the hot water supply line is looped and the circulation process is started.
The flow leaves the boiler, passes in a circle and returns to the heating container.
All that remains is to adjust the speed of movement to ensure the supply of water at the standard temperature for all subscribers of the line.
Circulation pumps are used for movement, although natural circulation is possible in small systems.
Heating schemes
Water heating
With forced circulation of the coolant there are two types - one-pipe and two-pipe. The difference between them is quite significant. Here, not only the pipe layout differs, but also their number, as well as the set of shut-off, control and control valves.
Single pipe heating system
Here we also need to consider two options, because there is a horizontal and vertical scheme.
The first option is very simple. All heating radiators are inserted into the network circuit in series. That is, the coolant flows from one device to another, followed by a return circuit to the boiler. Each device is equipped with Mayevsky taps, through which air is removed from the system, as well as taps or valves, with which you can cut off part of the system or one small section. A pump installed in such a scheme will be very relevant.
There is one point here that needs special attention. This scheme for a multi-storey building is used in a variation, when each floor has its own separate branch from the riser
The vertical diagram is simplified. In it, the riser rises above the last floor, where the pipe is lowered to the upper floor and distributed among the radiators in a horizontal pattern from device to device. Next, the pipe is lowered to the floor below, where the horizontal routing is repeated. And so on until the first floor. Now you understand that the radiators on the first floor will always be cooled.
Two-pipe heating system
Drawing of a two-pipe heating system
This scheme also contains two types of wiring - horizontal and vertical. In turn, the horizontal diagram is divided into:
- Dead end;
- Along the way;
- Collector.
What are the differences between these three schemes?
The first is the simplest, but it is very difficult to control the temperature. Each radiator has its own circuit, and the further the radiator is from the boiler, the longer this circuit is.
In the second scheme, these circuits are the same, which makes it easy to regulate the process. But this increases the length of the pipeline itself.
But the third scheme is the most effective, because each radiator has its own separate pipeline, and coolant is supplied through it. In this case, uniformity of heat is ensured. There is only one drawback - large material costs for purchasing a large amount of materials and considerable labor costs for installation work.
The vertical circuit is also divided into two types - with lower wiring and with upper wiring. The first option has a distinctive structural element - the coolant supply riser passes through all floors and on the top it enters the radiator, from which the return flows. Through this pipe, water flows to the lower floor, where it also goes directly to the radiator. And so on until the boiler. That is, in any room you will have two pipes.
More options for forced heating schemes
The second option is completely different. Here the riser rises vertically from the boiler to the attic, where pipes are routed to each radiator on the upper floor. And from them a pipe goes down to the lower floor. This return flows to the lower floor radiator as a coolant supply. That is, in each room you will always have one pipe connecting radiators on different floors.
As you can see, heating systems have different designs. When choosing any of them, you need to decide one very important question - how much money is allocated for installing heating in your home.
Two-story house
In two-story country houses, it is recommended to use a closed heating system with a circulation pump. The list of necessary equipment here includes: a boiler, an expansion tank, a piping system, as well as the required number of heating radiators.
Copper pipes are connected to each other using special silver-based solder. The downside of this material is its high price, but it is distinguished by high quality and reliability. Metal pipes also transfer heat well, but they are often destroyed by corrosion.
Two-pipe heating system for a two-story house with natural circulation and top wiring
In two-story buildings, three types of wiring can be used: collector, two-pipe or single-pipe. When connecting heating devices using a single-pipe scheme, it is quite difficult to regulate the temperature in the rooms, because the maximum amount of heat will reach the first radiators from the boiler, while the last radiators will heat up much less than the others.
A two-pipe heating system is considered a more suitable option for a two-story country house. Here, two pipes are connected to each of the heating devices: hot water from the boiler flows through one of them, and the liquid that gives off heat flows into the other. The coolant temperature in the main supply line will be the same.
Selecting a circulation pump
Circulation pump
To choose the right pump, you need to take into account only two of its qualities. It should be:
- Energy saving.
- Simple and reliable to use.
Indicators such as power and pressure are determined by the size of the house itself. Eg:
- House area is 250 square meters - choose a pump with a capacity of 3.5 cubic meters per hour and a pressure of 0.4 atmospheres.
- Area 250-350 cubic meters - power 4.5 cubic meters per hour, pressure - 0.6 atm.
