The ability to use water as a coolant allowed humanity to invent effective heating of their homes. An open heating system is a classic option that is still popular due to its simple operating principle and the minimum number of necessary devices.
What an open system looks like in practice
Methods for connecting the boiler to the heating circuit
The composition of the equipment and the boiler piping directly depends on the selected type of heating circuit, the method of circulation of the coolant and the degree of automation of the process, such as fine-tuning the climate or simply adjusting the heating of the coolant.
The task of the entire strapping complex is:
- Ensure uniform heat distribution throughout the heating circuit.
- Protect people and equipment from any emergency situations and minimize the consequences of a breakdown.
- Reducing the influence of frequency in the operation of a solid fuel boiler, since the main power is released only after the next load of fuel is ignited, while as it burns out, the heat transfer decreases.
Types of structures
Heating circuit - elements used as a heating system by transferring thermal energy into the air. The most popular systems are those that use boilers or boilers connected to a water supply as a heating source. The liquid, crossing the heating elements, reaches the set temperature, heading into the heating circuit.
Coolant movement is ensured by two methods:
- natural;
- forced.
With forced circulation through pipes
Systems with natural movement of coolant are simple and reliable. Efficiency depends on the proper design of the heating circuit. In the latter case, a pump is introduced that creates pressure. The coolant moves through the pipeline.
Heat sources for heating liquids are boiler rooms and boiler equipment. The operating mechanism is based on the conversion of one type of energy into heat. Depending on the raw material and heating source, boilers operate on gas, solid fuel, electricity, or fuel oil.
All types of boiler units can be used to heat a private home. Gas and solid fuel devices are popular.
Depending on the connection of heating devices in the heating circuit, there are: single-pipe and two-pipe systems. Single-pipe system - when the batteries are connected in series, the water, crossing each element, returns to the boiler.
Single-pipe scheme
The downside is the uneven heating of the room. Each subsequent radiator receives less thermal energy.
In a two-pipe heating circuit, the batteries are connected parallel to the riser. The negative side of the system is the complexity of the design and high consumption of material. In multi-storey buildings, only a two-pipe heating system can be used.
Two-pipe scheme
How to install heating correctly
In order for a finished heating system with a natural circulation type to function correctly and efficiently, it is important to adhere to certain rules when installing it. In general, the installation diagram looks like this:
In general, the installation diagram looks like this:
- Heating radiators must be installed under the windows, preferably at the same level and maintaining the required indentations.
- Next, install the heat generator, that is, the selected boiler.
- Install the expansion tank.
- The pipes are laid out and the previously fixed elements are joined into a single system.
- The heating circuit is filled with water and a preliminary check for the tightness of the connections is performed.
- The final stage is to start the heating boiler. If everything works correctly, then the house will be warm.
Please pay attention to some nuances:
- The boiler should be located at the lowest point of the system.
- The pipes must be installed with a slope towards the return flow.
- There should be as few turns in the pipeline as possible.
- To increase heating efficiency, pipes with a larger diameter are required.
We hope this article will be useful to you, and you will be able to independently install a heating system without a circulation pump in your country house.
A heating system with natural circulation of liquid is a closed device of the gravitational (gravity) type, which allows you to heat rooms in a private house regardless of the power supply.
This advantage of the design makes it possible to use it in regions with problems or complete absence of a central electrical network. The system is economical, but for its proper functioning you will need to make accurate calculations.
Requirements for installation and operation
When arranging the heat supply at home, you need to take into account that an open heating system has a number of features:
- The boiler (solid fuel, gas, liquid fuel) should be located at the lowest point of the line, and the expansion tank at the very top.
- It is most convenient to place the expansion tank in an insulated attic; if the roof is cold, the tank itself and the lines are thermally insulated.
- The fewer turns and connecting elements in the line, the more efficiently the coolant moves during natural circulation.
- The speed of the coolant in the gravity system does not exceed 0.3 m/s, so it is important to monitor the temperature of the liquid in the boiler and prevent it from overheating and boiling - this will damage the main pipes and heating devices.
- Before the onset of cold weather, water is drained from an unused heating system so that the pipes and boiler jacket do not burst when the liquid freezes.
- It is regularly necessary to add water to the expansion tank, as it evaporates over time, and a lack of coolant will lead to the formation of air pockets and the system stopping. You can organize a recharge unit or fill it manually from a bucket - this is easier in a small individual house.
- An open heating system dictates the use of water as a coolant. This is due to the fact that antifreeze is a toxic substance, and its fumes from an open tank are harmful to humans. In addition, it will have to be topped up regularly, increasing heating costs. If the heating is supposed to be used irregularly, but you want to avoid the hassle of constantly draining liquid from the circuit, you can add antifreeze, but in this case the expansion tank is equipped with a lid with a small hole to reduce the rate of evaporation of the antifreeze.
- The key stage in arranging gravity-type heating is design, since it is important to correctly calculate the cross-section of pipes and the slope of the pipeline. The relevant standards are specified in SNiP 2.04.01-85. The length of the circuit should be no more than 30 meters; on horizontal sections of the main line, pipes are installed with a slope of at least 2-3 mm per meter of length.
The boiler must be located below the lowest radiator
Single-pipe heating circuit
From the heating boiler you need to draw a main line representing a branch. After this action, it contains the required number of radiators or batteries. The line, drawn according to the building designs, is connected to the boiler. The method creates coolant circulation inside the pipe, heating the building completely. The circulation of warm water is adjusted individually.
A closed heating scheme for Leningradka is planned. In this process, a single-pipe complex is installed according to the current design of private houses. At the owner's request, the following elements are added:
- Radiator controllers.
- Thermostats.
- Balancing valves.
- Ball valves.
Leningradka regulates the heating of certain radiators.
In what cases can you do without a pump?
The movement of coolant inside the heating circuit occurs under the influence of the laws of physics. This means that when heated, the liquid rises, and as it cools, it falls again, thereby heating the room.
Most of all, a heating system without a circulation pump is in demand precisely in country houses and dachas, since in suburban conditions the power supply is not always stable or absent altogether. In this regard, heating equipment with a forced circulation type is impractical.
