A gas boiler is often located in houses outside urban areas, in small businesses and shopping centers. Its task is to maintain the required air temperature in the room, and in some cases, to provide hot water supply. Smart automation in modern boilers turns on heating only if the temperature of the coolant (usually water) or the air in the room drops below a predetermined level. In this way, it is expected not only to save fuel, but also to reduce wear and tear on the device as a whole. In certain scenarios, so-called clocking may occur. Let's talk about him.
Principle of operation
Gas boilers are equipment in which natural gas is burned, transformed into thermal energy. Propane-butane or methane is used as fuel.
The operating principle of the heating device is as follows:
- Gas under pressure enters the unit while a spark is automatically supplied to the igniter;
- The gas in the burner is ignited by the igniter;
- The flame from the burner heats the heat exchanger through which the coolant circulates;
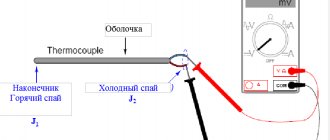
- When the temperature rises above the specified limit, the thermocouple (temperature sensor) closes the gas supply valve;
- When the temperature of the coolant decreases, the thermocouple opens the valve and the burner is re-ignited.
The described operating principle is relevant for automated equipment. In outdated imported boilers or in budget domestic units, ignition of the burner and adjustment of temperature indicators is carried out manually using a button and a regulator.
When planning gas heating, we take into account the minimum permissible gas pressure specified in the equipment parameters. The pressure indicator must correspond to the pressure in the gas distribution network.
Most modern Western European boilers are designed for an operating pressure of 20 mbar (millibar). At the same time, the pressure in the gas distribution networks of the Moscow region does not exceed 15 mbar. What could be the difference between these parameters?
If there is insufficient pressure in the network, the wall-mounted gas boiler operates with less power than stated in the technical data sheet. Moreover, in winter, when natural gas consumption increases, the pressure in the network further decreases. Therefore, in the cold season, the boiler has to be set to maximum temperature settings.
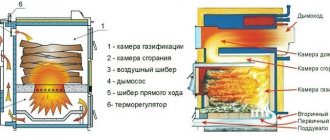
Construction of gas boilers with a closed combustion chamber
| Illustrations | Elements and components in the boiler design |
| Smoke removal system . The photo shows a coaxial chimney with a fan for forced removal of exhaust gases. This solution is used in most automatic wall-mounted boilers. | |
| Heat exchanger . This is a radiator with coolant flowing inside. The heat exchanger is heated by the burner, and the temperature of the coolant inside it rises. | |
| Burner . This structural unit is located under the heat exchanger and heats its lower part with flame from the nozzles. | |
| Expansion tank . This structural unit compensates for pressure unevenness when the coolant temperature changes. |
The construction of a gas boiler can be without a built-in tank, then the expansion tank is installed externally.
In non-automated models, the control unit is a shut-off valve, through which the gas supply is manually shut off or increased.
Types of gas boilers
| Circulation pump . The pump circulates coolant with constant pressure inside the heating system. | |
| Control block . Automated models use an electronic control unit, from which you can manually set parameters such as temperature, operating time, etc. |
| Illustrations | Classification by type of location |
| Wall mounted . A wall-mounted gas boiler can be installed in any room, including a kitchen or bathroom. That is, there is no need for a gas boiler room. |
A distinctive characteristic of wall-mounted models is their low price and low power (no more than 100 kW).
Strapping elements are integrated into the design of the device
.
Piping elements are not included in the package of floor-standing boilers, and therefore they must be installed separately
.
| Floor-standing . These are massive models with high power (up to 500 kW). Due to the large weight and large dimensions, the base of the floor is specially strengthened for the location of equipment and an auxiliary room is allocated. |
| Illustrations | Classification by functional purpose |
| Single-circuit . This equipment is intended only for heating the coolant in the heating system. | |
| Dual-circuit . A double-circuit boiler heats not only the coolant, but also water for hot water supply (DHW). |
Depending on the modification of the device, water for domestic hot water is heated either in a flow-through or in a storage heat exchanger.
| Illustrations | Classification by type of traction |
| Natural cravings . These boilers are equipped with an open combustion chamber, that is, the air necessary for combustion comes from the room. Gas combustion products are discharged outside by natural draft. |
The instructions for installing equipment on natural draft provide for good ventilation in the boiler room.
| Forced draft . Most modern gas boilers operate on this principle. Combustion air is taken from the street and exhaust gas is discharged there. Gas combustion products are discharged outside through a chimney with a built-in fan. |
| Illustrations | Classification by ignition type |
| Piezo ignition . This type of ignition is equipped with non-volatile boilers, most often old imported or budget domestic units. |
The advantage of this ignition scheme is that it can be used in the absence of electricity.