- Area 350-800 cubic meters - power 11 cubic meters per hour, pressure - 0.8 atm.
Of course, it is difficult to say exactly which pump is best to use for a particular home. Here you will have to make a calculation that can only be performed by a specialist. After all, for this it is necessary to take into account many factors. This must include:
- The diameter of the pipes and the material from which they are made.
- Length of the entire system.
- The number of radiators, shut-off valves and other devices, as well as their type.
- The type of fuel the boiler will operate on.
Glandless circulation pump for all water heating systems
As you can see, it is very difficult to take into account all the factors and make a calculation on your own; only a specialist can do this.
And one last thing. Often on forums you can hear complaints from private developers that there is no circulation in the heating system. What to do?
There can only be one reason - air pockets inside. To remove them, it is necessary to install Mayevsky taps on each radiator. This is an effective means of combating air that remains inside the system after it is filled with water. So you need to splurge and buy these devices.
By the way, currently such taps are produced with automatic air release. An excellent option in which there is no need to control the formation of air pockets.
In water heating systems, it is not uncommon for a problem to arise that leads to a deterioration in water circulation within the circuit. The problem has a specific name - airing in the heating system. The uninterrupted operation of water heating is based on the principles of circulation of hot water (coolant) inside the circuit and heat transfer through radiators that heat the rooms. Air in the system leads to the appearance of air pockets and, as a result, to the ineffective functioning of the entire system due to reduced heat transfer.
To begin solving the problem, it is necessary to establish the reasons for the appearance of air: natural or artificial. A natural reason is airing of the system due to the ability of heated water to release air. The higher the temperature of the coolant, the more air bubbles are released. According to physical laws, the accumulation of bubbles occurs in the upper part of the circuit, since air is lighter than water.
The remaining reasons are considered artificial. It is difficult to give a complete list, but the main reasons are considered to be the following:
- insufficient pressure in the system;
- installation errors of the heating circuit (for example, incorrect pipe slope);
- errors when putting the system into operation (for example, filling the circuit with water too quickly);
- high concentration of air in the water used;
- incorrect operation of the shut-off equipment (possibly loose connections of individual elements);
- clogged pipelines;
- consequences of repair and maintenance work;
- corrosion on metal surfaces of circuit elements;
- incorrect operation of air vents or their absence.
No circulation, heating failure - why
Failure in the heating system, deficiencies, imperfections, all lead to cold radiators.
If there is no coolant circulation, then the reason needs to be determined. Most often, the answer to why the heating does not work is on the surface, obvious. Let's look in order at the main causes of heating malfunctions, why water does not circulate through the pipes, and what needs to be done first.
Let's start with the simplest and most obvious reasons.
It's clogged and clogged.
Every heating system must have a coarse filter. A very small device with a fine mesh and a sump (installed downwards! or at least to the side) saves equipment, pumps, and the boiler from coolant contamination that will be present in any system. Wood shavings, broken threads, rust, water sediment…. everything is retained by the mesh in the filter.
The sedimentation tank must be periodically untwisted and the mesh cleaned.
If the circulation in the heating system of a private house is disrupted, then the first thing you need to do is check the filter, which should be installed on the return line in front of the boiler.
Air in the system, airing
Airing can occur in any closed piping system where air removal measures have not been taken. Air is always present in the coolant, including in a dissolved state, is released during pressure changes, and accumulates at the highest points. Including in the boiler.
Automatic air vents are installed at characteristic, highest points of the system, as well as on collectors and special separators - the normal circuit is equipped with a special air catching device in which air bubbles are released from the coolant.
In addition, Mayevsky valves (manual air vents) should be on each radiator, and also possibly in other elevated places.
Checking the air supply, bleeding the air, installing air vents are common actions if circulation stops and the batteries are cold.
The circulation pump does not work
In private homes, the reason why the heating system stops working is a breakdown of the electrical equipment that controlled the movement of the coolant through the pipes.
If the heating suddenly stops working, then you need to check the functionality of the circulation pump near the solid fuel boiler or the pump in the automated boiler. In addition, the same unit can be installed in each circuit, which must work properly.
Bad polypropylene pipes
Often the consumer (customer) believes that polypropylene pipes are absolutely reliable and cannot cause heating problems or cold radiators.