It is noteworthy that it is quite possible to install heating with natural coolant circulation yourself. In addition, such a system is very convenient to use.
Bivalent hybrid heating systems based on heat pumps
A hybrid heating system (bivalent) consists of a main heat source, a peak heater and a buffer storage tank. This system allows you to use the heat pump as efficiently as possible with minimal investment.
Functioning of the bivalent system
As you know, heating equipment is selected according to the heat loss of the room at a minimum outdoor temperature (for Kyiv -22 ° C). This means that the selected boiler must heat your room in the temperature range: from -22 to +8 °C. If we analyze Climatology, it turns out that the number of days in the heating season when the temperature drops below -15 °C is less than 5%. Therefore, it is inappropriate to select a heat pump for the lowest possible outdoor temperature; it is much more profitable to purchase a heat pump of lower capacity and an inexpensive backup heat source (a peak heater - the cheapest electric boiler) that will be activated exclusively at temperatures below the bivalence point (usually -15 °C). The advantage of this system is also the redundancy of the heating system.
Main Pros:
- Heating system redundancy
- Possibility of purchasing a heat pump with lower heating capacity
Main Cons:
No
How much power does a heat pump need?
If you have a new house made of aerated block, insulated with 100-120-150 mm of mineral wool or polystyrene foam (walls and foundation to frost depth), good double-chamber energy-saving double-glazed windows, insulated roof (150-200 mm), insulated floor on the ground (minimum 100 mm), then the heat loss of your home is 50 W/m2 (at -22 °C):
- House 100 m2 – 5 kW
- House 150 m2 -7.5 kW
- House 200 m2 – 10 kW
- House 250 m2 – 12.5 kW
- House 300 m2 – 15 kW
- House 350 m2 – 17.5 kW
- House 400 m2 – 20 kW
- House 450 m2 – 22.5 kW
- House 500 m2 – 25 kW
- Building 1000 m2 - 50 kW
In principle, such body losses can be easily covered by an air-to-water heat pump of the Zubadan series:
- House 100 m2 – 5 kW – PUHZ-SW50VHA
- House 150 m2 -7.5 kW – PUHZ-SHW80VHA
- House 200 m2 – 10 kW – PUHZ-SHW112VHA/PUHZ-SHW112YHA
- House 250 m2 – 12.5 kW – PUHZ-SHW140YHA
- House 300 m2 – 15 kW – PUHZ-SHW140YHA + reserve 3 kW
- House 350 m2 – 17.5 kW – PUHZ-SHW230YKA
- House 400 m2 – 20 kW – PUHZ-SHW230YKA
- House 450 m2 – 22.5 kW – PUHZ-SHW230YKA + reserve 3 kW
- House 500 m2 – 25 kW – PUHZ-SHW230YKA + reserve 5 kW
- Building 1000 m2 - 50 kW - Cascade of 2 heat pumps PUHZ-SHW230YKA + reserve 4 kW
When choosing the power of a heat pump, you should also take into account the power required to heat ventilation, a swimming pool, hot water, etc. Therefore, before purchasing, consult an expert and perform a heat loss calculation.
Types of open heating schemes
In an open heating system, the coolant moves in two different ways. The first option is natural or gravitational circulation, the second is forced or artificial stimulation from a pump.
The choice of scheme depends on the number of floors and area of the building, as well as on the expected thermal conditions.
Natural circulation in heating
The gravitational system does not have any mechanism to ensure the movement of the coolant. The process is carried out solely by the expansion of hot water. For the operation of the circuit, an accelerating riser is provided, the height of which is at least 3.5 m.
If you neglect to install a vertical transit riser, then there is a high probability that the coolant coming from the boiler will not develop a sufficient speed
The natural circulation heating system is optimal for buildings with an area of up to 60 square meters. m. The maximum length of the circuit capable of providing heat is considered to be a 30 m mainline. An important factor is the height of the building and the number of storeys of the house, which allows the installation of an accelerating riser.
The natural circulation scheme is not suitable for low-temperature applications. Insufficient expansion of the coolant will not create the proper pressure in the system.
Possibilities of the gravity circuit:
- Connection to heated floors . A circulation pump is mounted on the water circuit leading to the floor. The rest of the system operates as usual. If the power goes out, the house will continue to be heated.
- Working with a boiler . The heating device is mounted at the top of the system - slightly below the expansion tank.
To ensure uninterrupted operation, a pump can be installed on the boiler. Then the heat supply and hot water production scheme automatically becomes a forced option. Additionally, a check valve is installed to prevent recirculation of the coolant.
Forced system with pump
In order to increase the speed of the coolant and reduce the time for heating the room, a pump is built in. The movement of water flow increases to 0.3-0.7 m/s. The intensity of heat transfer increases, and the branches of the main heat up evenly.
Pumping circuits are constructed of both open and closed types. In open circuits, the expansion tank is installed at the highest point of the system. The presence of a pump allows you to increase the pipeline between the heating boiler and the batteries, both in height and length
Important points in organizing a compulsory system:
- The circuit with a built-in pump is volatile. To ensure that the heating of the room does not stop during a power outage, the pumping equipment is placed on the bypass.
- The pump is installed in front of the boiler inlet on the return pipe. The distance to the boiler is 1.5 m.
- When installing the pump, the direction of water movement is taken into account.
Two shut-off valves and a bypass elbow with a circulation pump are mounted on the return line. If there is current in the network, the taps close - the coolant moves through the pump. If there is no voltage, then the valves must be opened - the system will switch to natural circulation.
A check valve must be installed on the supply pipeline. The element is placed immediately after the boiler and prevents recirculation of the coolant during pump operation
Emergency options
Every piping scheme must include a circuit in case of emergency situations. His task includes:
— protection against pressure drops;
— protection against temperature increases above the permitted limit;
— prevention of moisture formation.
Safety valve in the harness
Its task is precisely to relieve excess pressure from the system. It is mounted at the boiler outlet separately or as part of a safety group.
Emergency heat exchanger in the solid fuel boiler connection system
Its task is most responsible - to prevent overheating of both the boiler and the system in general. Overheating can happen for 2 reasons:
— too much fuel was loaded into the boiler. The heat received exceeded the demand.
