Today, many are wondering how and what is the best way to heat their home if there is no gas. Firewood and coal are among the most affordable types of fuel. Therefore, the right solution here would be to build a heating stove, or even better, add a cooking stove function to it. There are a lot of design options both in form and in operating principles.
In this article I will introduce you to the features of the Kuznetsov furnace, its advantages and a step-by-step scheme for constructing such a unit yourself.
How does a bell furnace work?
Before choosing this heating system as your main one, you need to understand how this stove works. The design of the kolapak furnace itself is small in size, which allows combustion products to move without obstacles.
- The main distinguishing feature of such a stove from conventional duct types is the smoke exhaust process.
- This process works by pushing out smoke and gas, which allows the stove to produce much more heat.
- This method of smoke exhaust also reduces the risk of fire blowing out, as well as the risk of carbon monoxide leakage, which can poison the human body.
In the designs of bell-type furnaces, two smoke exhausts play an important role, due to which high efficiency is achieved.
This is due to the fact that thermal energy is better accumulated. One chimney (external) performs the function of removing smoke outside, and the second is internal, which helps reduce the speed of movement of gases and remove them to the outside.
Basics
Most of the advantages of Kuznetsov furnaces come from the principle of free passage of gases. Let us explain again with an example.
Let's imagine a stove with a complex system of smoke ducts: an ethermark, a four-five-turn Dutch oven. In this cramped labyrinth, strong turbulence will inevitably arise. Have you heard the furnace humming? This is only a minor manifestation of the vortex energy raging within her. And there’s nowhere to get it from except from the fuel stash. If the channels are long and narrow enough, then at first glance there is nothing terrible here: the vortices, by the time they reach the pipe, will dissipate, cooling, and will still give their energy to the body of the furnace, and it to the room. But in reality, nuances appear, which will be discussed later in the text. Because of them, the efficiency of a channel furnace over 60% is an exceptional rarity.
In a channel stove, while it is being heated, a huge flow of energy rushes about, and only a small part of it can be used for heating or heating water without disturbing its operation. Such a furnace is somewhat similar to a nuclear reactor. Don’t be alarmed, just because of the synergy, i.e. along the paths of energy circulation in it. A nuclear reactor has to be loaded with tens of times more fuel than is necessary to ensure the design energy output. Otherwise, the neutrons will simply fly out without having time to meet the uranium atoms ready to receive them. In a channel furnace, hot vortices, without having time to cool, will fly out into the chimney or, conversely, will cool down immediately, producing smoke and soot.
But the Kuznetsovkas (details below) are closer in synergy to the thermonuclear reactors of the future. “Thermonylus” sounds scary, but this is only due to its association with the hydrogen bomb. In fact, fusion reactors are quite safe.
Why? Because they generate exactly as much energy as the consumer needs, and the technological power reserve required for rarefied plasma is scanty. If suddenly the chamber of a tokamak or stellarator suddenly completely collapses, the plasma will be completely emitted (there are no heavy atoms in it) and will cool down before it reaches the walls of the room. The repairmen will curse - maybe the duty department is sharpening their laces - but after 5 minutes. will be able to blunt to elimination without protective equipment.
So what do Kuznetsov furnaces have in common with thermonuclear reactors? The fact that the energy of the flue gases, thanks to the principle of free passage, does not rotate many times in the flow until it is pushed into the body of the furnace, but saturates it immediately. And now she has nowhere to go from there except into the room and/or the water heating register.
What bell furnace models are there?
It is worth noting that there are a lot of types of these furnaces, because each master has his own version of the furnace design. One of the most popular models are two-bell stoves, which differ from conventional ones by the presence of two hoods, one of which is located above the second.
Having a small size, this stove can be installed in small rooms, and the design of a bell-type stove with two bells is not very complicated.
There are other types of these furnaces, including:
- Bell-type ovens with a built-in chamber for making baked goods.
- Sauna bell stoves.
- Bell-type stoves, which are used only for space heating.