But polypropylene is much more insidious than old steel or metal-plastic pipelines. Each place of soldering (welding) is a potential increased resistance in the system or a cause of cessation of circulation (weakened movement of water through the batteries), due to deposits of material inside.
It is impossible to control the quality of connections from the outside; all that remains is to cut out pieces, resolder, and remake polypropylene pipes.
Poor performance of a polypropylene system is a real problem for the home installer. Good professionals don’t take on this material at all.
Bad project
It is not uncommon for poor circulation to occur where there is poor design. Typically, the batteries are not connected correctly, according to some sequential circuit, where the last battery in the circuit receives much less coolant.
Another bad design is single-pipe circuits, where it is also difficult to establish the necessary coolant circulation through each battery.
If the radiators do not heat up evenly, or there is poor coolant circulation on individual heating devices, first of all you need to consider how the connection corresponds to the classic circuits - shoulder, associated, radial. It is necessary to bring home heating to normal design standards, and then expect good circulation and uniform heating of the radiators.
Small diameter, overgrown pipes
Old steel pipes become overgrown with rust and deposits from the inside, their throughput capacity decreases significantly over time, and there is only one solution - they need to be replaced with modern ones.
But even during installation, for the sake of economy, mistakes can be made with the choice of pipeline diameter - on mains, on groups of heating devices, diameters of 16 or 20 mm can be installed. The result is noise in the pipes, excessive consumption of electricity, and insufficient coolant flow. What pipe diameters should you choose?
A complex system
A type of bad design is an incorrectly designed complex heating system consisting of many heating circuits and several boilers. Here entire circuits will not work correctly if the work of one affects the neighboring one.
As a rule, one boiler (the backup one does not count) and three circuits - boiler, radiators, heated floors with their pumps are coordinated normally, and no questions arise. But if you connect another working boiler plus a circuit (for example, heating a garage and greenhouse), then the system will become complex. It is difficult to say how the coolant will circulate in it without equalizing the pressures at the connection points.
In complex systems, a competent design is important, installing a hydraulic arrow or an equal pressure ring; more information about the hydraulic separator can be found here
No balancing
Many home heating schemes involve balancing; balancing and control valves are installed in them. For example, between floors, between shoulders, and for each radiator. The taps cover the direction with less hydraulic resistance; accordingly, more coolant will flow to other points.
Children can play with the taps. Or the system is initially unbalanced. Setting up, as a rule, is no problem, you just need to find this tap... How to set up home heating
Neighbors don't provide heat
But complex heating project schemes are of little concern to residents of high-rise buildings, who have a separate riser for each radiator in the apartment. And if any radiator stops heating up normally, it means there is no circulation through the riser, therefore...
You need to contact the heating network, housing office (service organization) to adjust the power in the risers, and if this does not help, then with the requirement to check the neighbors.
Often, unauthorized connection or replacement of radiators and pipes in central heating systems leads to a redistribution of pressure, circulation through individual batteries decreases and disappears.
No circulation in gravity system
In gravity systems, the pressure difference is low; they are especially sensitive to air pockets, pipe diameters, and gaps in radiators.
In old circuits, gradual deposits occur in radiators and pipes; circulation may decrease over time, and the only cure for this is replacing everything with a more modern one.
You also need to pay attention to the correctness of the circuit itself - the middle heating line is below the cooling line (the boiler heat exchanger is below the radiators), and also - the hot feed rises up to the highest point, and from there it drops to the radiators... Read more about gravity flow circuits below
Various breakdowns in heating systems
- The taps and valves are closed - check that everything is open to ensure circulation.
- There is a leak in the system - there is not enough coolant, check the pressure, eliminate the leak.
- Installation with flexible pipes - the pipe is pinched.
- Failure of automatic equipment - thermal heads on mixing units, radiators, the mixing units themselves - silting, failure, it is necessary to check the correct operation. Also – electronic failure.
- Incorrect balancing on the distribution collector - in beam circuits, complex systems, collectors with balancing and tuning equipment can cause a lack of circulation anywhere due to breakdowns and incorrect settings.
- Low pressure, no air in the expansion tank - check the pressure in the pipes and the pumping of the tank; automated units will not work at all without the required pressure.