— the electricity was turned off and the pump stopped working.
For normal operation of this circuit, it is also necessary to install a temperature sensor with a valve and a cooling unit in the water supply pipe to the boiler. As soon as the coolant temperature exceeds the maximum allowed, the sensor signals this and provokes the opening of the valve.
After the valve is activated, water begins to fill the cooling unit, reducing the temperature of the main coolant.
Auxiliary heating circuit for a solid fuel boiler
One of the options for cooling the system. Its peculiarity is that you will need to connect a storage tank for the DHW circuit.
This scheme will work as follows: in normal operating mode, the pump will operate, creating a certain pressure. It will prevent the auxiliary circuit from coming into operation. But as soon as the electricity is turned off, the pump will stop working, the pressure will disappear, and the backup circuit will come into operation.
Result: the water temperature in the system will drop to the desired value.
Let’s say right away that this scheme is suitable for absolutely any type of heating system!
This mixer maintains the lowest temperature of the coolant at the inlet to the boiler so that condensation does not form on the walls of the device. what we talked about at the very beginning of the article. Thus, in a solid fuel boiler this is one of the most necessary components!
The mixer is installed on the return pipe using a bypass.
If the temperature in the return pipe is low (below the set value), the thermomixer will provide an influx of hot water.
Types of circulation pumps
A pump with a “wet” rotor is made of stainless steel, cast iron, bronze or aluminum. Inside there is a ceramic or steel motor
To understand how this device works, you need to know the differences between the two types of circulation pumping equipment. Although the fundamental design of a heating system based on a heat pump does not change, the two types of such units differ in their operating features:
- A pump with a “wet” rotor is made of stainless steel, cast iron, bronze or aluminum. Inside there is a ceramic or steel motor. The technopolymer impeller is mounted on the rotor shaft. When the impeller blades rotate, the water in the system is set in motion. This water simultaneously functions as an engine cooler and a lubricant for the working elements of the device. Since the “wet” device circuit does not provide for the use of a fan, the operation of the unit is almost silent. Such equipment only works in a horizontal position, otherwise the device will simply overheat and fail. The main advantages of a wet pump are that it does not require maintenance and also has excellent maintainability. However, the efficiency of the device is only 45%, which is a minor drawback. But for domestic use this unit is perfect.
- A pump with a “dry” rotor differs from its counterpart in that its motor does not come into contact with the liquid. As a result, the unit has less durability. If the device operates “dry,” then the risk of overheating and failure is low, but there is a risk of leakage due to abrasion of the seal. Since the efficiency of a dry circulation pump is 70%, it is advisable to use it to solve utility and industrial problems. To cool the engine, the device circuit provides for the use of a fan, which causes an increase in the noise level during operation, which is a disadvantage of this type of pump. Since in this unit water does not serve as a lubricant for working elements, during operation of the unit it is necessary to periodically carry out technical inspection and lubricate parts.
In turn, “dry” circulation units are divided into several types according to the type of installation and connection to the engine:
- Console. In these devices, the engine and housing have their own place. They are separated and firmly fixed on it. The drive and working shafts of such a pump are connected by a coupling. To install this type of device, you will need to build a foundation, and maintaining this unit is quite expensive.
- Monoblock pumps can be used for three years. The body and engine are located separately, but are combined by a monoblock. The wheel in such a device is installed on the rotor shaft.
- Vertical. The service life of these devices reaches up to five years. These are sealed advanced units with a seal on the end side made of two polished rings. For the manufacture of seals, graphite, ceramics, stainless steel, and aluminum are used. When the device is running, these rings rotate relative to each other.
There are also more powerful devices on sale that have two rotors. This dual circuit allows you to increase the performance of the device at maximum load. If one of the rotors fails, the second can take over its functions. This allows not only to enhance the operation of the unit, but also to save energy, because with a decrease in heat requirements, only one rotor works.
Wiring of a solid fuel heating boiler, diagram
All heat generators operate on this principle.
They receive the energy necessary for work from various solid fuels. It should be noted that they have some operational features that must be taken into account when connecting such boilers to the heating system. It should be noted that the piping diagram of a solid fuel boiler includes several elements and devices that must be used. so that the heating system operates for a long time.
The wiring diagram for a solid fuel boiler is the necessary devices and elements that together form a single heating system. This heating system includes:
- Boiler.
- Circulation pump.
- Expansion tank.
- Emergency power system.
- Co-mixing system.
- Buffer capacity.
- Emergency circuit
- Corrosion protection system.
- Pressure gauge, drain cock, special valve. It's all collected in one block
- Thermal valve.
- Float valve.
Is it possible to make open systems from polypropylene?
A gravity-flow heating system made of polypropylene pipes is one of the affordable and easy-to-install options. Reinforced polypropylene pipes have an operating temperature within 70°C and peak performance at 95°C. An analogue of steel and cast iron structures is distinguished by its ability to withstand pressures of 20 Bar and above, and also has high thermal insulation, anti-corrosion resistance and hygiene. If the installation rules are followed, the system can last 50 years.
As you understand, PPR pipes can be used to make open heating systems, but from an aesthetic point of view, steel pipes will look better in the house. They can always be restored to a civilized appearance, while polypropylene pipes will become less presentable over the years.
What is the difference between solid fuel boilers
In addition to the fact that these heat sources produce thermal energy by burning various types of solid fuel, they have a number of other differences from other heat generators. These differences are precisely a consequence of burning wood; they must be taken as a given and always taken into account when connecting the boiler to a water heating system. The features are as follows:
- High inertia. At the moment, there are no ways to quickly extinguish a solid fuel fire in a combustion chamber.
- Formation of condensation in the firebox. The peculiarity manifests itself when coolant with a low temperature (below 50 ° C) enters the boiler tank.
Note. The phenomenon of inertia is absent only in one type of solid fuel units - pellet boilers. They have a burner into which wood pellets are fed in doses; after the supply is stopped, the flame goes out almost immediately.