How a home becomes smart
Today, the capabilities of manufacturers exceed the needs of the customer. Using automation, you can control at least a hundred heating circuits, but this is not required. More often there are situations when there are two circuits in the house - one for the radiator, the second for underfloor heating. In some more complex systems, when there is forced ventilation, a pool or several levels, there can be up to 10 of these circuits.
In addition to the heating system, modern cottages also have ventilation and air conditioning systems. It is inconvenient for the homeowner to use 5-6 control panels to separately turn on convectors, radiators, heated floors, ventilation, and air conditioning. For this purpose, there are controllers that allow you to combine all controlled devices of systems into one remote control. Let's say you set the temperature to 22 degrees. In summer, the air cooled by the air conditioner will be supplied through the ventilation. If our temperature “overboard” has dropped, the controller will give a command to heat the house - it will open the servo drive for the heated floor or radiators, and turn on the convector fan. This level of automation already refers to such a concept as “Smart Home”. Its functions also include light control, blinds, etc.
The heating system can be automated to different levels. All these methods of thermoregulation are evolutionary steps from the simplest control on the boiler to more complex control through electronic devices that maintain a comfortable temperature in our presence and save energy when the house is empty.
Let's sum it up
Now you know what the structure of a single-circuit and double-circuit gas boiler is and on what principle this equipment works. You can find more interesting information on the topic by watching the video in this article. If you have any questions, ask them in the comments.
Heating equipment is most widely used in private cottages that are not connected to a hot water supply system and have autonomous heating. Residents of such households have to purchase electric water heaters or double-circuit gas appliances.
In this case, the advantage is on the side of the latter, which is due to their design features and, as a consequence, the ability to prepare the required volumes of hot water in the shortest possible time. We will try to explain the principle of operation of a double-circuit gas boiler so that you can make the right choice.
Types of boiler equipment
Modern boiler equipment is presented in a wide range. It not only has different manufacturers, but also significant design and functional differences. If we consider gas appliances, they are
Moreover, each type contains different models. Depending on the design features, they can be:
While the former are used exclusively for space heating, the functionality of the latter allows for the preparation of hot water in the required quantity. Moreover, this ability in no way affects the heating of the room.
Using non-freezing liquid as a coolant
Antifreeze
If you plan to use antifreeze liquid (ethylene glycol or propylene glycol) as a coolant, then you should find out whether this is allowed by the manufacturer.
In the event of a breakdown, you may be denied warranty repairs. My opinion here is that antifreeze can only be a necessary measure.
For example, at the dacha, where you don’t want to drain the system every time in the fall. In other cases, the best choice is prepared water.
Construction of gas apparatus
All heating boilers have the same basic components and, as a rule, differ in details. If we look at their drawings, they all consist of a thermally insulated body, inside of which there are:
As for the burner, its shape and design differ for devices operating on different types of fuel. For example, in gas models it is a chamber in which fuel combustion occurs, releasing heat and oxidation products.
Its main function is to generate the energy necessary to heat the coolant. A heat exchanger is located above the burner - this is a container with coolant.
The combustion products rising along its walls transfer heat to water, which is then distributed through the pipes of the heating system. In this case, the cooled combustion products enter the chimney and are discharged outside.
Depending on the design features of the device for heat transfer, devices are distinguished:
- with double (plate)
- with bithermic
Let's look at the features of each of them. A dual heat exchanger consists of two. One is for the heating circuit; it consists of copper pipes and plates, the surface of which is covered with a special protective layer that protects against corrosion. Its main function is heat transfer.
The second one prepares hot water. It consists of plates, they transfer heat to the heated medium. For its design it received the name - plate.