- Violation of the circuit, excess bypass - check that the installation complies with the design, the logic of the circuit, whether there are any short circuits in the jet, parallel branches to radiators and circuits.
A little about hydraulics
The choice of pipe diameter, wiring diagram and circulation pump power is inextricably linked with the concept of hydraulic calculation of a horizontal two-pipe heating system. It is performed with the aim of either calculating the pressure drop in a given section, or calculating the required pipeline diameter.
We will deliberately not provide a complete description of the methods and formulas by which the hydraulic calculation of a two-pipe horizontal heating system can be performed: take my word for it, they are VERY complex and give quite large errors.
We will only mention the main factors influencing the calculations.
- Pipe surface roughness. It is greatest for asbestos cement and steel pipes after a long period of service due to the large amount of rust and deposits.
As already mentioned, polymer and metal-polymer pipes have the lowest roughness. What is especially pleasing is that the resistance of polypropylene and cross-linked polyethylene to water movement does not change over time.
- Increasing and decreasing the section.
- Turns, radial bends. Each pipe bend increases its hydraulic resistance by several degrees.
- Pressure difference between supply and return pipelines.
- Section and shape of channels in heating devices.
- Number of heating devices.
- Shut-off valves - type and quantity.
The optimal speed of coolant movement is in the range of 0.3 - 0.7 meters per second.
At lower values, we will get periodic airing of the heating system; in addition, single-pipe and two-pipe heating systems with a slowly moving coolant will produce too wide a temperature spread across the heating devices.
At higher speeds the heating will become too noisy. What is at least as unpleasant is that the erosion of the pipe walls by inevitable abrasive particles - sand and slag - will accelerate many times over.
Regulator for pressure regulation
To comply with all measures for the safe operation of the heating system, it is necessary to constantly monitor the temperature and pressure of the coolant.
The pressure is monitored using a Bourdon tube pressure gauge. This device has an elastic measuring component, which, under the influence of a compressive load, is deformed in a certain way.
Photo 1. Pressure gauge installed in the heating system. The device allows you to measure pressure readings.
The conversion of changes is reflected in the rotational movement of the hand, showing the exact value on the dial in familiar terms.
Important! After water hammer, pressure gauges need to be checked, because
subsequent readings may be overestimated.
- at the inlet and outlet of the coolant line (centralized heating);
- before and after the heating boiler (individual heating);
- before and after the circulation pump (forced circulation);
- near filters, related regulators and valves.
How to adjust indicators
There are several proven methods for this procedure:
- Correct design, including hydraulic calculations and installation of pipelines:
- the supply line should be at the top and the return line at the bottom;
- for risers, pipes of 20-25 mm are needed, and for bottlings - 50-80 mm;
- pipes for risers are also used for supplying heating devices.
- Change in water temperature. When heated, the coolant expands, thereby increasing the pressure in the heating system. For example, at 20°C it can jump by 0.13 MPa, and at 70°C - by 0.19 MPa. Therefore, reducing the temperature will lead to its corresponding adjustment.
- The use of circulation pumps to provide heat to apartments on the upper floors in high-rise buildings.
Photo 2. Circulation pumps installed in a multi-story building. The devices circulate coolant through the heating system.
- Introduction of expansion tanks. With individual heating, the “extra” volume of heated coolant will go into the container, and the cooled volume will return to the system, maintaining pressure stability.
- Use of special regulators. Such devices are able to prevent airing of the system during sudden pressure surges in the lines. Installation is carried out on the pump bypass line or on a jumper placed between two pipelines - supply and return.
Advantages and disadvantages
The open heating system has not yet lost its relevance, and recently it has even experienced a rebirth, and there are reasons for this. Many homeowners are concerned about the energy independence of their communications, and the open tank scheme allows this to be achieved. She has other advantages:
- Filling an open heating system and bleeding air is easier than in a closed one. There is no need to monitor the maximum pressure, and when filling, the air leaves the pipelines very quickly through the open expansion tank. All that remains is to ventilate the radiators;
- it’s easier to refill: again, pressure control is not required, and water can be added to the container even with a bucket;
- the operation of the system does not depend on the presence of leaks: here the operating pressure is very low, so as long as there is water in the heating network, it will function properly.