The danger of inertia is the possible overheating of the water jacket of the heater, as a result of which the coolant in it boils. Steam is generated, which creates high pressure, rupturing the body of the unit and part of the supply pipeline. As a result, there is a lot of water in the furnace room, a lot of steam and a solid fuel boiler unsuitable for further use.
A similar situation can arise when the heat generator piping is done incorrectly. After all, in fact, the normal operating mode of wood-burning boilers is maximum; it is at this time that the unit reaches its rated efficiency. When the thermostat reacts to the coolant reaching a temperature of 85 °C and closes the air damper, combustion and smoldering in the firebox still continues. The water temperature rises another 2-4 °C, or even more, before its growth stops.
In order to avoid excess pressure and a subsequent accident, an important element is always involved in the piping of a solid fuel boiler - a safety group, which will be discussed in more detail below.
Another unpleasant feature of the unit operating on wood is the appearance of condensation on the inner walls of the firebox due to the passage of not yet heated coolant through the water jacket. This condensate is not God’s dew at all, since it is an aggressive liquid that quickly corrodes the steel walls of the combustion chamber. Then, having mixed with the ash, the condensate turns into a sticky substance that is not so easy to tear off from the surface. The problem is solved by installing a mixing unit in the piping circuit of a solid fuel boiler.
This coating serves as a heat insulator and reduces the efficiency of a solid fuel boiler.
It is too early to breathe a sigh of relief for owners of heat generators with cast iron heat exchangers that are not afraid of corrosion. Another misfortune may await them - the possibility of destruction of cast iron from temperature shock. Imagine that in a private house the electricity was turned off for 20-30 minutes and the circulation pump driving water through the solid fuel boiler stopped. During this time, the water in the radiators has time to cool down, and in the heat exchanger it has time to heat up (due to the same inertia).
Electricity appears, the pump turns on and directs the cooled coolant from the closed heating system into the heated boiler. Due to a sharp temperature change, the heat exchanger experiences a temperature shock, the cast iron section cracks, and water runs onto the floor. It is very difficult to repair; it is not always possible to replace a section. So even in this situation, the mixing unit will prevent an accident, which will be discussed below.
Emergency situations and their consequences are described not with the aim of scaring users of solid fuel boilers or encouraging them to purchase unnecessary elements of piping schemes. The description is based on practical experience, which must always be taken into account. If the heating unit is connected correctly, the likelihood of such consequences is extremely low, almost the same as with heat generators using other types of fuel.
Pipes for gravity flow
An important decision point is the choice of material from which the pipes of the gravity heating system are made.
Let's look at the currently most common pipes:
- Copper pipes. The advantages of these pipes: maximum heat transfer, incredibly long service life - up to 100 years, beautiful appearance. But there are disadvantages: the colossal cost of the material, the need to use soldering on all connections during installation work, its complexity, because finding a good craftsman for such work is very difficult, and the cost of his work will also be high.
- Polypropylene pipes. It is an average option. Average service life is up to 25 years. They have a smooth internal surface, which reduces the possibility of the formation of deposits, lightweight material that is resistant to corrosion - these are the main positive aspects of these pipes. Among the disadvantages: installation is carried out with a specialized tool, it is difficult to do it yourself, the high cost of pipes, although less than that of copper, also reduces the attractiveness of the material.
- Steel pipes. The most accessible material of all. This type of pipe is very resistant to any mechanical stress. There are disadvantages of the material: installation is carried out using welding, a large number of fittings, and this material also has a risk of corrosion and overgrowing with deposits.
How to connect a solid fuel boiler
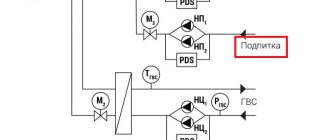
The canonical connection diagram for a solid fuel boiler contains two main elements that allow it to function reliably in the heating system of a private home. This is a safety group and a mixing unit based on a three-way valve with a thermal head and a temperature sensor, shown in the figure:
Note. The expansion tank is not shown here, since it can be located in different places in different heating systems.
The presented diagram shows how to connect the unit correctly and should always accompany any solid fuel boiler, preferably even a pellet one. You can find various general heating schemes anywhere - with a heat accumulator, an indirect heating boiler or a hydraulic arrow, on which this unit is not shown, but it must be there. This is explained in more detail in the video:
The task of the safety group, installed directly at the outlet of the supply pipe of a solid fuel boiler, is to automatically relieve pressure in the network when it rises above a set value (usually 3 Bar). This is done by a safety valve, and in addition to it, the element is equipped with an automatic air vent and a pressure gauge. The first releases the air appearing in the coolant, the second serves to control the pressure.
Attention! It is not allowed to install any shut-off valves on the section of the pipeline between the safety group and the boiler
How the scheme works
The mixing unit, which protects the heat generator from condensation and temperature changes, operates according to the following algorithm, starting from kindling:
- The firewood is just starting to burn, the pump is on, the valve on the side of the heating system is closed. The coolant circulates in a small circle through the bypass.
- When the temperature in the return pipeline rises to 50-55 °C, where the attached remote-type sensor is located, the thermal head, at its command, begins to press the three-way valve stem.
- The valve slowly opens and cold water gradually enters the boiler, mixing with hot water from the bypass.
- As all the radiators warm up, the overall temperature increases and then the valve closes the bypass completely, passing all the coolant through the heat exchanger of the unit.
This piping scheme is the simplest and most reliable; you can easily install it yourself and thus ensure the safe operation of the solid fuel boiler. There are a couple of recommendations regarding this, especially when piping a wood-burning heater in a private house with polypropylene or other polymer pipes:
- Make the section of the pipe from the boiler to the safety group from metal, and then lay plastic.
- Thick-walled polypropylene conducts heat poorly, which is why the surface-mounted sensor will openly lie, and the three-way valve will lag. For correct operation of the unit, the area between the pump and the heat generator, where the copper flask is located, must also be metal.
Another point is the installation location of the circulation pump. It is best for him to stand where he is shown in the diagram - on the return line in front of the wood-burning boiler. In general, you can install the pump on the supply side, but remember what was said above: in an emergency, steam may appear in the supply pipe. The pump cannot pump gases, so if steam gets into it, the circulation of the coolant will stop. This will speed up a possible explosion of the boiler, because it will not be cooled by water flowing from the return.