- Cooking bell furnaces, which are made of ceramic bricks.
- Cooking and heating furnaces.
- Bell-type stoves, which are equipped with a fireplace.
Preparation before construction of the stove
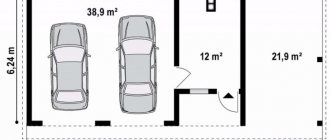
After choosing a model of the furnace structure, the master carries out preparatory processes before starting installation of the heating structure. At this stage, a place for the construction of the stove is selected, and individual elements are purchased.
Cast iron parts for the stove Source glavspec.ru
The efficiency of a heating brick structure largely depends on the location of the structure. When choosing it, they are guided by existing fire safety requirements. If the walls of the house are built of wood, then the following rules are observed:
- The minimum distance from the stove to the wooden walls should be 10 cm.
- A heat-resistant basalt or asbestos layer is created between the wall of the building and the stove structure when the heating structure is built into a previously prepared niche.
- The minimum distance from the chimney to the floor beams and rafters should be 15 cm.
Preparatory work also includes the construction of a foundation for the furnace structure. The durability of the entire heating structure depends on its strength.
Important! The reinforced concrete base of the stove should not be monolithically connected to the foundation of the house. After all, the shrinkage of these two structures may differ, because unequal loads will act on them. When they are combined, it is possible that cracks will appear on the walls of the stove and the house due to mutual influence.
The stove foundation is not connected to the base of the house Source ad-cd.net
A bell-type heating structure is a dome stove. Regardless of the name, a building for heating premises can be built in a house that has long been put into operation. However, in this case, the floor is dismantled to construct a pit in which the foundation will be poured.
Important! The perimeter of a monolithic concrete foundation should be 0.5-0.8 cm larger than the base of the furnace.
Sometimes houses are built on a slab foundation. Therefore, the furnace structure also has to be built on the same foundation. To minimize the likelihood of deformation of structures, experts recommend building a lightweight stove. This is exactly what “Kuznetsovka” is.
On a note! It is recommended to bury the reinforced concrete base of the stove structure at least 30-50 cm into the soil.
How to prepare a place for the stove
To properly install such a stove, you need to carefully study the step-by-step installation instructions, features and recommendations. In general, this process consists of a preparatory stage, laying the first and second stages.
To properly install the stove, you will need some tools, including:
- Scoop and bayonet types of shovels.
- Reinforced metal rods.
- Formwork.
- Polyethylene film.
- Cement mortars.
- Sand material.
After preparing all the material and tools, you need to start preparing the place for the stove.
This process is carried out in several stages:
- Preparing a hole measuring one and a half meters by one meter, the depth should be eighty centimeters.
- Covering the bottom with sand material. The size of the layer of sand material should not exceed fifteen centimeters.
- After covering, the pit is left for two days to allow the sand materials to settle.
- Preparation of formwork, which is made from plywood or waste boards.
- Performing reinforcement using rods made of steel materials.
- Pouring cement mortar. It is necessary to distribute the solution evenly.
After all these activities, you need to leave it all for a certain period of time for the mortar and foundation to harden.
Varieties for different purposes
Igor Kuznetsov and his team have created a large number of universal and specialized models. Some are intended only for heating rooms, others are supplemented with elements for cooking or heating water. Fireplaces are a separate area.
Drawings of options tested in practice are collected on the inventor's website. For convenience, the structures are assigned alphanumeric designations.
Heating
Kuznetsov's heating stove for a two-story house allows you to save on fuel.
Various dome layout options make it possible to construct designs for heating one- and two-story houses.
Heating models are abbreviated as OIK (heating models by I. Kuznetsov). You can find options with a firebox located inside the room or in the utility room.
For variety and to give the desired qualities, there are stoves supplemented with warm beds (OIK -6 bed. AND OIK 19 bed.) and seats (OIK-7s).
Some products have built-in ovens. In this case, the letter D is added to the code designation, for example, OIK-5D.