As usual, there were some drawbacks, due to which such systems began to be gradually replaced by closed-type circuits with a membrane expansion tank. Due to the direct contact of the coolant with atmospheric air, two processes occur in the container at once: natural evaporation of hot water and its saturation with oxygen. This leads to the following requirements:
- you need to monitor the water level in the tank and replenish it on time;
- Do not fill the heating network with antifreeze, which releases harmful substances when evaporated.
Oxygen saturation of the coolant leads to a decrease in the service life of steel parts of the boiler. For the above reasons, the open system has not been used in apartment buildings for a long time, although in the 60-70s of the Soviet era such practice took place in low-rise residential buildings. It is also undesirable to operate it with high-temperature heat sources when the coolant is close to the boiling point. The fact is that with increased pressure in a closed network, this threshold increases, and there is nowhere for water to evaporate. In an open system, the amount of water will quickly decrease, freeing up the entire volume of the expansion tank for air.
Bypass sections in single-pipe systems with horizontal and vertical distribution
In heating systems with vertical and horizontal pipe distribution, short bypass sections are used.
Bypass sections in a single-pipe heating system
Without going deeply into theory, I will inform you that the bypass pipe should have a smaller diameter compared to the rest of the supply pipe. Or, throttling equipment is installed on the bypass section - special valves (3-way thermostat valves, single-pipe thermostat valves with an adjustable bypass).
Unfortunately, such valves can only be used in single-pipe heating systems.
Expansion tank
Located in the attic. Since the attic is usually an unheated room, the tank must be insulated, otherwise the water in it may freeze in winter. The tank compensates for temperature fluctuations in the water level. In addition, sometimes water in the system can boil (this happens if you start heating the boiler too quickly), and the bubbles significantly increase the volume. This is what the excess volume in the expansion tank is for.
It is advisable to provide for the possibility of draining excess water from the tank when it overflows. To do this, water can be discharged either into the sewer or simply onto the street.
It should be borne in mind that water from an open system evaporates. Therefore, it is necessary to replenish the system with water. This can be done manually, periodically climbing into the attic and adding water, or you can make an expansion tank similar to a toilet - with automatic topping up of water.
But they rarely do this. Usually they just use a container.
It is better to close the top of the tank with a lid so that less water evaporates.
Consequences of cold return
Circuit for heating return
Sometimes, with an incorrectly designed design, the return flow in the heating system is cold. As practice shows, the fact that the room does not receive enough heat with a cold return is half the trouble. The fact is that at different supply and return temperatures, condensation may form on the walls of the boiler, which, when interacting with carbon dioxide released during fuel combustion, forms acid. It can also damage the boiler much ahead of time.
To avoid this, it is necessary to carefully consider the design of the heating system, special attention must be paid to such a nuance as the return temperature. Or include additional devices in the system, for example, a circulation pump or boiler, which will compensate for the loss of warm water
Radiator connection options
Now we can more than confidently say that when designing a heating system, the supply and return must be perfectly thought out and configured. If the design is incorrect, more than 50% of the heat can be lost.
There are three options for inserting a radiator into the heating system:
- Diagonal.
- Lateral.
- Bottom.
The diagonal system gives the highest efficiency coefficient, and is therefore more practical and efficient.
The diagram shows a diagonal inset
Methods for installing heating equipment
The connection of all elements of the heating structure can be carried out in different ways. According to the method of installation to the main line, radiator heating systems can be:
The vertical system has a bottom-up connection. The heating elements of all floors in the building are carried to one riser. This method is effective, but expensive.
The horizontal system is used in buildings with one floor. The room usually has a large area, so the heating design must be complex. Radiators are connected along a horizontal path. The distribution of risers is placed in the corridor or entrance.
A simple look at the problem.
The expansion tank plays an important role in the cooling system. Its main function is to dampen pressure fluctuations in pipelines that arise as a result of an increase (decrease) in the volume of antifreeze during heating (cooling). Thanks to the presence of such a container, mechanical loads on system elements are reduced, water hammer and the appearance of air locks are prevented.
In fact, the tank replenishes the lack of fluid in the lines during cooling and serves to receive excess fluid when heating. Structurally, it is made in the form of a plastic sealed container.
A mandatory part of the design is a safety valve for releasing excess pressure into the atmosphere.
