The arrangement of drainage solves several problems at once. The main ones are the drainage of high-lying groundwater and high water from the buried foundation of a house, reducing the load on the waterproofing of basement walls and underground technical floors, and draining areas on moist soils. The standard drainage system consists of water receivers and pipes laid in the ground. After reading the article, you will learn how a drainage pipe works and how the design of a drainage pipe allows you to simultaneously collect water and drain it into special wells or off-site.
Drainage pipes are easy to recognize by their corrugated surface and perforations. Source vse-o-kanalizacii.ru
Signs of the need to install a drainage system
Owners of houses with regularly flooded basements have no doubt about the advisability of installing a drainage system. But even without going to such extremes, one can understand that a drainage system on the site is necessary.
Signs of excess moisture in the area that require a drainage system: √
abundance of precipitation in the region of residence;
√
the house is located in a low-lying area;
√
the site has clay soil with poor absorption;
√
the house is located on a slope or under a hill;
√
the soil is prone to seasonal flooding;
√
The region is characterized by harsh winters with prolonged snow melting.
Clay soils do not conduct water well, contributing to its accumulation on the site. This leads to the appearance of stationary puddles and constant humidity in the garden area. It is not only the soil that suffers from the leaching of black soil. With prolonged exposure to excess water, the paths are deformed, and moisture penetrates into the foundation. When the building is located in a low-lying area, all precipitation from the surrounding area flows into the yard, causing inconvenience to the owners and troubles to the house. Under the influence of moisture, the foundation and walls become damp and become covered with fungus, and over time they crack.
Rain flows and melted snow masses coming down from the slopes become a real disaster for areas without a drainage and drainage system. The yard covering is destroyed, and the plantings are dying due to swampiness. The proximity of a groundwater layer or the seasonal passage of pressure flows can render the foundation of a house unusable in a matter of years. Not to mention the unpleasant odor, mold and other accompanying excess moisture. Installation of drainage systems and proper organization of drainage from the site neutralize the inconvenience caused by moisture and maintain an optimal balance of humidity in the local area.
Uponor double-wall drainage pipe Ø110/95x3m SN8 bell-shaped, perforated Price: 2174.00 RUB
Uponor drainage well SOK 315/110 mm H=1m Price: 6015.00 RUB
Uponor Manhole bottom T2 Ø315/110mm PP Price: 7400.00 RUB
Purpose and types of drainage systems
Drainage systems include drainage systems for both surface and deep groundwater, helping to drain the site. There are two main types of systems: ground
- open - made in the form of gutters and channels located on the surface of the earth with slopes towards the drainage tank or drainage drain outside the site;
deep
- is an underground pipeline system laid in the ground at a deep location.
Open drainage system
Installation of a ground drainage system is relevant for areas with heavy rainfall and households located in the lower reaches of the relief.
Water coming from the surface is collected in drainage channels or gutters and flows into a collector reservoir or natural environment outside the site.
Surface drainage system
They are also called storm drainage systems, since their main purpose is to remove excess precipitation and melt water. They can be connected to drainage pipes that provide drainage from the roof of the building.
Closed drainage
It is used for draining lawns and lawns, as well as draining the underground part of the building. It is carried out using special perforated pipes that absorb underground moisture. Considering the fact that after all the work, the drainage pipes will be unavailable for inspection, it is necessary to take a very serious approach to the selection of both the pipes themselves and the selection of the required number of drainage wells - through which inspection and, if necessary, cleaning (from sand and silt) is carried out. .
Wall drains
Wall drainage structures are organized near the foundation. The main feature of such communication is that it contains waterproofing materials. A ditch is dug along the entire foundation. The depth of such a ditch should correspond to the depth of laying the foundation or exceed it.
Wall drainage is done in order to remove moisture from the foundation of the building
The necessary waterproofing is installed on the foundation walls, and the pre-dug ditch is filled with drainage materials. In this case, it is allowed to use special drainage mats, the filter of which is made of geotextile. Such mats are usually waterproofed with polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Note! Pipes can be laid in the trench to drain rainwater collected from the roof. In this case, it is recommended to use plastic pipes without perforation. With the help of such pipes, water is removed from the tray structures into a special well.