Way to reduce the cost of strapping
The condensate protection circuit can be reduced in cost by installing a three-way mixing valve of a simplified design that does not require connecting an overhead temperature sensor and thermal head. It already has a thermostatic element installed, set to a fixed mixture temperature of 55 or 60 °C, as shown in the figure:
Special 3-way valve for solid fuel heating units HERZ-Teplomix
Note. Similar valves, which maintain a fixed temperature of mixed water at the outlet and are intended for installation in the primary circuit of a solid fuel boiler, are produced by many well-known brands - Herz Armaturen, Danfoss, Regulus and others.
Installing such an element definitely allows you to save on piping the TT boiler. But in this case, the possibility of changing the temperature of the coolant using a thermal head is lost, and its deviation at the output can reach 1-2 °C. In most cases, these shortcomings are insignificant.
Selecting an expansion tank for closed heating
The coolant in heating systems of private houses is usually ordinary water. When heated, water tends to expand, thereby increasing the pressure in the system. If the pressure in a sealed system exceeds a critical point, a pipeline rupture may occur. How to make a closed heating system that will not damage pipes?
To solve this problem, expansion tanks were created that eliminate excess fluid, thereby preventing pressure build-up.
The expansion tank consists of two parts: a metal body and an elastic diaphragm, which is located inside and divides the body into two halves. The “back” part of the tank is filled with air or gas, and the expanded liquid enters the lower part. As the temperature rises, the water continues to increase in volume, affecting the membrane, which begins to shrink.
Membranes in tanks can be of two types:
- Fixed
. Such a membrane is fixed around the perimeter of the expander and ensures stable operation, but if it is damaged, the entire tank will need to be replaced. - Replaceable
. Membranes of this type are usually produced in the form of bulk rubber products that are filled with water. Replaceable membranes are installed on the tank flange, and if they rupture, you can replace them yourself.
Conclusion
The heating system is an important element of the house, and its calculation must be carried out in accordance with all rules. The question of which is better: a closed heating system with your own hands or one built by professionals remains open, but it is not the most important.
It is very important to choose the right system elements that will ensure maximum efficiency and cost-effectiveness, are reliable and of high quality. A closed heating system, the diagram of which is shown in the photo, can be an excellent choice to ensure that all requirements are met
If everything was done correctly, the closed heating system will heat the building for many years, creating a cozy and comfortable environment.
Forced circulation system
Equipment of this type for two-story cottages is considered more preferable. In this case, the circulation pump is responsible for the uninterrupted movement of coolants along the lines. In such systems, it is allowed to use pipes of smaller diameter and a boiler of not too high power. That is, in this case, a much more efficient single-pipe heating system for a two-story house can be installed. The pump circuit has only one serious drawback - dependence on electrical networks. Therefore, where the current is turned off very often, it is worth installing the equipment according to the calculations made for a system with a natural coolant current. By adding a circulation pump to this design, you can achieve the most efficient heating of your home.
A gas boiler without electricity is a traditional model of a floor-standing appliance that does not require additional energy sources to operate. It is advisable to install devices of this type if there are regular power outages. For example, this is relevant in rural areas or dacha areas. Manufacturing companies produce modern models of double-circuit boilers.
Many popular manufacturers produce different models of energy-independent gas boilers, and they are quite efficient and of high quality. Recently, wall-mounted models of such devices have appeared. The design of the heating system must be such that the coolant circulates according to the principle of convection.
This means that the heated water rises up and enters the system through the pipe. To ensure that the circulation does not stop, the pipes must be placed at an angle, and they must also be large in diameter
And, of course, it is very important that the gas boiler itself is located at the lowest point of the heating system
A pump that is powered from the mains can be connected separately to such heating equipment. By connecting it to the heating system, it will pump coolant, thereby improving the operation of the boiler. And if you turn off the pump, the coolant will again begin to circulate by gravity.
Operating principle
In a water heating system, liquid is a means of transporting thermal energy to devices that transmit heat to the air. These devices can be radiators or the pipeline circuit itself inside the floor or along the walls (in the latter case, large cross-section pipes are used: 8-10 cm).
Thanks to this, the heat from the boiler (which is the only source of heat) is sufficient even to supply heat to several rooms located at a distance from the heat generator. In addition, by changing the number of radiators, you can evenly heat rooms of different sizes. This is the advantage of water heating over installing a conventional stove, which can only heat the rooms adjacent to it.
Due to physical laws, the movement of liquid along the circuit can be carried out by gravity: the density of the heated coolant is lower than that of the cooled one. In addition to the principle of thermodynamics, operation is ensured by installing pipes at a certain slope. You can also use a circulation pump to increase efficiency. Many people mistakenly believe that a pump is an attribute only of a closed system: in open circuits, forced circulation of coolant is also permissible.
An open heat supply system is characterized primarily by an open-type expansion tank. It is a container without a lid for excess coolant formed as a result of thermal expansion of water. The reservoir allows you to automatically stabilize the pressure in the system. And to ensure that the liquid does not spill out according to the principle of communicating vessels, the expansion tank is mounted at the highest point of the circuit. The reservoir simultaneously performs the function of an air valve: through it, air from the system escapes into the atmosphere (during its filling and operation).
Detailed diagram of the operation of an open heating system
Heating of the house is provided according to the following principle
:
- supply - the coolant is heated in the boiler and moves to the radiators;
- return - the liquid that has cooled in the expansion tank and radiators tends to “go” to the lowest point and, due to the inclination of the pipes, enters the boiler.
Installing a circulation pump makes the process more intense, but the principle of operation does not change.
Types of heating systems with gravity circulation
Despite the simple design of a water heating system with self-circulation of coolant, there are at least four popular installation schemes. The choice of wiring type depends on the characteristics of the building itself and the expected performance.
To determine which scheme will work, in each individual case it is necessary to perform a hydraulic calculation of the system, take into account the characteristics of the heating unit, calculate the diameter of the pipe, etc. You may need professional help when performing the calculations.