A bithermal heat transfer device is a pipe within a pipe. Moreover, its inner part is used for preparing hot water, and its outer part is used for heating the room.
The ignition option also plays a significant role for gas appliances. This device is responsible for burning fuel. Ignition can be of two types:
In this case, it is necessary to take into account the flow of air into the combustion chamber. There are several options. For open ones - air is supplied from the room. In closed cells, both natural and forced ventilation can be used.
Of the devices that are necessarily used in most gas appliances, it remains to consider automation. It controls the operation of all components of the device and in the latest models is made on microprocessor systems. This allows you to control the operation of the device by setting the necessary program, everything else is done automatically.
The main components of a wall-mounted boiler with a closed combustion chamber.
Figure 4 1 Safety relief valve (3 bar) 2 Gas valve 3 Primary filter 4 Ignition transformer 5 Injection burner 6 Temperature sensor (NTC) 7 Ignition electrodes 8 Combustion chamber 9 Primary heat exchanger 10 Sealed vacuum chamber 11 Differential combustion products flow relay 12 Fan 13 Coaxial air inlet-removal system for combustion products 14 Expansion tank 15 Ionization electrode 16 Temperature sensor OL (NTC) 17 Automatic air vent valve 18 Pump 19 Pressure sensor 20 Bypass with adjustable bypass valve 21 Three-way priority valve 22 Plate heat exchanger 23 Cold flow sensor water 24 Cold water filter 25 Charge valve 26 Drain tap A Supply line (FL) B Hot water outlet C Gas inlet D Cold water inlet E Return line (RL) F Drain pipe
Operating principle
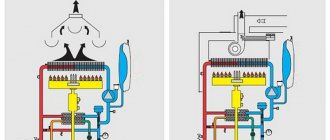
The design of a double-circuit gas boiler allows it to operate in two modes:
In the first case, the coolant located inside the heat exchanger is heated. It serves as ordinary water. Depending on how hot it should be at the outlet and heating is carried out - from 35 to 80º C.
The heating mode is started by a thermostat that responds to changes in room temperature. When it decreases, it transmits a signal to start the pump, which creates a vacuum in the return pipeline. This process leads to the fact that the water heated in the heat exchanger enters the heating system, while the pressure is taken into account; if it is more than 0.45 bar, then the relay contacts are closed and the burner is ignited, which is controlled by the microprocessor.
Positioning the thermometer correctly
There are two types of thermostat:
- Built-in - measures the temperature of the coolant, does not respond to external conditions.
- Remote - measures the air temperature in the room, does not react to the temperature inside the boiler.
With the first type, everything is clear - nothing can be changed, the thermometer does not involve transfer. The remote type must be positioned correctly - otherwise, every ventilation or operation of household appliances will disrupt the heating operation throughout the house.
Experienced craftsmen advise placing the device in the part of the room that cools most slowly. As a rule, it is located at a considerable distance from the boiler, so heating is also extended over time. Reducing the temperature to the lower limit will mean cooling the entire room - the heating will begin to operate normally.
In order for the burner to perform long, uniform cycles, you should not install a thermometer:
- Near windows, doors, cracks in walls.
- Near household appliances.
- Close to the floor or ceiling.
- In the basements.
Operation of the device in DHW mode
In the warm season, when there is no need to heat the room, the boiler can be turned on in summer mode. In this case, only the DHW circuit will function.
The principle of operation of a gas double-circuit boiler in this mode is as follows: a three-way valve closes the heating line, and the coolant from the primary heat exchanger is supplied to the secondary one.
Passing through it, cold water heats up and enters the DHW circuit. This process is started using a pressure switch, which closes when water flow exceeds 2.5 liters.
First, a command is automatically given to ignite the burner, and then the gas valve opens and the power gradually increases to maximum. The device operates in the specified mode until the water is heated, and then goes to the step of smooth control.
Moreover, the burner is automatically adjusted to the amount of liquid consumed. It turns off when the temperature rises by 5ºC, and turns on when it drops by 1ºC.
When operating in this mode, the heating circuit is switched off and heat from the burner is transferred to a stationary coolant, and through it to the DHW circuit.