Rainwater must not be discharged into the drainage system, as this may lead to overflow of the structure. If the drainage structure overflows, the water will rise into the foundation of the building, which is fraught with unpleasant consequences.
Surface drainage system designs
Structurally, drainage systems on the surface are distinguished:
⊕ open - the channels are located on the ground without being covered by anything; for convenience, they are located along the site along paths and house buildings;
⊕ backfill - the channel capacity is filled with a drainage mixture of stones and sand, more often used on lawns and flower beds;
⊕ closed - gutters or channels are covered with gratings, which provides wider possibilities for using the territory.
The installation of surface drainage systems does not require significant investments in consumables, nor labor-intensive excavation and engineering work for laying and installation. Despite all their advantages, such systems are not effective in combating groundwater and soil flooding. In these cases, a deep soil drainage system will help to protect the house and site from high humidity and flooding.
Uponor Storm drain d.200 mm Price: 4991.00 RUB
Uponor Rainwater inlet SK 300 with cast iron cover 5t Price: 14284.00 RUB
Uponor Hatch for well 315 mm (plastic) Price: 2094.00 RUB
style=”padding: 10px;” title=”Laying the Uponor drainage pipe in granite crushed stone, when carrying out work to drain the foundation.” align=»right»>The underground drainage system is manufactured as follows: ⊕ laying drainage pipes; ⊕ installation of inspection wells to inspect the condition of the system; ⊕ installation of backup drain wells; ⊕ arrangement of a central drainage or storage tank.
The creation of such a system requires material costs and thorough excavation work with preliminary calculations and design of the pipeline diagram. In addition to the pipeline layout, it is necessary to calculate the location of the wells and the directional slope of the pipes for accurate and efficient drainage of drainage waste.
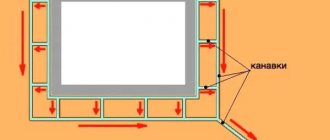
As a rule, underground drainage systems are installed in a closed ring around the building, limiting the access of water to the foundation. The ring is placed close to the walls of the house, or at a distance of one and a half to three meters. Hence their names - ring and wall drainage systems.
When installing a wall drainage system, you can additionally carry out waterproofing work on the foundation. This measure will reliably protect the base from water penetration inside. Another advantage of the deep system is convenience - the pipes are located underground and do not interfere with the use of the landscape.
Raising the area
If even deep drainage does not help to completely get rid of the negative manifestations of ground water, you will have to start grading and backfilling an area with a high groundwater level.
This method is expensive, but provides a real and lasting effect. Regardless of the height of the site, the work plan is approximately the same.
- Territory planning. A detailed plan of the site is drawn up, indicating the elevation level, the location of the surface aquifer, and the thickness of the fertile layer. This will help determine where, how much and what exactly to add. If the geology of the area is complex (swampiness is combined with a high groundwater level, there is a clay layer or voids), it is better to entrust the planning to a specialist.
- Demolition of old buildings (if any).
- Clearing the area. It is freed from vegetation, debris, and the roots are uprooted.
- Laying the drainage system (if it does not already exist). Backfilling alone will not solve the problem of excess moisture. It still needs to be diverted using the closed or open method described earlier.
- Filling the area. A low strip foundation is laid around the area so that the poured material is not washed away by rain. After the concrete has hardened, materials are poured layer by layer (10-15 cm each). Each layer is compacted using a vibrating rammer. After laying all the lower layers, they are left for a couple of weeks for natural shrinkage of 2-3 cm, only then comes the turn of fertile soil. To prevent the layers from mixing, they are separated by geotextiles.
Design of a deep drainage system
Before installation work on the installation of an underground drainage system, the layout of communications should be calculated. Design consists of the following elements: 1. determining the location of the drain - a well or the natural environment - and its exact location on the site; 2. number and location of intermediate wells (if provided); 3. marking the pipeline diagram and installation points for inspection wells.
For drainage, it is recommended to choose the lowest point of the terrain to ensure spontaneous flow of drainage water. If there is a landscape slope, it is easier to maintain a decline in the pipeline in the direction of the waste tank.