Closed system with gravity circulation
Otherwise, closed-type systems work like other heating schemes with natural circulation. The disadvantages include the dependence on the volume of the expansion tank. For rooms with a large heated area, you will need to install a spacious container, which is not always advisable.
Open system with gravity circulation
The open type heating system differs from the previous type only in the design of the expansion tank. This scheme was most often used in old buildings. The advantage of an open system is the ability to independently manufacture a container from scrap materials. The tank usually has modest dimensions and is installed on the roof or under the ceiling of the living room.
The main disadvantage of open structures is the entry of air into pipes and heating radiators, which leads to increased corrosion and rapid failure of heating elements. Airing of the system is also a frequent “guest” in open-type circuits. Therefore, radiators are installed at an angle; Mayevsky valves must be provided to bleed air.
Single-pipe self-circulating system
A single-pipe horizontal system with natural circulation has low thermal efficiency and is therefore used extremely rarely.
The essence of the circuit is that the supply pipe is connected in series to the radiators. The heated coolant enters the upper branch pipe of the battery and is discharged through the lower outlet. After this, the heat flows to the next heating unit and so on until the last point. The return flow returns from the outermost battery to the boiler.
This solution has several advantages:
- There is no pair pipeline under the ceiling and above the floor level.
- Saves money on system installation.
The disadvantages of this solution are obvious. The heat transfer of heating radiators and the intensity of their heating decreases with distance from the boiler. As practice shows, a single-pipe heating system for a two-story house with natural circulation, even if all slopes are observed and the correct pipe diameter is selected, is often redone (by installing pumping equipment).
Closed system diagrams
The following types of wiring are used for heating country and country houses:
- Single-pipe. All radiators are connected to a single main line running along the perimeter of the room or building. Since the hot and cooled coolant move through the same pipe, each subsequent battery receives less heat than the previous one.
- Two-pipe. Here, heated water enters the heating devices through one line and leaves through the second. The most common and reliable option for any residential buildings.
- Passing (Tichelman loop). Same as two-pipe, only the cooled water flows in the same direction as the hot water, rather than returning in the opposite direction (shown in the diagram below).
- Collector or beam. Each battery receives coolant through a separate pipeline connected to a common comb.
Single-pipe horizontal distribution (Leningrad)
The single-pipe horizontal scheme justifies itself in one-story houses with a small area (up to 100 m²), where heating is provided by 4-5 radiators. You should not connect more to one branch, the last batteries will be too cold. The option with vertical risers is suitable for a building of 2-3 floors, but during the implementation process it will be necessary to go through ceiling pipes in almost every room.
Single-pipe scheme with top distribution and vertical risers
The two-pipe circuit with dead-end branches (shown at the beginning of the article) is quite simple, reliable and definitely recommended for use. If you are the owner of a cottage with an area of up to 200 m² and a height of 2 floors, then lay out the mains using pipes with a flow area of DN 15 and 20 (external diameter - 20 and 25 mm), and to connect radiators, use DN 10 (external diameter - 16 mm).
Associated pattern of water movement (Tichelman loop)
The Tichelman loop is the most hydraulically balanced, but more difficult to install. The pipelines will have to be laid around the perimeter of the rooms or the entire house and pass under the doors. In fact, a “hitch ride” will cost more than a two-pipe one, but the result will be approximately the same.
The beam system is also simple and reliable, in addition, all wiring is successfully hidden in the floor. The connection of nearby batteries to the comb is carried out with 16 mm pipes, and the remote ones with 20 mm pipes. The diameter of the line from the boiler is 25 mm (DN 20). The disadvantage of this option is the price of the collector unit and the complexity of installation with the laying of highways when the floor covering is already done.
Scheme with individual connection of batteries to the collector
Heating a house without a pump. Two time-tested options
Until the 90s of the last century, heating a house without a pump was the only option available, since the direction of manufacturing circulation pumps and promoting them to the masses was not developed. Thus, owners and developers of private houses were forced to install heating in their houses without a pump.
But when good boiler equipment, pipes and compact circulation pumps began to be brought to the CIS in the 90s, the situation changed dramatically. Everyone started installing heating systems. which do not work without a pump. They began to forget about gravity systems. But today the situation is changing. Developers of private houses are once again thinking about heating a house without pumps. Since interruptions and shortages of electricity, which is so necessary for the operation of the circulation pump, can be traced everywhere.
The issue of quality and quantity of electricity supply is especially acute in new buildings.
That is why today, more than ever, one proverb comes to mind: “Everything new is well-forgotten old!” This proverb is very relevant today for heating a house without a pump.
For example, previously only steel pipes, homemade boilers and open expansion tanks were used for heating. The boilers had low efficiency, steel pipes were bulky, and it was not recommended to hide them in walls.
Expansion tanks were located in attics. Because of this, there was heat loss and the threat of the roof flooding or the pipes in the tank freezing. Which in turn often led to a boiler explosion, pipe rupture and human casualties.
Today, thanks to modern boilers, pipes and other heating devices, it is possible to create a luxurious, economical heating system without a pump. Thanks to modern, efficient boilers, significant savings can be achieved.
Modern plastic or copper pipes can be easily hidden in walls. Today, home heating can also be done with both radiators and heated floors.
Today there are two main home heating systems without a pump.
The first and most common system is called Leningradka. or with horizontal spill.
The main thing in home heating systems without a pump is the slope of the pipes. Without a slope, the system will not work. Due to the slope, Leningradka is not always suitable, since the pipes run along the entire perimeter of the house. Also, due to the fact that the slope may not be enough, you have to lower the boiler below the level of your floor. In this case, the boiler is inconvenient to heat and clean.
Also, when installing a heating system at home without a Leningradka pump, doorways along the route of the pipes interfere. In this case, it is necessary to make window sills with a height of at least 900 mm.
This is necessary so that the radiator is mounted and there is enough height for the pipes along the slope. Otherwise, the system is quite functional, namely with cast iron, steel and aluminum radiators.
The second home heating system without a pump is called a "Spider" or vertical top-spout system.