When antifreeze heats up, it expands, filling the free space of the tank, and the evaporation rate increases. This leads to an increase in pressure in the volume. An increase in pressure above a threshold value triggers the built-in valve.
The only situation when antifreeze is thrown out of the expansion tank is when the valve fails to perform its assigned functions.
Coolant circulation through radiators
Heating of the room in which the heating radiator is installed is carried out according to the following principle:
- the coolant water heated to the required temperature is supplied through a single-pipe or two-pipe piping system to one of the end sockets of the radiator, intended for the inlet of hot liquid in accordance with the selected connection diagram for heating radiators in this house or apartment;
- the coolant supplied to the input of the heating battery circulates through all its sections, giving off the brought heat to the material of the radiator walls;
- the walls of the radiator, heated from the inside, radiate heat from the outer surface into the surrounding environment, thereby heating the room;
- the coolant, which has thoroughly cooled down inside the radiator when passing through its sections, leaves the battery through the upper or lower end socket, designed by the selected connection diagram for the outlet of the cold coolant;
- The cooled water leaving the radiator is carried through the outlet pipeline (commonly called “return”) to the heat source for subsequent heating and passage of the next circulation circle.
The presence of four input/output sockets at the ends of the mounted battery (two on each opposite side) predetermined the existence of several options for the movement of hot water inside the radiator, depending on how they are connected. With any fluid circulation scheme inside the volume of batteries assembled from 6-8-12 or more sections, there is an uneven distribution of heat flows both in height and along the battery. The figure shows a thermogram of a cast iron radiator with bottom supply. The temperature spread in height or length can reach 10 degrees.
Thermogram of a cast iron radiator with bottom supply
In reality, the temperature spread is much greater, since scale and lime deposits settling in the lower cavities of the sections prevent the passage of hot water at the bottom of the radiator. The hot coolant immediately rushes through the free upper ducts to the exit, without even washing the distant sections. In fact, the temperature of such clogged sectional areas remote from the entrance can reach only 25-30 degrees.
The efficiency of each heating device individually and the entire heating system of the house depends on the connection diagram of the heating radiators, which determines the route of movement of the coolant inside the assembled sections and affects the intensity of hot water circulation when it washes the internal surfaces of the sections.
Equipment and principle of operation of the system
In a water heating system, liquid acts as an intermediary in the transfer of thermal energy from the boiler plant to the radiators. Coolant circulation can be carried out over long distances, providing heating for houses and rooms of different sizes. This explains the widespread introduction of water heating.
The operation of an open type heating system is possible without the use of a pump. Coolant circulation is based on the principles of thermodynamics. The movement of water through pipes occurs due to the difference in density of hot and cold liquids, as well as due to the slope of the laid pipes.
The density of warm water is lower than that of cold water, so hydrostatic pressure forms in the system. Pressurized hot water moves towards the radiators
An indispensable element of the system is an open expansion tank into which excess heated coolant flows. Thanks to the reservoir, the liquid pressure is automatically stabilized. The container is installed above all system components.
The entire process of functioning of “open heating” is conventionally divided into two stages:
- Innings. The heated coolant moves from the boiler to the radiators.
- Return. Excess warm water enters the expansion tank, cools and returns to the boiler.
In one-pipe systems, the function of supply and return is performed by one line; in two-pipe systems, the supply and return pipes are independent of each other.
The single-pipe scheme is considered the simplest and most accessible for self-installation. The design of the system is elementary.
The basic package of one-pipe heat supply includes:
- boiler;
- radiators;
- expansion tank;
- pipes.
Some people refuse to install radiators and place a pipe with a diameter of 8-10 cm around the perimeter of the house. However, experts note that the efficiency of the system and ease of use with this solution are reduced.
The open type gravitational single-pipe system is energy-independent. The costs of purchasing pipes, fittings and equipment are relatively low. Can work with different types of boilers
The two-pipe heating option is more complex in design and more expensive in execution. However, the costs and complexity of the construction are fully offset by the elimination of the standard disadvantages of single-pipe systems. A coolant with an equal temperature is supplied almost simultaneously to all devices; the cooled water is collected by the return line and does not flow into the next battery.
To service each device, a supply and return line are installed in a two-pipe heating circuit, due to which the temperature system supplies coolant of equal temperature to all points, and the cooled water is collected and sent to the boiler by a return line - a line independent of the supply (+)