After calculating the design of the drainage system, you need to prepare consumables in accordance with the design data: √ drainage pipes - a special modification with perforated sides for accumulating water, the footage is calculated according to the diagram; √ inspection wells - containers for connecting plastic pipes with inlet holes, purchased according to the estimated quantity; √ container for the drain tank; √ connecting parts for the pipeline; √ drainage materials - sand and crushed granite; √ geo-fabric - a special filter fabric to protect pipes from silt and debris. In addition, you will need an entrenching tool for digging trenches and pits.
Tips for choosing
For deep drainage, the most popular in civil engineering are two-layer corrugated pipes made of polymer materials with an additional filter shell. And the same profile, but without the geotextile winding, is used for the construction of closed-type storm drains.
The internal walls have a smooth surface, which ensures high self-cleaning and does not create prerequisites for silting of the horizontal part of the drainage system.
The outer walls are corrugated with a ring profile, which provides the required rigidity. The corrugated surface also allows the use of O-rings when connecting pipes with couplings and tees.
For installation in areas with normal operating conditions (blind areas, lawns, pedestrian paths), ring stiffness class SN4, SN8 is sufficient.
For drainage installation under access roads or parking areas, pipes with ring stiffness class SN16-SN24 are selected.
Installation of deep drainage system
Further installation work is carried out according to the algorithm src=»https://www.promstok.com/upload/medialibrary/11d/montaj_dreinagnoi_systemi_20180430171916.jpeg» class=»aligncenter» width=»400″ height=»400″[/img] • preparation pit for a drain tank; • preparation of trenches for laying a pipeline with marking of installation sites for inspection wells; • compaction of the bottom of communications with sand; • laying the geotextile in trenches and pouring a layer of crushed stone (about 10 cm thick); • laying pipes in compliance with the slope and filling them with crushed stone to a depth of 20 cm; • wrapping pipes in geotextile; • connection of all elements of the drainage system; • covering with soil. The depth of the trenches depends on the depth of the foundation - trenches should be dug deeper to avoid water penetration.
Where to buy drainage pipes: average cost on the Russian market
In our age of high technology, drainage systems can be purchased without leaving your home via the Internet. At the same time, many online sellers provide such a service as free delivery, which is also good news. Let's try to figure out the average prices for similar products.
| Name | Length, m | Diameter, mm | Cost, rub./m |
| With perforation in geotextile | 50 | 110 | 130 |
| With perforation in geotextile | 40 | 200 | 350 |
| With perforation without filter | 50 | 160 | 100 |
| Corrugated HDPE | 40 | 50 | 70 |
As you can see, the cost of such products is low.
Drainage plays a very important role in maintaining the foundation of a building.
Installation of ground drainage system
To equip a drainage system on the surface, large-scale excavation and pipe laying will not be required. After drawing up a plan for the location of the channels and the drainage location, you can begin installation.
The channels are dug about half a meter deep according to the design scheme. Be sure to maintain a slope towards the drain. It is recommended to do it at the rate of 1-2 cm per meter of drainage channel. The bottom is compacted with a layer of sand, with which you can smooth out any irregularities and errors that arise. After this, installation is carried out according to the selected type of drainage system: • laying gutters; • filling with drainage composition (sand and crushed stone); • installation of concrete drains or laying out tiles. Upon completion of installation, the drainage channels of the drainage system are covered with gratings or left open. Open gutters can be filled in or decorated with stone, depending on the design. Drains from surface drainage systems, as a rule, are directed outside the site or into a drainage well for discharge into deep layers of soil.
Dosing chamber
The dosing chamber will ensure the gradual removal of liquid into the drainage field Source nk.pl
The dosing chamber is a container that has a capacity of up to 1 cubic meter. For construction, a ready-made plastic container corresponding to the required volume can be used.
The bottom of the excavation is leveled, where the container is then loaded. Uninterrupted operation of the system at the outlet of the tank is achieved by installing a siphon, which has a diameter of 100 millimeters and an elbow height of 200 millimeters. As the siphon fills, it will self-charge, then self-empty. Thanks to this, the purified liquid is supplied to the pipelines for distribution.