Installation Features
Installation of this type of equipment is a very responsible matter. To ensure its proper functioning and your own safety, you must approach this issue with the utmost care. First of all, you should pay attention to the following points:
- The place where it is planned to install the boiler must comply with all regulatory parameters. It is necessary to coordinate its location in advance with representatives of the gas service.
- The connection project is initially drawn up on paper and then sent for approval to the appropriate organization.
- After receiving permission, its employees will personally install the necessary metering devices to monitor fuel consumption.
- Before starting installation, you need to make sure that the unit is fully equipped. If some parts are missing, such a device cannot be installed. This may lead to an emergency situation.
- First of all, installation points are determined on the wall surfaces, only then do they begin the phased installation of all elements.
- Upon completion of the installation activities, the system is connected in series. Test filling the circuit with water, then heat the boiler.
- If you find any problems or smell gas, you should not try to fix the problem yourself. In such cases, you should immediately call a specialist who will assess the condition of the structure on the spot and carry out the necessary repair work.
Profitable and convenient
Having examined the operating principle and design of double-circuit gas boilers, we can draw a conclusion regarding their application:
- firstly, they allow you to save money and avoid purchasing water heating equipment
- secondly, even if the secondary circuit fails, they can operate in heating mode, which allows them to be used in the cold season
- thirdly, replacing this circuit will cost less than repairing a similar bithermic unit.
Consequently, the use of a double-circuit gas boiler is not only convenient in terms of its functionality, but also profitable.
To prepare hot water for household needs, each manufacturer of gas heating systems offers modifications with an additional circuit. When purchasing a water heating unit for your home, it will be useful to understand the scheme by which a double-circuit gas boiler operates. This will help you choose the right one for your needs and operating conditions.
Navien double-circuit boiler design
The pump is not working well
Users of gas boilers sometimes encounter various problems with the operation of the pumping unit. Such equipment stops pumping water if the rotor fails or a significant amount of air has accumulated in the internal part. To prevent such a breakdown, it is necessary to unscrew the nut from the unit and drain the water, after which the axle is forced to rotate using a flat screwdriver.
Pump in a gas boiler
Types of gas double-circuit boilers
According to their design and principle of operation, double-circuit gas installations are divided into 3 types:
- using one common (bithermic) heat exchanger to heat water and coolant;
- heating water for domestic hot water supply in a separate high-speed flow heat exchanger;
- with a flow-through heat exchanger and storage tank.
Units with bithermic heat exchanger
Installations of the first type are equipped with copper heat exchangers of complex configuration. Each tube is as shown in the picture.
In this case, the operating principle of a double-circuit gas boiler is to heat water for hot water supply and heating in two separate tubes located in one device. Coolant for the heating system flows through the outer tube, and water for hot water flows through the inner tube. The movement of flows is organized in a passing direction, that is, the coolant and water flow in the same direction. There is a gas burner device under the heat exchanger; its operation is controlled by an automatic gas valve. The algorithm is as follows:
- In heating mode, the water flowing through the outer tubes is heated to a temperature limited by the thermostat. When this temperature is reached, the gas valve turns off the burner, and when the coolant cools down, it turns it on again.
- When one or more hot water taps in the house are opened, its movement begins in the internal tubes of the heat exchanger, the circulation of coolant in the heating system stops and the boiler operates in DHW mode. The coolant moves in a small circle inside the boiler, transferring its energy to the water in the internal tubes, the burner operates constantly.
- When the domestic hot water taps in the house are closed, the circulation of coolant in the heating system is resumed.
Other reasons
We can say that all cases when the radiator does not heat are unique in their own way. For example, the radiator, which is the last one in the system, does not heat. This means that the coolant simply does not reach it or the heat is “lost” along the way to it. If the latter, then the system is incorrectly calculated or the diameter of the pipes is incorrectly selected and, accordingly, the ratio of the amount of water/circulation intensity is incorrectly selected.
An expansion tank can help solve many problems. For example, airing can be removed by pumping coolant through the entire system. To do this, some install a valve in the lower part of the heating system, to which a tap and fitting are connected. After putting on the hose, you can pump water until air comes out through the expansion tank.
But this approach is quite risky - excess water, and there will be a lot of it, will fill the tank and flow out of it. In this case, work with an assistant who will monitor the water level in the expansion tank.