Today this is the most reliable and practical home heating system without a pump. The main thing is that the “Spider” system is devoid of all the disadvantages of the “Leningradka”, with the exception of the slope of the return line, due to which the boiler also has to be lowered below the floor.
Otherwise, the Spider system is the most efficient system. You can attach any radiators and heated floors to the Spider system. You can mount valves under the thermal head on radiators in the “Spider” system and hide pipes in the walls, and so on.
Today, it is increasingly necessary to recommend the “Spider” system to developers, because... Today this is the ideal home heating system without a pump.
Thank you for reading this article!
Where to put
It is recommended to install a circulation pump after the boiler, before the first branch, but on the supply or return pipeline it doesn’t matter. Modern units are made from materials that can withstand temperatures up to 100-115°C. There are few heating systems that work with a hotter coolant, so considerations of a more “comfortable” temperature are untenable, but if you feel safer, put it in the return line.
Can be installed in the return or direct pipeline after/before the boiler up to the first branch
There is no difference in hydraulics - the boiler, and the rest of the system; it makes absolutely no difference whether there is a pump in the supply or return branch. What matters is the correct installation, in terms of strapping, and the correct orientation of the rotor in space
Nothing else matters
There is one important point regarding the installation location. If the heating system has two separate branches - on the right and left wings of the house or on the first and second floor - it makes sense to install a separate unit on each, and not one common one - directly after the boiler. Moreover, the same rule remains on these branches: immediately after the boiler, before the first branch in this heating circuit. This will make it possible to set the required thermal conditions in each part of the house independently of the other, and also in two-story houses to save on heating. How? Due to the fact that the second floor is usually much warmer than the first floor and much less heat is required there. If there are two pumps in the branch that goes up, the speed of movement of the coolant is set much lower, and this allows you to burn less fuel, without compromising the comfort of living.
There are two types of heating systems - forced and natural circulation. Systems with forced circulation cannot work without a pump; systems with natural circulation work, but in this mode they have lower heat transfer. However, less heat is still much better than no heat at all, so in areas where electricity is often cut off, the system is designed as hydraulic (with natural circulation), and then a pump is installed into it. This gives high heating efficiency and reliability. It is clear that the installation of a circulation pump in these systems is different.
All heating systems with heated floors are forced - without a pump, the coolant will not pass through such large circuits
Forced circulation
Since a forced circulation heating system without a pump is inoperative, it is installed directly into the gap in the supply or return pipe (of your choice).
Most problems with the circulation pump arise due to the presence of mechanical impurities (sand, other abrasive particles) in the coolant. They can jam the impeller and stop the motor. Therefore, a mesh dirt filter must be placed in front of the unit.
Installing a circulation pump in a forced circulation system
It is also advisable to install ball valves on both sides. They will make it possible to replace or repair the device without draining the coolant from the system. Turn off the taps and remove the unit. Only that part of the water that was directly in this piece of the system is drained.
Natural circulation
The piping of the circulation pump in gravity systems has one significant difference - a bypass is required. This is a jumper that makes the system operational when the pump is not working. One ball shut-off valve is installed on the bypass, which is closed the entire time the pumping is running. In this mode, the system operates as forced.
Installation diagram of a circulation pump in a system with natural circulation
When the electricity goes out or the unit fails, the valve on the jumper is opened, the valve leading to the pump is closed, and the system operates as a gravity system.
Installation features
There is one important point, without which the installation of the circulation pump will require rework: it is necessary to rotate the rotor so that it is directed horizontally. The second point is the direction of flow. There is an arrow on the body indicating which direction the coolant should flow. This is how you turn the unit so that the direction of movement of the coolant is “in the direction of the arrow”.
The pump itself can be installed both horizontally and vertically, just when selecting a model, make sure that it can work in both positions. And one more thing: with a vertical arrangement, the power (pressure created) drops by about 30%. This must be taken into account when choosing a model.
Heating system pipe routing
The most popular are 2 schemes: one-pipe and two-pipe. Let's look at what they are.
A single-pipe system is the most basic option, however, not the most effective. It is a closed circle of pipes, shut-off valves, and automation, the center of which is the boiler. A pipe runs from it along the lower plinth to all rooms, connecting to all radiators and other heating devices.
Plus diagrams. ease of installation, small amount of material for constructing the circuit.
Minus. uneven distribution of coolant across radiators. The radiators in the outer rooms will warm up worse, since they are the last ones in the path of water movement. However, this problem can be solved by installing a pump or increasing the number of sections in the latest radiators.
A two-pipe system is a more effective method, since it solves the problem of uniform distribution of water throughout all heating devices. The pipes can be placed at the top (this option is preferable, because then the water can circulate naturally) or at the bottom (then a pump will be required).
Features of assembling a forced circuit
In order for the forced system to justify itself and function properly, it is necessary to correctly select the circulation pump and correctly “embed” it into the heat supply line.
Selecting a circulation pump
The main parameters for choosing pumping equipment: device power and pressure. These characteristics are determined based on the area of the heated room.
Indicative indicators:
- for houses of 250 sq.m., a pump with a power of 3.5 cubic meters per hour and a pressure of 0.4 atm is suitable;
- in rooms measuring 250-350 sq.m, install the device at 4.5 cubic meters per hour with a pressure of 0.6 atm;
- if the area of the house is 350-800 sq.m, then it is advisable to purchase a pump with a capacity of 11 cubic meters per hour, the pressure of which is at least 0.8 atm.
In a more scrupulous selection, specialists take into account the length of the heating system, the type and number of radiators, the material of manufacture and the diameter of the pipes, as well as the type of boiler.
Installing the pump in the main
The pump is placed on the return line so that the coolant that is not too hot passes through the device. It is possible to install modern models made of high-temperature resistant materials on the supply line.
When inserting the pump, the water circulation should not be disrupted. It is important that at any point in the pipeline when the pumping unit is operating, the hydrostatic pressure remains excessive.
Four acceptable schemes for heating systems with pump circulation and an open expansion tank. Hydrostatic pressure is maintained at the desired level
Option 1. Raising the expansion tank. A simple way to convert a natural circulation system to a forced one. To implement the project you will need a high attic space.