Heating stoves also include stoves with a built-in fireplace.
Models RTIC (Russian heated heater by I. Kuznetsov) are needed for heating large rooms. They are massive and need a strong foundation.
Options with fireplace
Model with a fireplace
Fireplaces, in addition to their heating function, serve as interior decoration. In this case, the firebox is open, the fire can be observed visually. The stoves are equipped with a firebox for conventional heating, which can be located on the facade, on the right, left side, or behind.
For construction, they choose an option in which it is convenient to service the stove from a utility room or hallway - you do not have to carry firewood into the living room. Working with waste (ash) also does not imply inevitable dirt in the room when cleaning the ash pan and the vent from the hallway.
Options for OIK-K have been developed with couches, built-in ovens and a corner fireplace.
Boilers
To organize a water heating circuit, options have been developed with the designation KIK (I. Kuznetsov boiler). A steel heat exchanger is built into the second dome. Water circulates through the system due to an electric pump.
Models are designed for power of 16, 17, 34 and 64 kW. The first option (16 kW) is equipped with a hob.
Heating and cooking
A heating and cooking model is a structure that completely exhausts the fuel resource.
Universal heating and cooking stoves are designed for homes with year-round occupancy. The model has built-in hobs and ovens, shelves for heating food and water.
The firebox can be located on the front or side, which allows you to choose an option for any interior design.
Installation of a bed is available as an option. For large rooms, elongated fireboxes are made, which allows the use of large-caliber firewood. They burn longer and you will have to add fuel less often.
The size of the hob depends on the composition of the family. For 2–3 people, choose a reduced surface, which saves fuel.
For the bath
I. Kuznetsov singled out sauna stoves as a separate area. There are three varieties: BIC, BIC BC and BIC PC. The abbreviation BIC corresponds to the purpose, and additional symbols indicate that the structure is equipped with a fireplace.
For different layouts, models are chosen that differ in the location of the firebox and fireplace - in the steam room, relaxation room or in the dressing room.
How to lay out the oven
The process of laying out stoves is a very important stage of the entire installation process, because the stability and efficiency of the stove will depend on it. The laying is carried out in two levels. At the first, you will need a solution for which you will need clay and water, a steel plate, and bricks made of refractory materials.
In addition, you will need a grinder with special attachments for stone materials, a drill with a hammer attachment and a grate.
The masonry process at the first level consists of:
- Laying a layer of alphabet on the foundation.
- Laying bricks on a layer of alphabet.
- Laying the second row of bricks, placing blowers and cleaning windows.
- Making partitions for the lower and upper compartments.
- Laying refractory bricks and installing a series of beams.
- Laying out the fireplace insert for the sixth row.
- Laying out the smoke exhaust in the seventh row.
- Laying out a special compartment for the firebox made of refractory bricks in the ninth row.
- Laying out gratings in the twelfth row.
- Making a ceiling made of refractory bricks to block access to the chimney.
- Closing all pipe passages with steel plates.
After completing the first level activities, you need to move on to the second, here you need:
- Lay out the oven roof.
- Close the exits to the chimneys.
- Install steam traps.
- Create a hood.
- Install a plate that serves as an intake and cover it with bricks.
- Lay out chimneys with a diameter of one brick.
Operation in various modes
In summer mode, Kuznetsov’s stove turns from a heating and cooking stove into a cooking stove. To do this, it is enough to open a special valve (it is called the summer valve), after which the flue gases will enter the chimney directly, bypassing the caps. Accordingly, only the hob will be subject to heating.
The temperature inside the cooking chamber can be regulated by a valve installed on the exhaust duct extending from it. By closing the valve and the chamber door, it can easily be turned into an oven. For ease of use, shelves for baking sheets can be fixed in the walls.
If you need to quickly warm up the room or dry out, open the door of the cooking chamber. At the same time, the temperature on the burners remains high enough for cooking.