Option 2. Moving the tank to a distant riser. The labor-intensive process of reconstructing the old system and installing a new one is not justified. Simpler and more successful methods are possible.
Option 3. Expansion tank pipe near the pump nozzle. To change the type of circulation, it is necessary to cut off the tank from the supply line, and then connect it to the return line - behind the circulation pump.
Option 4. The pump is included in the supply line. The simplest way to reconstruct the system. The disadvantage of the method is unfavorable operating conditions for the pump. Not every device can withstand high temperatures.
The principle of operation of a gravity heating system
The principle of heating operation looks simple: water moves through a pipeline, driven by hydrostatic pressure, which appears as a result of different masses of heated and cooled water. This design is also called gravity or gravity. Circulation is the movement of cooled and heavier liquid in the batteries under the pressure of its own mass down to the heating element, and the displacement of light heated water into the supply pipe. The system operates when the natural circulation boiler is located below the radiators.
In open-type circuits, it communicates directly with the external environment, and excess air escapes into the atmosphere. The volume of water that increased due to heating is eliminated, and the constant pressure is normalized.
Natural circulation is also possible in a closed heating system if it is equipped with an expansion tank with a membrane. Sometimes open-type structures are converted into closed ones. Closed circuits are more stable in operation, the coolant in them does not evaporate, but they are also independent of electricity. What affects circulation pressure
The circulation of water in the boiler depends on the difference in density of the hot and cold liquid and on the magnitude of the height difference between the boiler and the lowest radiator. These parameters are calculated before the installation of the heating circuit begins. Natural circulation occurs because The return temperature in the heating system is low. The coolant manages to cool down, moving through the radiators, becomes heavier and with its mass pushes the heated liquid out of the boiler, forcing it to move through the pipes.
Water circulation diagram in the boiler
The height of the battery level above the boiler increases the pressure, helping the water more easily overcome the resistance of the pipes. The higher the radiators are located in relation to the boiler, the greater the height of the cooled return column and the greater the pressure with which it pushes the heated water upward when it reaches the boiler.
Density also regulates pressure: the more the water warms up, the less its density becomes in comparison with the return. As a result, it is pushed out with more force and the pressure increases. For this reason, gravity heating structures are considered self-regulating, because if you change the heating temperature of the water, the pressure on the coolant will also change, and therefore its flow will change.
Symptoms and diagnosis
If a characteristic hum appears in the pipes, it is possible:
- a large amount of sediment has accumulated on the pipe walls, which has led to a narrowing of the lumen;
- there is a water leak from the system;
- The system contains devices with too small a diameter.
To determine the cause of the noise more accurately, you should inspect all elements of the heating system and find the location of the leak.
If the pipes look undamaged, no steam or streams of flowing water are visible, you need to pay attention to the connecting elements and shut-off valves, perhaps the leak is occurring here
Sometimes it is difficult to determine the location of the leak, since it is hidden by a layer of insulation. To accurately diagnose the problem, you should call a professional plumber.
If there are no leaks, but the pipes are humming, you need to find the source of the sound. Most likely, this is where the pipe clearance has become too small due to accumulated mineral deposits or debris that has entered the system. Eliminate the problem by flushing the heating system. This is described in detail in the video:
Usually, a good plumber can identify parts of the system that are not properly sized, causing the pipes to hum. This item may need to be replaced or modified. Of course, such work should be carried out as best as possible, in full accordance with technology, so that new reasons for unpleasant noise in pipes do not appear.
Clicking sounds and the characteristic sound of bubbling water can be caused by air trapped in the system. To fix the problem, it is enough to bleed excess air from the radiators, for example, using a Mayevsky tap. Clicking sounds may also indicate the presence of foreign objects or debris in the pipes. In this case, you should clean the system.
If air gets into the heating system, it can cause clicking and bubbling sounds. To bleed air from the system, use the Mayevsky valve
Intermittent crackling, knocking and clicking noises may appear if:
- there are small foreign particles in the pipes;
- system parts are worn out;
- the ventilation valve has broken;
- unstable operation of the system caused expansion of the metal.
To stop the crackling in heating pipes, sometimes it is enough to drain some of the water and debris. In other cases, you will need the help of a professional plumber to repair or replace damaged elements.
Sometimes the cause of noise in the heating system is a heating pipe overgrown with deposits and particles of rust. This pipe should be flushed or replaced.
The breakage of the ventilation valve is often caused by its incorrect installation, for example, when the valve is installed in the wrong direction. Such an error can lead to significant damage to the entire heating system.
The reason for the tapping may also be the condition of the brackets on which the pipes and heating radiators are mounted. A loose bracket moves under the influence of metal expansion and contraction processes, which causes knocking. To stop this unpleasant phenomenon, it is enough to strengthen the old brackets or replace them with new ones. Sometimes special gaskets are installed between the pipe and the bracket.
Varieties of radiator connection diagrams
It is typical that for good heating it is not enough that the boilers heat the water well.
It is very important for the coolant to flow into the radiators to connect them correctly. In practice, an unregulated series connection is used for a single-pipe connection. True, this problem can be avoided if you use a two-pipe system. This system also does not use a regulator, however, if the radiator becomes airy, the system will function since water will flow through the jumper (bypass). True, this option is not suitable for a system such as a warm floor.
You can read more about the need to install a bypass here:
Installing two ball valves behind the jumper allows, by blocking the flow, to remove or turn off the radiators, without the need to stop the system. So, the correct calculation of heating radiators will allow you to equip the room with a heat accumulator.
Multi-level floor
To zone the space, craftsmen install floors at different levels. They advise installing a podium to separate the kitchen and dining room. This option is considered one of the most practical because, among other things, the owners have additional free space where they can hide something.
It is convenient to use boxes or crates for this. Wicker baskets will look good. But such space can remain free.
However, such a design should not be made if there are small children in the family, since the podium can become an obstacle for him. In addition, various floor coverings can be used.
They will zone the space between the living room and the kitchen and protect the podium from damage. For example, tiles are laid in the kitchen area, and laminate flooring in the dining room. The main thing is to choose colors and textures and combine the finishes correctly.
Date: September 25, 2022