Pros and cons of bell-type furnaces
Before installing such stoves, you need to study the list of advantages and disadvantages.
Among the advantages are:
- Cost-effective materials.
- The installation process is simple, because the design does not require a complex mechanism, and the laying process does not require additional skills.
- Easy to use. These stoves require almost no maintenance, and there are no special requirements for fuel materials.
- Fast and efficient heating due to its design.
- Possibility to make a stove in any design.
The disadvantages include:
- Uneven heating of the oven.
- Limited design options.
- High fuel consumption.
Why blacksmiths?
But is it worth focusing specifically on Kuznetsov’s stoves? Worth it because they are worth it. From the very beginning, Igor Viktorovich viewed Russian-style stoves not as a protected relic of the past or an expensive luxury item, but as an indispensable attribute of the economical energy sector of the future, which is now the present. The rest realized, as they say, when the roast rooster pecked.
As a result, a 4 kW blacksmith heats a house of 100 square meters. m. the same as a 12 kW firebox. Which, by the way, does not speak about the invention of a perpetual motion machine, but about the fact that branded advertisers are creating their prospectuses, perhaps, sniffing out the “path of happiness.” In any case, it is a fact that Kuznetsov constantly receives orders from the USA, Canada, Sweden, Finland, which themselves are not trailing behind the furnaces. Specifically, the advantages of blacksmiths are as follows:
- High efficiency - 80% is not surprising for Kuznetsov furnaces.
- High temperature of fuel combustion without the use of technologies and materials that require industrial production.
- As the first consequence of the previous one - omnivorousness. In blacksmiths, any fuel burns to ash, and soot deposition is minimal.
- The second consequence is easy care: because. Soot also burns, Kuznetsov stoves may not be cleaned for years.
- Lower material consumption combined with uniform heat transfer between fireboxes: in a city apartment with central heating, the temperature fluctuates more during the day than in a house heated by a blacksmith with 2 fireboxes per day.
- Wide possibilities for integrating a water heating circuit without compromising the technical parameters of the furnace.
- Good draft with a short chimney, which reduces the cost and simplifies construction and installation work during its construction.
- The plasticity of the design and appearance as a consequence of the two-bell design (see below): without deteriorating the stove, it can be designed to suit almost any room and design requirements.
- Automatic redistribution of thrust among the channels during the transition from heating to cooling, which guarantees against waste: the view almost never needs to be closed; it is intended more for emergency operating modes.
Note: the method of thrust redistribution invented by I.V. Kuznetsov is fundamentally different from the well-known gas view. Through it, the flow created by the draft is passed past the heated parts of the furnace body by special downstream channels, and when the flame burns in the firebox, convection from it pulls the air flow towards itself. As a result, a separate room ventilation system is not required. In addition, a gas tube can be blown out by reverse draft when blowing into a pipe, or, conversely, pulled out in a strong wind, and in a blacksmith any air flow will pass by everything that it could blow out.
Photo of a bell-type stove for heating a house or bathhouse
Recommendations for self-construction
If you decide to build a stove according to one of Kuznetsov’s plans with your own hands, get ready for careful and scrupulous work. On the diagrams you will find a graphic representation of each row, but before starting laying you need to become familiar with the features of the technique, in particular:
- selection and pre-processing of bricks;
- purchase of metal parts (plates, dampers, doors, valves);
- determining the most suitable location;
- preparation of the base and foundation;
- possibility of installing a chimney, etc.
Fireclay refractory brick (Sh-5, ShB-8) is recognized as the best material for the internal masonry of “smiths”, and ceramics (M-150) for external decoration. To strengthen brick walls, metal elements (rebar, wire) are used. In order for the stove to function with maximum heat output, experienced craftsmen hone not only their skills, but also every brick - literally. They polish every detail, which is why projects completed by professionals look flawless.
Fireclay brick masonry
Having the author's order in hand, we recommend not to experiment, but to follow the designated order. Deviations from the diagram do not guarantee complete heat transfer.